Method for treating multiple sclerosis
a multiple sclerosis and multi-sclerosis technology, applied in the field of mammals, can solve the problems of inability to tolerate many ra patients, frequent side effects of alternative drugs, retinal lesions and kidney and bone marrow toxicity, etc., and achieve the effect of prolonging the survival of grafts upon transplantation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Murine Heart Graft Model using anti-CD11a Antibody
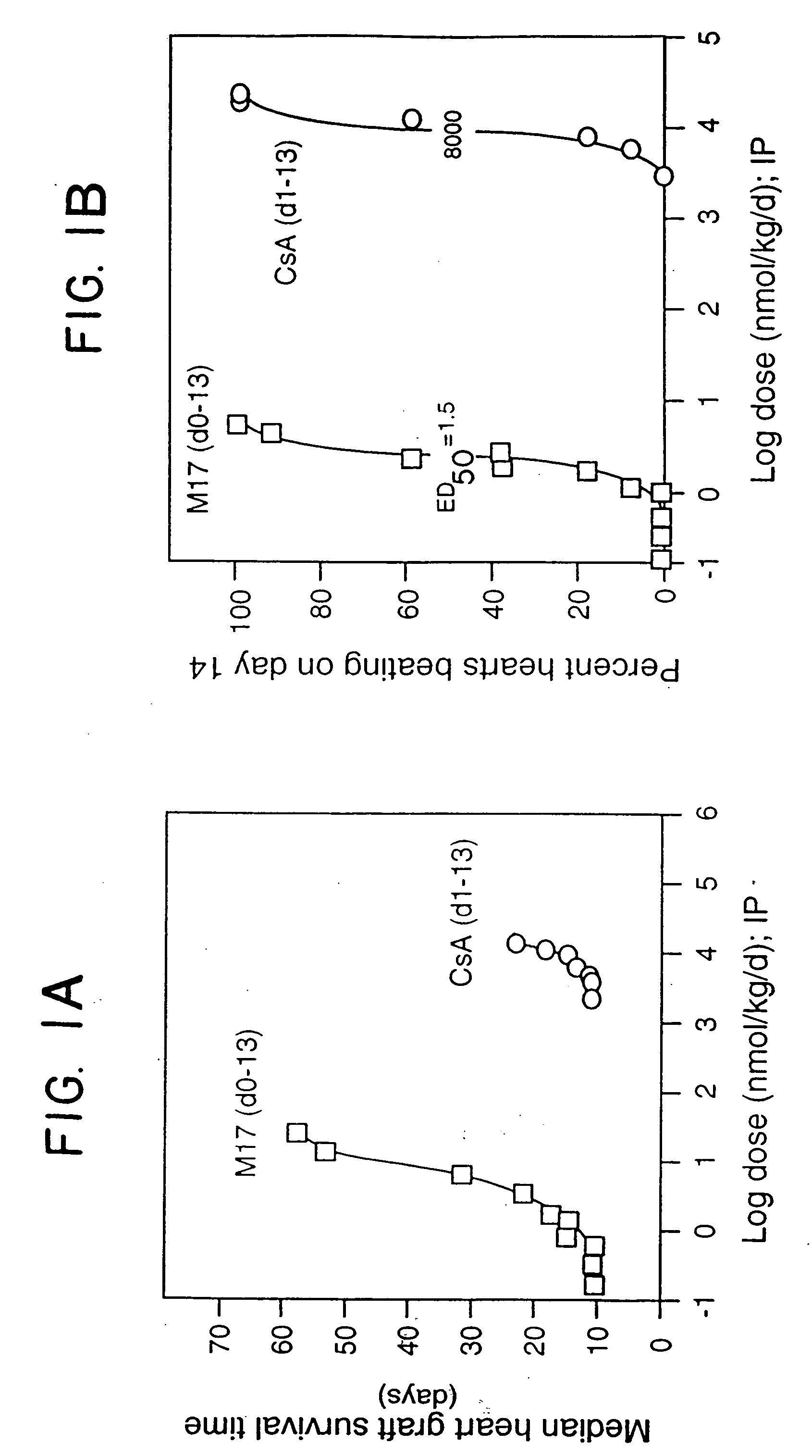
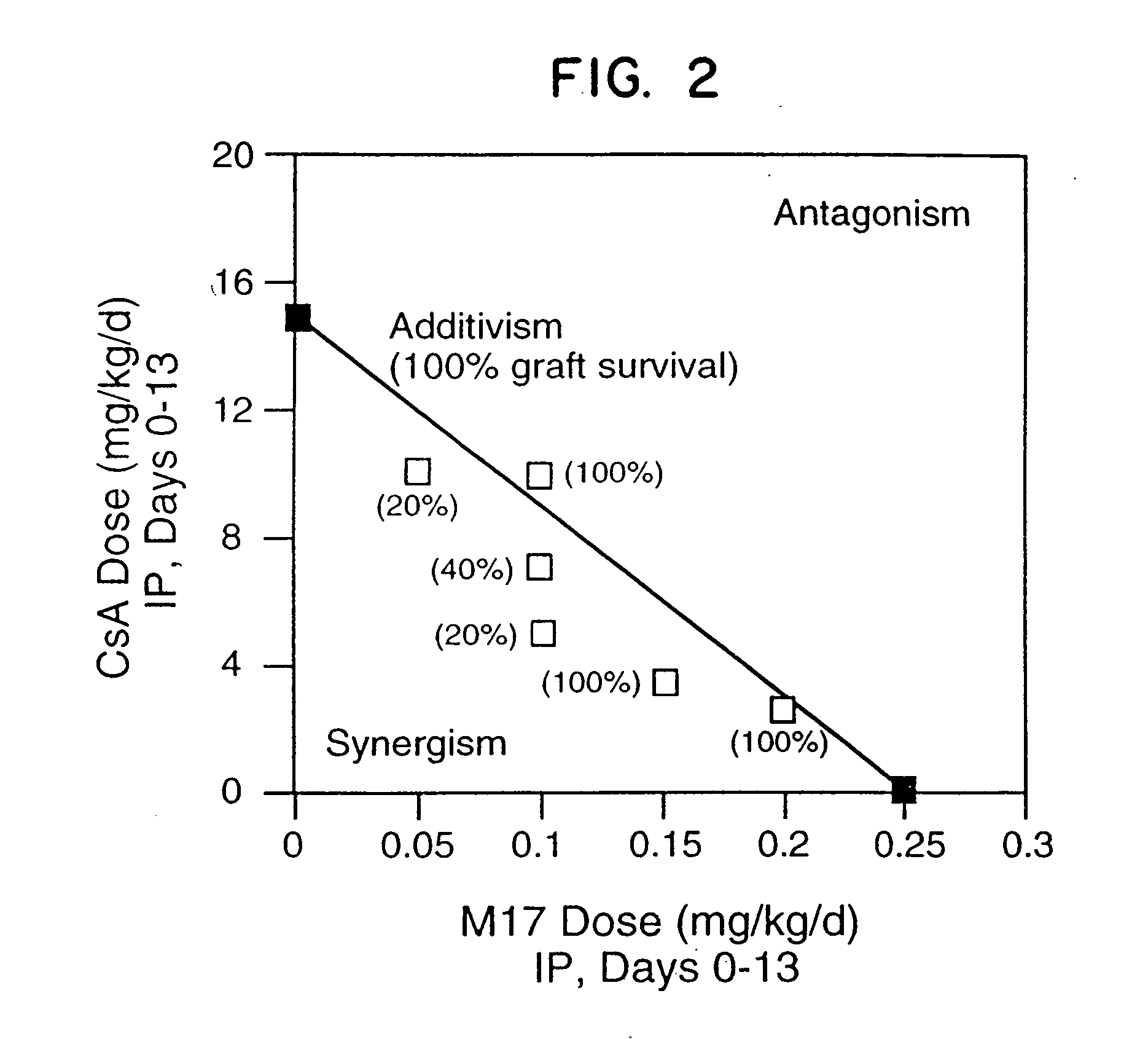
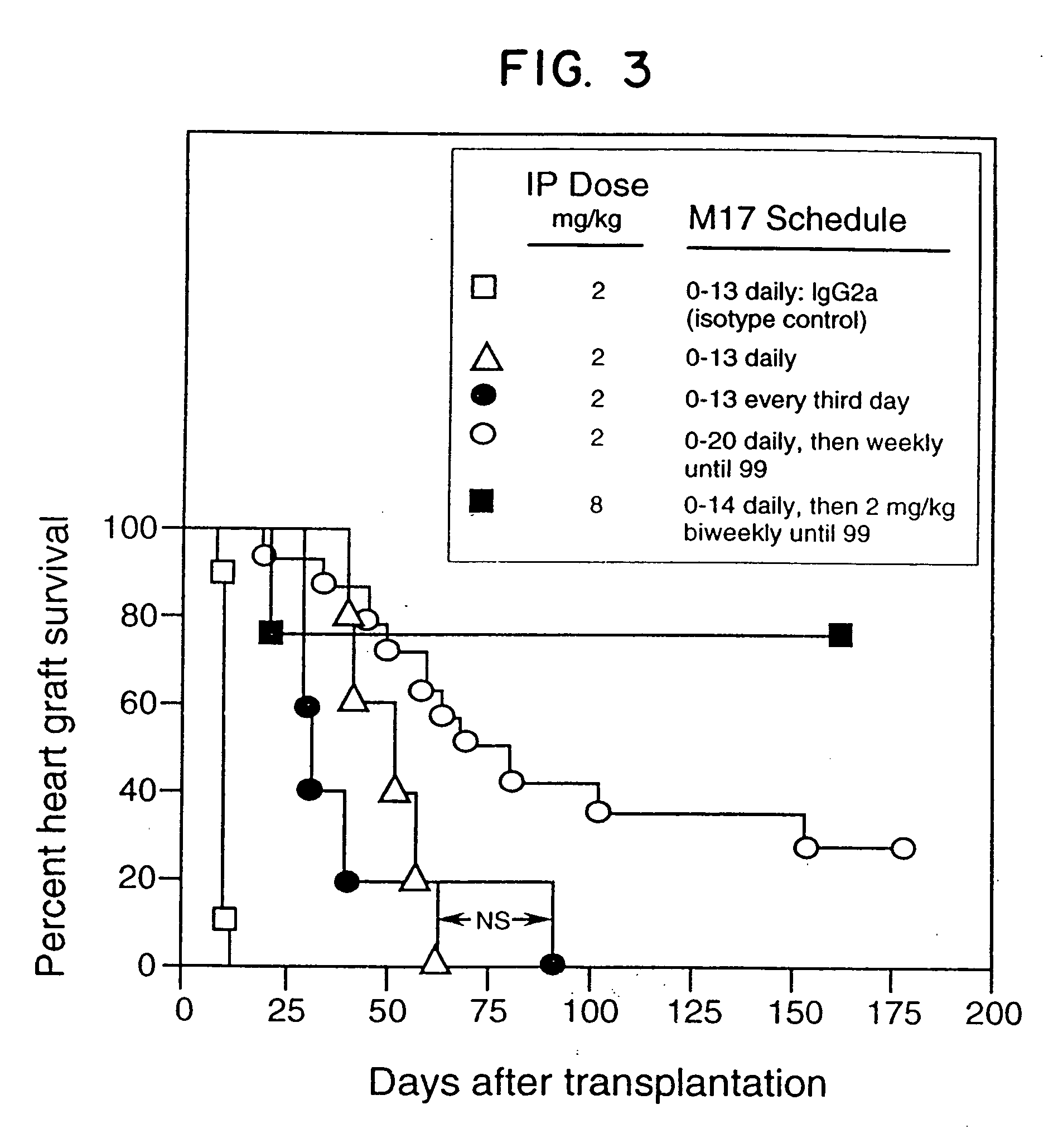
[0097] Neonatal BALB / c (H-2d) hearts were transplanted into the dorsal ear pinnae of male adult (8 to 10 weeks old) C3H(H-2k) mice as described in Babany et al., J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 244: 259 (1988). All mice were raised under specific pathogen-free conditions and were obtained from the Department of Comparative Medicine, Stanford University Medical Center. The reagents employed were M17 (clone M17 / 4.411.9, rat IgG2a anti-murine CD11a MAb purified from ascites, obtainable from the American Type Culture Collection, Rockville, Md. (ATCC Accession No. TIB 217), cyclosporin A (CsA; i.v. formulation, Sandoz, East Hanover, N.J.), or IgG2a (rat isotype control, Zymed. S. San Francisco, Calif.). M17 (n=3-9 / dose group) or CsA (n=5-20 / dose group) was administered to the mice daily i.p. for two weeks starting on the day of transplantation (M17) or on the first post-transplant day (CsA). The results are shown in FIGS. 1A and 1B, representi...
example 2
Encelhalomyelitis Model Using Anti-CD11a Antibody
[0116] Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) is an inflammatory condition of the central nervous system with similarities to multiple sclerosis. In both diseases, circulating leukocytes penetrate the blood-brain barrier and damage myelin, resulting in impaired nerve conduction and paralysis.
[0117] EAE is induced in Lewis rats by subcutaneous injection of 50 μg guinea-pig basic protein (GPBP) [Vandenbark et al., Nature, 341: 541 (1989)]+400 μg Mycobacteria in complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA). One group of rats is untreated and one group of rats is injected subcutaneously with 1-10 mg / kg / day daily of M17 mixed with CFA and 100 μg Mycobacteria at either day −4, day −3, day −2, day −1, day 0, day 1, day 2, day 3, day 4, day 5, day 6, day 7, day 8, day 9, day 10, day 11, day 12, or day 13, with day 0 being the day when the GPBP is given. This administration is continued up to day 21. Then, oh days 28 and 35, each rat is injecte...
example 3
In Vitro Mixed Lymphocyte Culture Model Using Anti-CD18 Antibody
[0119] This mixed lymphocyte culture model, which is an in vitro model of transplantation [A. J. Cunningham, “Understanding Immunology,”Transplantation Immunology, p. 157-159 (1978)], examines the effects of various A-ICAM, a-LFA-1 antibodies, and soluble ICAM in both the proliferative and effector arms of the human mixed lymphocyte response.
I. Protocol:
[0120] A. Mixed Lymphocyte Response
[0121] Part 1: Isolation of Cells: Mononuclear cells from peripheral blood (PBMC) were separated from heparinized whole blood drawn from healthy donors. Blood was diluted 1:1 with saline, layered, and centrifuged at 2500×g for 30 minutes on LSM (6.2 g Ficoll and 9.4 g sodium diatrizoate per 100 ml) (Organon Technica, N.J.). Cells were resuspended in RPMI 1640 medium (GIBCO, Grand Island, N.Y.) supplemented with 5% heat-inactivated pooled human AB serum (Peninsula Memorial Blood Bank, Burlingame, Calif.), 1 mM sodium pyruvate, 3 mM ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com