Method for plating resin material
a resin material and surface technology, applied in the field of methods, can solve the problems of high cost of palladium, significant price fluctuations, and large environmental burden, and achieve the effects of improving adhesion strength, reducing cost, and increasing density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
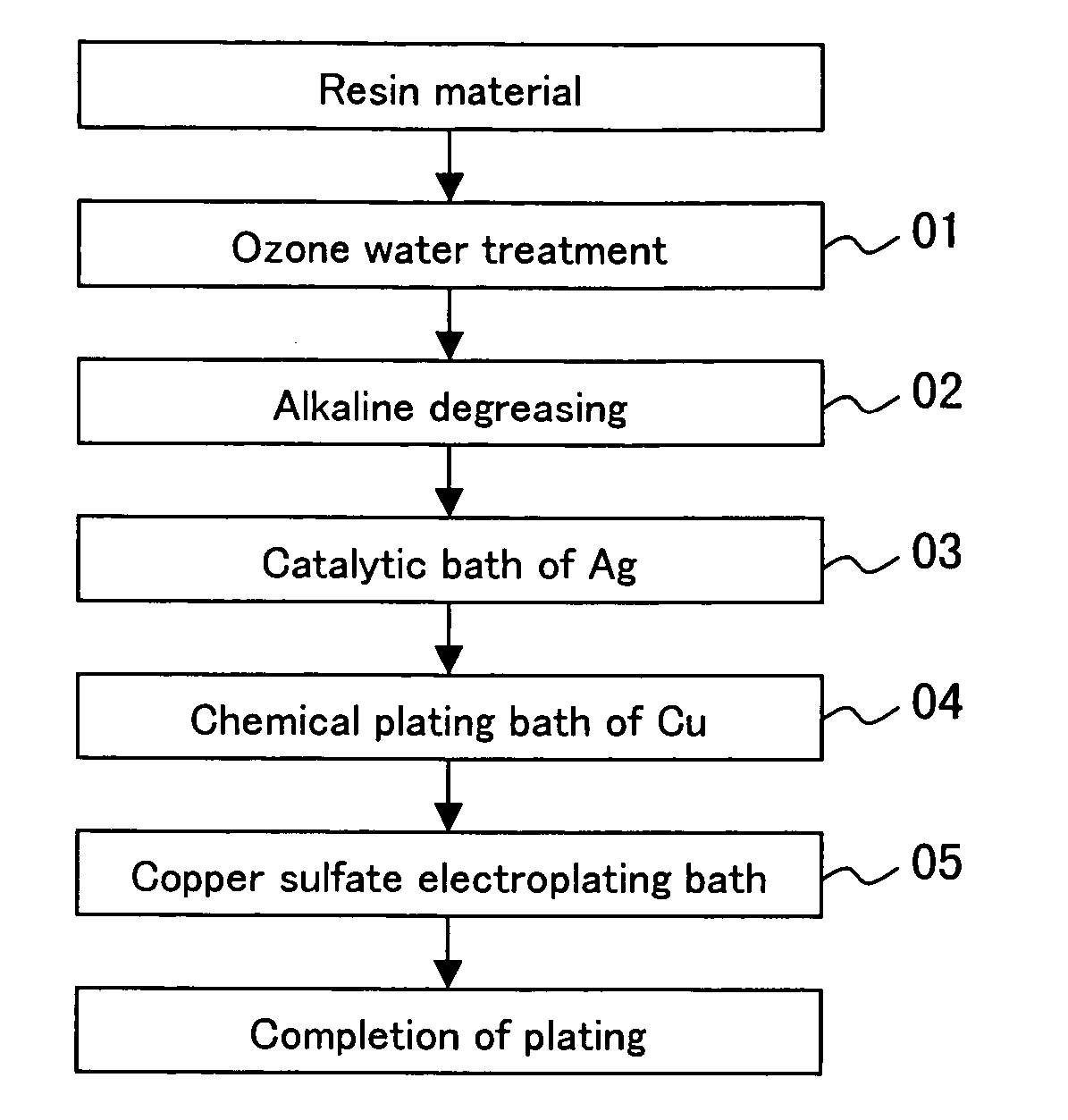
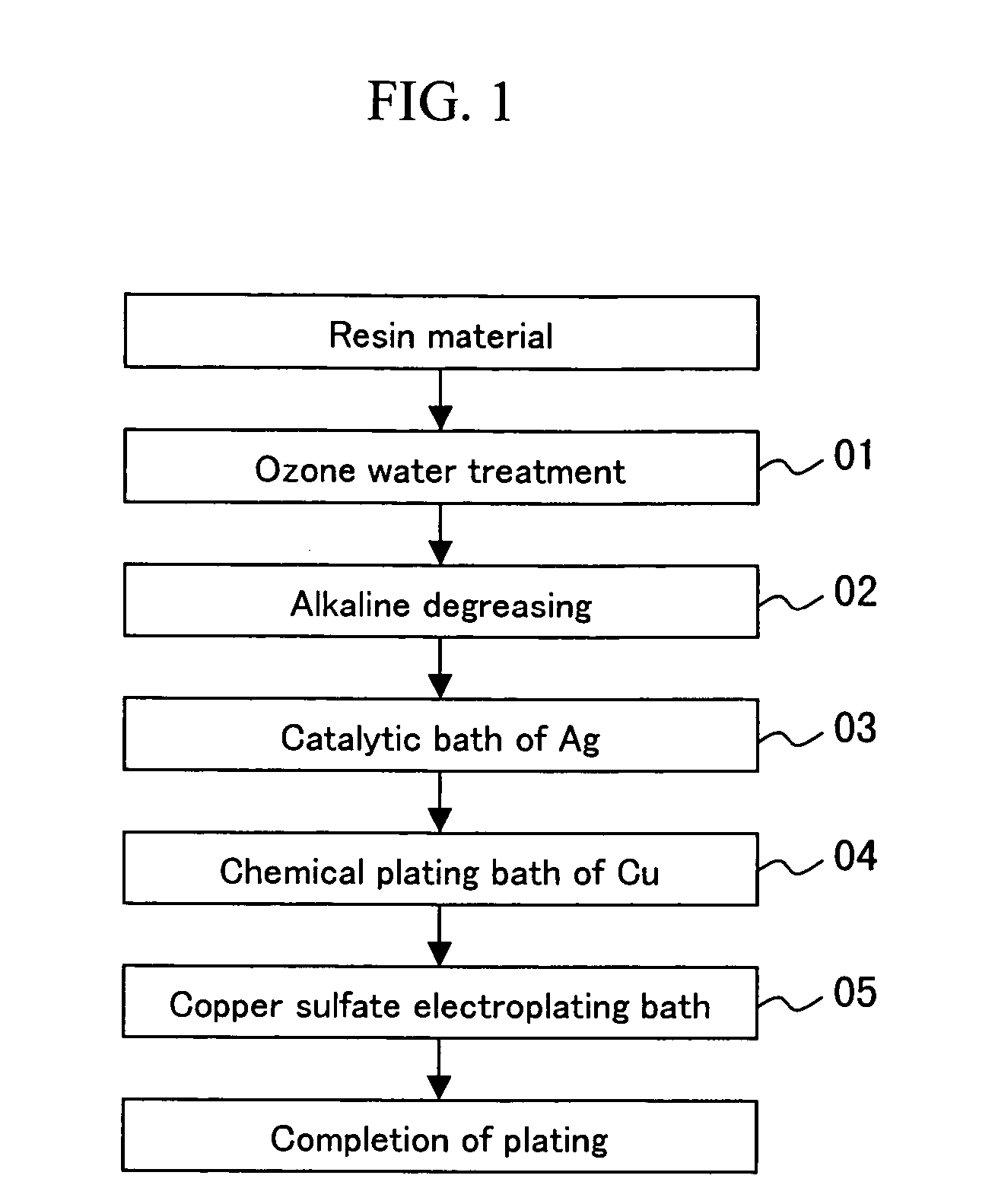
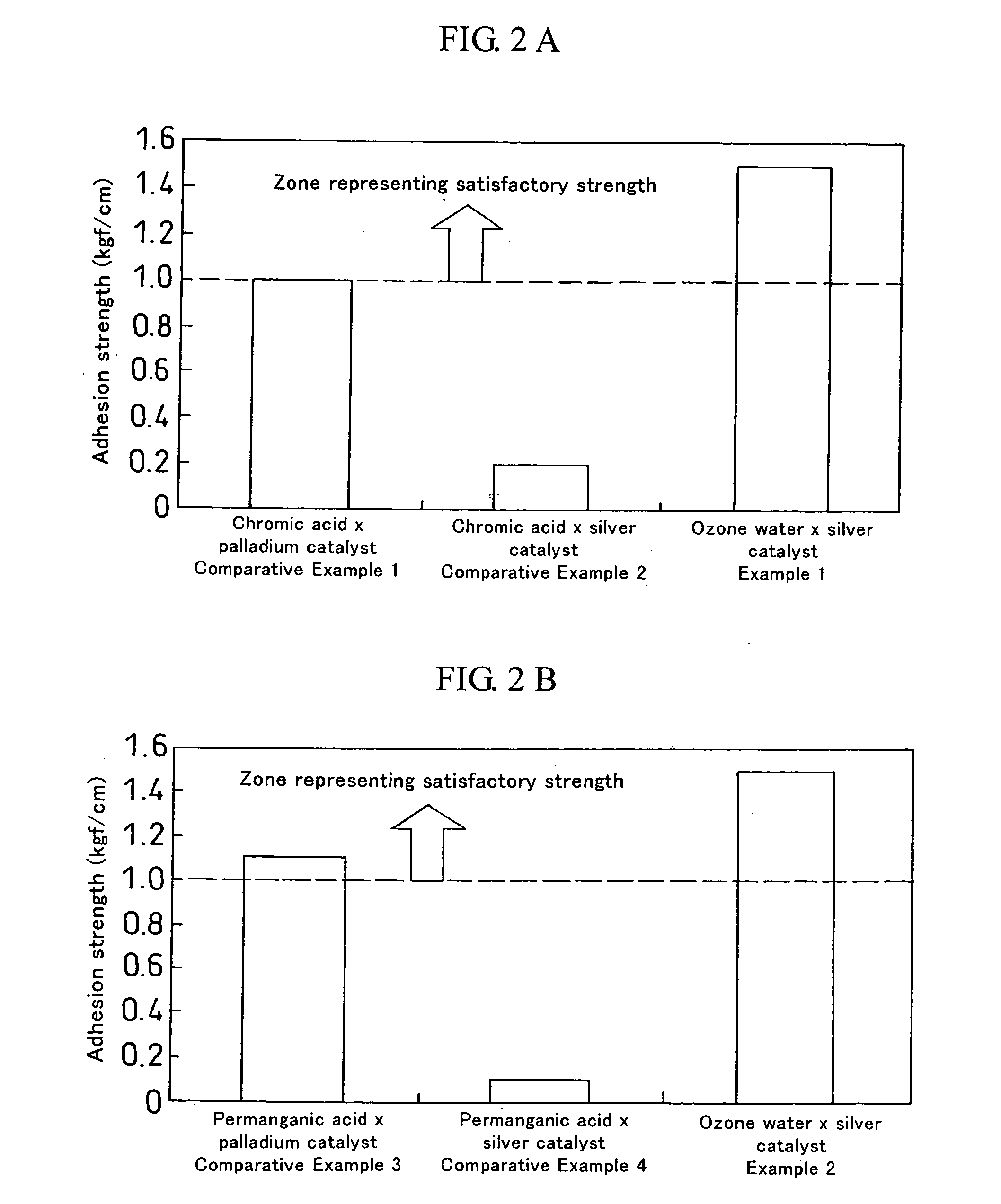
[0038] An ABS resin substrate was treated with ozone water of 50 to 100 ppm for 2 to 10 minutes (step 01). The substrate was then subjected to alkaline degreasing in a 50 g / l aqueous solution of NaOH at 60° C. for 13 minutes (step 02). If the resin substrate is sufficiently clean, this step of alkaline degreasing can be omitted. Subsequently, the substrate was subjected to a catalytic bath of Ag in a 0.5 g / l aqueous solution of an Ag catalyst at 30° C. for 30 minutes (step 03). The substrate was then subjected to chemical plating with copper in a plating solution containing 3 g / l of copper sulfate, 2 g / l of formalin, and 2 g / l of NaOH at 30° C. for 10 minutes (step 04). Further, the substrate was subjected to electroplating of 2.0 A / dm2 in a plating solution containing 200 g / l of copper sulfate, 50 g / l of sulfuric acid, 0.125 g / l of hydrochloric acid, and additives at 30° C. for 30 minutes (step 05). A copper-plated layer with a thickness of 100 μm was deposited on the ABS resin sub...
example 2
[0041] Copper plating was carried out in the same manner as in Example 1, except that an epoxy resin substrate was used instead of an ABS resin substrate.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adhesion strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com