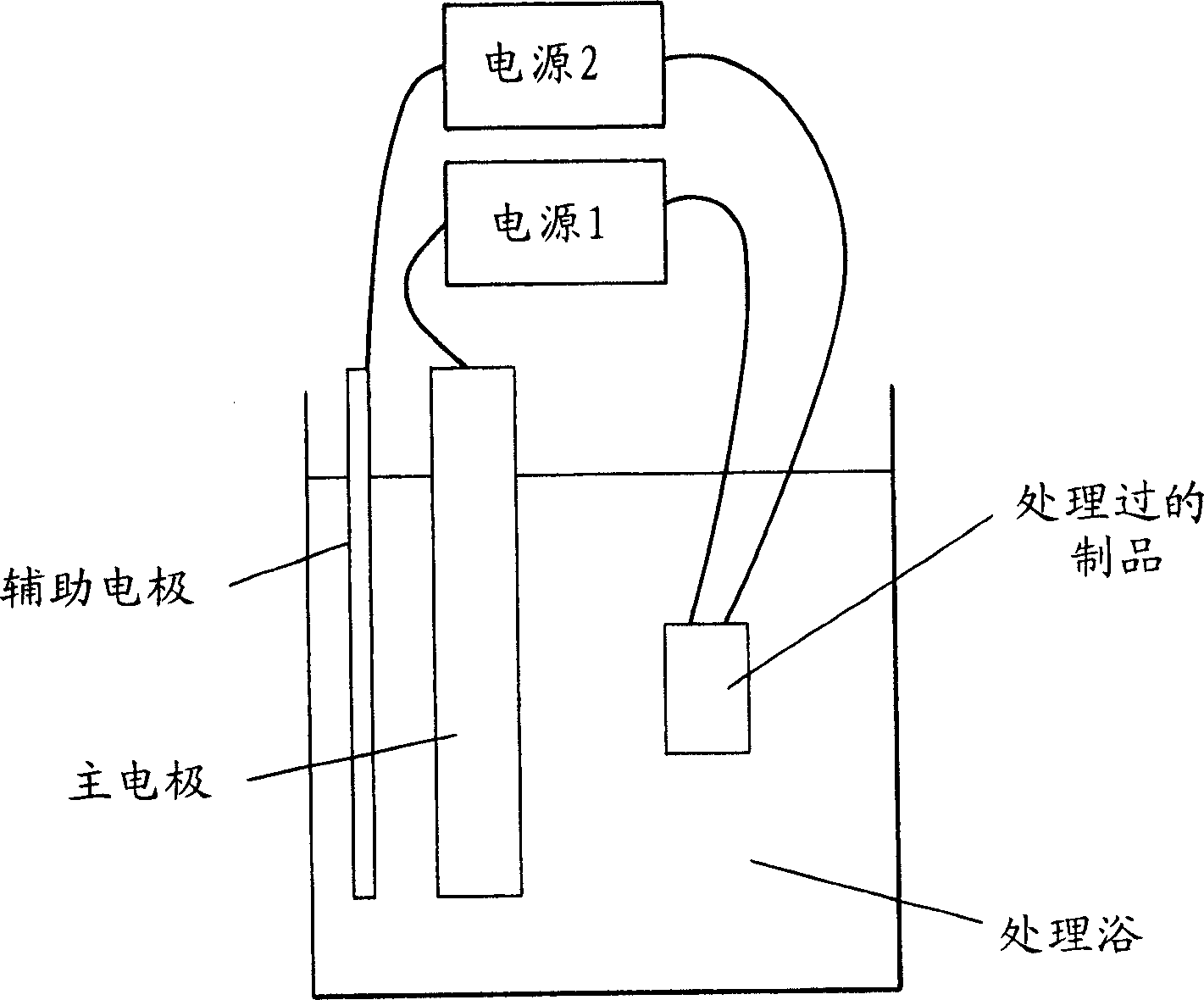
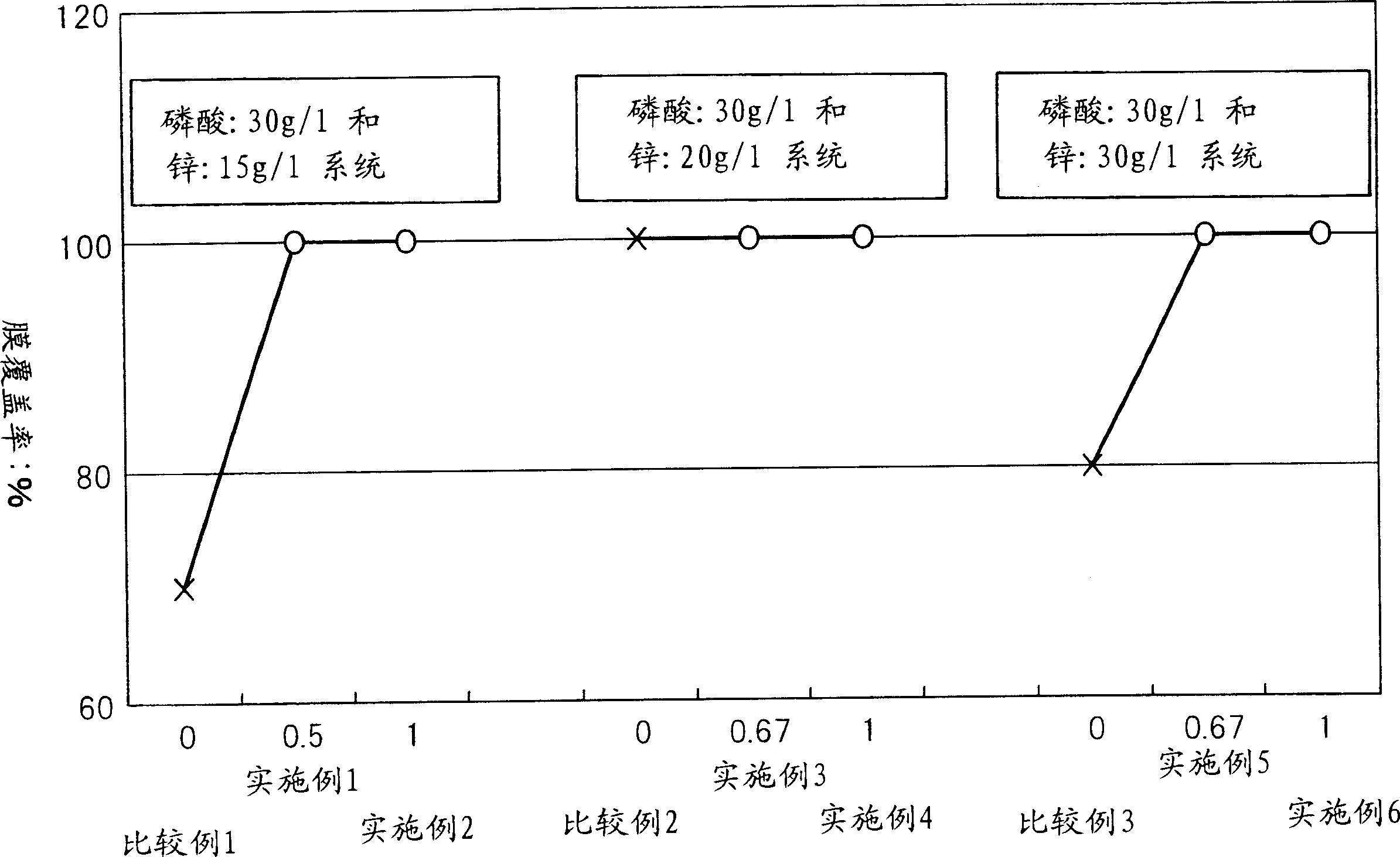
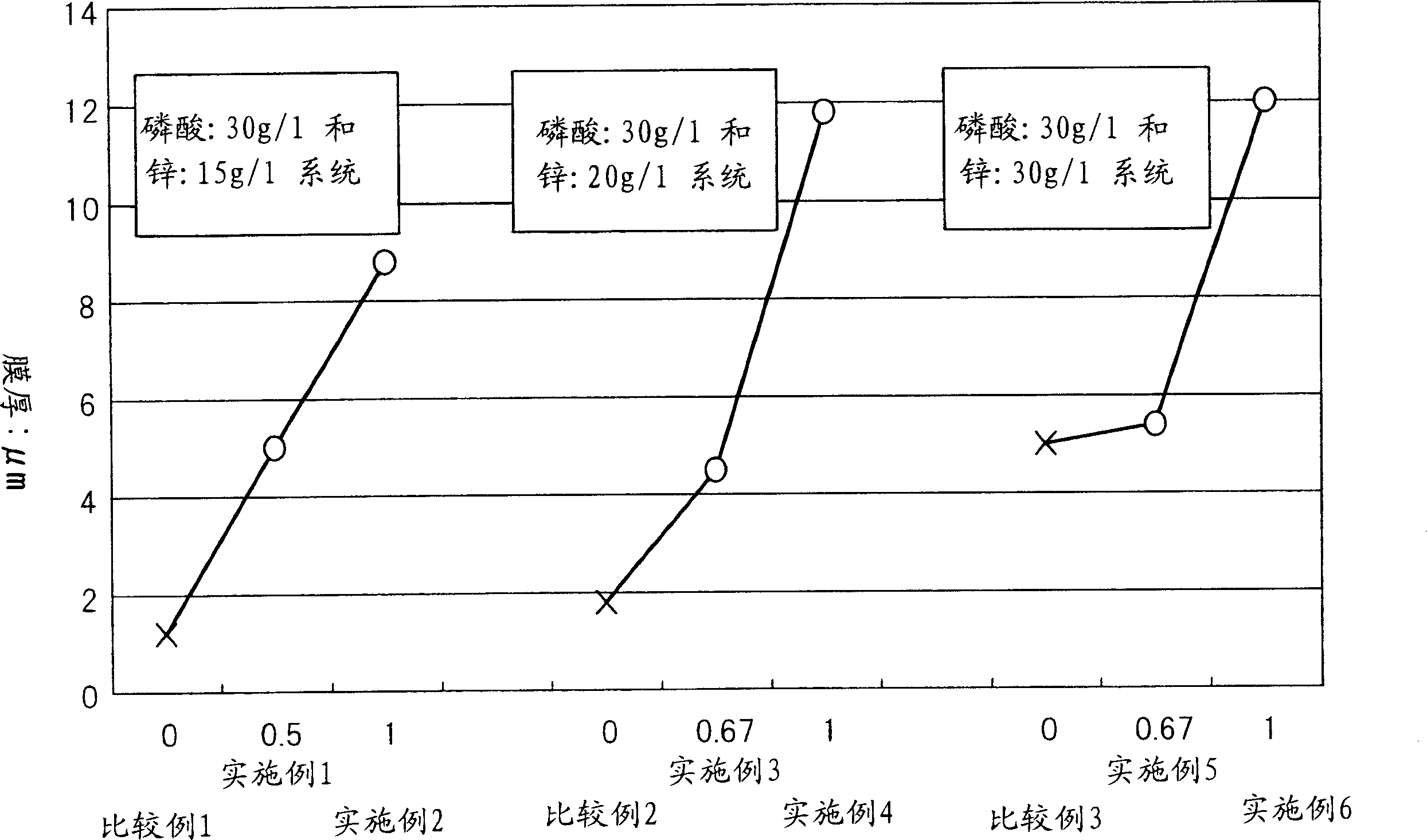
Electrolytic phosphating process
A technology of electrolytic phosphating and process, which is applied in the field of electrolytic phosphating process of phosphate film, can solve problems such as insufficiency, and achieve the effects of lowering temperature, omitting manpower, and reducing size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-6 and comparative example 1-3
[0093] Examples where Fe ions are not included in the treatment bath:
[0094] The test piece used in Examples 1-6 and Comparative Examples 1-3 was a mild steel material (SPCC material: cold-rolled steel plate) having a size of 50 mm×25 mm×1 mm(t). After degreasing, each test piece was immersed in a titanium type colloid solution and subjected to a phosphating process to form a film. The electrolytic phosphating process is performed by anodic treatment (7 seconds) → cathodic treatment (23 seconds). The electrolytic treatment time is 30 seconds, which is shorter than that in the prior art.
[0095] Table 1 lists the conditions and results of the implementation of Examples and Comparative Examples. In other words, Table 1 lists the composition of the phosphating treatment bath, electrolysis conditions, pH value (hydrogen ion concentration) of the treatment bath, ORP (oxidation-reduction potential), temperature, total acidity (from 0.1N caustic soda And titrate 10ml of this tr...
Embodiment 7 and 8 and comparative example 4
[0105] Examples 7 and 8 and Comparative Example 4 are cases of using actual elements (material: SUJ2: high-carbon chromium bearing steel: C: 1%, Cr: 1.45%). This component is a component used in a car brake system and is formed into a gear-like structure by cold forging after lubricating treatment. This forming process is to Figure 5 The shape shown becomes Figure 6 the shape shown. Therefore, used in Examples 7 and 8 and Comparative Example 4 is Figure 5 components shown.
Embodiment 9
[0117] In Example 9 and Comparative Examples 5 and 6, the degree of dissociation of phosphoric acid was adjusted by dissolving iron in phosphoric acid instead of dissolving zinc in phosphoric acid.
[0118] Table 3 gives a summary of the examples. In Example 9 and Comparative Examples 5 and 6, by [H 2 PO 4 - : 100 parts by weight + Zn 2+ : 25 parts by weight] / [H 3 PO 4 ]+[H 2 PO 4 - : 100 parts by weight + Zn 2+ : 25 parts by weight] (mass ratio) [Zn 25% dissolved phosphate ion solution ratio] is all zero. [Zn 25% Dissolved Phosphate Ion Solution Ratio] = 0 Same as in Comparative Examples 1-3. However, it is novel to regulate the degree of dissociation of phosphoric acid by dissolving iron in phosphoric acid.
[0119] Example 10
Example 11
Comparative Example 5
Comparative example 6
Example 9
24
25
26
27
28
treatment bath
composition
Dissociation Index of Phosphoric Acid
[H ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com