Method of preparing polymer composite using unidirectionally solidified giant magnetostrictive material
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0039] Preparation of Polymer Composite using Tb0.3Dy0.7Fe1.32
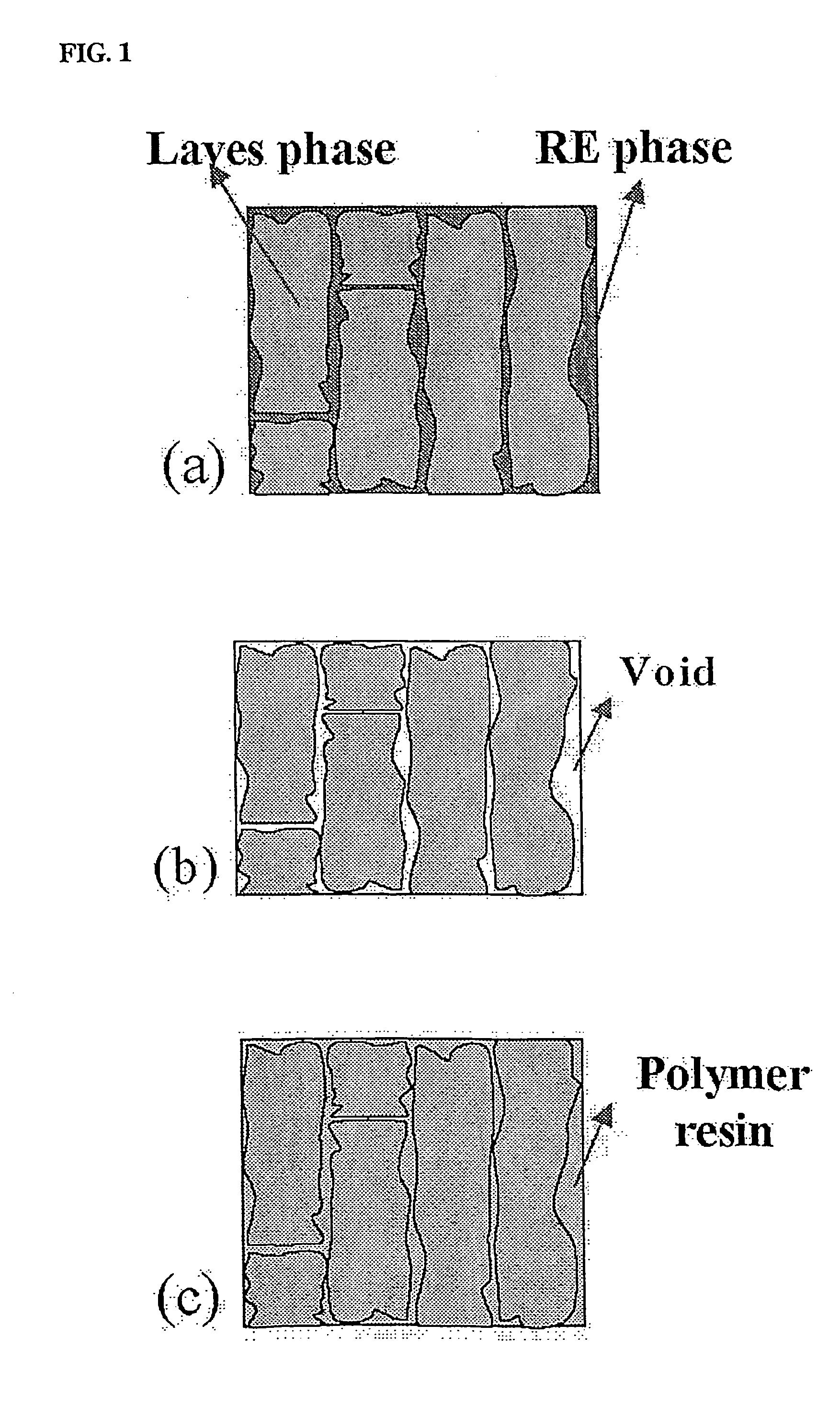
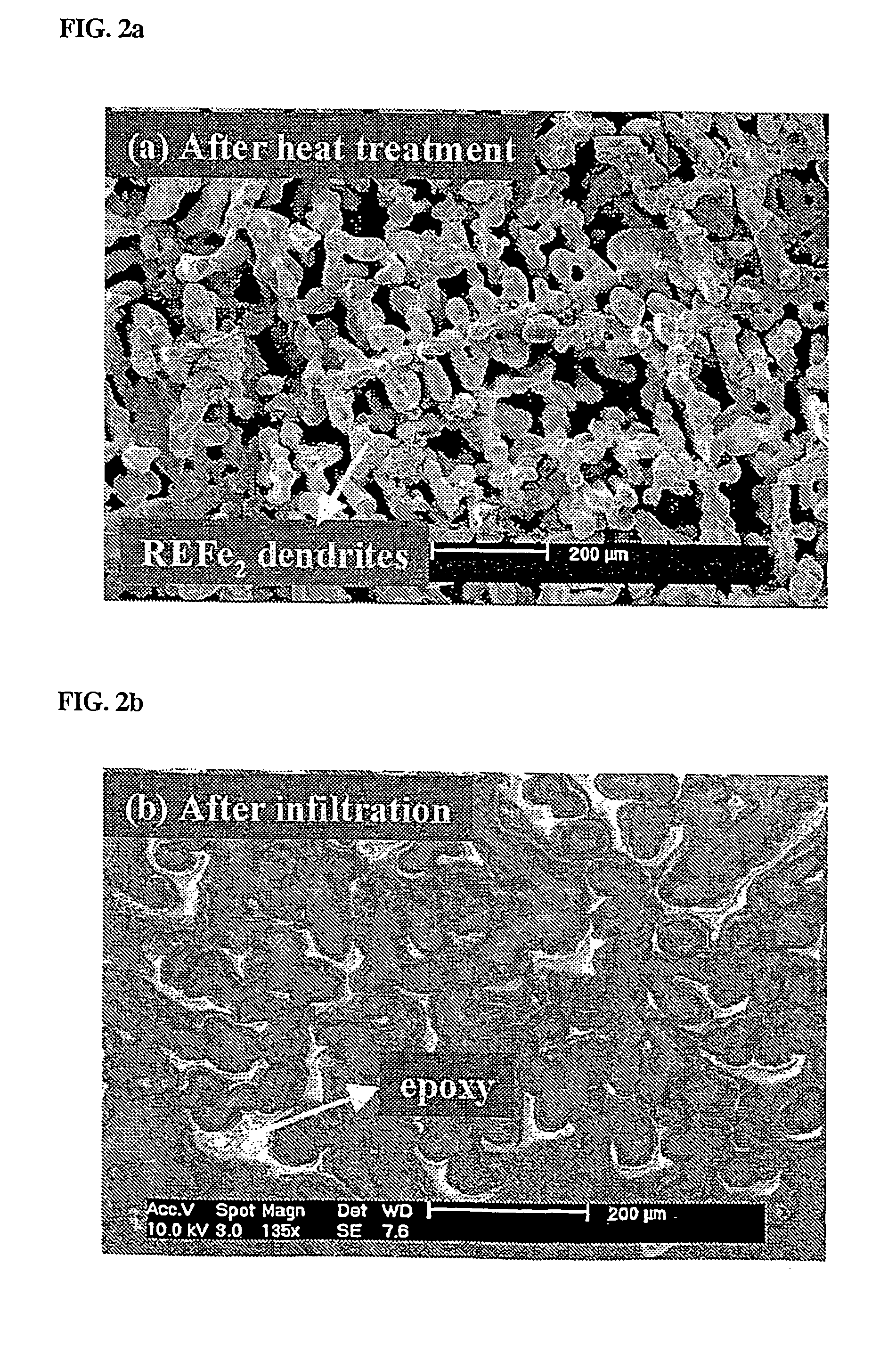
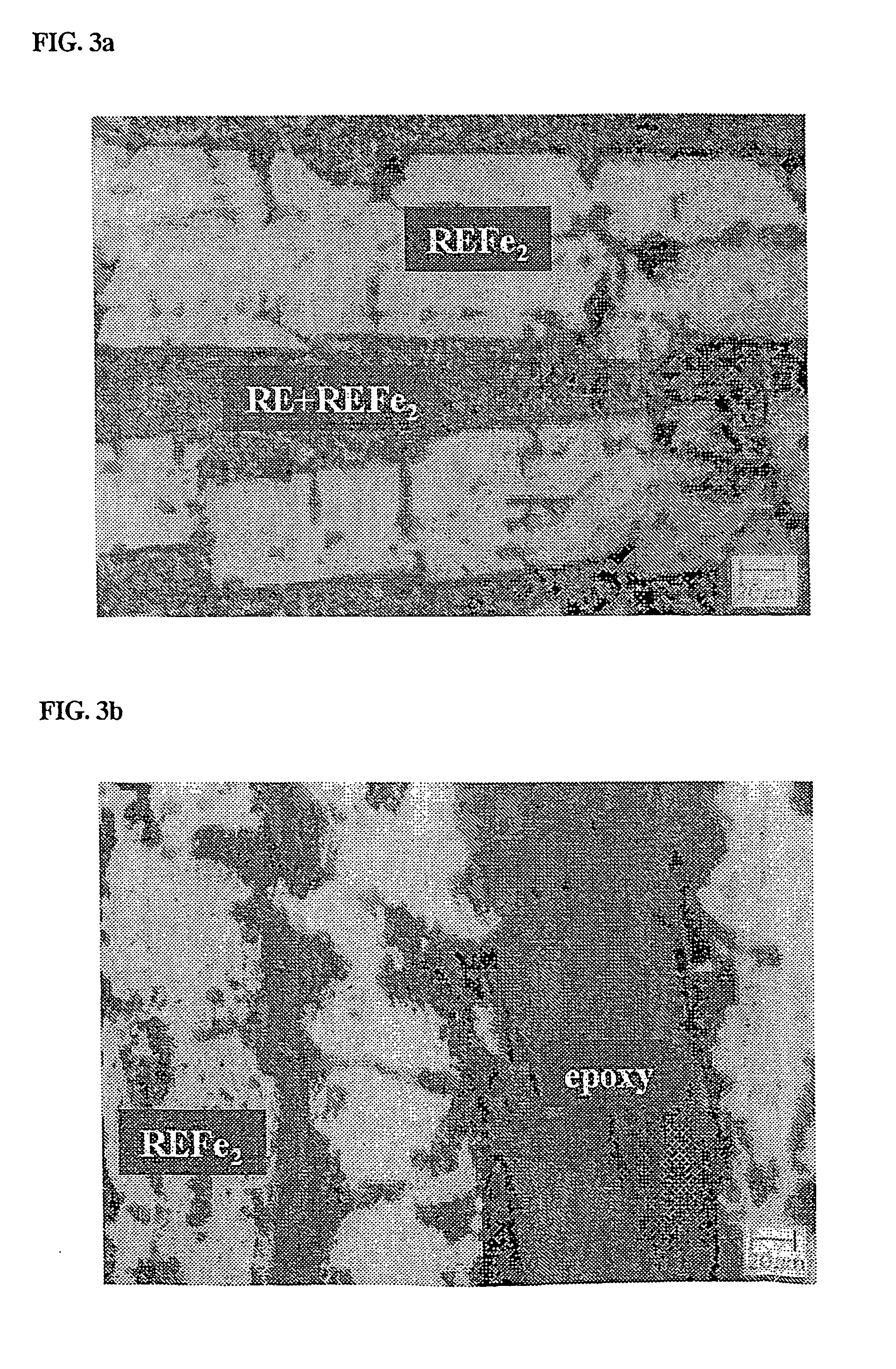
[0040] In the present example, as a giant magnetostrictive material, an alloy comprising 90 vol % of primary REFe2 phase and 10 vol % of eutectic phase was used. In FIG. 4 showing a pseudobinary phase diagram of the alloy, terbium (Tb) and dysprosium (Dy) form a complete solid solution. The “RE” in the drawing means a rare earth phase of TbxDy1-x, and REFe2 is defined as a Laves phase having giant magnetostrictive property.
[0041] To prevent the alloy rod from being oxidized at a high temperature, the alloy rod was charged into a quartz tube, which was then filled with highly pure argon gas, and the tube was sealed, followed by performing annealing process at 1000° C. for 6 hours to remove the eutectic phase. A sample having fine open pores was infiltrated with YD-114 epoxy resin as follows. Into a chamber (autoclave) capable of being subjected to evacuation and pressurization, the epoxy resin heated up to 80° C. and the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com