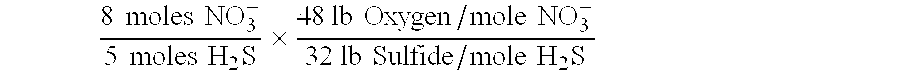Patents
Literature
637 results about "Nitrate ion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
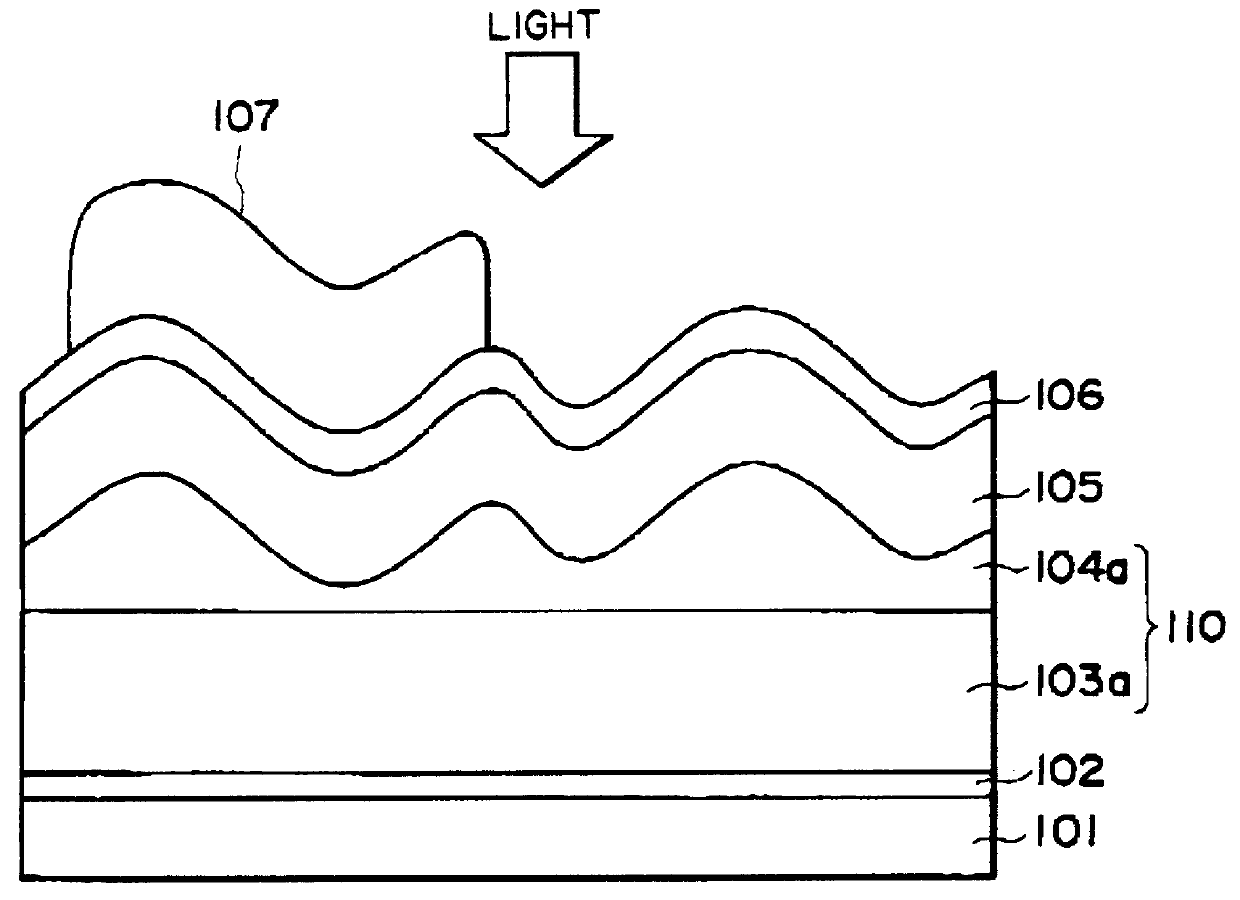
Process for producing photo-electricity generating device
InactiveUS6123824AInhibition of abnormal growthReduce leakage currentElectrolytic inorganic material coatingSurface reaction electrolytic coatingElectricityPower flow
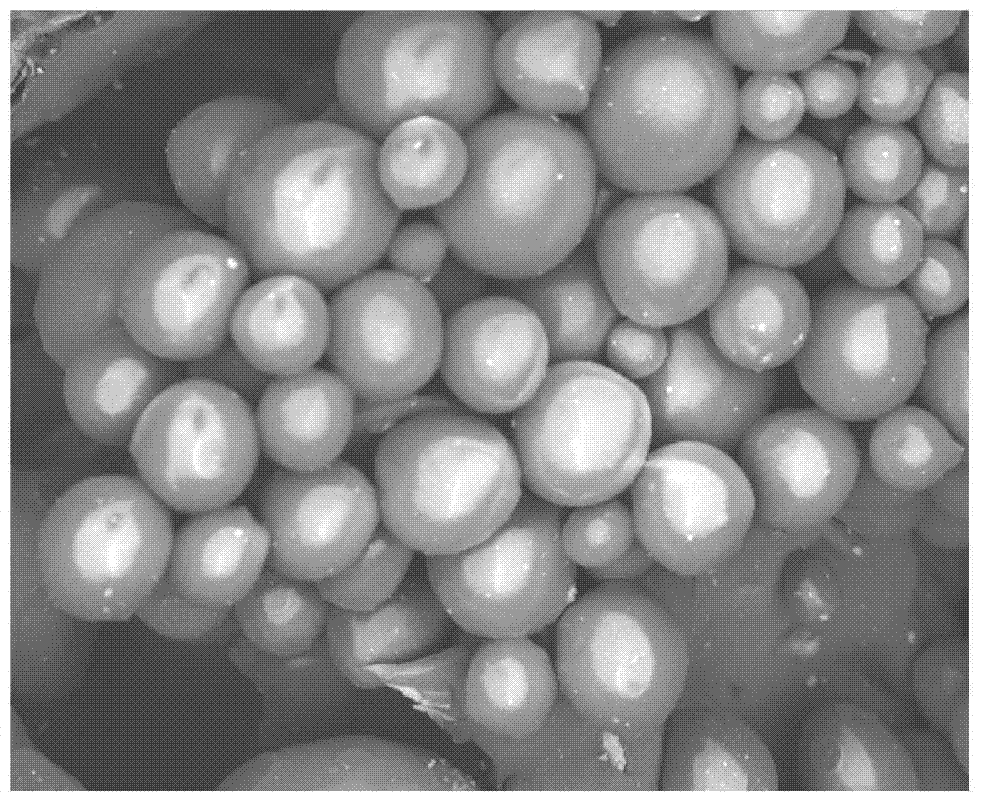
A photo-electricity generating device is produced through the steps of: immersing an electrode and an electroconductive substrate in an aqueous solution comprising nitrate ions and zinc ions, supplying a current passing through a gap between the electrode and the electroconductive substrate to form a first zinc oxide layer on the electroconductive substrate, etching the first zinc oxide layer, and forming a semiconductor layer on the zinc oxide layer. The zinc oxide layer may preferably be formed in two zinc oxide layers under different electrudeposition conditions. In this case, the etching step may preferably be performed between steps for forming these zinc oxide layers. The zinc oxide layer is provided with an unevenness at its surface suitable for constituting a light-confining layer of a resultant photo-electricity generating device.
Owner:CANON KK
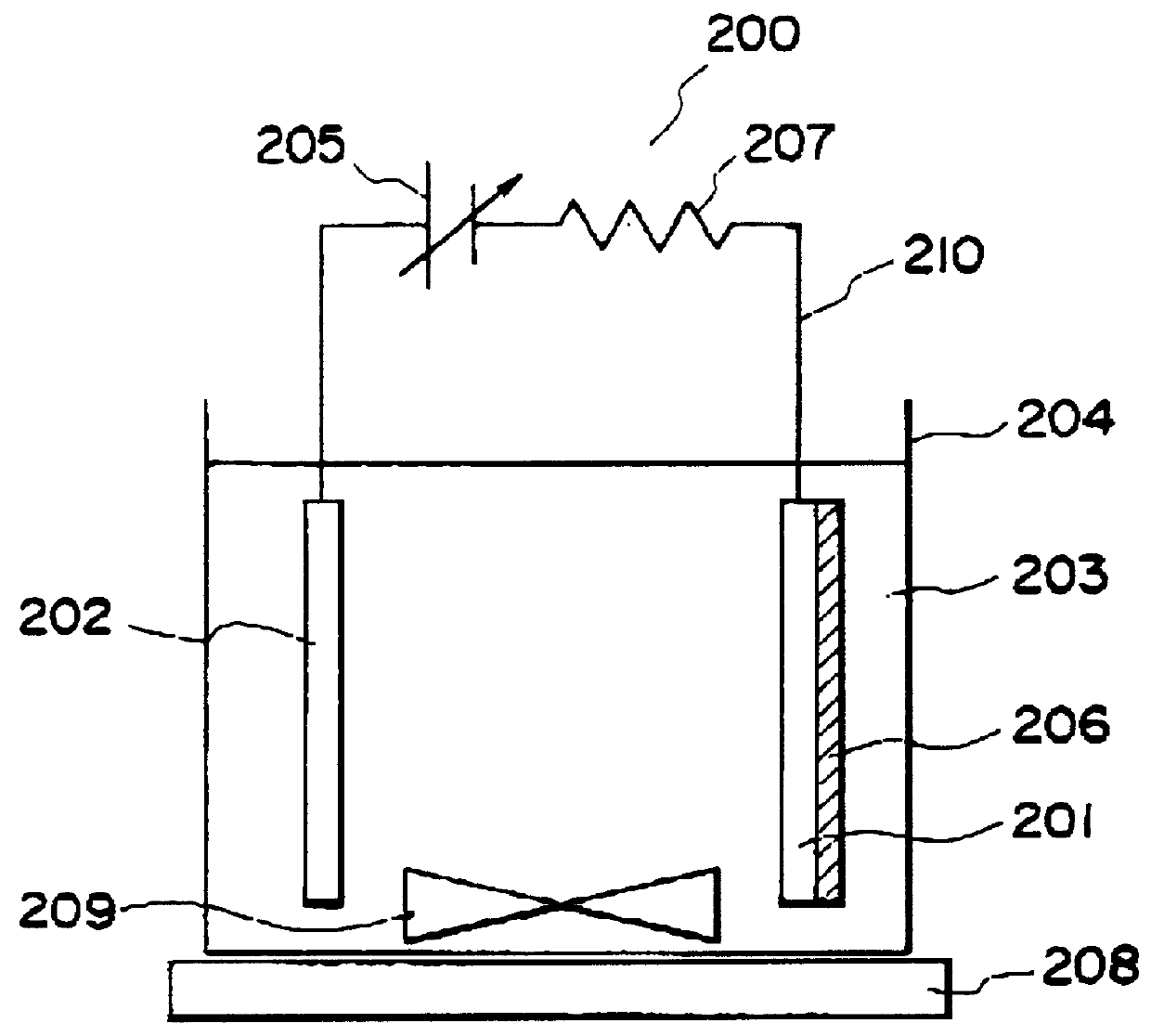
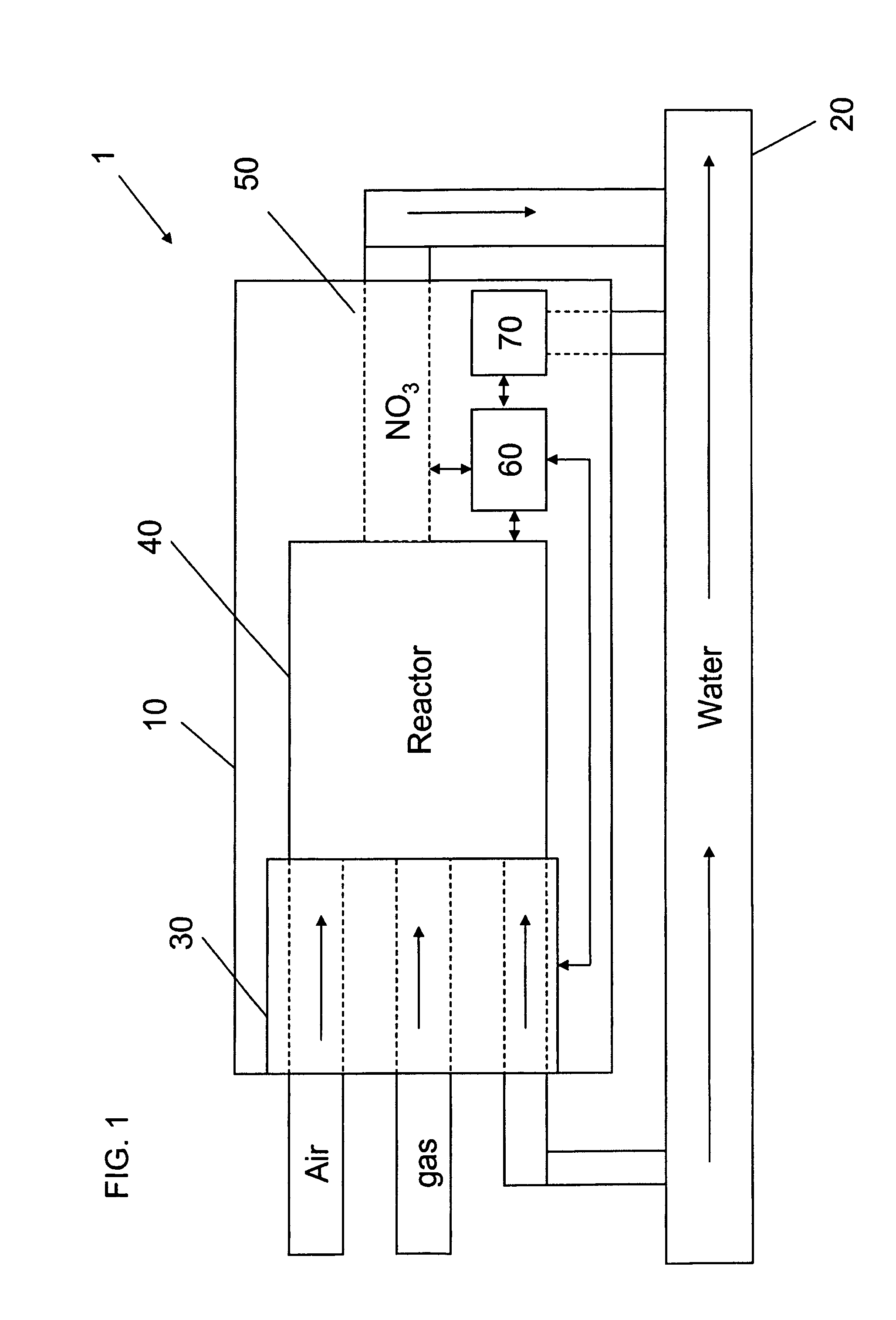
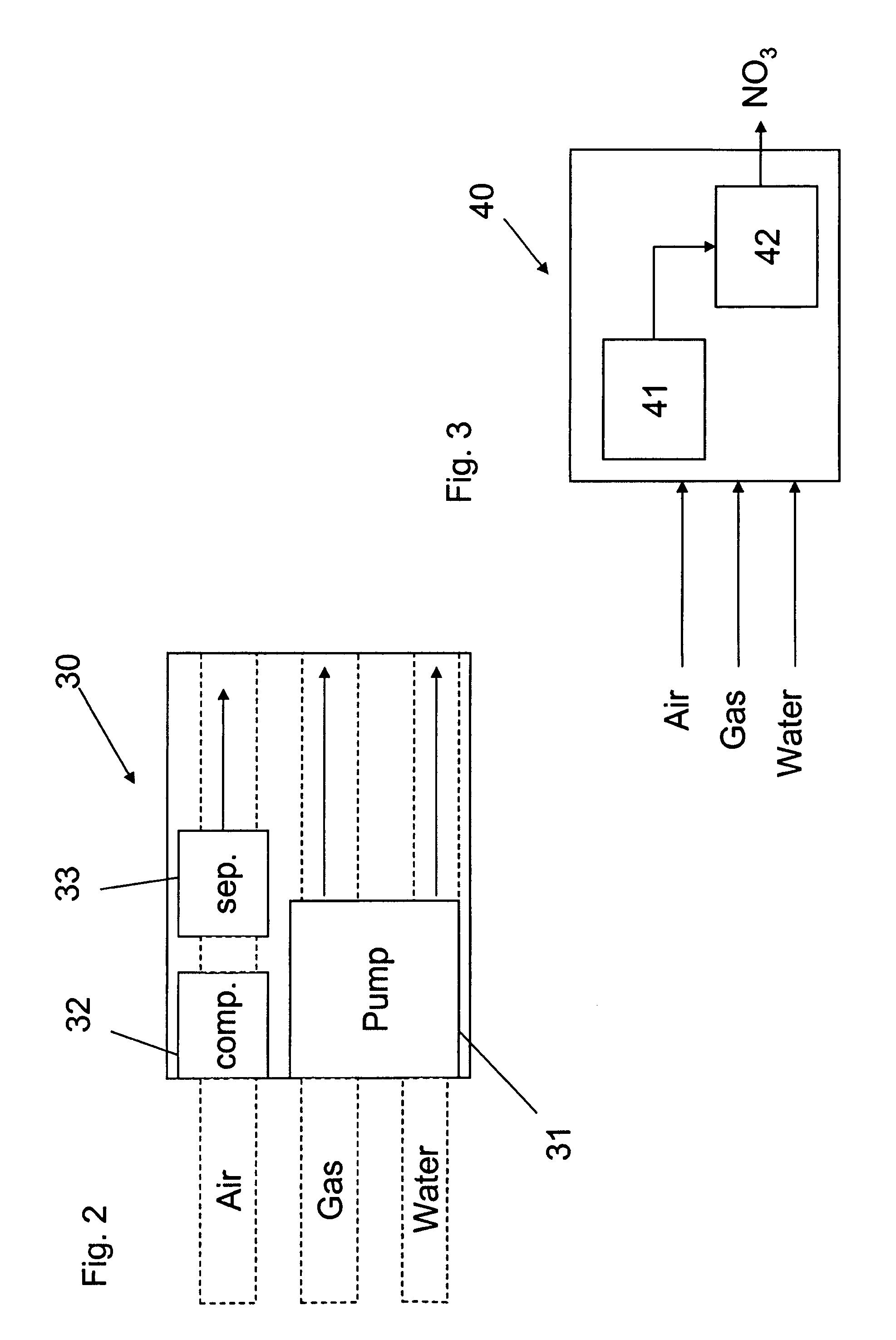
Apparatus for on-site production of nitrate ions
InactiveUS7514058B1Enhanced overall recoveryWater treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsMicrobial enhanced oil recoverySulfate-reducing bacteria
An apparatus and method produces nitrate ions on-site from water, natural gas and air extracted in proximity to the apparatus. The apparatus generates nitrate ions and brings the nitrate ions into contact with an aqueous system. Hydrogen sulfide present in the aqueous system is removed and the production of hydrogen sulfide by sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) is eliminated by introducing into the system nitrate ions, whereby denitrifying microorganisms, using nitrate, outcompete the sulfate-reducing bacteria for the available carbon nutrients, thus preventing the SRB from producing hydrogen sulfide. Nitrate ions generated by the apparatus and added to the aqueous system which contains the denitrifying microorganisms can enhance oil recovery by means of microbial enhanced oil recovery mechanisms.
Owner:NITRA GEN LLC
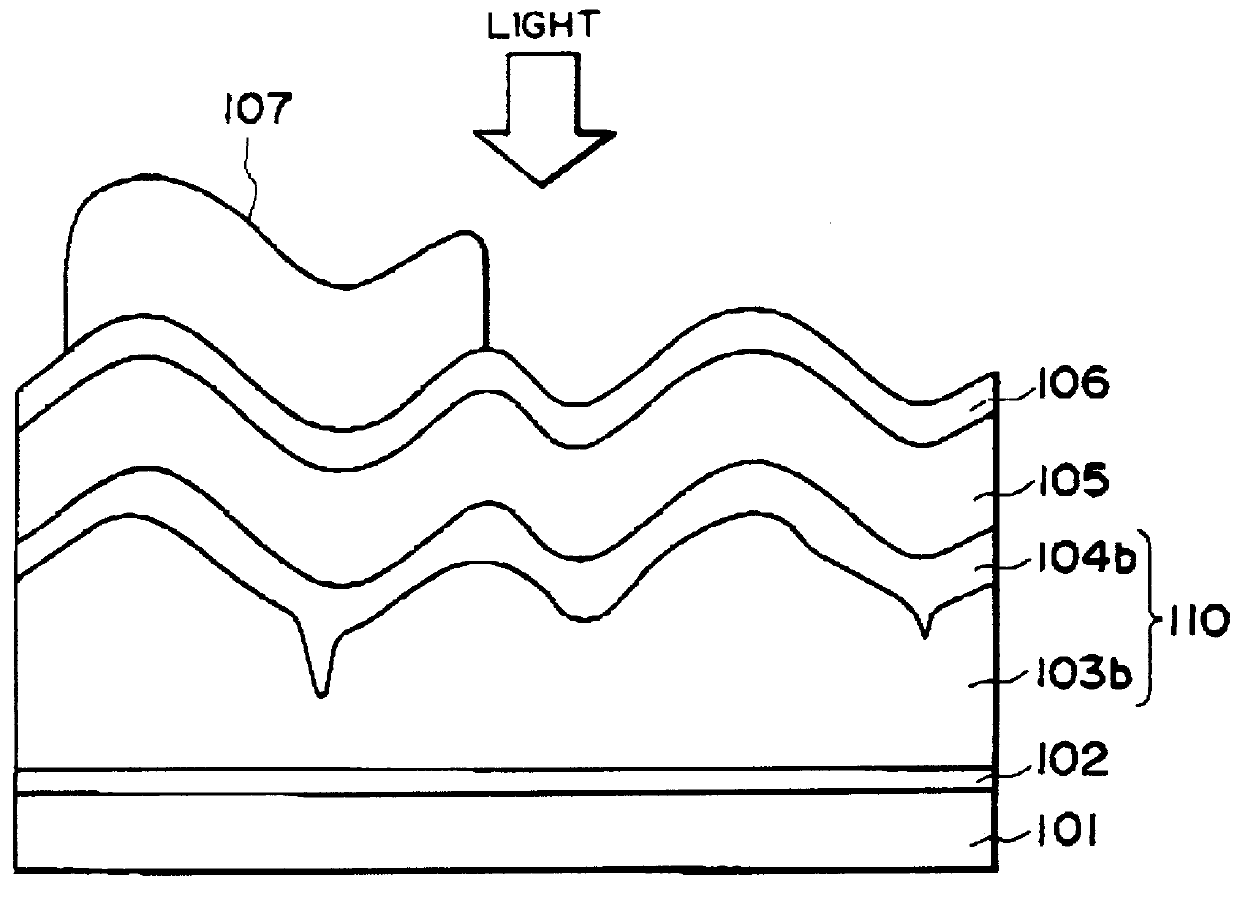
Process for forming zinc oxide film and processes for producing semiconductor device substrate and photo-electricity generating device using the film
InactiveUS6106689AHigh production yield and reliabilityEnhanced light absorptionElectrolytic inorganic material coatingFinal product manufactureElectricitySurface roughness
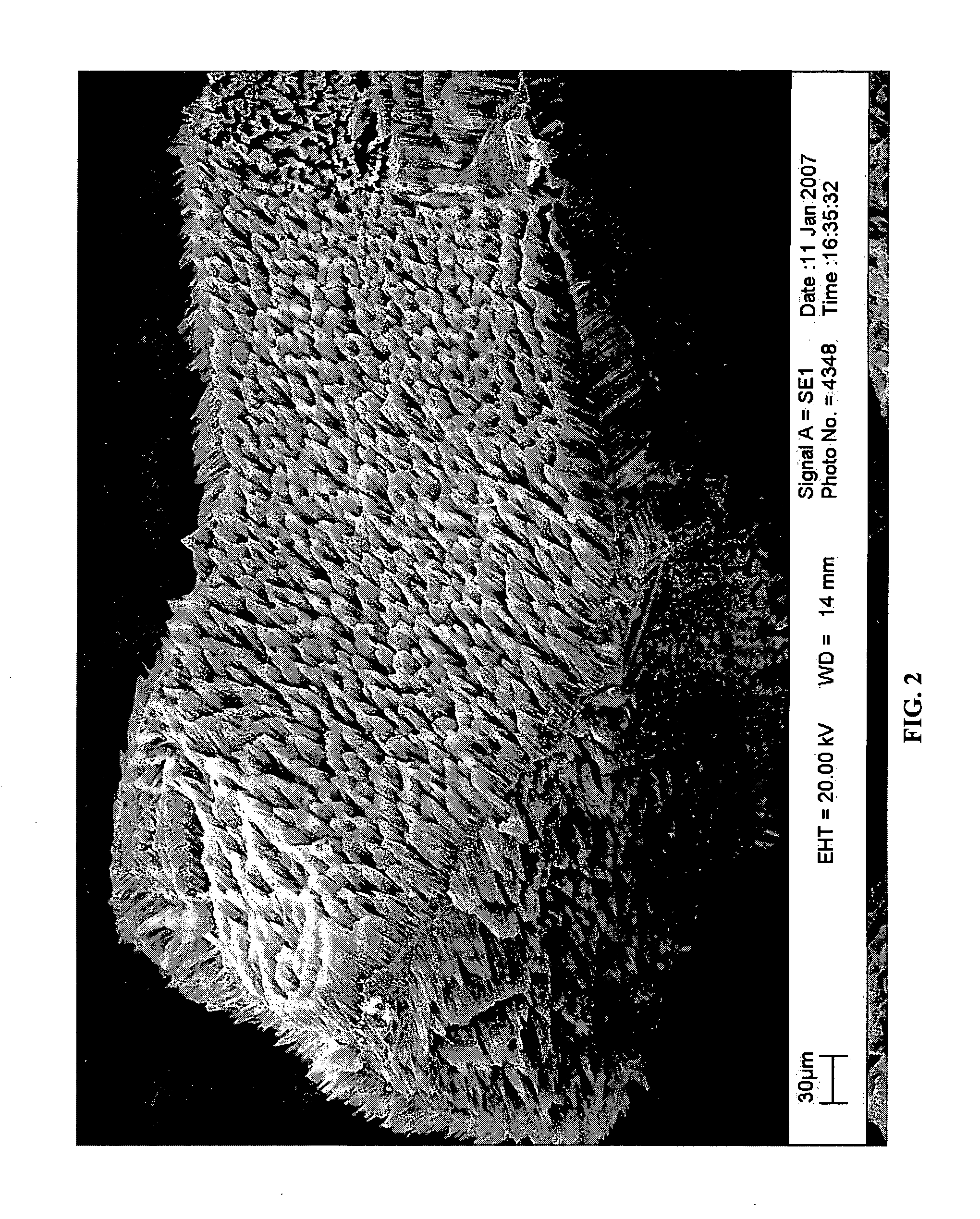
A process for forming a zinc oxide film including immersing an electroconductive substrate having a surface including a plurality of linear projections in an aqueous solution containing at least nitrate ions and zinc ions to form a zinc oxide film on the electroconductive substrate by a liquid-phase deposition. The plurality of linear projections may preferably provide an uneven surface which has a center-line average surface roughness Ra(X) of 15-300 nm when scanned in a direction parallel to the linear projections, a center line average surface roughness Ra(Y) of 20-600 nm when scanned in a direction perpendicular to the linear projections, and an Ra(X) / Ra(Y) ratio of at most 0.8. The thus formed zinc oxide film is provided with an uneven surface suitable for an optical-confinement layer of a photo-electricity generating device excellent in photoelectric performances.
Owner:CANON KK
Process and equipment for nitrogen oxide waste conversion to fertilizer
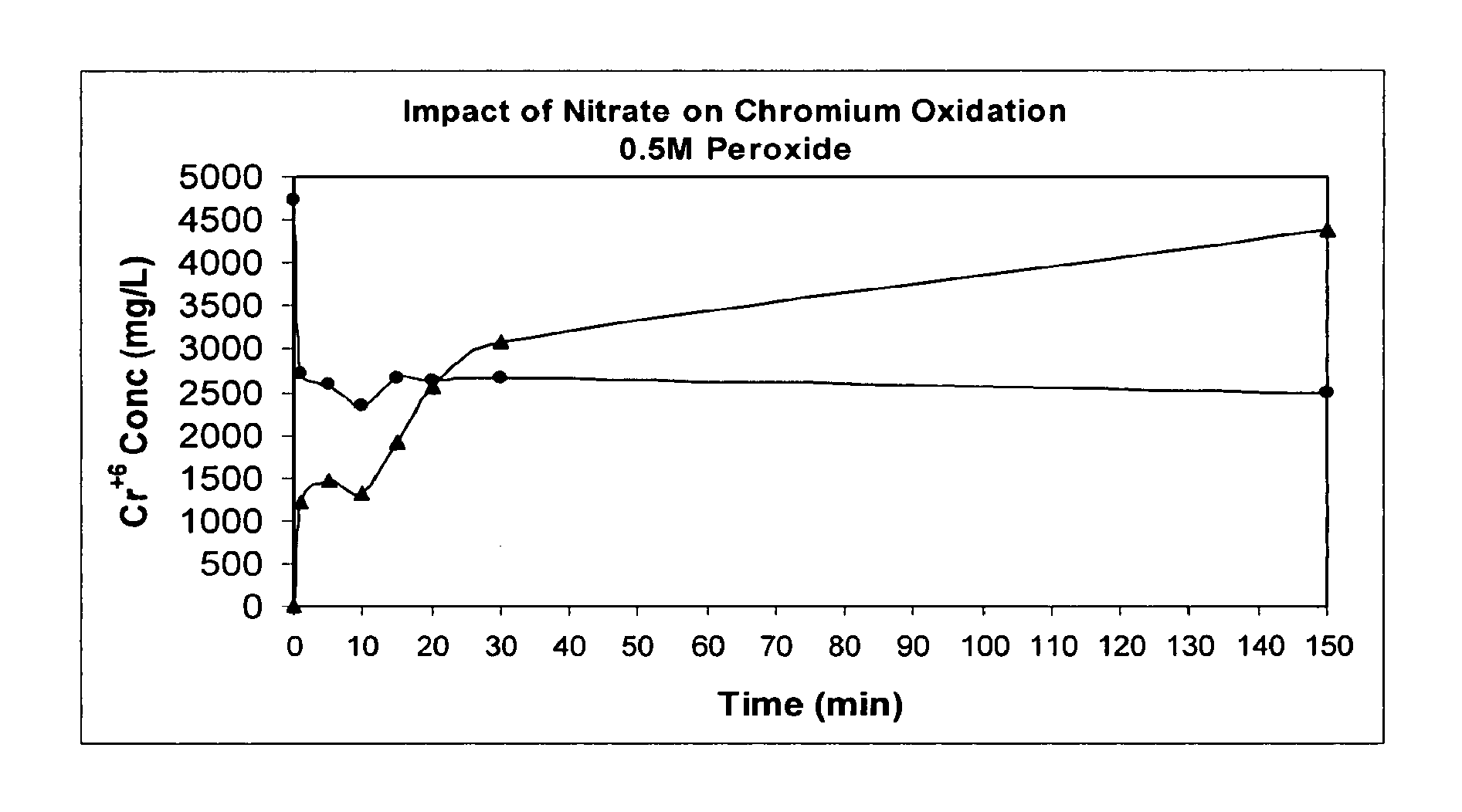
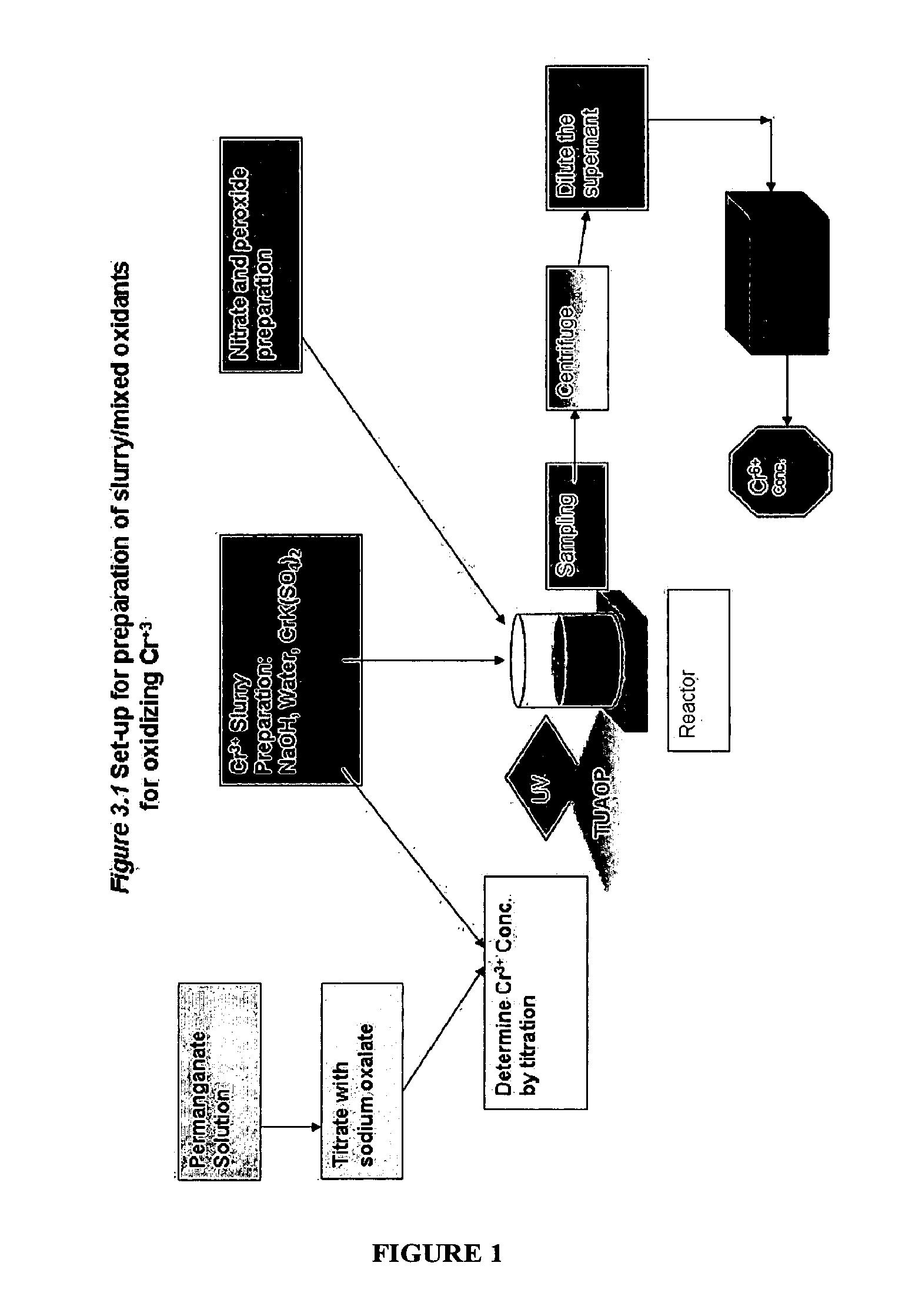
The present invention describes a process for converting vapor streams from sources containing at least one nitrogen-containing oxidizing agent therein to a liquid fertilizer composition comprising the steps of: a) directing a vapor stream containing at least one nitrogen-containing oxidizing agent to a first contact zone, b) contacting said vapor stream with water to form nitrogen oxide(s) from said at least one nitrogen-containing oxidizing agent, c) directing said acid(s) as a second stream to a second contact zone, d) exposing said second stream to hydrogen peroxide which is present within said second contact zone in a relative amount of at least 0.1% by weight of said second stream within said second contact zone to convert at least some of any nitrogen oxide species or ions other than in the nitrate form present within said second stream to nitrate ion, e) sampling said stream within said second contact zone to determine the relative amount of hydrogen peroxide within said second contact zone, f) adding hydrogen peroxide to said second contact zone when a level of hydrogen peroxide less than 0.1 % by weight in said second stream is determined by said sampling, g) adding a solution comprising potassium hydroxide to said second stream to maintain a pH between 6.0 and 11.0 within said second stream within said second contact zone to form a solution of potassium nitrate, and h) removing said solution of potassium nitrate from said second contact zone.
Owner:NAT AERONAUTICS & SPACE ADMINISTATION U S GOVERNMENT AS REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTATOR
Thermal energy storage materials
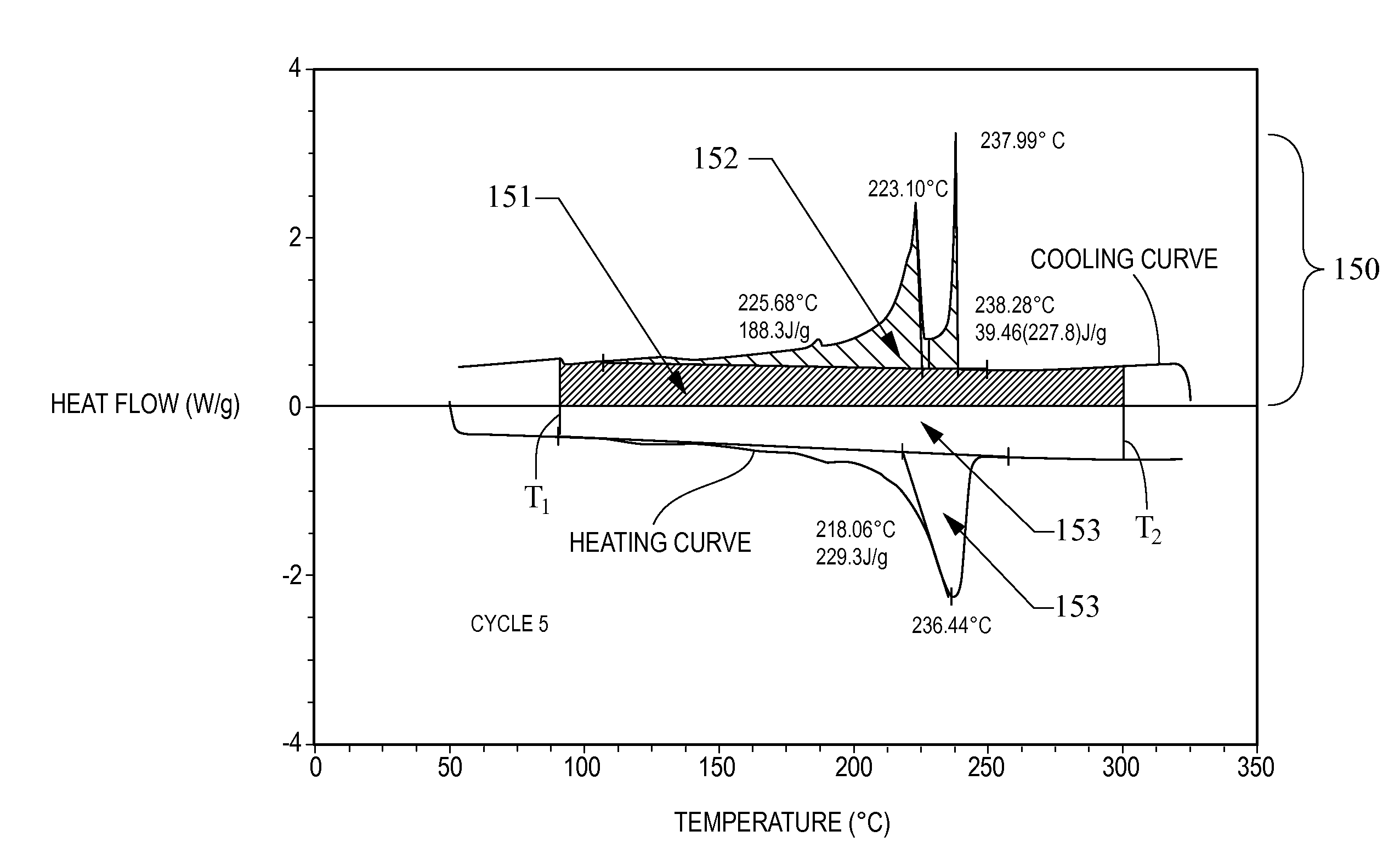
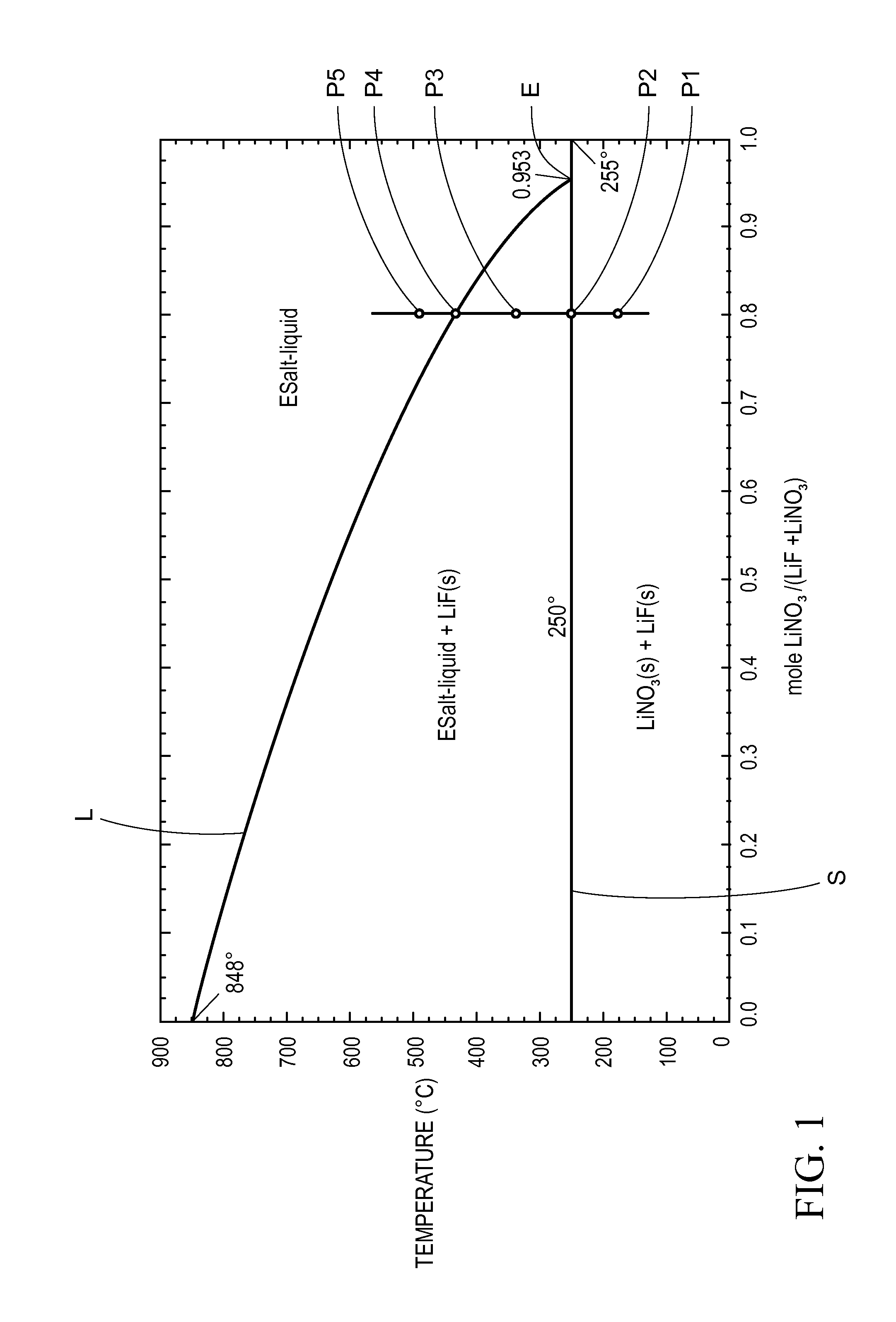
A thermal energy storage material (TESM) system (and associated methods) that reproducibly stores and recovers latent heat comprising i) at least one first metal containing material including at least one first metal compound that includes a nitrate ion, a nitrite ion, or both; ii) at least one second metal containing material including at least one second metal compound; and iii) optionally including water, wherein the water concentration if any is present is less than about 10 wt. %; wherein the TESM has a liquidus temperature, TL, from about 100° C. to about 250° C.; and wherein the TESM exhibits a heat storage density from 300° C. to 80° C. of at least about 1 MJ / l; so that upon being used in a system that generates heat, at least a portion of the heat is captured and stored by the TESM and subsequently released for use, and the system is generally resistant to corrosion at temperatures of about 300° C.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Organic biomass fractionation process
InactiveUS20030041982A1Economical and efficientLow costPretreatment with acid reacting compoundsWaste based fuelFractionationNitration
A method for fractionating fibrous biomass comprising cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin components to separate said lignin, cellulose and hemicellulose from one another comprises: (a) shredding said fibrous biomass; (b) concurrently with or subsequent to said shredding, contacting said biomass with an aqueous solution of a nitrate ion source at a concentration of about 0.1-0.3% at a temperature in the range of about 60° to about 80° C. to initiate nitration of the lignin component of said biomass; (c) submerging said partially nitrated biomass in an aqueous solution of a nitrate ion source in the presence of an aluminum compound at a temperature within the range of about 75-100° C. for a time sufficient to complete the nitration of said lignin component; (d) contacting the nitrated biomass produced in step (c) with an alkaline extraction liquor comprising NH4OH at an initial concentration sufficient to solubilize said nitrated lignin component and said hemicellulose component from said cellulose component of said biomass; e) recovering said cellulose from said extraction liquor containing said solubilized nitrated lignin and hemicellulose components, wherein said cellulose comprises at least about 88% alpha cellulose; (f) treating said extraction liquor with an acid to precipitate lignin contained therein, and (g) separating said lignin from soluble hemicellulose in said extraction liquor. The recovered cellulose component comprises at least 88% alpha cellulose and is useful as a starting material for the production of ethanol.
Owner:PRIOR ERIC S
Oxidative Treatment Method
InactiveUS20100320156A1Quickly and efficiently decomposeEffective treatmentWater/sewage treatment by irradiationDecorative surface effectsElectrolysisWaste stream
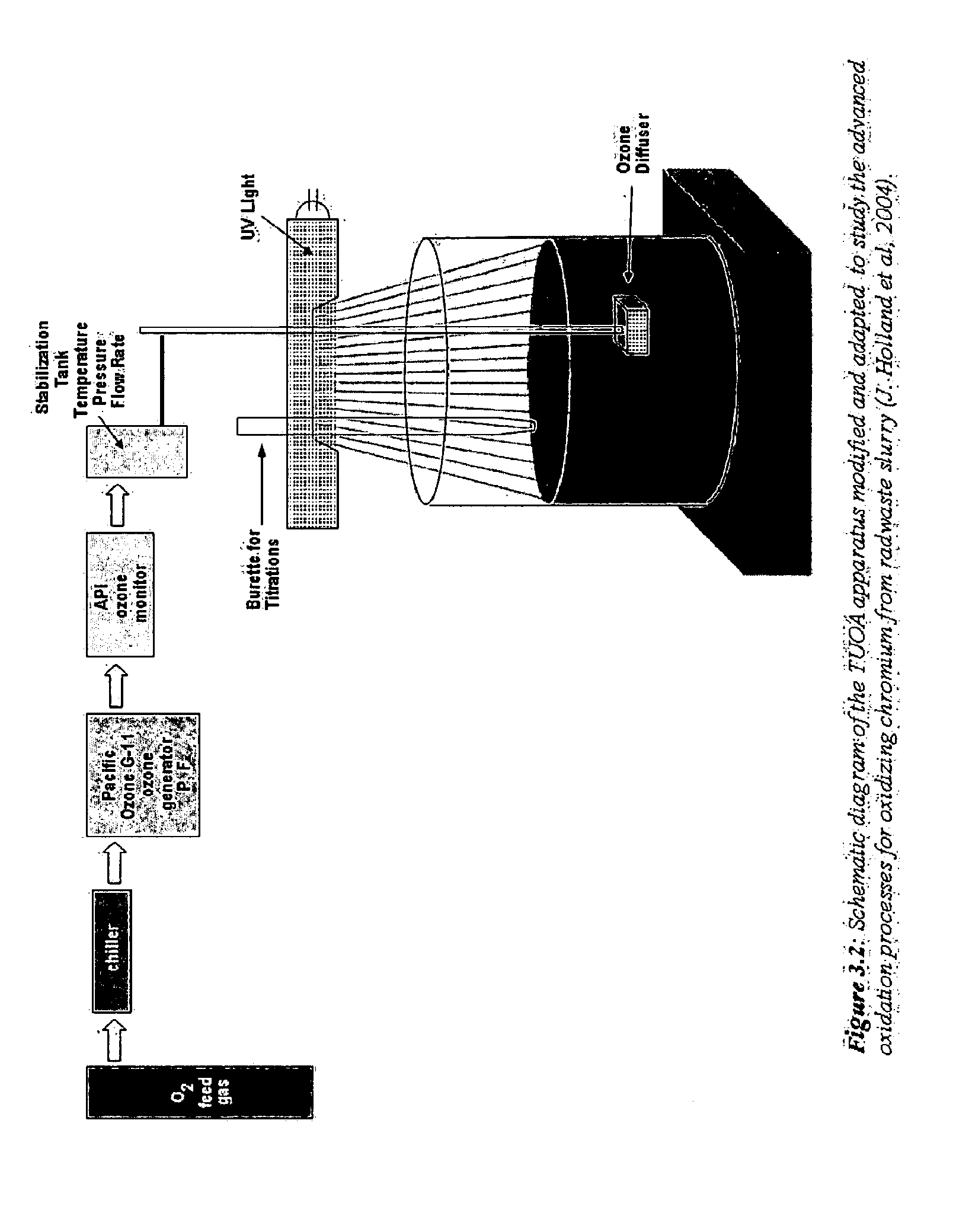
The present invention provides a method for oxidizing a substance (e.g., in a waste stream, drinking water, a paper pulp slurry, or on a surface), which uses free radicals and reactive species generated from multiple oxidants. The method comprises combining peroxynitrite or peroxynitrous acid and at least one additional oxidizing agent for a period of time sufficient to oxidize the substance of interest. The peroxynitrite or peroxynitrous acid preferably is formed by irradiation of nitrate ion and / or nitric acid (e.g., with UV or gamma rays). The yield of free radicals and reactive species, which are the intermediate species that perform the oxidation may be increased by addition of a catalysts, electromagnetic radiation, sonic waves, and / or electrolysis.
Owner:TULANE EDUCATIONAL FUND
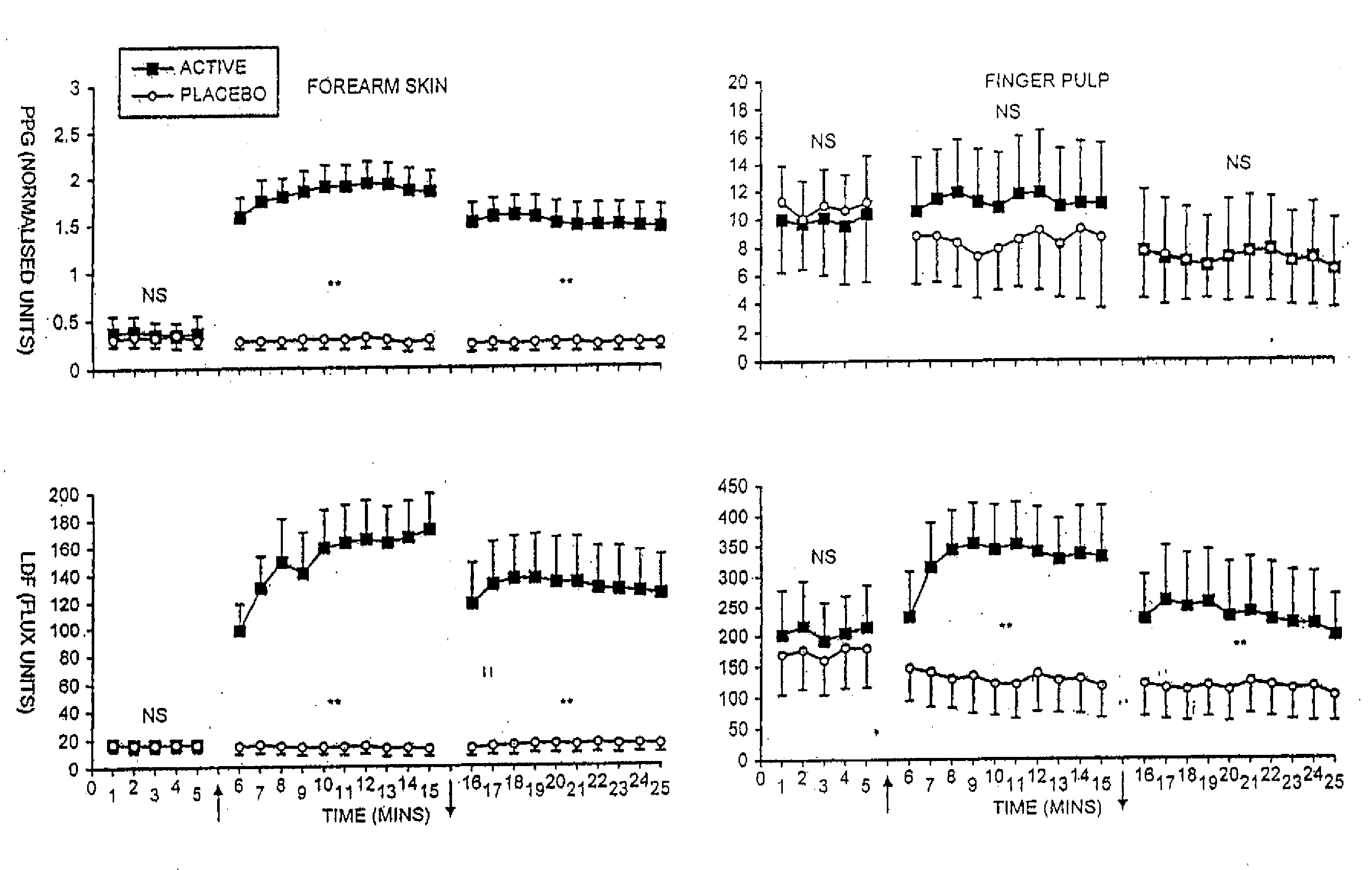
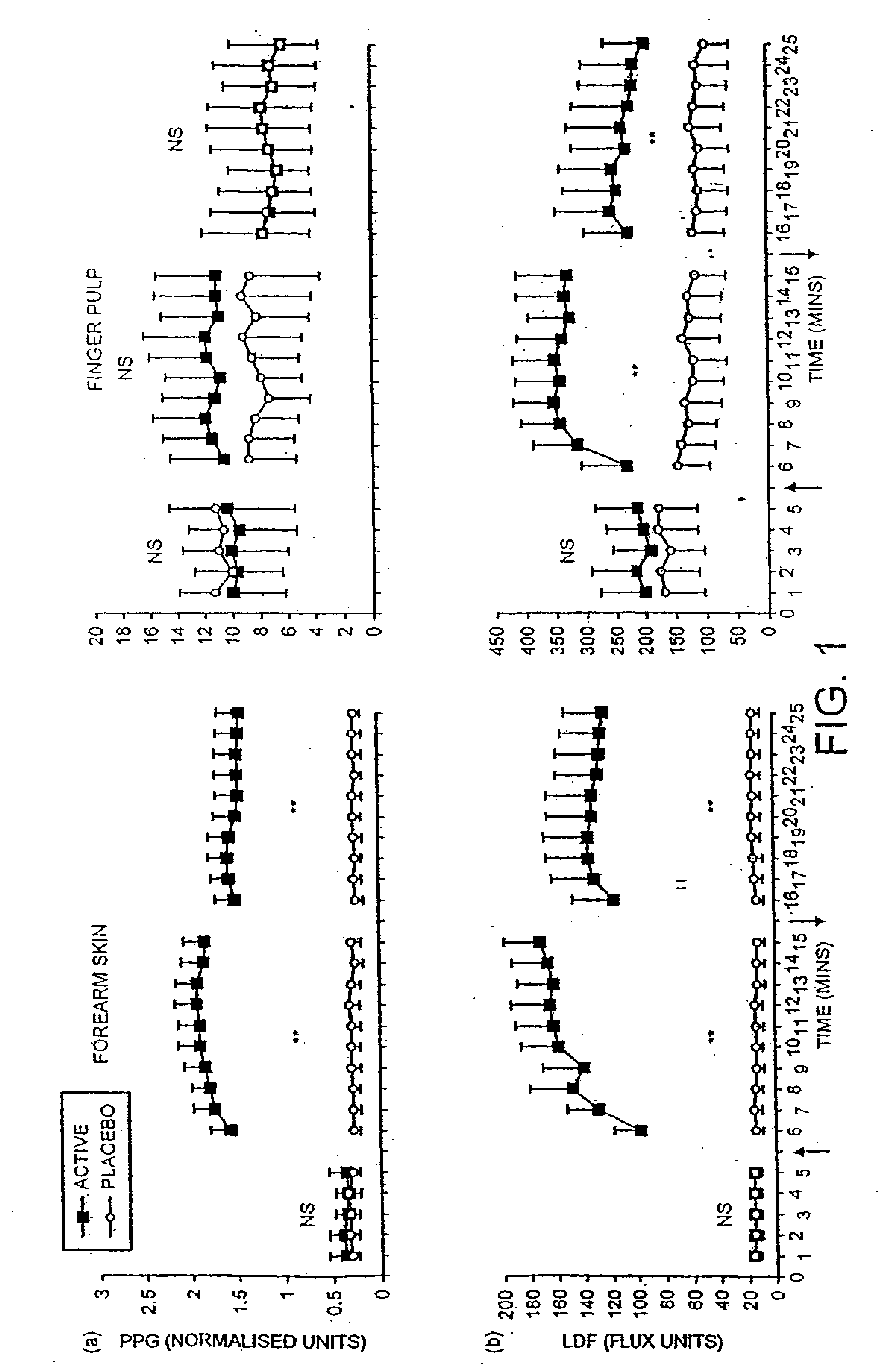
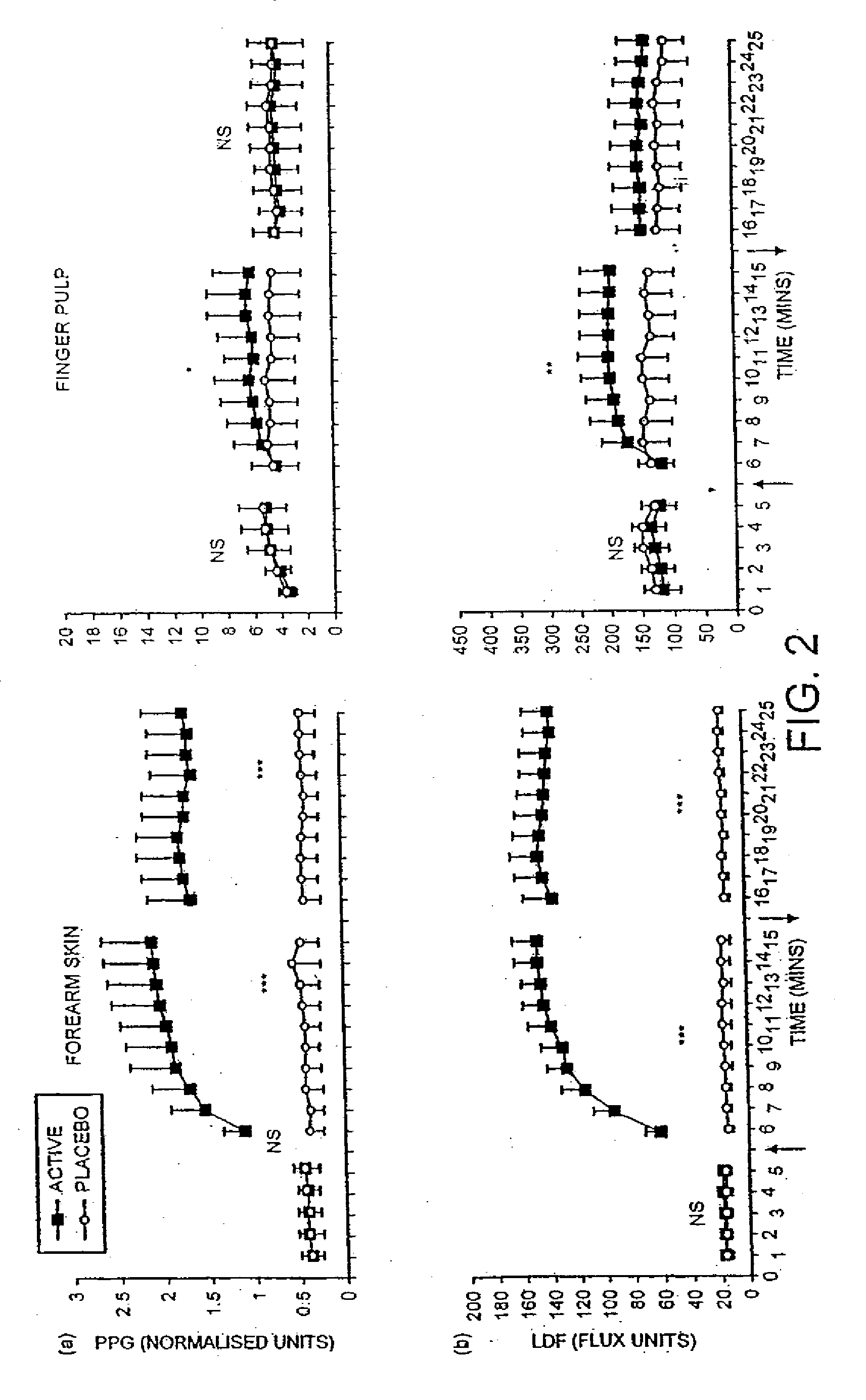
Pharmaceutical composition containing nitrate source and an acidifying agent for treating skin ischaemia
InactiveUS20050142218A1Direct contact guaranteePermitted diffusionBiocidePharmaceutical delivery mechanismSkin surfacePeripheral ischaemia
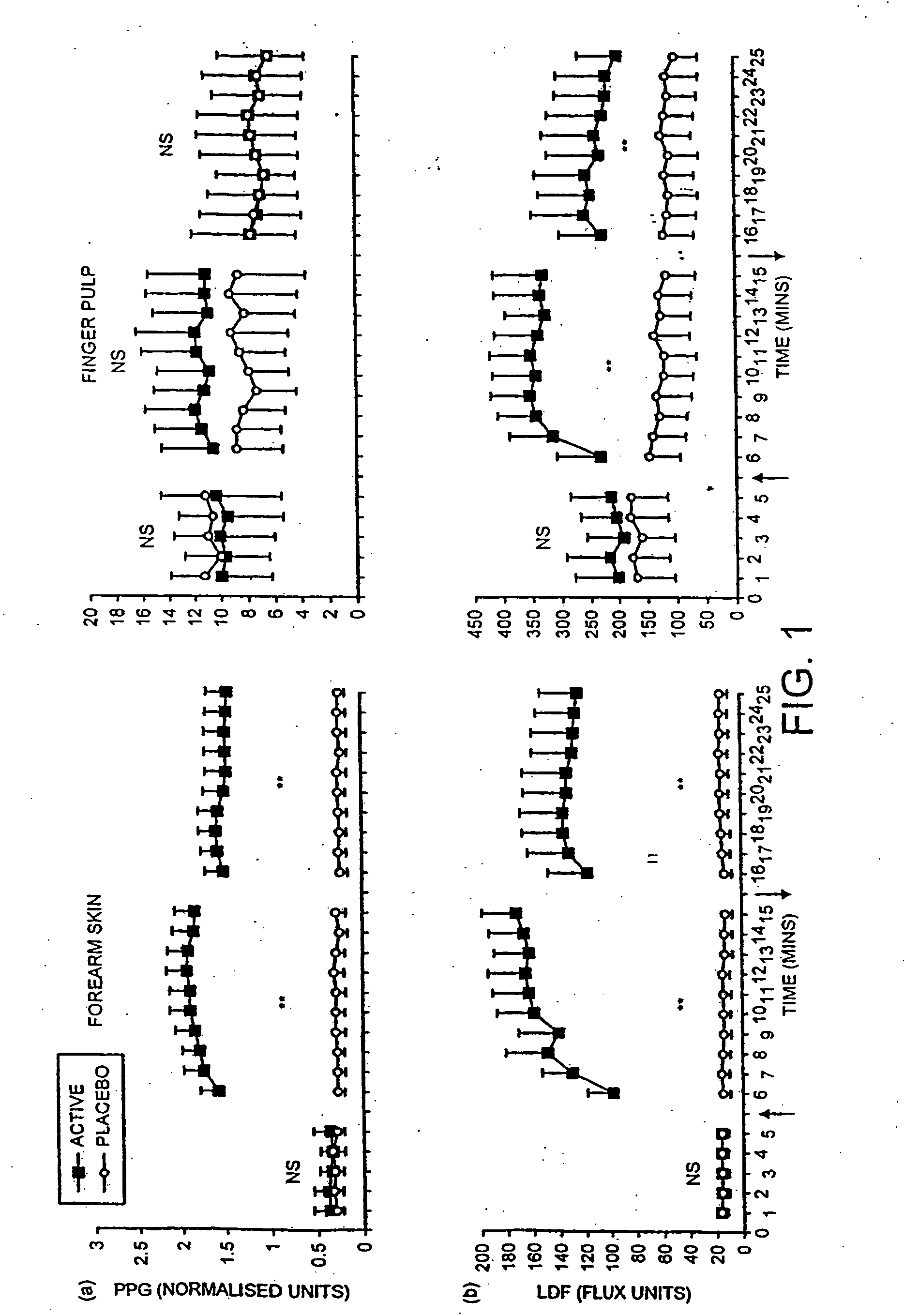
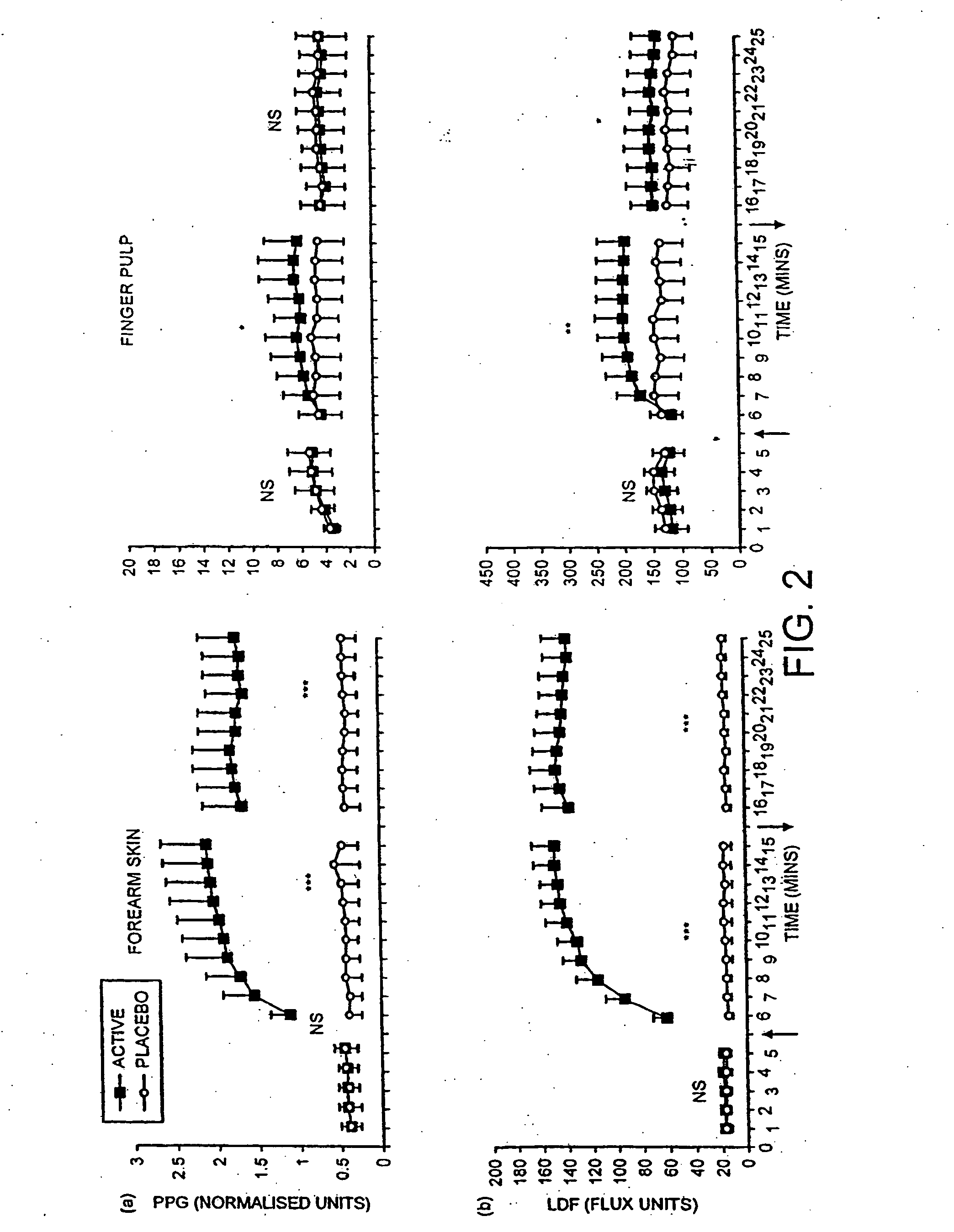
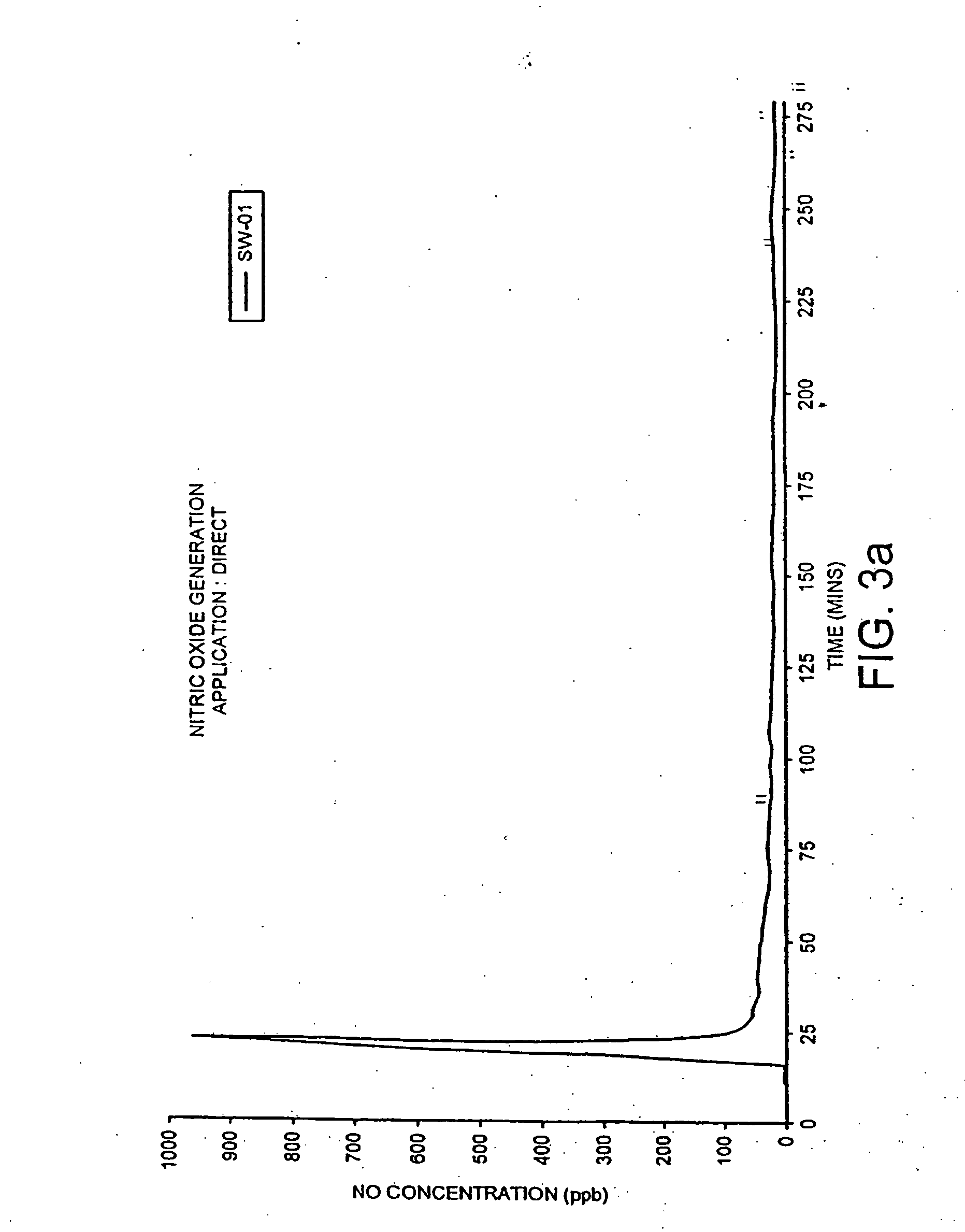
The use of acidified nitrate as an agent to produce local production of nitrate oxide at the skin surface is described in the treatment of peripheral ischaemia and associated conditions. The dosage form may be in any pharmaceutically acceptable carrier means and comprises an acidifying agent adapted to reduce the pH at the environment. A barrier consisting of a membrane allows diffusions of the nitrate ions while preventing direct contact of the skin and acidifying agent. Amongst the many potential applications for the invention is the management of chronic skin wounds, peripheral ischaemia conditions such as Raynaud's phenomenon. Compositions and methods of use for these applications are described.
Owner:QUEEN MARY UNIV OF LONDON
Antistatic polyester film and antistatic film laminate
InactiveUS6103368AIncrease resistanceIncrease productivityRecord carriersMagnetic materials for record carriersCarbon numberPolyester
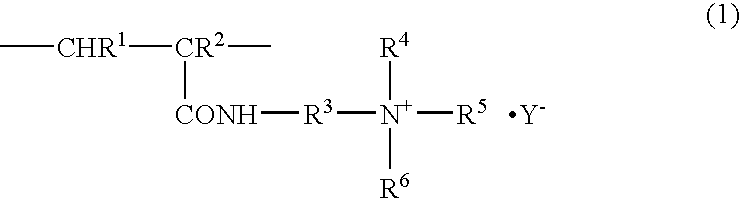
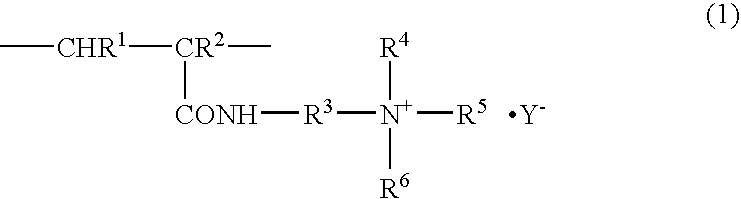
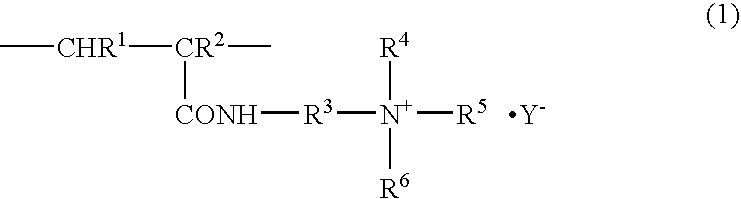
PCT No. PCT / JP97 / 02341 Sec. 371 Date Feb. 27, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Feb. 27, 1998 PCT Filed Jul. 7, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 02308 PCT Pub. Date Jan. 22, 1998The present invention provides an antistatic polyester film having an antistatic layer formed of an antistatic agent (A) composed mainly of a polymer having a recurring unit of a structure expressed by the following formula (I) on at least one surface of a polyester film wherein R1 and R2 are each H or CH3, R3 is an alkylene group having a carbon number of 2 to 10, R4 and R5 are each a saturated hydrocarbon group having a carbon number of 1 to 5, R6 is an alkylene group having a carbon number of 2 to 5, n is a number of 0 to 40, m is a number of 1 to 40, and Y- is a halogen ion, a mono- or polyhalogenated alkyl ion, nitrate ion, sulfate ion, an alkylsulfate ion, sulfonate ion or an alkylsulfonate ion.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
Ternary Zn-Ni-Mn phosphorizing solution
InactiveCN1847455AImprove stabilityExtended service lifeMetallic material coating processesPhosphate ionElectrophoresis
The present invention discloses one kind of ternary Zn-Ni-Mn phosphorizing solution and its preparation process. The ternary Zn-Ni-Mn phosphorizing solution consists of zinc ion, phosphate radical ion, nickel ion, manganese ion, chlorate radical ion, nitrate radical ion, fluorine ion, promoter A, additive B and complexing agent C in certain proportion. The present invention can form compact and homogeneous phosphide film with high base resistance and high corrosion resistance, and is suitable for the phosphorizing treatment of cathode before electrophoresis coating.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Trivalent-chromium blue-white passivator for zinc-plated permanent magnetic material and passivation method thereof
InactiveCN102041497AAvoid pollutionAvoid damageMetallic material coating processesRare-earth elementNickel salt
The invention provides a trivalent-chromium blue-white passivator for a zinc-plated permanent magnetic material and a passivation method thereof. The trivalent-chromium blue-white passivator contains a main film-forming agent, an auxiliary film-forming agent, a stabilizer, an oxidant and a surfactant, wherein the main film-forming agent is a soluble salt of trivalent chromium, the stabilizer is selected from at least one of fluoride, citric acid and oxalic acid, the auxiliary film-forming agent is selected from at least one of soluble cobalt salt, soluble nickel salt or soluble salts of rare-earth elements, the oxidant is nitrate ions or hydrogen peroxide, and the surfactant is NPE (Nonylphenol Polyoxyethylene Ether) or sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate. The trivalent-chromium blue-white passivator provided by the invention has a low cost, does not pollute the environment, and also does not cause damage to the health of operators.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONG KE SAN HUAN HI TECH +1
Ammonium sulfate nitrate
Ammonium sulfate nitrate composite materials useful as fertilizers having desirable levels of nitrate ions, superior stability against detonation, higher density, greater resistance to moisture, and a method for their manufacture. The ammonium sulfate nitrate composites have as essential constituents ammonium sulfate and the NH4SO4.2(NH4NO3) double salt with less than 5 wt. % in combined total of the more hazardous NH4SO4.3(NH4NO3) double salt and ammonium nitrate. The composites of the invention are formed by reacting ammonium sulfate with ammonium nitrate in a molar ratio of about 0.9:1 to about 1.1:1 in the presence of a small amount of water in a narrow range of temperatures and then cooling to solidification at a sufficiently rapid rate to prevent macroscopic segregation of the reaction products.
Owner:ADVANSIX RESINS & CHEM LLC
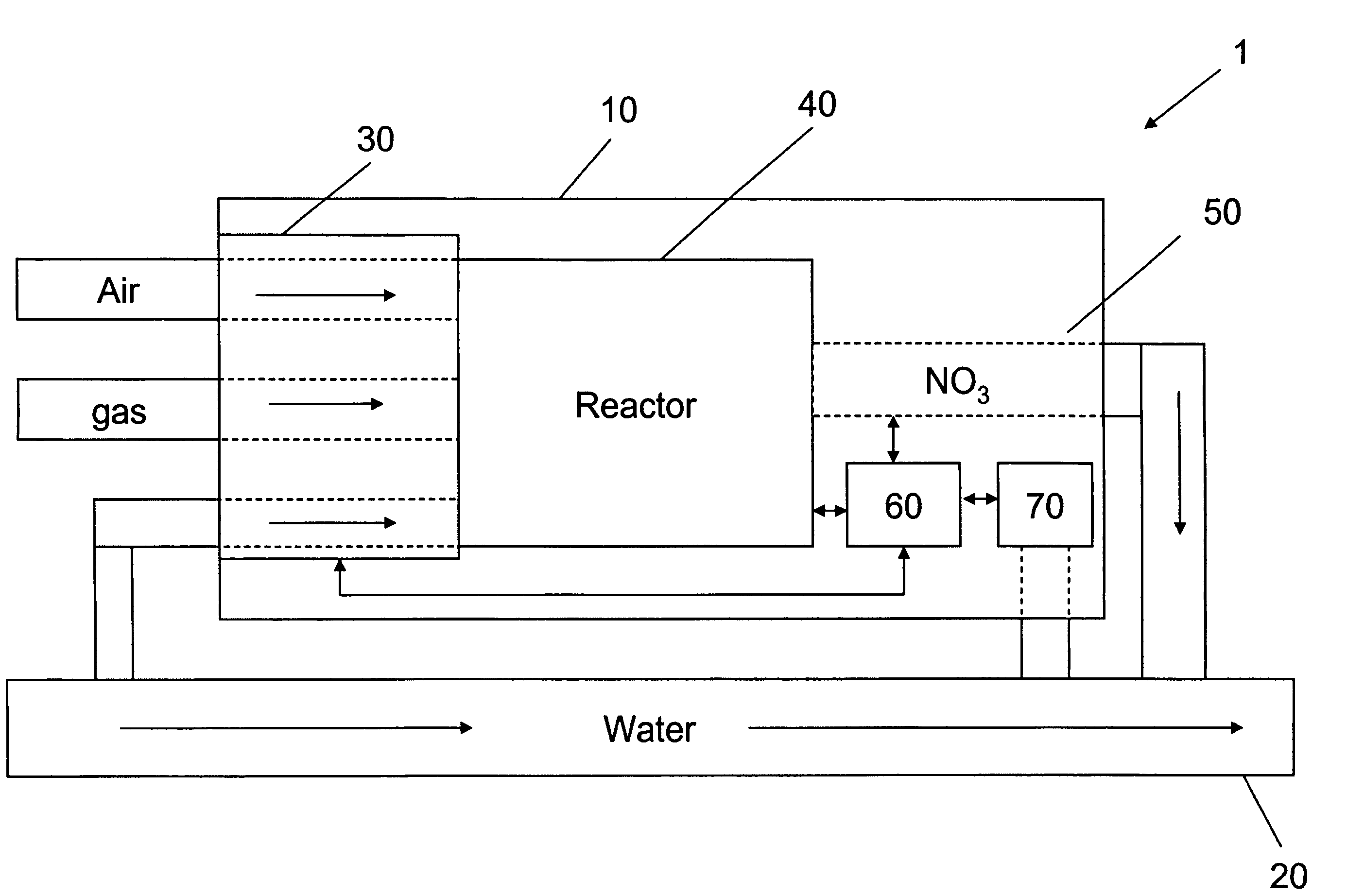
Online automatic monitoring system of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in seawater and monitoring method thereof
InactiveCN101655501ARealize online simultaneous digestionRealize online measurementPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsMonitoring systemTotal nitrogen
The invention provides an online automatic monitoring system of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in seawater and a monitoring method thereof. The system comprises an automatic seawater liquid feedcontroller, an ultraviolet microwave digestor, a total nitrogen measuring flow passage, a total phosphorus measuring flow passage and a spectrophotometer, wherein the automatic seawater liquid feed controller is connected with the ultraviolet microwave digestor by a liquid feed pipeline; digested sample flows into an electronic cooler from a liquor drainage pipeline of the ultraviolet microwave digestor to be cooled and respectively enters into the total nitrogen measuring flow passage and the total phosphorus measuring flow passage; the total nitrogen measuring flow passage comprises a nitrate ion reducing device, a sample reaction pipeline is connected with the spectrophotometer, and the front end of the sample reaction pipeline is provided with a nitrite color reagent injecting valve; and the total phosphorus measuring flow passage comprises the structure that the sample reaction pipeline is connected with the spectrophotometer, and the front end of the sample reaction pipeline is provided with an orthophosphate color reagent injecting valve. The invention can complete work procedures such as automatically sampling seawater, digesting, reducing, washing, measuring, and the like,at one time.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Process for removal of dissolved hydrogen sulfide and reduction of sewage BOD in sewer or other waste systems
InactiveUSRE37181E1Substantial eliminationEliminate the problemTreatment using aerobic processesSpecific water treatment objectivesSulfideSewage
Removal of dissolved hydrogen sulfide and a reduction in BOD is achieved by the addition of nitrate ions to waste systems in an amount sufficient to stimulate growth of bacteria which utilize dissolved hydrogen sulfide in their metabolism. Specifically, about 2.4 lbs. <INS-S DATE="20010522" ID="INS-S-00001">nitrate <INS-E ID="INS-S-00001">oxygen per lb. of sulfide is required.
Owner:UNITED STATES FILTER CORPORATION
Akali zinc secondary cell and method for preparation thereof
InactiveUS20020164530A1Excellent in maintaining alkaline aqueous solutionIncrease internal resistanceCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersNon-aqueous electrolyte cellsAlkaline waterElectrical battery
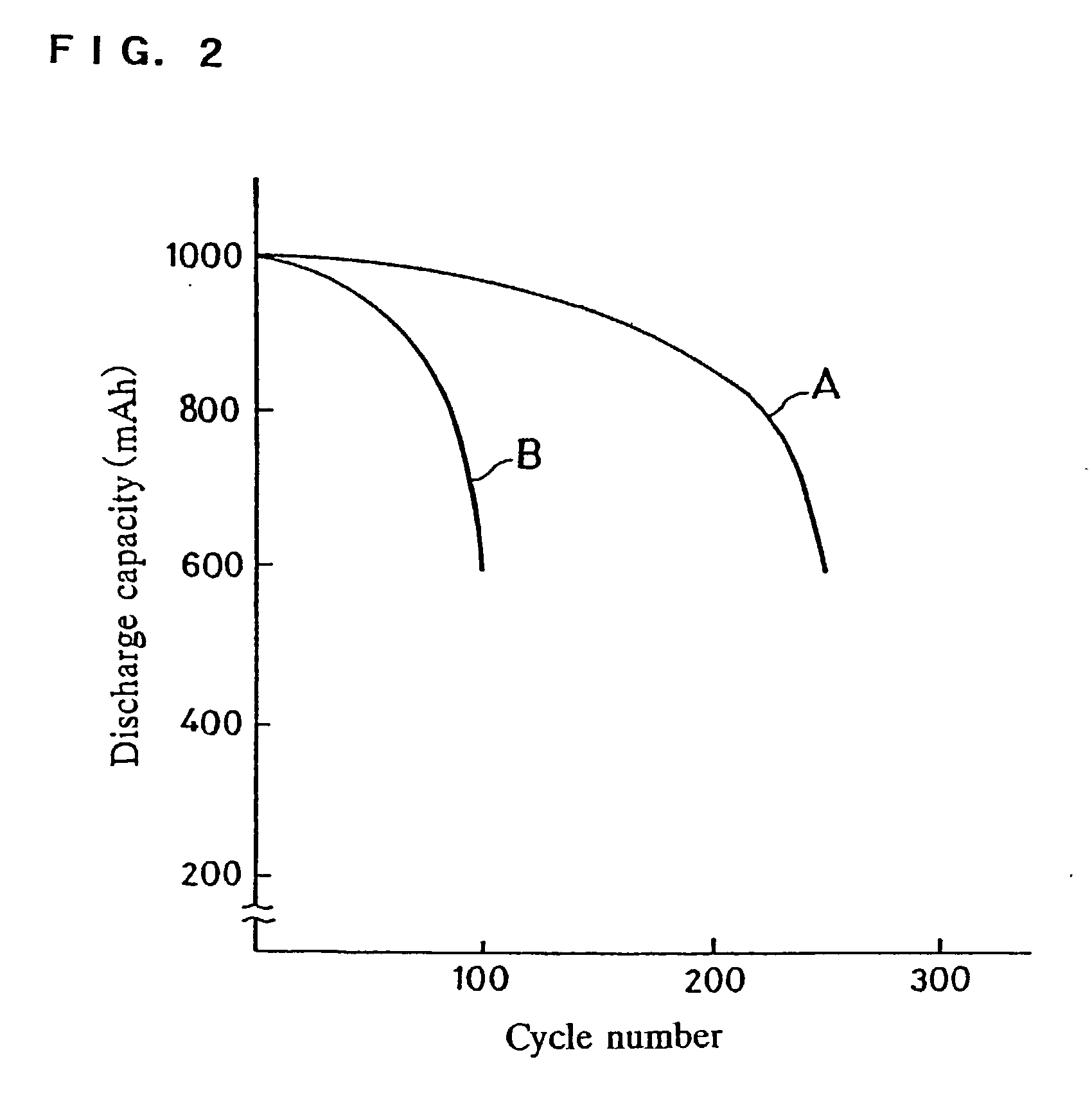
An alkaline zinc secondary battery in accordance with the present invention comprises a separator layer comprising a gel electrolyte comprising a water absorbent polymer and an alkaline aqueous solution, disposed between a negative electrode comprising at least one selected from the group consisting of zinc and zinc oxide and a positive electrode. Because the separator layer is in a gel form, transfer of zinc ions is limited. Thereby, deformation of the negative electrode and generation of dendrite due to charge and discharge of the battery are substantially inhibited. Moreover, since impurity ions such as nitrate ions become less prone to move, self-discharge of the battery is also inhibited.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
A method of fabricating structured particles composed of silicon or a silicon-based material and their use in lithium rechargeable batteries
InactiveUS20110269019A1Easy to operateReduce operating costsDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical batteryLithium-ion battery
A process for etching silicon to form silicon pillars on the etched surfaces, includes treating silicon with an etching solution that includes 5 to 10M HF 0.01 to 0.1M Ag+ ions and 0.02 to 0.2M NO3− ions. Further, NO3− ions in the form of alkali metal, nitric acid or ammonium nitrate salt is added to maintain the concentration of nitrate ions within the above range. The etched silicon is separated from the solution. The process provides pillars, especially for use as the active anode material in lithium ion batteries. The process is advantageous because it uses an etching bath containing only a small number of ingredients whose concentration needs to be controlled and it can be less expensive to operate than previous processes.
Owner:NEXEON LTD
Microbial fuel cell
A microbial fuel cell having a pathway for passage of effluent from the anode to the cathode is provided, in addition to an ion exchange membrane between the chambers. Effluent may also pass from cathode to anode forming a continuous loop. Oxidation of effluent at the anode creates ammonium ions and produces electrons for an external circuit. The ammonium ions undergo nitrification at the cathode. Alternatively a nitrification reactor may be provided in the effluent pathway. Electrons are received by the cathode from the external circuit to reduce nitrate ions created by the nitrification process.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Method for removing acidic gases from waste gas
A method for removing acidic gases from waste gases is disclosed. The invention relates to a method for removing acid gases, in particular from SO2 and NOx, by contacting the waste gas with an emulsion of water in organic sulfoxides, in particular of water in oil-derived-sulfoxides. The organic sulfoxide phase can be regenerated after the emulsion is loaded with polluants, by letting the emulsion to settle down and separate into two phases. The aqueous phase obtained after the separation contains sulfate and nitrate ions which can be collected and used as valuable chemicals.
Owner:LEXTRAN
Copper-based SCR catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104128200AThe production process is simpleLow temperature activeCatalyst carriersMolecular sieve catalystsCopper(II) chlorideOxygen
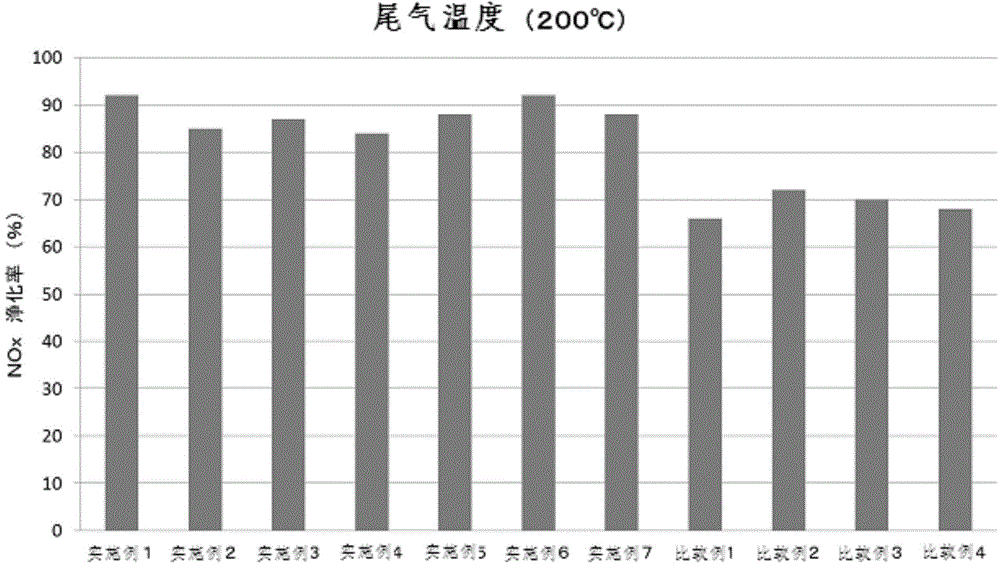
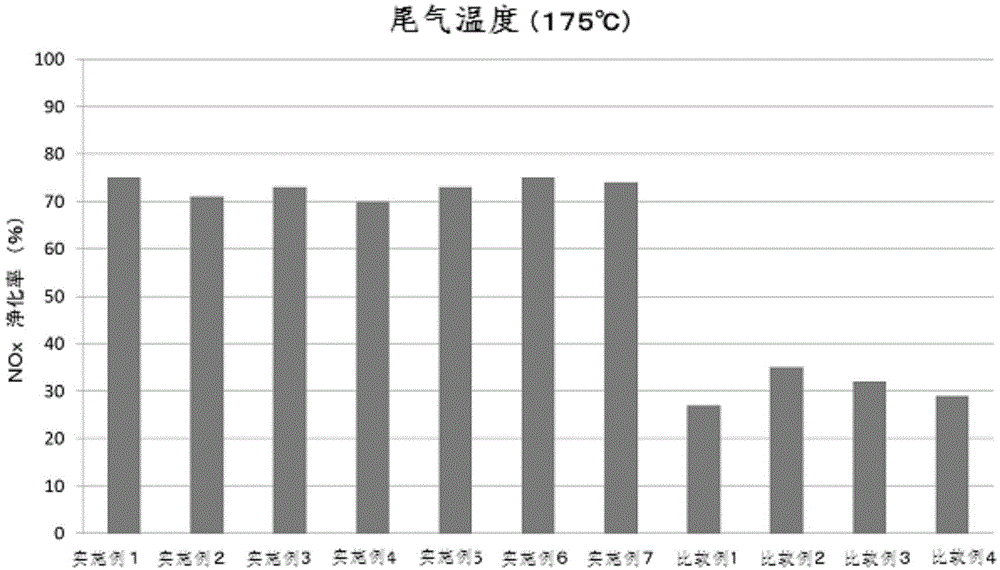
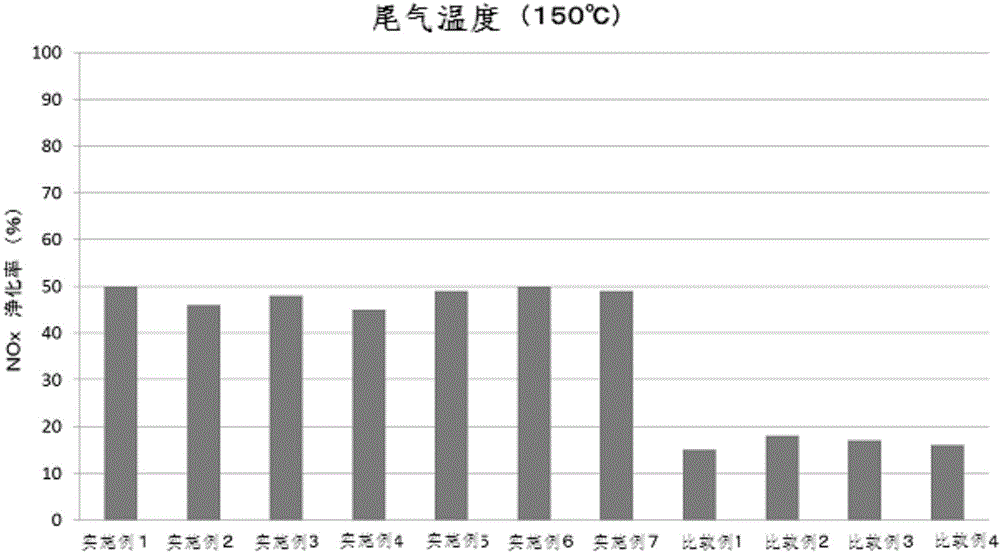
The invention provides a simple method for preparing a copper (II) ion-supported SCR catalyst having a NOx purifying performance at a low temperature. The SCR catalyst is prepared by mixing hydrogenation synthesized zeolite crystals with the largest oxygen ring number of 8-12 and a three dimensional structure with an aqueous solution of copper (II) nitrate ions or copper (II) chloride ions with the pH value of 0.1-3.0 without filtering or washing. The BET specific surface area of the copper-based SCR catalyst is 50-80m<2> / g, the copper-based SCR catalyst has low temperature activity, hydrothermal durability and NOx purifying performance, and the exhaust gas NOx purifying rate of the copper-based SCR catalyst at below 200DEG C reaches above 80%.
Owner:清华大学苏州汽车研究院(吴江) +1
Process for removal of dissolved hydrogen sulfide and reduction of sewage BOD in sewer or other waste systems
InactiveUSRE36651E1Elimination and substantial reductionEliminate the problemTreatment using aerobic processesBiochemical fibre treatmentSewageOxygen
Removal of dissolved hydrogen sulfide and a reduction in BOD is achieved by the addition of nitrate ions to waste systems in an amount sufficient to stimulate growth of bacteria which utilize dissolved hydrogen sulfide in their metabolism. Specifically, about 2.4 lbs. nitrate oxygen per lb. of sulfide is required.
Owner:UNITED STATES FILTER CORPORATION
Chitosan and chitosan quaternary ammonium salt composite magnetic microsphere and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104258822AImprove adsorption capacityStrong pH adaptabilityOther chemical processesAnion exchangersPhosphate ionMicrosphere
The invention discloses a chitosan and chitosan quaternary ammonium salt composite magnetic microsphere and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the steps of preparing a water phase, stirring and dissolving chitosan, chitosan quaternary ammonium salt and a pore-foaming agent PEG or PVP according to a ratio in an acetic acid aqueous solution, and adding magnetic particles for stirring and ultrasonic treatment; preparing an oil phase, and stirring liquid paraffin and Span80 to obtain the oil phase; gradually adding the water phase into the oil phase drop by drop while stirring is carried out to obtain a liquid mixture; adding a sodium polyphosphate aqueous solution into the liquid mixture drop by drop, carrying out stirring, and adding a glutaraldehyde aqueous solution for reaction; carrying out centrifugation and washing to obtain the chitosan and chitosan quaternary ammonium salt composite magnetic microsphere. The composite magnetic microsphere disclosed by the invention is higher in adsorption to electronegative materials such as humic acid, anionic dyes, arsenate ions, phosphate anions and nitrate ions, is higher in pH adaptability, magnetic separation property and regeneration performance, and is high in exchange capacity, high in adsorption speed and easy to separate.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Pharmaceutical composition containing nitrate source and an acidifying agent for treating skin ischaemia
InactiveUS20080226751A1Direct contact guaranteePermitted diffusionBiocideInorganic active ingredientsSkin surfacePeripheral ischaemia
The use of acidified nitrate as an agent to produce local production of nitrate oxide at the skin surface is described in the treatment of peripheral ischaemia and associated conditions. The dosage form may be in any pharmaceutically acceptable carrier means and comprises an acidifying agent adapted to reduce the pH at the environment. A barrier consisting of a membrane allows diffusions of the nitrate ions while preventing direct contact of the skin and acidifying agent. Amongst the many potential applications for the invention is the management of chronic skin wounds, peripheral ischaemia conditions such as Raynaud's phenomenon. Compositions and methods of use for these applications are described.
Owner:QUEEN MARY UNIV OF LONDON
Disinfecting nitrous acid compositions and process for using the same
InactiveUS20030175362A1Significant antimicrobial activityMinimum corrosionHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseNitrite ion
The present invention relates generally to compositions and methods for the use of nitrous acid solutions to disinfect inanimate surfaces and animal tissues, and to treat diseases and wounds. More specifically, the invention deals with the partial and selected conversion of nitrite ion to nitrous acid in order to optimize the germicidal efficacy and duration of the nitrous acid consistent with the nature of the intended application.
Owner:KROSS ROBERT D +1
Treating solution for forming black hexavalent chromium-free chemical coating on zinc or zinc alloy plated substrate, and method for forming black hexavalent chromium-free chemical coating on zinc or
InactiveCN1729311ACorrosion resistanceImprove corrosion resistanceSuperimposed coating processZinc alloysCoordination complex
It is an object of the present invention to provide a processing solution used for forming a hexavalent chromium free, black conversion film, which is applied onto the surface of zinc or zinc alloy plating layers, and which has corrosion resistance identical to or higher than that achieved by the conventional hexavalent chromium-containing conversion film. <??>According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a processing solution for forming a hexavalent chromium free, black conversion film on zinc or zinc alloy plating layers, the processing solution comprising: nitrate ions and trivalent chromium in a mole ratio (NO<3-> / Cr<3+>) of less than 0.5 / 1, wherein the trivalent chromium is present in the form of a water-soluble complex with a chelating agent; and cobalt ions and / or nickel ions, wherein the cobalt ions and / or nickel ions are stably present in the processing solution without causing any precipitation by forming a hardly soluble metal salt with the chelating agent; wherein the solution reacts with zinc when it is brought into contact with the zinc or zinc alloy plating to form a hexavalent chromium free, black conversion film containing zinc, chromium, cobalt and / or nickel, and the chelating agent on the plating.
Owner:DISPOL CHEMICALS CO LTD
Method for preparing active silver electrode
InactiveCN101235515ALarge specific surface areaImprove electrocatalytic activityElectrolytic organic productionElectrodesOxidation statePhenol
The invention provides a method for preparing an active silver electrode, the method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out anode oxidation reaction to the silver electrode to form a silver oxidation state layer on the surface of the silver electrode in water solution with anion,, secondly, changing polarity of the silver electrode, and carrying out cathode oxidation reaction to cathode of the silver electrode to obtain the active silver electrode, wherein anion is compounded by one, or two, or more than two following ions, namely, (1) perchlorate ion, (2) hypochlorous acid ion, (3) hydroxide ion, (4) nitrate ion, (5) sulfate ion, (6) carbonate ion, (7) halide ion, (8) organic acid ion and (9) phenol hydroxyl root ion, the active silver electrode which is obtained according to the method of the invention is not only provided with a more specific surface, but also provided with higher electro-catalysis activity, longer electro-catalysis performance and less power loss, and the obtained active silver electrode can be used to electrolyze 3,4,5,6-tetrachloropicolinic acid and to compound 3,6-dichloropicolinic, which not only has lower energy consumption, but also has higher production efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method and applications of graphene aerogel
The invention provides a preparation method and applications of graphene aerogel. The graphene aerogel is prepared by the following steps: oxidizing a graphene water solution, and then preparing the graphene aerogel through a hydrothermal method. The graphene aerogel can be used as an ion-selective electrode, and can be especially used as an ion-selective electrode to detect the nitrate ions. The graphene aerogel is innovatively used as an ion-selective electrode applied in electrochemical detection, the detection results are excellent, and the application range of graphene aerogel based materials is enlarged.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for producing alpha-alumina powder
A method for producing α-alumina powder is described. The method comprises the steps of removing water from a compound containing the following (1), (2), (3) and (4), and calcining the results: (1) α-alumina precursor, (2) seed crystal, (3) water, (4) nitrate ion in an amount of from 2.8 to 3.3 mol per mol of aluminum (Al) contained in the α-alumina precursor and the seed crystal.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Antistatic laminated polyester film
InactiveUS20060035070A1Reduce processing costsMaintain good propertiesOther chemical processesFilm/foil adhesivesPolyesterPolymer science
An antistatic film having an antistatic coating film on at least one surface of a polyester film, the antistatic coating film comprising a polymer having a polymerized unit represented by the following formula (1): wherein R1 and R2 each independently represent a hydrogen atom or a methyl group, R3 represents an alkylene group having 2 to 10 carbon atoms, R4 and R5 each independently represent an alkyl group having 1 to 5 carbon atoms, R6 represents a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group having 1 to 5 carbon atoms or a hydroxyalkyl group having 2 to 10 carbon atoms, and Y− represents a halogen ion, a halogenated alkyl ion, a nitrate ion, a sulfate ion, an alkyl sulfate ion, a sulfonate ion or an alkyl sulfonate ion. The film is used in such applications requiring an antistatic property such as a protective film for a liquid crystal polarizing plate.
Owner:TEIJIN DUPONT FILMS JAPAN
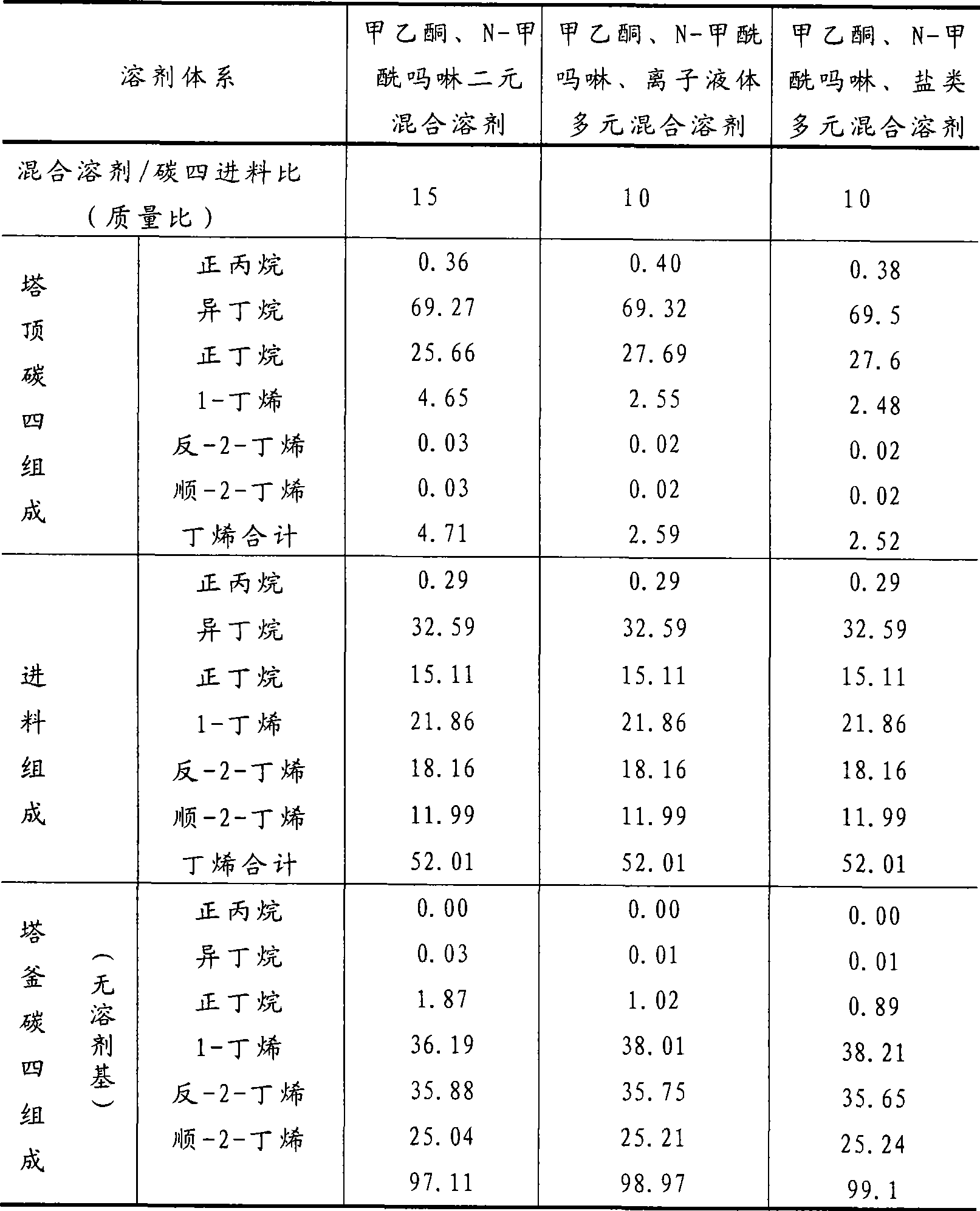
Method for separating butane and butene by using multiple mixed solvent
InactiveCN101417913ARetain solubilityImprove solubilityDistillation purification/separationBulk chemical productionSodium sulfocyanateTetrafluoroborate
The invention relates to a method for spearing butane from butylene with the multicomponent compound of ionic liquid, saline, ethyl methyl ketone and N-formylmorpholine. The content of ionic liquid in the multicomponent compound is 1.0 to 95 percent; the content of the saline in the multicomponent compound is 0.5 to 20 percent; the electropositive ion of the ionic liquid is iminazole electropositive ion, alkyl imidazole electropositive ion or alkyl quaternary ammonium ion, or the compound thereof; the electronegative ion is tetrafluoroborate electronegative ion, hexafluorophosphoric acid electronegative ion, nitrate ion, tetrachloro aluminic acid iron, heptachlor bi aluminic acid iron, chloride ion, bromine electronegative ion or the mixture; and the ionic liquid can be dimethylformamide potassium thiocyanate compound salt, dimethylformamide sodium sulfocyanate compound salt, or the compound; the saline is potassium thiocyanate, sodium sulfocyanate, ammonium thiocyanate, sodium nitrate, potassium nitrate, sodium iodide, potassium iodide, zinc chloride, copper chloride, zinc chloride, potassium bromide, or the compound thereof.
Owner:YANTAI UNIV
Process for the collective pretreatment of steel, galvanized steel, magnesium and aluminum before bonding to rubber
A process for the production of a rubber-to-metal bond on steel, galvanized steel, aluminum and / or magnesium is provided The process comprises at least the following steps:a) chemical pretreatment of the metal parts,b) intermediate rinsing, andc) vulcanizing-on of natural or synthetic rubber using primers and / or binders.The chemical pretreatment in step a) is carried out with an aqueous solution with a pH value of 3.5 to 5.5 which contains:4 to 20 g / l of phosphate ions,0.1 to 1 g / l of free or complexed fluoride, and0.04 to 1 g / l of nitrate ions.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com