Compound semiconductor material and method for forming an active layer of a thin film transistor device
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
[0024] Embodiment 1
[0025] In the solution process, all of the oxides of group II-VI compounds can use 2-methoxy-ethanol or other alcohols as the solvent. When choosing the solvent, the factors concerned are the solubility of a solute, the ability for film formation of the solution, the removing of the solvent, and the growth of the grain.
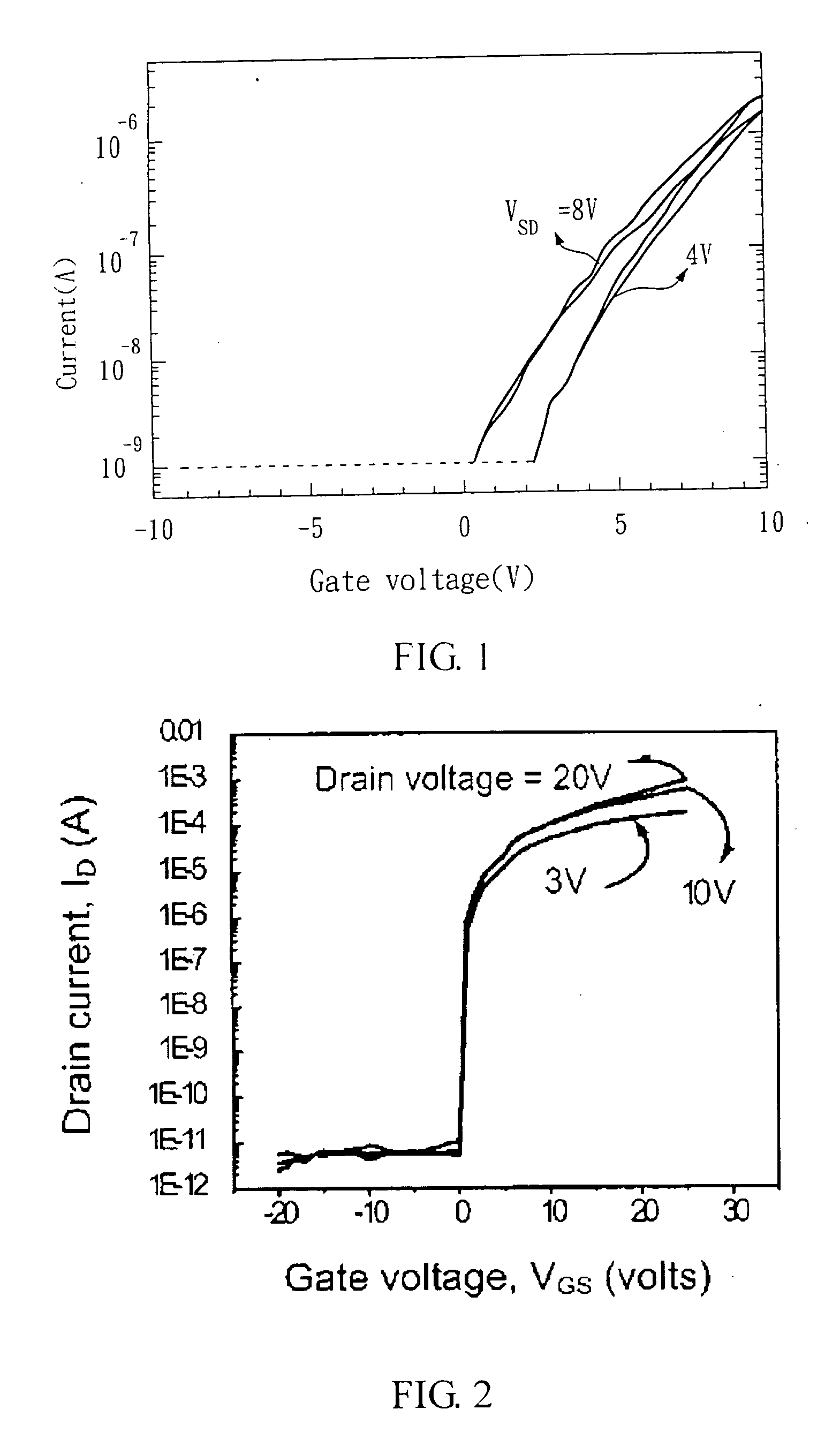
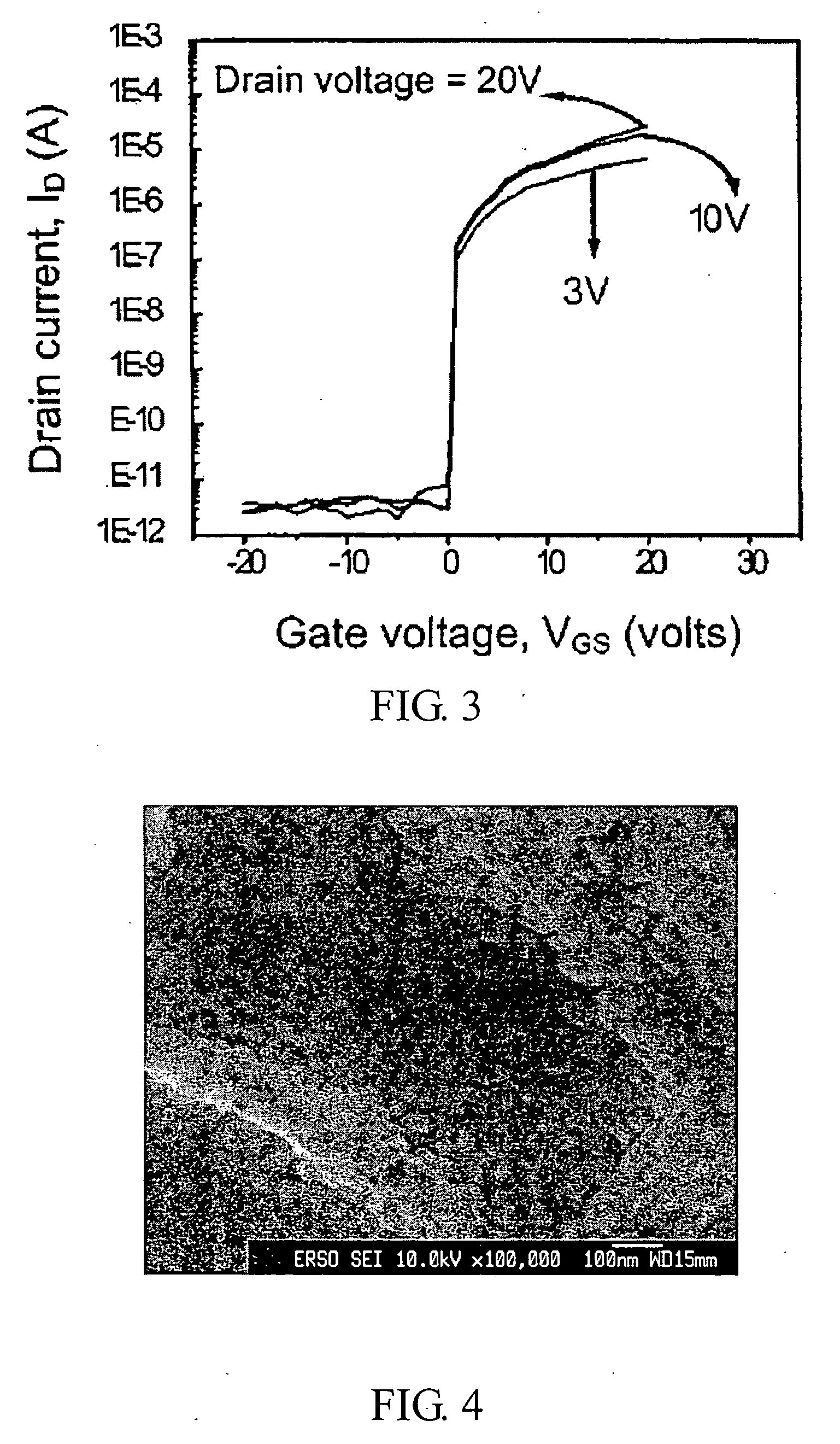
[0026] In the present embodiment, ZnO is doped with Mg to form a compound semiconductor material. First, 100 ml of solvent, i.e. 2-Methoxy-ethanol is mixed with 4.58 g of monoethanol amine. Then, 0.06 mole of zinc acetate and 0.015 mole of MgCl2 are further added into the solvent and stirred at 60 degrees C. for 30 minutes to prepare a precursor solution of Zn(0.8)Mg(0.2)O. Afterwards, the precursor solution is coated at the channels of the transistors by Inkjet Printing. Finally, the precursor solution coated at the channels of the transistors is annealed at 500 degrees C. for 2 hours in an oven. With reference to FIG. 4, the SEM picture shows tha...
embodiment 2
[0027] Embodiment 2
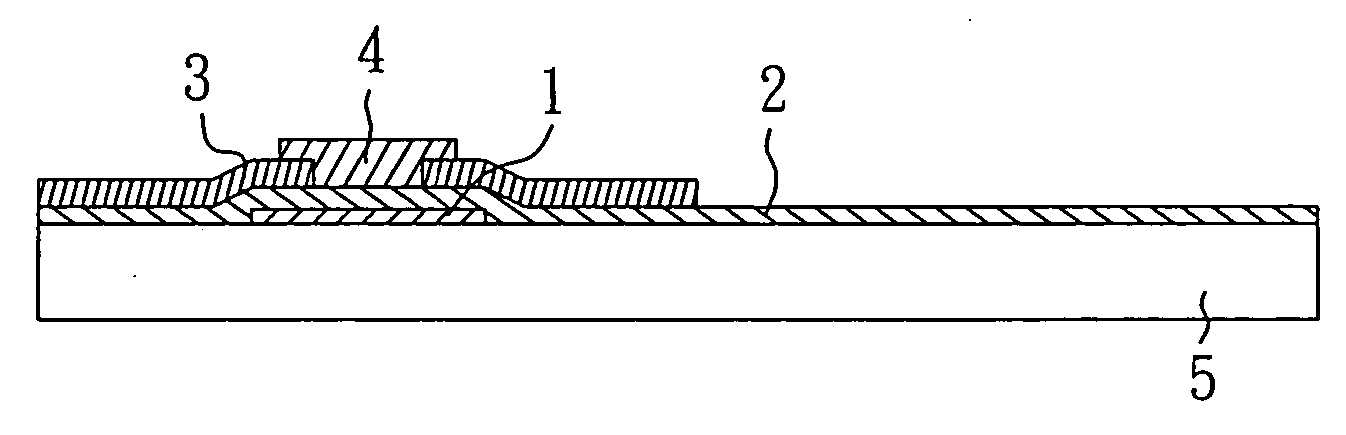
[0028] With reference to FIGS. 5A-5D, the process flow for manufacturing a thin film transistor is shown, wherein the bottom gate of the thin film transistor is formed with the compound semiconductor material of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 5A, a glass substrate 5 is provided, and then a first electrode layer is formed thereon. The first electrode layer is made of electrically conductive material, such as ITO, Cr, Al, Mo, Au, Pt, Ag, etc. Next, the first electrode layer is patterned by photolithography and etching processes and a gate electrode 1 is formed. As shown in FIG. 5B, an insulating layer 2 is subsequently deposited on the gate electrode 1. The insulating layer 2 can be made of silicon oxides, silicon nitrides, or PZT. The insulating layer 2 can be deposited by any conventional method. Preferably, the insulating layer 2 is deposited by physical vapor deposition or chemical vapor deposition. As shown in FIG. 5C, a second electrode layer 3 is for...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com