Enteric-coated proliposomal formulations for poorly water soluble drugs
a technology of oral medicaments and proliposomes, which is applied in the field of entericcoated proliposome formulations for poorly water soluble drugs, can solve the problems of instability, leakage and potential destruction, and reduced therapeutic efficacy of many drugs, and achieves the effects of enhancing stability and bioavailability of pharmaceutically active agents, facilitating oral administration of medicaments, and simple and inexpensiv
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0039] Halofantrine and distearoyl phosphatidylcholine (1:3 ratio) were dissolved in chloroform and the solvent was evaporated using nitrogen gas. The dry powder was passed through a # 60 mesh screen. Cellulose acetate phthalate (50 mg) was dissolved in acetone (6 ml) and sprayed on the halofantrine and distearoyl phosphatidylcholine mixture.
[0040] Dissolution was carried out using 40 mg of the formulation using a Type II USP dissolution apparatus. The dissolution medium (250 ml) was phosphate buffered saline (pH 7.4). The temperature of the dissolution media was maintained at 37±0.5° C. and the rotation of the paddle was set at 50 rpm. Samples (5 ml) were withdrawn at 5, 10, 15, 30, 45, 60, 90, 120, 180 and 240 minutes. Equal volumes of phosphate buffered saline were added to maintain a constant volume of dissolution media.
[0041] The samples were analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). In the mobile phase, 46.5:53.5 (0.025 M potassium phosphate / sulfuric acid / tr...
example 2
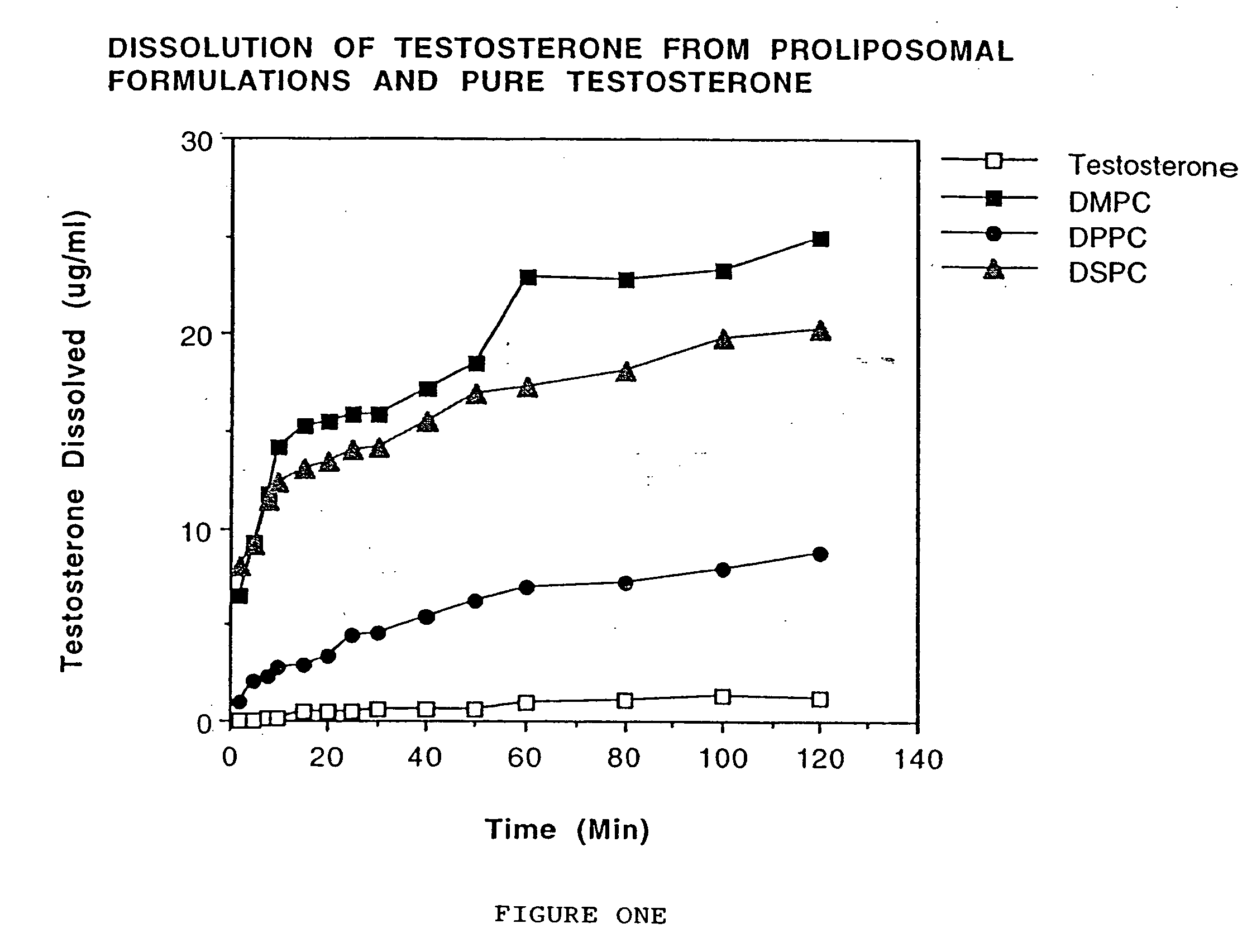
[0045] Testosterone and phospholipid (DMPC, DPPC or DSPC; 1:1 ratio) were dissolved in chloroform. Chloroform was evaporated using nitrogen gas.- The dry powder was passed using a # 60 mesh sieve. Cellulose acetate phthalate (40 mg) was dissolved in acetone (5 ml) and the resulting solution was sprayed on the solid dispersion containing the testosterone and phospholipid. Nitrogen gas was used to dry the powder.
[0046] Dissolution was carried out using 45 mg of the formulation using a Type II USP dissolution apparatus. The dissolution medium (300 ml) was phosphate buffered saline (pH 7.4). The temperature of the dissolution media was maintained at 37±0.5° C. and rotation of the paddle was set at 50 rpm. The samples (5 ml) were withdrawn at 2, 5, 8, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 40, 50, 60, 80, 100, and 120 minutes. Equal volumes of phosphate buffered saline were added to maintain a constant volume of dissolution media. Dissolution samples were analyzed by measuring the absorbance at 254 nm.
[0...
example 3
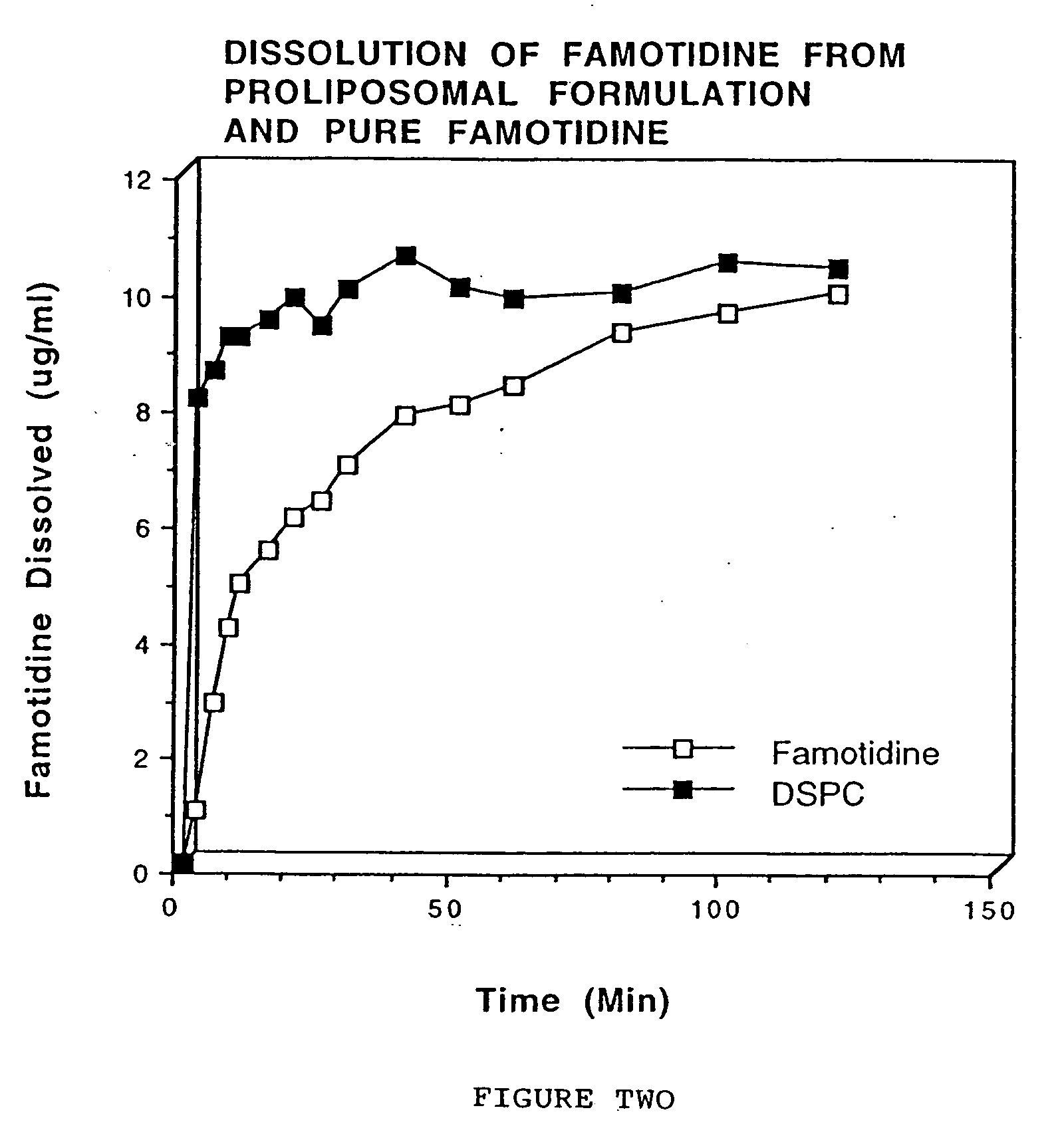
[0048] Famotidine and distearoyl phosphatidylcholine (DSPC; 1:3 ratio) were dissolved in chloroform. Chloroform was evaporated using nitrogen gas. The dry powder was passed using a # 60 mesh sieve. Cellulose acetate phthalate (50 mg). was dissolved in acetone (5 ml) and the resulting solution was sprayed on the solid dispersion containing testosterone and phospholipid. Nitrogen gas was used to dry the powder.
[0049] Dissolution was carried out using 87 mg of the formulation using a Type II USP dissolution apparatus. The dissolution medium (300 ml) was phosphate buffered saline (pH 7.4). The temperature of the dissolution media was maintained at 37±0.5° C. and the paddle rotation was set at 50 rpm. The samples (5 ml) were withdrawn at .2, 5, 8, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 40, 50, 60, 80, 100, and 120 minutes. Equal volumes of phosphate buffered saline were added to maintain a constant volume of dissolution media. Dissolution samples were analyzed by measuring the absorbance at 285 nm.
[0050]...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com