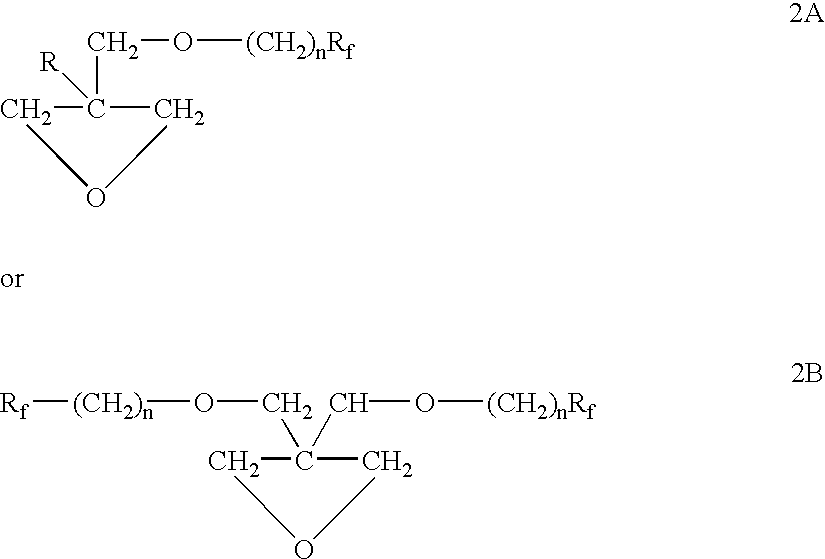
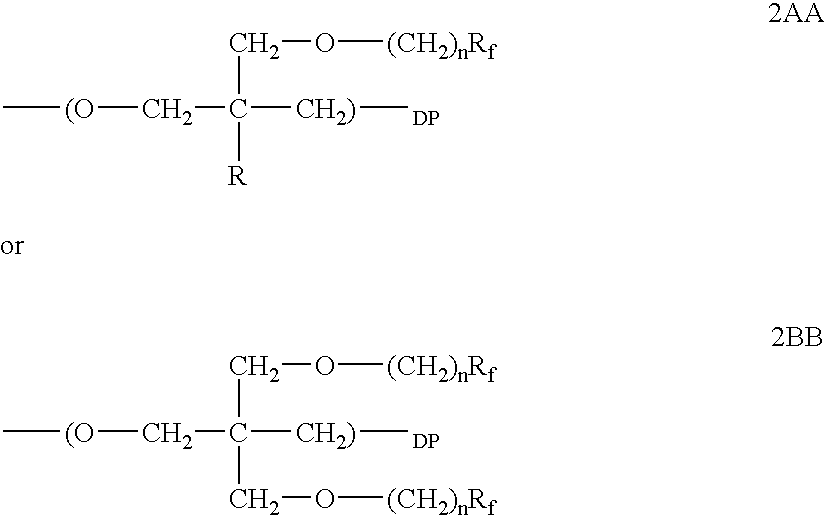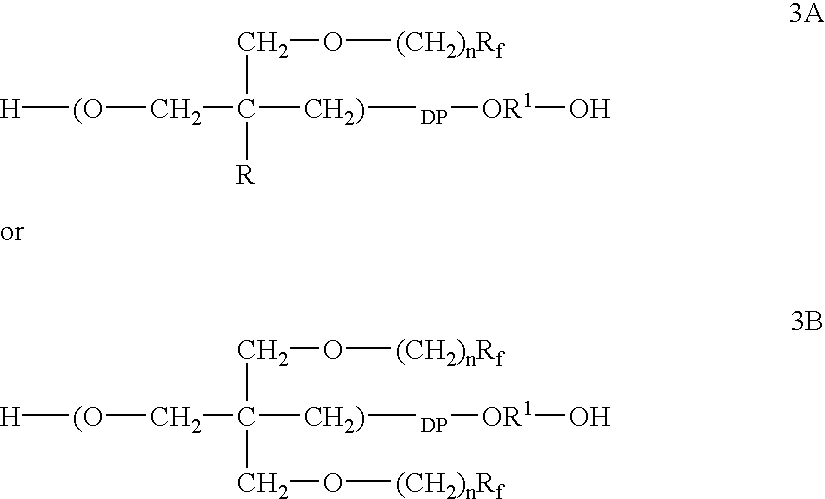Polymeric surfactants derived from cyclic monomers having pendant fluorinated carbon groups
a technology of cyclic monomers and surfactants, which is applied in the field of polymeric surfactants derived from cyclic monomers having fluorinated carbon groups, can solve problems such as limiting utility, and achieve the effects of good optical properties, good distinctness of image, and high gloss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example m2
Preparation of 7-FOX Using PTC Process 3-(2,2,3,3,4,4,4-1Heptafluorobutoxy-methyl)-3-Methyloxetane
[0049] A 2 L, 3 necked round bottom flask fitted with a reflux condenser, a mechanical stirrer, a digital thermometer and an addition funnel was charged with 3-bromomethyl-3-methyloxetane (351.5 g, 2.13 mol), heptafluorobutan-1-ol (426.7 g, 2.13 mol), tetrabutylammonium bromide (34.4 g) and water (85 mL). The mixture was stirred and heated to 75.degree. C. Next, a solution of potassium hydroxide (158 g, 87% pure, 2.45 mol) in water (200 mL) was added and the mixture was stirred vigorously at 80.degree.-85.degree. C. for 4 hours. The progress of the reaction was monitored by GLC and when GLC analysis revealed that the starting materials were consumed, the heat was removed and the mixture was cooled to room temperature. The reaction mixture was diluted with water and the organic layer was separated and washed with water, dried and filtered to give 566 g (94%) of crude product. The crude p...
example m3
[0054] Sodium hydride (50% dispersion in mineral oil, 18.4 g, 0.383 mol) was washed with hexanes (2.times.) and was suspended in DMF (200 mL). Then trifluoroethanol (38.3 g, 0.383 mol) was added dropwise over 45 min while hydrogen gas was evolved. The mixture was stirred for 30 min and a solution of 3,3-bis-(hydroxymethyl)oxetane di-p-toluenesulfonate (30.0 g, 0.073 mol) in DMF (50 mL) was added. The mixture was heated to 75.degree. C. for 64 h when .sup.1H NMR analysis of an aliquot showed that the starting sulfonate had been consumed. The mixture was poured into water and extracted with methylene chloride (2.times.). The combined organic extracts were washed with brine, 2% aqueous HCl, water, dried (MgSO.sub.4), and evaporated to give 17.5 g (100%) of 3,3-bis-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxymethyl)oxetane as an oil containing DMF (<1%). The oil was purified by bulb-to-bulb distillation at 42.degree. C.-48.degree. C. (10.1 mm) to give 15.6 g (79%) of analytically pure B6-FOX, colorless oil: ...
example m4
Anhydrous Preparation of 9-FOX Monomer
[0055]
1 Weight Mole Material Scale (S .times. Ratio) g MW mmoles Ratio nonafluorohexanol 1000 1000.00 264.09 3786.59 1.00 BrMMO 656.11 165.02 3975.91 1.05 18-crown-6 25.00 322.37 77.55 0.020 KOH (86%) 271.71 56.10 4165.25 1.10 5% ammonium 615.70 18.01 34186.56 9.03 chloride Water 588.10 18.01 32654.08 8.62 Theoretical 1311.1 Yield, (g) Expected Yield, 983.3 low (g) Expected Yield, 1245.5 high (g) Solids Loading, % 67.1 ml Volume after 1,440.8 KOH addn. Volume after 2056.5 quench Volume after 1185.5 phase split Volume after wash 1773.6
[0056] A 3 liter 3-necked round-bottomed flask was equipped with a mechanical stirrer, nitrogen inlet and outlet, temperature probe, dean-stark trap, and reflux condenser. Nonafluorohexanol (1000 grams, 3.78 moles), BrMMO (656.11 grams, 3.97 moles), 18-crown-6 (25.00 grams) and 200 ml hexane were added, and the solution was allowed to heat to 79.degree. C. Ground solid Potassium hydroxide (271.71 grams, 86%, 4.16 mm...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight percent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volumes | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com