Reflective optical element, optical system and EUV lithography device
a technology of optical elements and lithography, applied in the field of reflective optical elements, optical systems and euv lithography devices, can solve the problems of degradation or contamination, inability to achieve desired imaging, and inability to achieve imaging errors and transmission losses, etc., to achieve less effect, high reflectivity, and lower intensities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
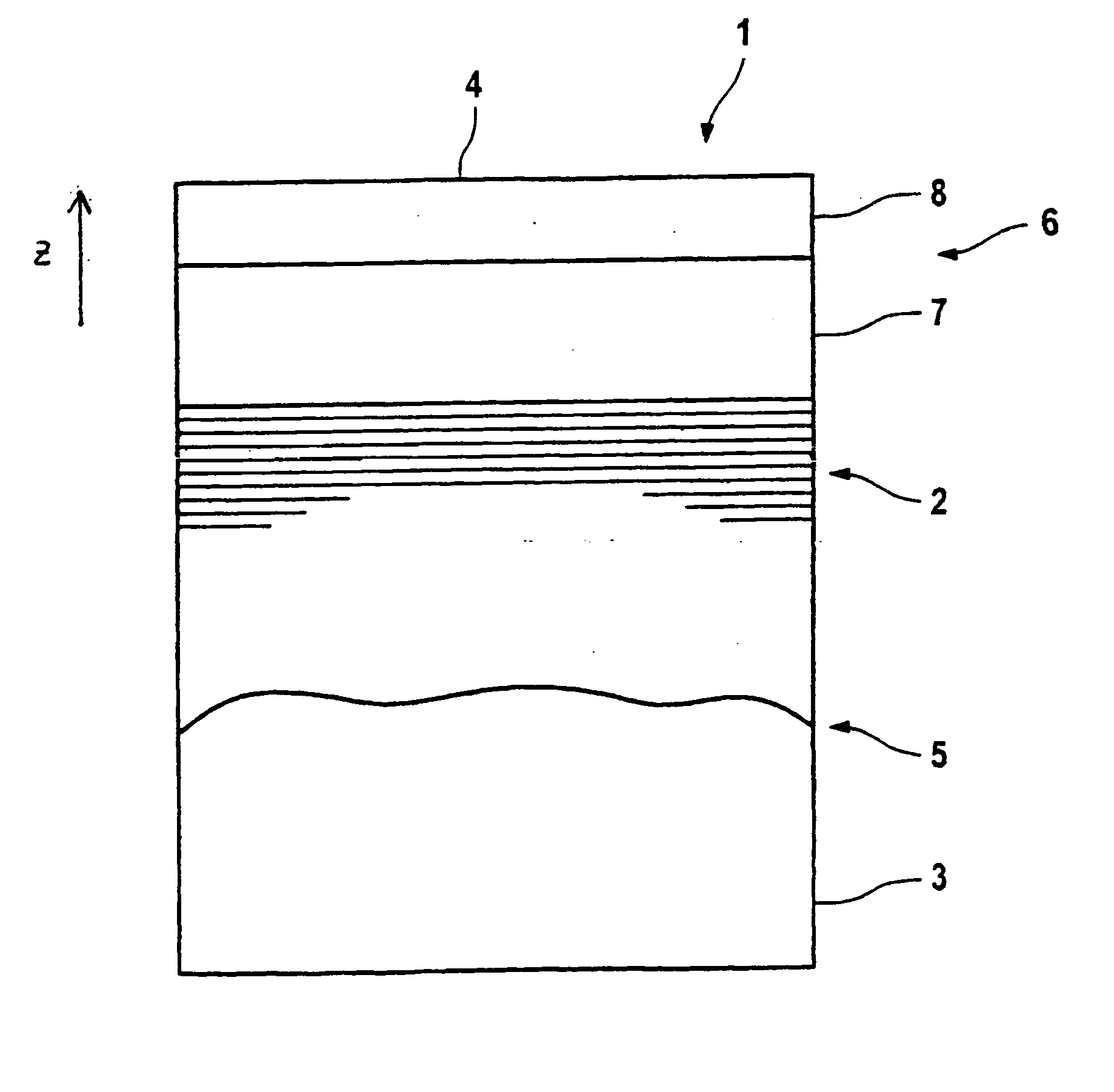
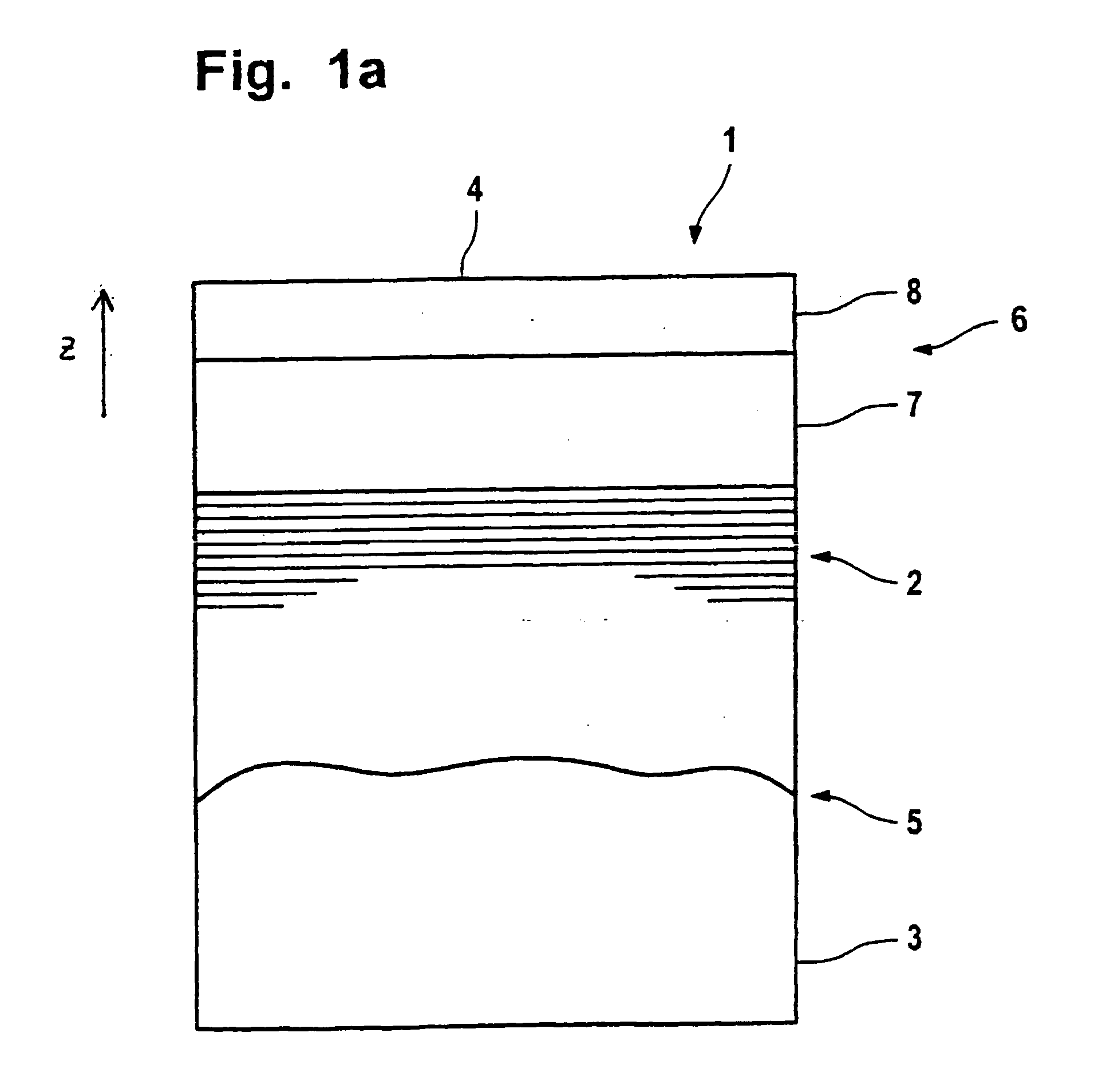
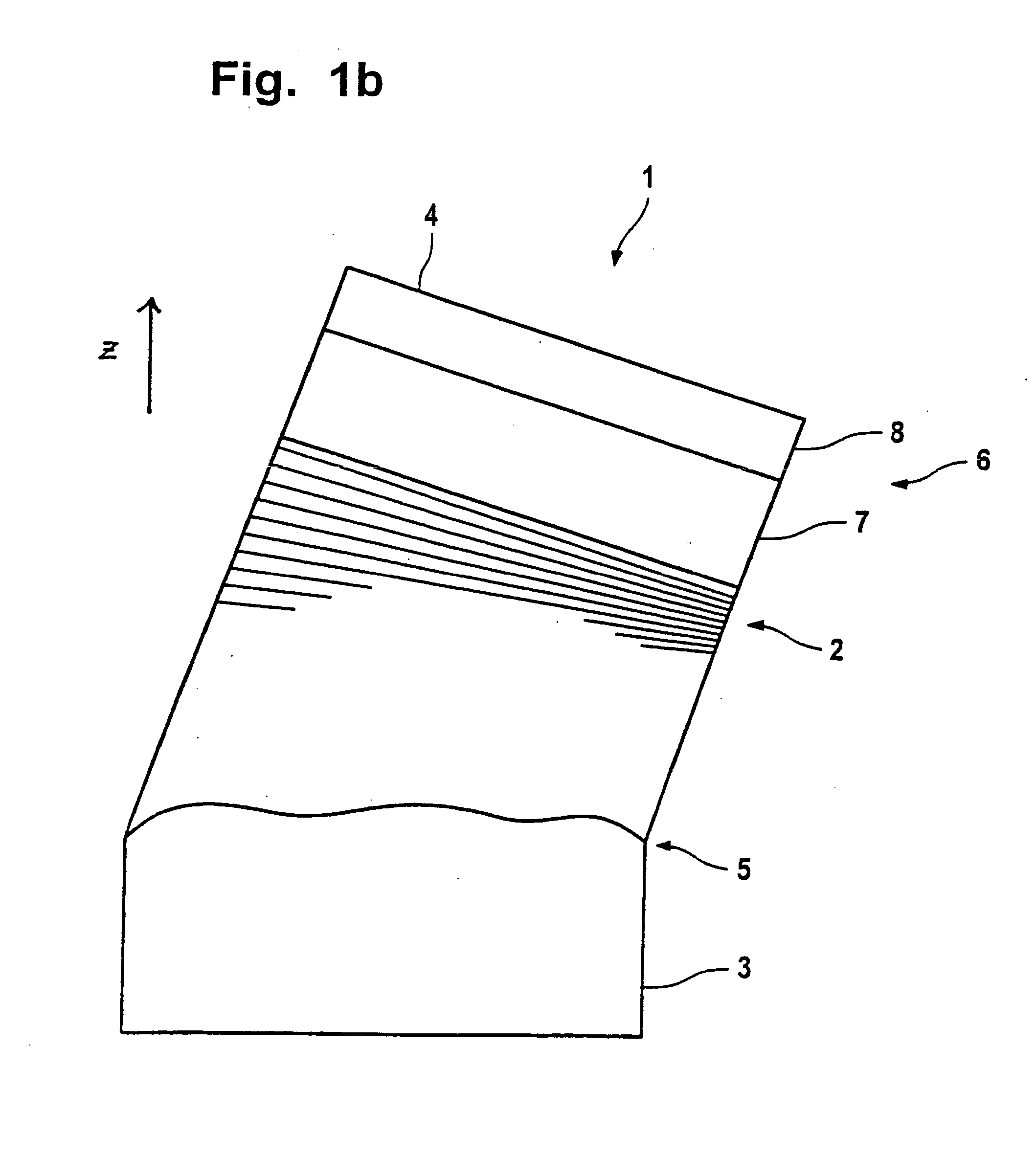
[0061]FIGS. 1a to c have already been explained.
[0062] In FIGS. 2 to 4, a first preferred embodiment of the invented optical element is described.
[0063]FIG. 2a shows the two-dimensional intensity distribution of incident EUV radiation for a first optical element with which the reflective optical element is to be utilized. The intensity increases from the outside to the middle.
[0064]FIGS. 2b and 2c show the intensity curve in the x and y direction corresponding to the broken lines drawn in FIG. 2a. This intensity curve in the xy-direction corresponds in monotonic manner to the thickness curve of the cover layer system. Where a high radiation intensity impinges on the reflective optical element, the cover layer system is also particularly thick. Where the intensity is less, the cover layer system is also thinner. Corresponding to FIGS. 1a-c, the thickness distribution designated as 7 pertains to the lower segment of the cover layer system and the thickness distribution designated a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com