Energy distribution network
a technology of energy distribution network and energy input, applied in the direction of energy input, electric/hybrid propulsion, process and machine control, etc., can solve the problems of global and regional conflict, essentially impossible to achieve, and uncertainty about the impact of greenhouse gas emissions on health and climate chang
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
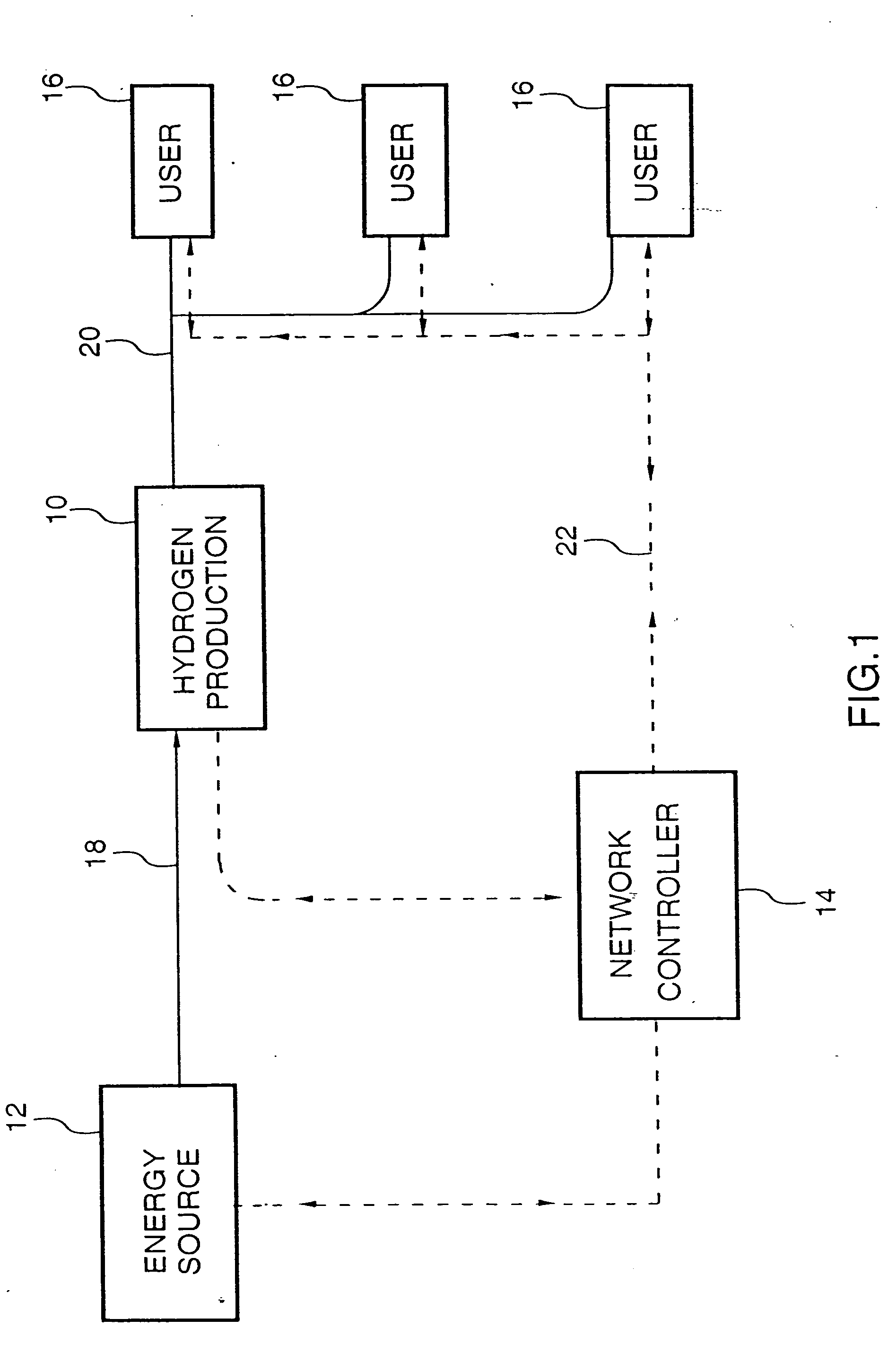
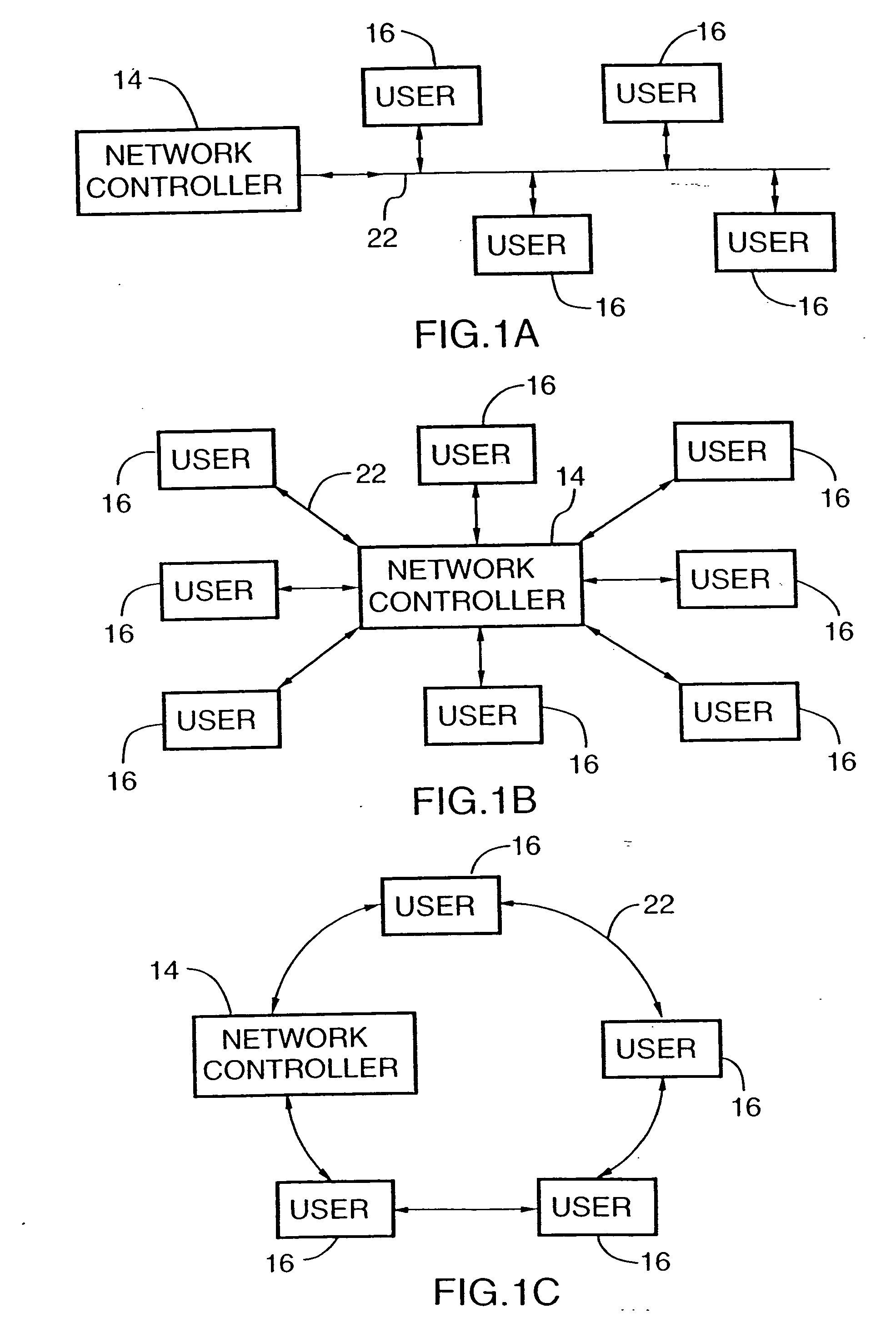
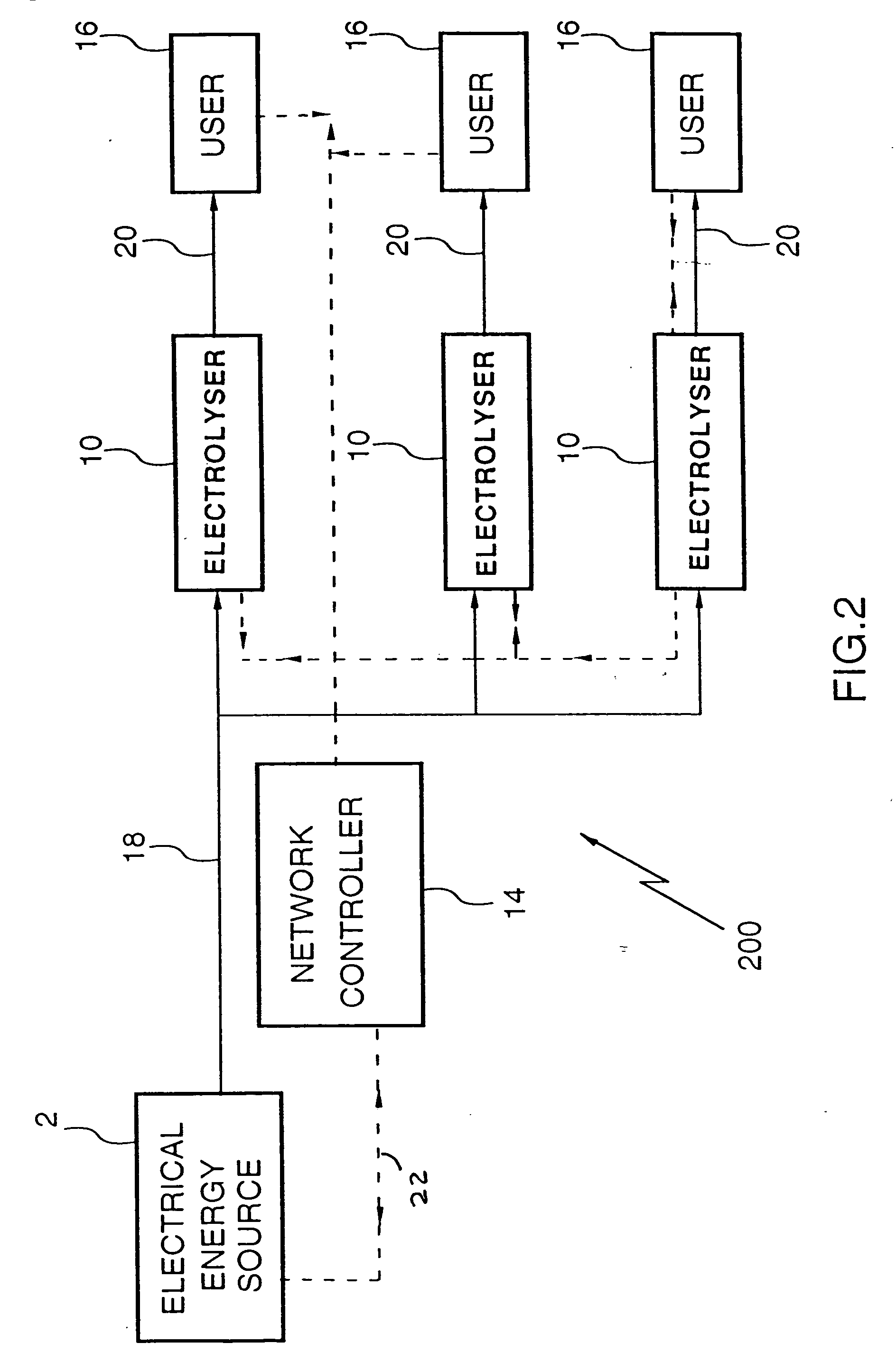
[0071] FIG. 1 represents an embodiment providing a broad aspect of the invention having a hydrogen production source 10, supplied by energy source 12 which may be an electricity generating power plant, or a natural gas, gasoline or methanol reforming plant or combinations thereof. A control unit 14 and users 16 are suitably linked by hardware input and output distribution conduits 18, 20, respectively, and electrical data transmission lines 22.
[0072] Users 16 define demands for hydrogen transmitted by means of, for example (i) use of a credit card, (ii) use of a smart card, (iii) use of a voice activation system, (iv) manual activation via front panel control, (v) use of a electronic, electric, or wireless infrared data transmission system to register a hydrogen demand on the network. Upon receipt of the demand, controller 14 determines the natures of the demand with respect to the quantity of hydrogen requested, the time to deliver the hydrogen, the conditions under which to delive...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrical energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature/pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com