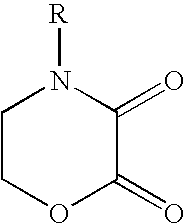
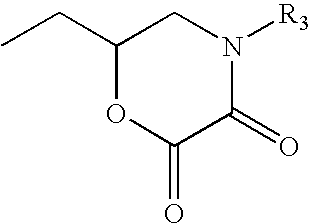
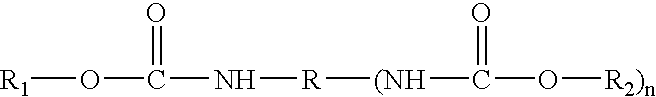Cathodic electrocoating composition containing morpholine dione blocked polyisocyanate crosslinking agent
a technology of morpholine dione and crosslinking agent, which is applied in the direction of electrolysis applications, coatings, polyurea/polyurethane coatings, etc., can solve the problems of high reactive isocyanate groups on the curing agent that must be blocked, block polyisocyanates, and require high temperatures to unblock and begin the curing reaction. , to achieve the effect of reducing bake-off loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of 4(2-hydroxyethyl)morpholine-2,3-dione monomer
[0062] A 4(2-hydroxyethyl)morpholine-2,3-dione was prepared by charging 125 g diethyl oxalate and 80 g n-butanol into a suitable reaction vessel and heated to 22° C. under nitrogen blanket. A mixture of 89.9 g diethanolamine and 72 g n-butanol was slowly charged into the reaction vessel while maintaining the reaction mixture below 50° C. After stirring for 30 minutes, the reaction mixture was refluxed for one hour and then allowed to stand at room temperature for 16 hours. The product was collected by filtration and the solid was washed twice with diethyl ether and dried under nitrogen to give 100 g (73.4% yield) of white crystals with 83.3° C.-84.4° C. melting point. IR (Nujol mull) 1759 (ester carbonyl), 1684 (amide carbonyl) cm−1. 1H NMR (500 MHz, acetone-d6) δ 4.592 (approx. triplet, 2H, J=5.0 Hz, ring CH2O), 3.903 (approx. triplet, 2H, J=5.0 Hz, ring CH2N), 3.767 (t, 2H, J=5.5 Hz, CH2OH), 3.597 (t, 2H, J=5.5 Hz, chain...
example 2
Preparation of 4(2-hydroxyethyl)morpholine-2,3-dione Monomer at Lower Temperature and Higher Yield
[0063] A 4(2-hydroxyethyl)morpholine-2,3-dione was prepared at low temperatures by the following procedure. Into a five-necked 22 liter round bottomed flask equipped with a reflux condenser, nitrogen bubbler, addition funnel, thermocouple well, and mechanical stirrer was charged 3000 g (20.53 mol) of diethyl oxalate and 2000 ml of isopropyl alcohol. The solution was cooled to 0 to 5° C. using a cold bath of ice and methanol. A solution of 2160 g (20.53 mol) of diethanolamine dissolved in 2000 ml of isopropyl alcohol was added through the addition funnel during a period of 5 to 6 hours. The reaction is exothermic. After addition was complete, the mixture was allowed to stand at room temperature overnight. The product is collected by filtration. After air drying, 2923 g (89.5% yield) of white crystals were obtained with identical spectral properties to the compound prepared in Example 1....
example 3
Preparation of Blocked Polyisocyanate Resin with 4(2-hydroxyethyl) morpholine-2,3-dione and diethylene glycol monobutyl ether
[0064] A new blocked polyisocyanate crosslinking resin solution was prepared by charging 338 parts Mondur® MR (methylene diphenyl diisocyanate, from Bayer Corp.), 113 parts methyl isobutyl ketone and 0.07 parts dibutyl tin dilaurate into a suitable reaction vessel and heated to 37° C. under a dry nitrogen blanket. 269 parts diethylene glycol monobutyl ether was slowly charged into the reaction vessel while maintaining the reaction mixture below 93° C. 142 parts 4(2-hydroxyethyl)morpholine-2,3-dione (prepared in Example 1) was then charged into the reaction vessel and kept the reaction temperature below 93° C . The resulting mixture was held at 110° C. until all of the isocyanate was reacted as indicated by infrared scan. 5 parts butanol and 133 parts methyl isobutyl ketone were added to the reaction mixture. The resulting resin solution had a nonvolatile cont...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com