Extraction of copper from waste etching liquid in chloride system circuit board
An extraction method and a technology of waste etching solution, which are applied in the field of electrodeposition and extraction of copper in the waste etching solution of the chloride system circuit board, can solve the problems of less precipitation, inability to treat the waste etching solution, and reduce the efficiency of direct current Faraday, etc., to achieve Effect of High DC Current Efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
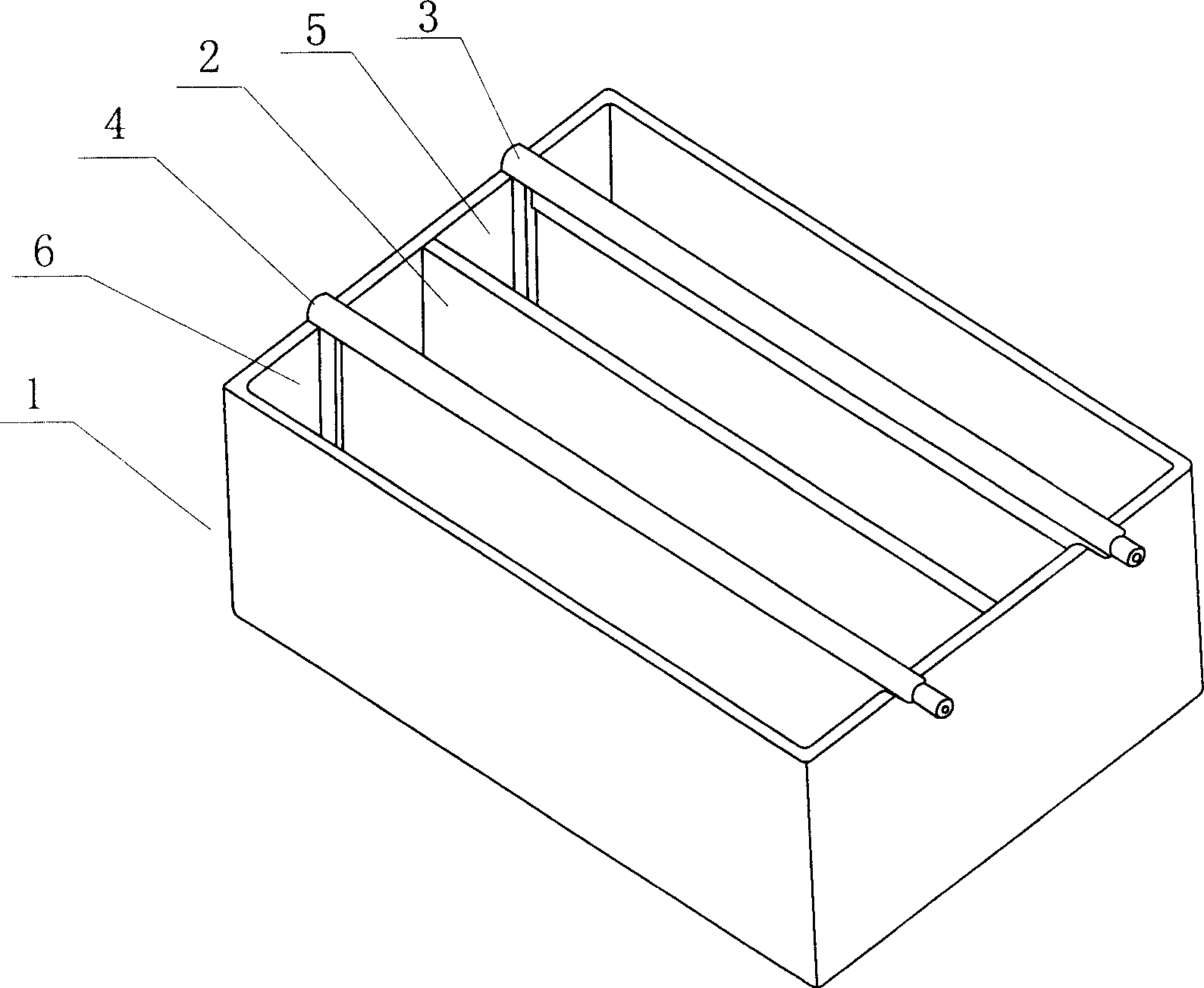
[0017] Example 1: In such as figure 1 In the cathode region 6 of the electrolytic cell shown, waste etching solution for circuit boards in a chloride system containing 105.29 g / L of copper is added, and a chloride conductive medium is added in the anode region 5 . And after adding the mixture of zinc and iron, the anode 3 and cathode 4 in the electrolytic cell are connected to the positive and negative terminals of the DC power supply to form a loop, and then the power is turned on for copper electrodeposition. The ambient temperature is 28°C, and the cathode 4 The current density is 700A / m 2 to 800A / m 2 , the amount of electricity fed into the electrodeposition operation is 105.6Ah, and the amount of deposited copper obtained on the cathode 4 is 124g. Calculated by divalent copper, the theoretical amount of copper deposited per Ah is 1.185g, and the DC current efficiency calculated from this is 99.1 %, no chlorine gas is released on the anode 3, and new compounds are genera...
Embodiment 2
[0018] Embodiment 2: in the electrolyzer identical with embodiment 1, add the compound identical with example 1 in the anode area 5, add new chloride system circuit version waste etching solution in the cathode area 6, electrode and DC power supply are connected into After the electrolysis circuit, turn on the electrolysis power supply, and operate the electrodeposition copper until all the copper in the etching solution is precipitated on the cathode 4, and the etching solution mainly presents a clear color, and the accumulated electrolytic power is 334.4Ah, and the cathode area 6 is obtained 384g of deposited copper is calculated to have a Faraday DC current efficiency of 96.9%.
Embodiment 3
[0019] Embodiment 3: by 4 such as figure 1 The shown monomer electrolyzers are connected in series to form a series of electrolyzers. In the cathode area 6 of each monomer electrolyzer, the waste etching solution of the circuit board of the chloride system is added. Add 170L of waste etching solution. Add potassium and sodium chloride solution conductive media in each anode area 5, the concentration of chloride is 200g / L to 220g / L, and add zinc and iron compounds in each anode area 5, connect the anode 3 of the electrolytic cell in series The cathode 4 is connected to the positive terminal and the negative terminal of the DC electrolysis power supply respectively, and the power is turned on for copper electrodeposition operation. The current density of the cathode 4 is about 900A / m 2 , Electrodeposition is carried out until the waste etching solution is clear and transparent, the cumulative total electricity input is 16372Ah, and 18.74Kg of copper products are obtained, and t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com