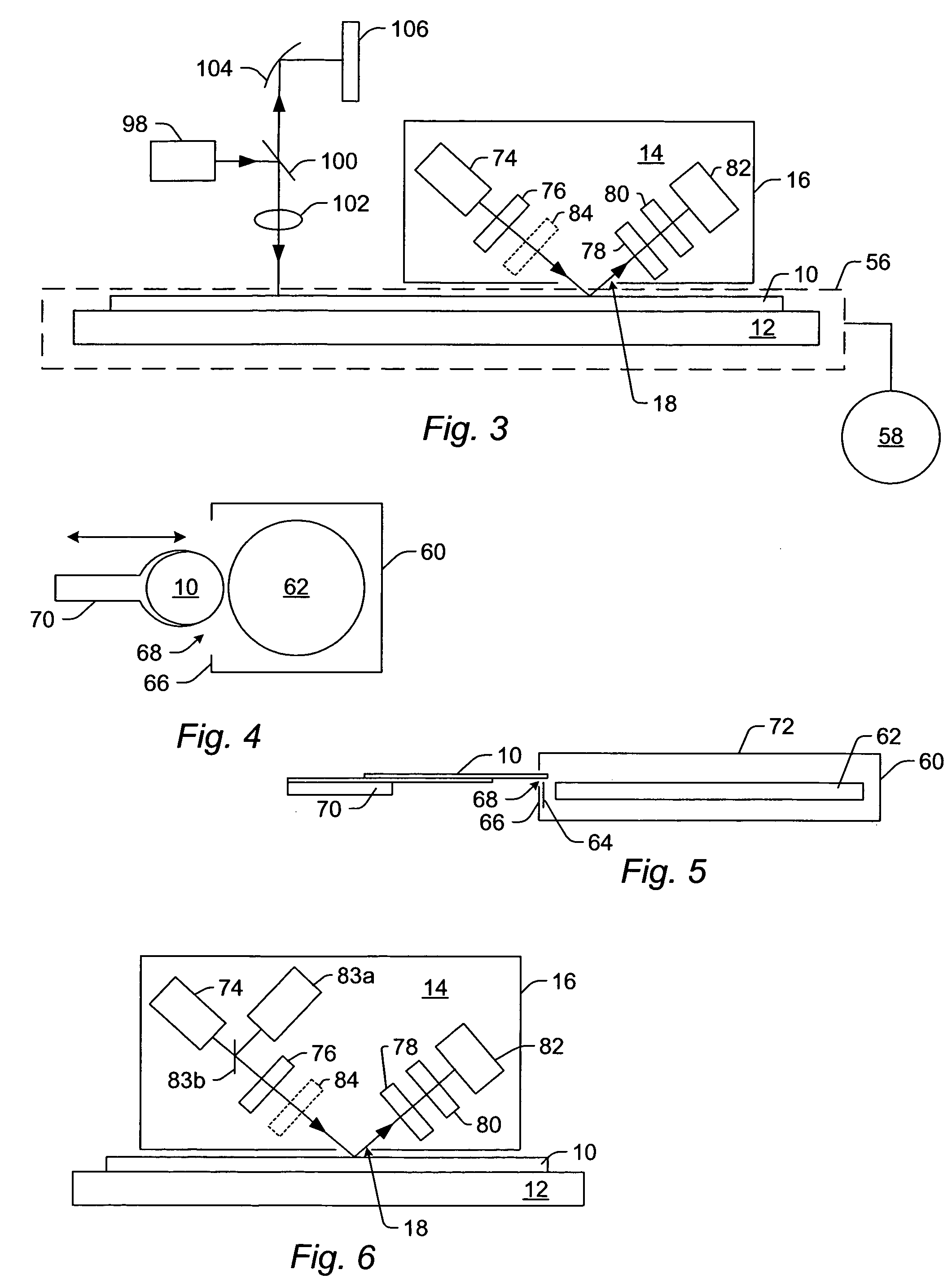
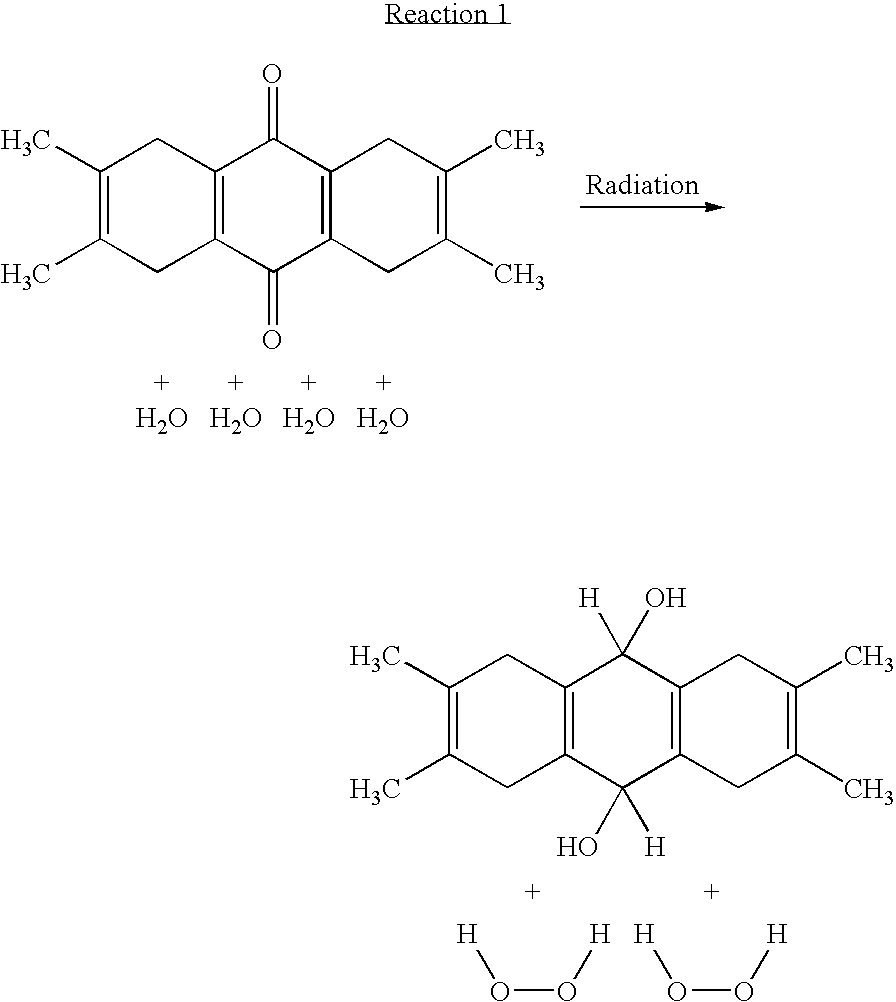
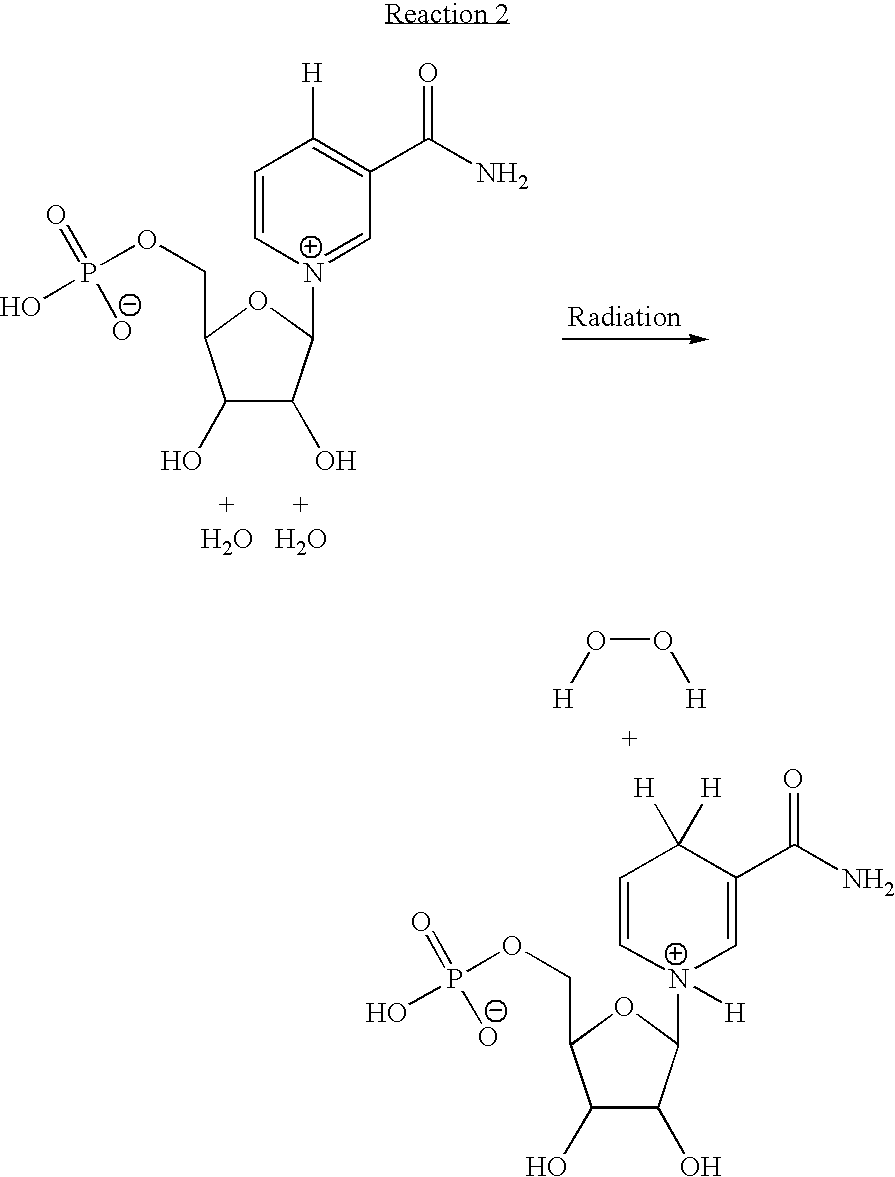
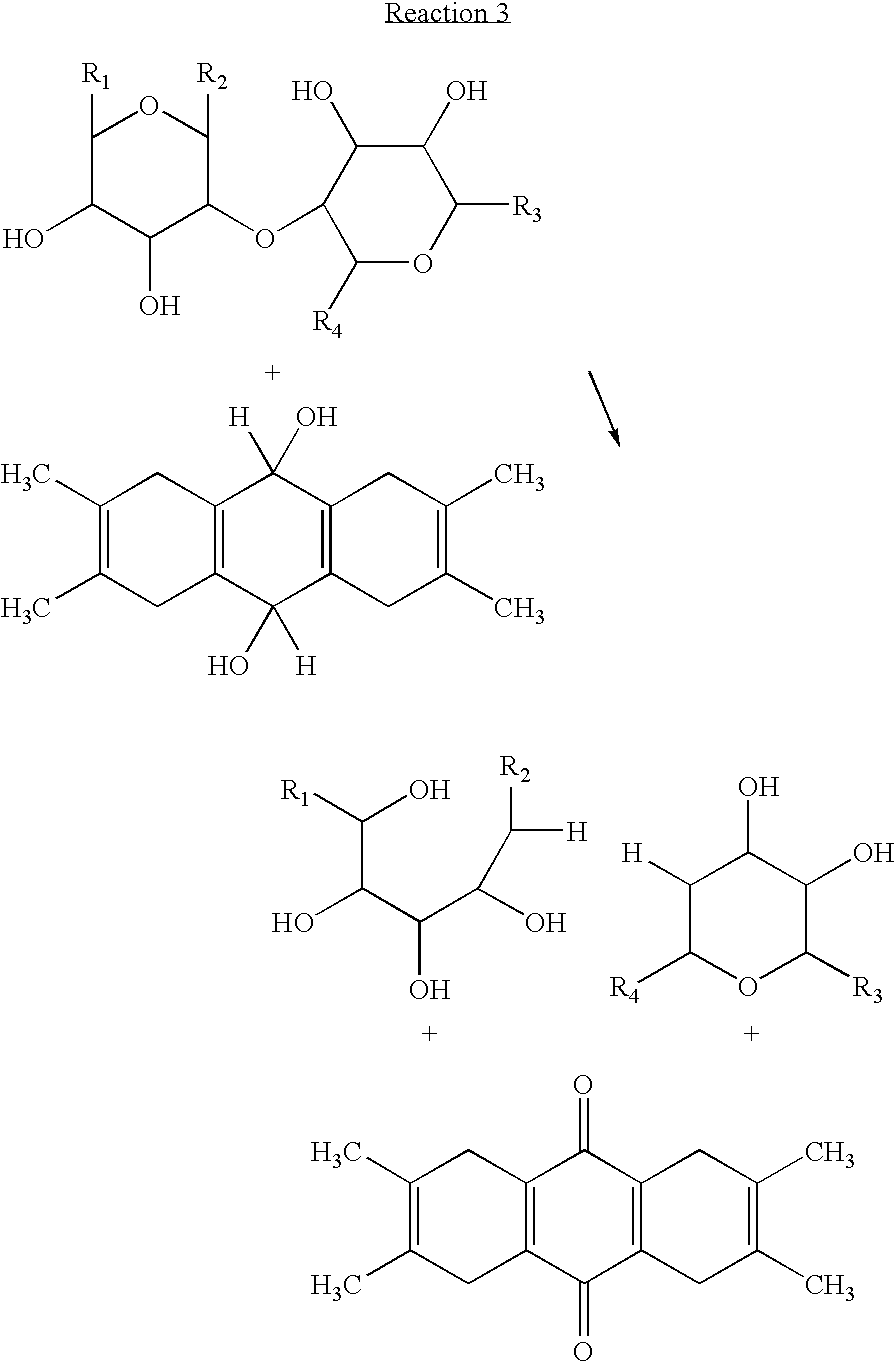
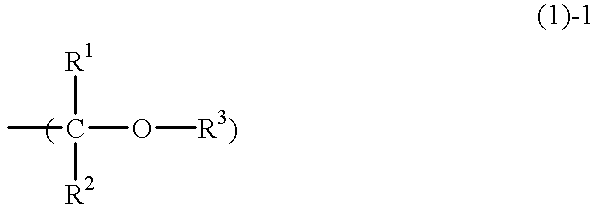Patents
Literature
312 results about "Soft X-rays" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
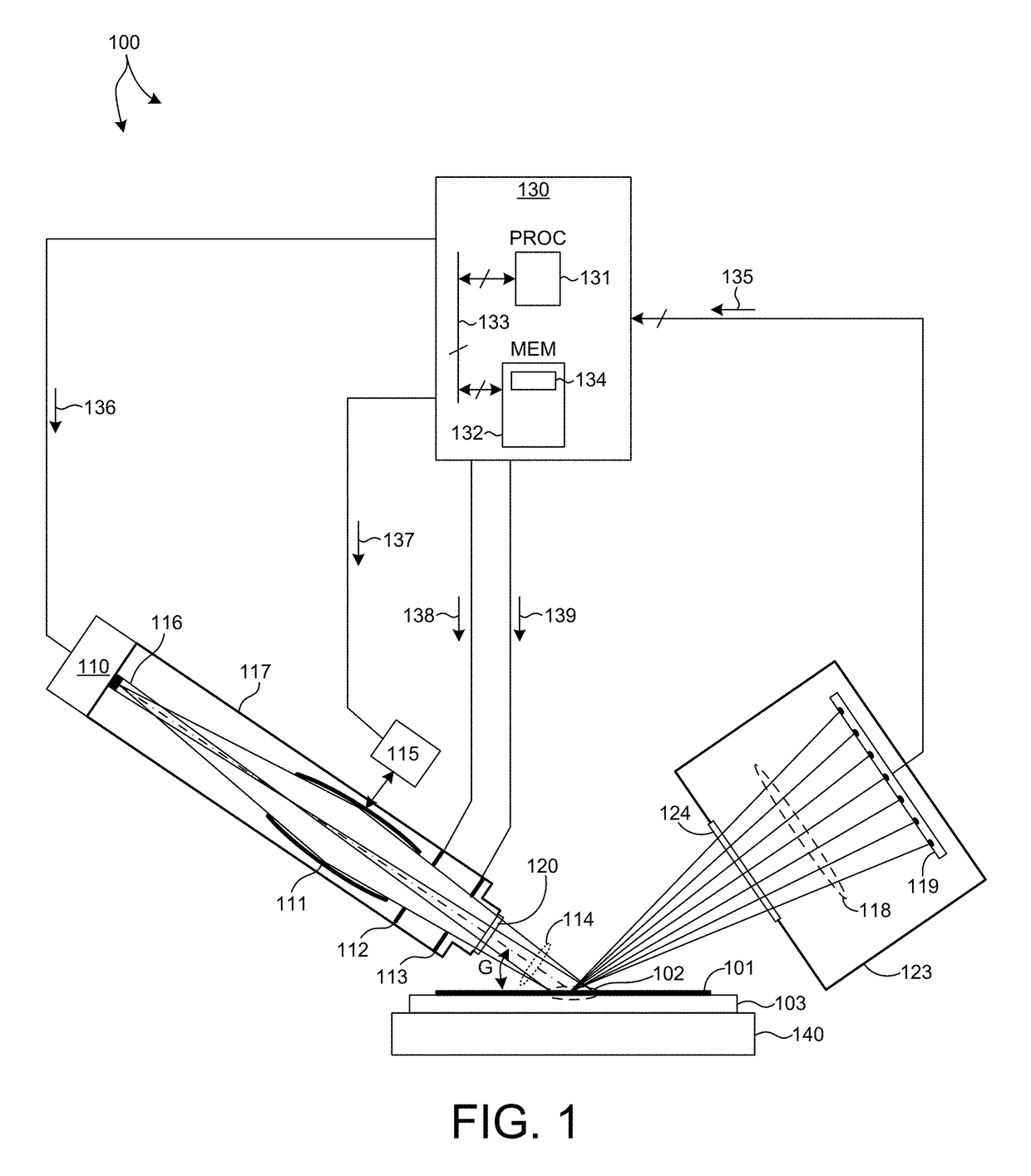
Method and apparatus for generating high output power gas discharge based source of extreme ultraviolet radiation and/or soft x-rays
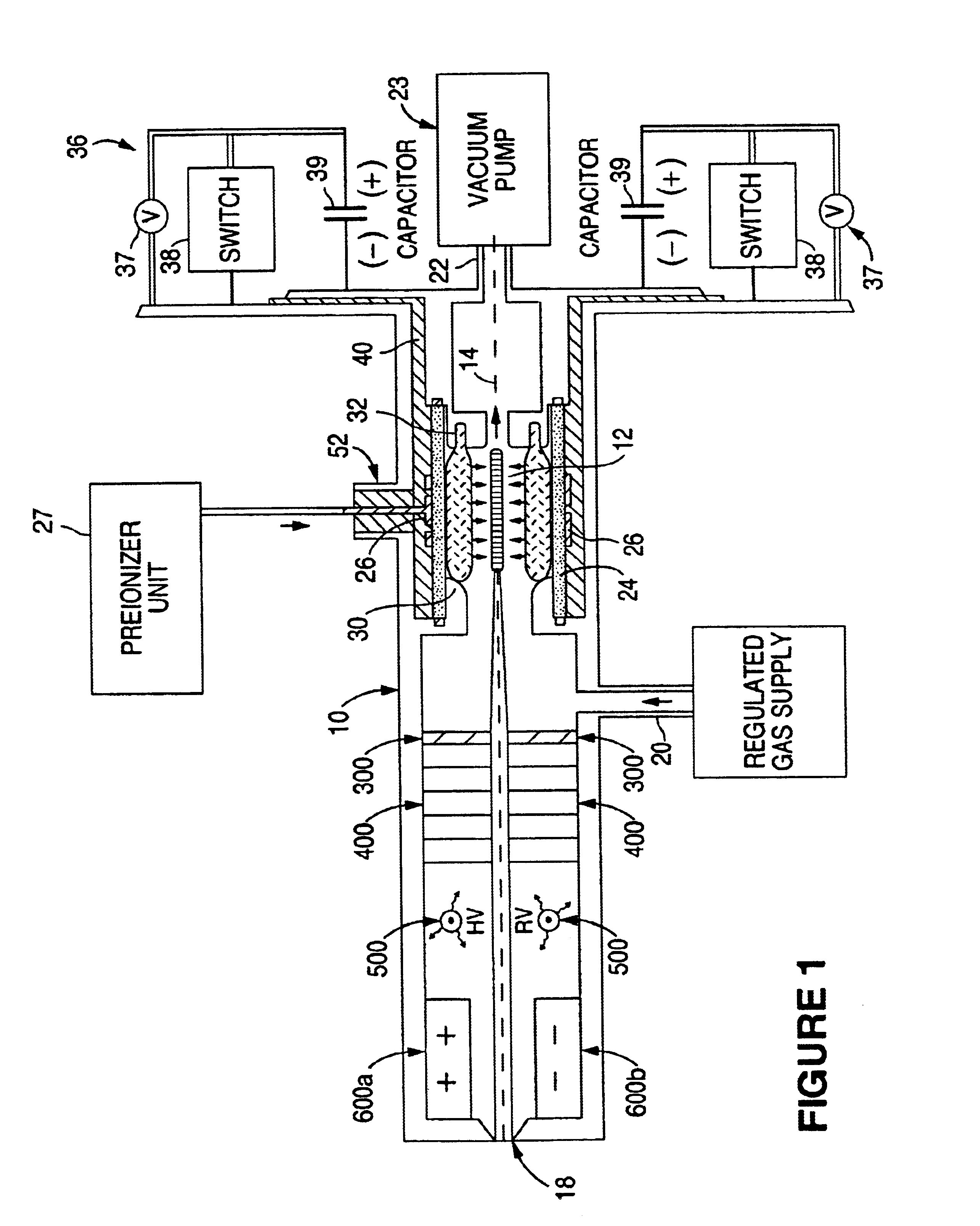
InactiveUS20020168049A1Avoid reflectionsReduce reflectionRadiation/particle handlingNanoinformaticsSoft x rayUltraviolet radiation
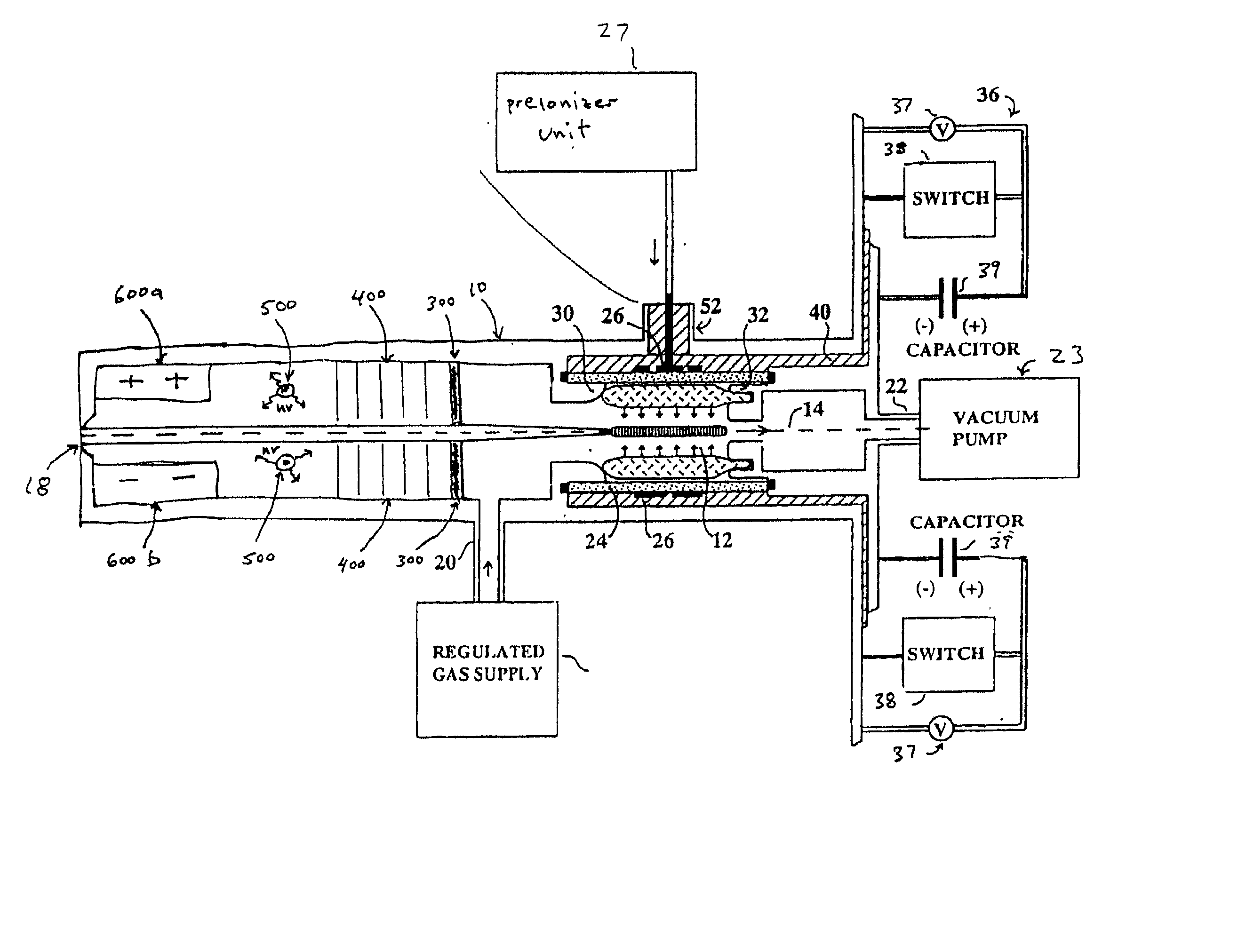
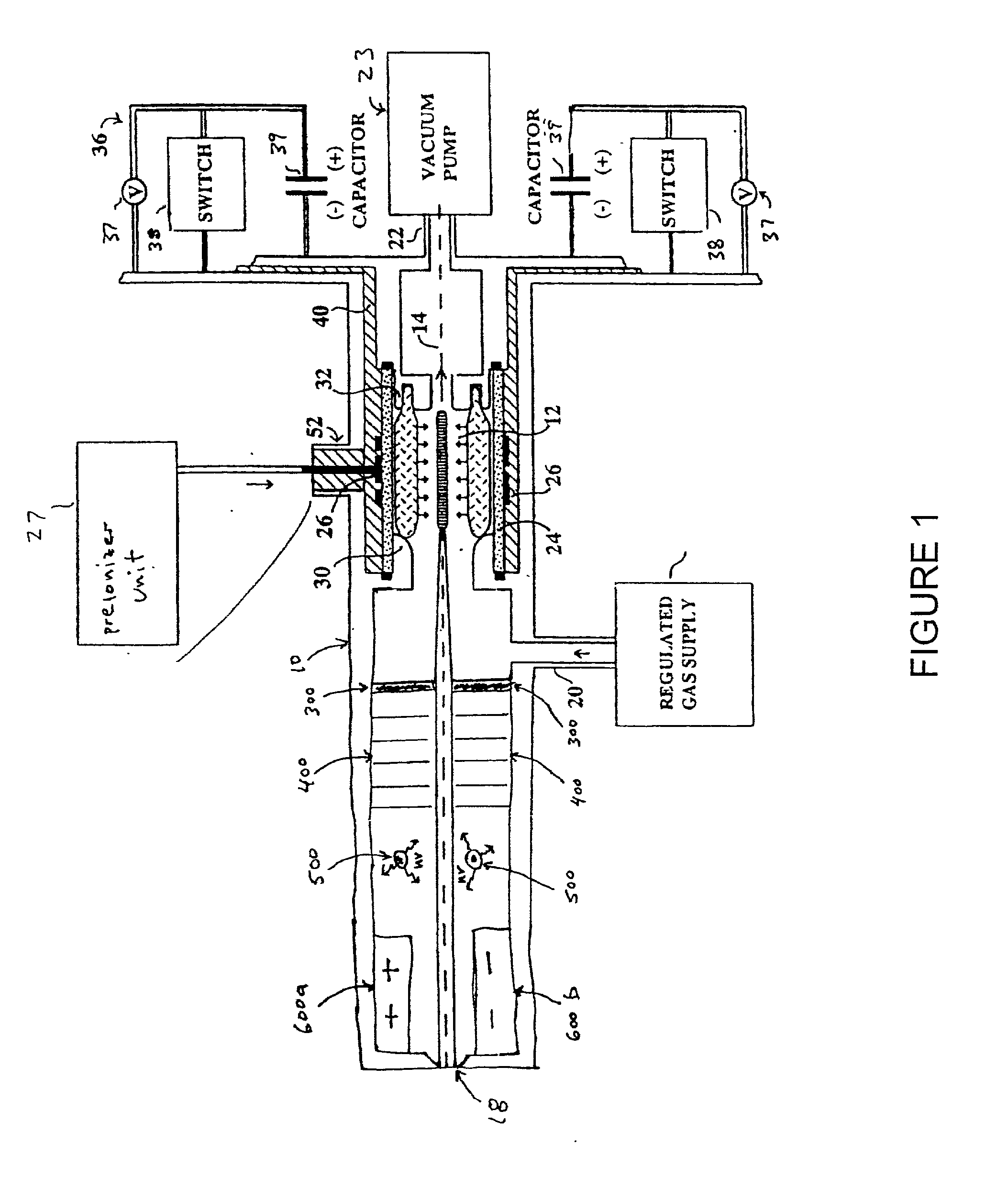
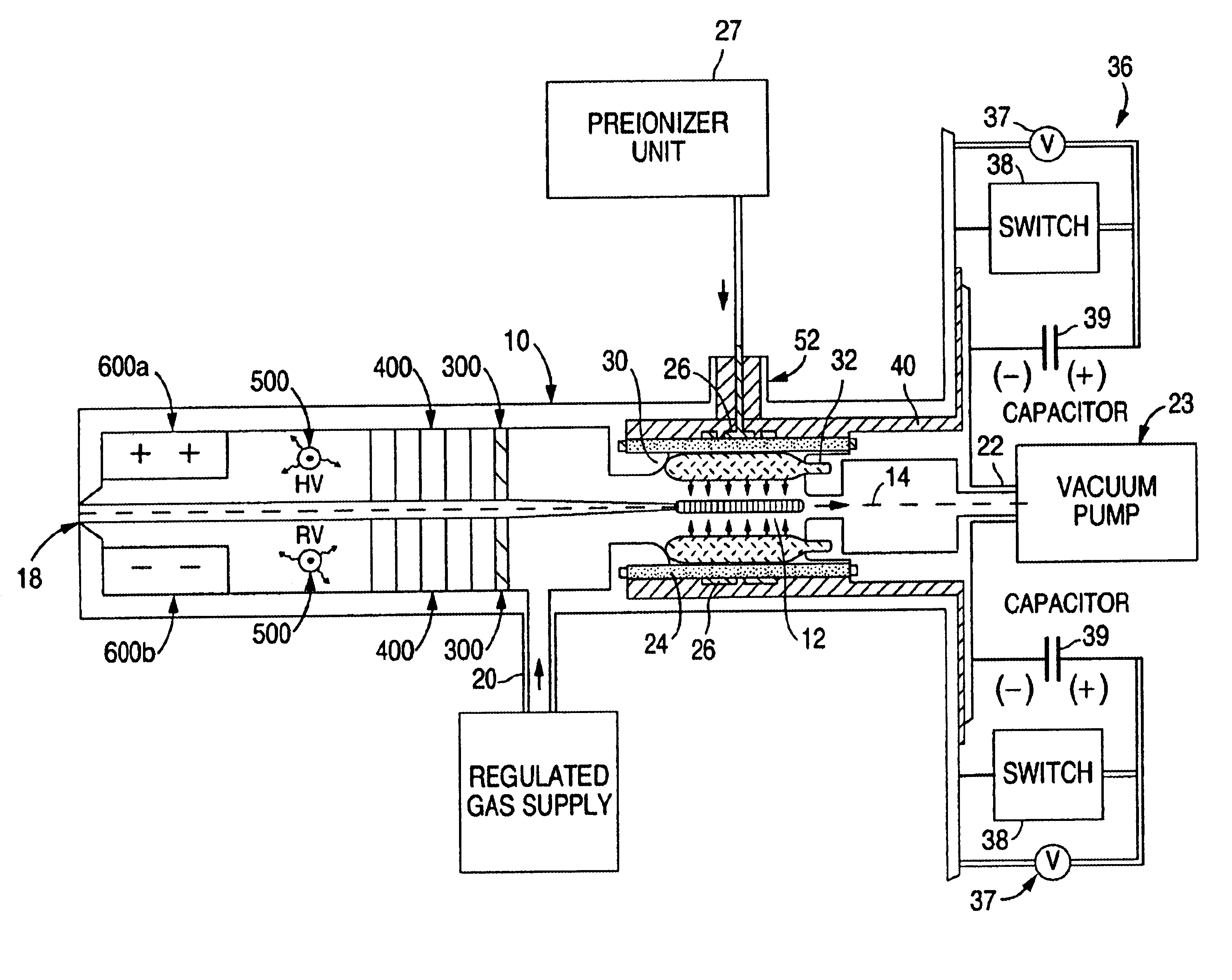
An EUV photon source includes a plasma chamber filled with a gas mixture, multiple electrodes within the plasma chamber defining a plasma region and a central axis, a power supply circuit connected to the electrodes for delivering a main pulse to the electrodes for energizing the plasma around the central axis to produce an EUV beam output along the central axis, and a preionizer for ionizing the gas mixture in preparing to form a dense plasma around the central axis upon application of the main pulse from the power supply circuit to the electrodes. The EUV source preferably includes an ionizing unit and precipitator for collecting contaminant particulates from the output beam path. A set of baffles may be disposed along the beam path outside of the pinch region to diffuse gaseous and contaminant particulate flow emanating from the pinch region and to absorb or reflect acoustic waves emanating from the pinch region away from the pinch region. A clipping aperture, preferably formed of ceramic and / or Al2O3, for at least partially defining an acceptance angle of the EUV beam. The power supply circuit may generates the main pulse and a relatively low energy prepulse for homogenizing the preionized plasma prior to the main pulse. A multi-layer EUV mirror is preferably disposed opposite a beam output side of the pinch region for reflecting radiation along the central axis for output along the beam path of the EUV beam. The EUV mirror preferably has a curved contour for substantially collimating or focusing the reflected radiation. In particular, the EUV mirror may preferably have a hyperbolic contour.
Owner:USHIO DENKI KK
Method and apparatus for generating high output power gas discharge based source of extreme ultraviolet radiation and/or soft x-rays
InactiveUS6804327B2Reduce impactPreventing electrode burnoutRadiation/particle handlingNanoinformaticsSoft x rayLight beam
The method and system herein pertain to an EUV photon source which includes a plasma chamber filled with a gas mixture, multiple electrodes within the plasma chamber defining a plasma region and a central axis, a power supply circuit connected to the electrodes for delivering a main pulse to the electrodes for energizing the plasma around the central axis to produce an EUV beam. The system can also include a preionizer for ionizing the gas mixture in preparing to form a dense plasma around the central axis upon application of the main pulse from the power supply circuit to the electrodes. A set of baffles may be disposed along the beam path outside of the pinch region to diffuse gaseous and contaminant particulate flow emanating from the pinch region and to absorb or reflect acoustic waves emanating from the pinch region away from the pinch region.
Owner:USHIO DENKI KK
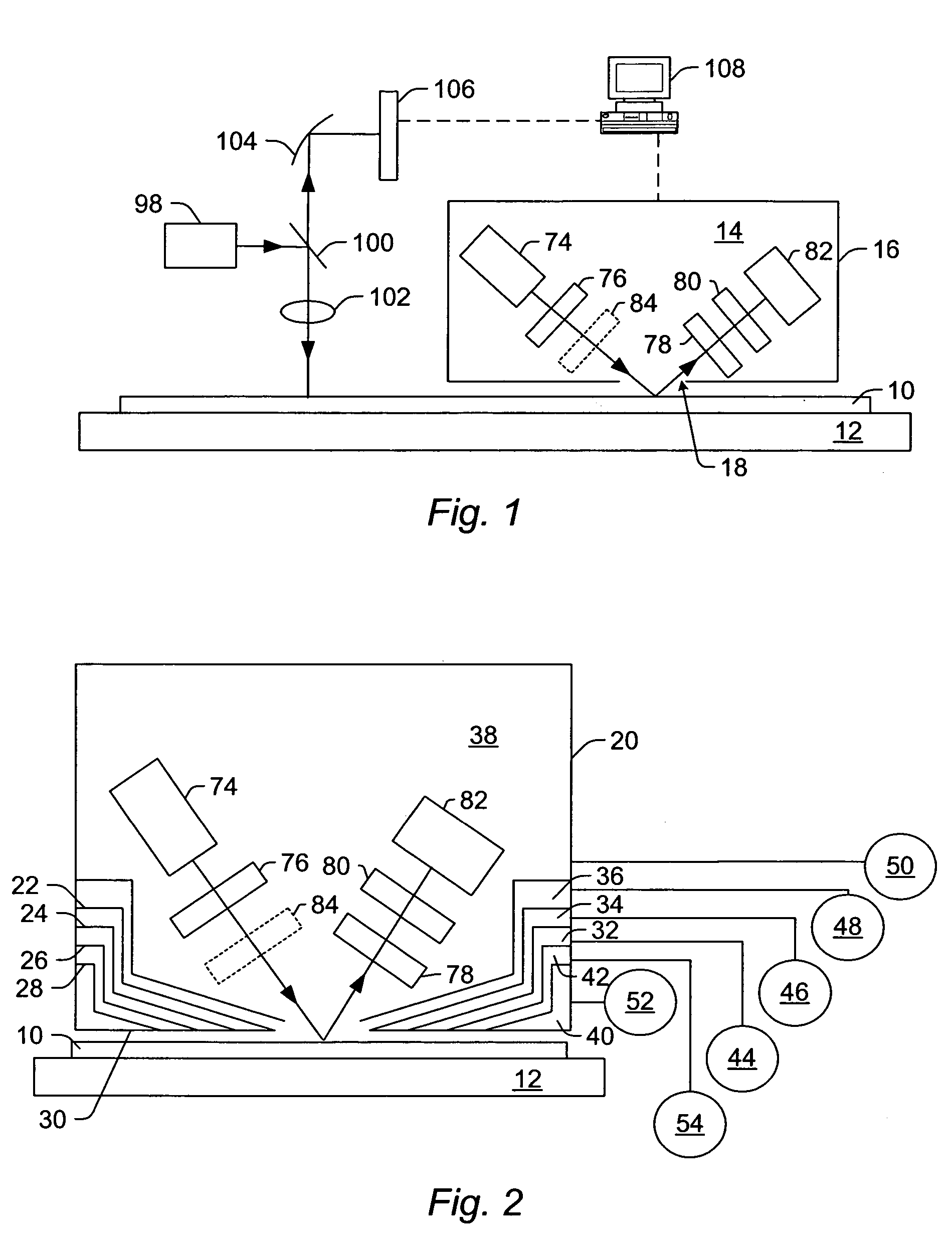
Systems and methods for measurement or analysis of a specimen using separated spectral peaks in light
ActiveUS7067819B2Improve accuracyRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSoft x rayProgram instruction
A system configured for measurement of a specimen is provided. The system includes an optical subsystem configured to perform measurements of the specimen. The optical subsystem includes a light source that is configured to generate light having a relatively large number of separated spectral peaks with substantially no continuous background. In some embodiments, the light may include vacuum ultraviolet light, extreme ultraviolet light, and / or soft x-rays. A carrier medium is also provided that includes program instructions executable on a computer system to analyze data generated by a detector of an optical subsystem by partitioning the data into individual peaks spaced apart across a wavelength spectrum. Partitioning the data preferably corrects for spectrum shift, drift, stretching, shrinking, or a combination thereof at the detector. The individual peaks correspond to separated spectral peaks in light generated by a light source of the optical subsystem.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Utilizing electromagnetic radiation to activate filtercake breakers downhole
A downhole wellbore filtercake breaker is disclosed comprising one or more breaker chemicals (or activators thereof) capable of being activated with radiation to form one or more breaker reaction products which in turn are capable of reacting with the filtercake to chemically break down the filtercake. There is also disclosed a conventional reservoir drilling fluid modified to include an inactive, delayed, or sequestered breaker chemical or an activator thereof, wherein the breaker chemical (or activator) may be activated directly or indirectly by radiation, such as, microwave, visible, uV, soft x-ray, or other electromagnetic radiation. Also disclosed are methods for creating these filtercakes, and then breaking them via deploying a source of radiation that can be energized proximate to the filtercake. The breaker may be regenerated downhole by reaction with the filtercake breakdown products, and subjected again to a source of radiation to continue the breakdown of filtercake.
Owner:HORTON AMY C +1
Extreme ultraviolet soft x-ray projection lithographic method and mask devices
InactiveUS6465272B1NanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionTi dopingSoft x ray
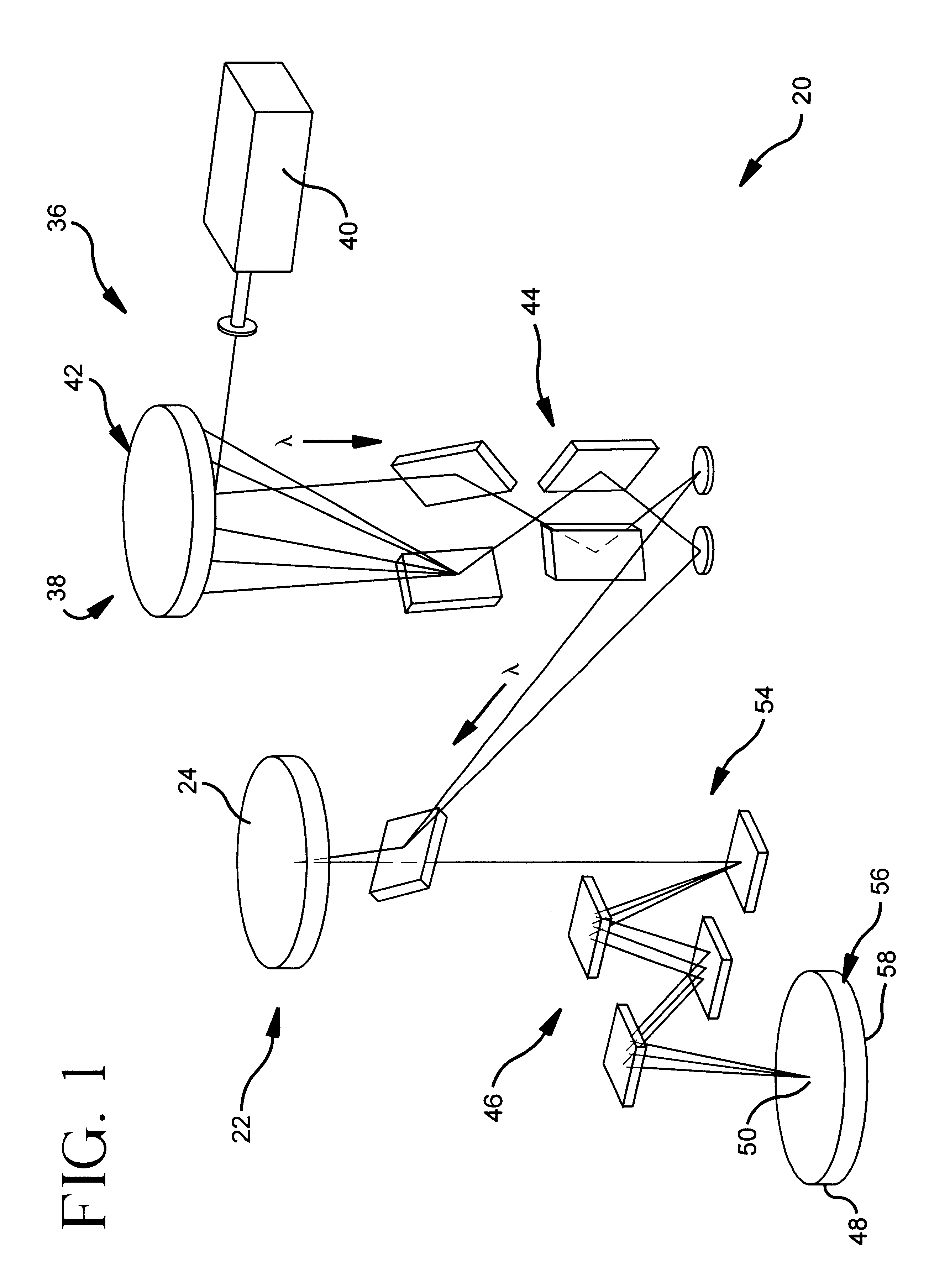
The present invention relates to reflective masks and their use for reflecting extreme ultraviolet soft x-ray photons to enable the use of extreme ultraviolet soft x-ray radiation projection lithographic methods and systems for producing integrated circuits and forming patterns with extremely small feature dimensions. The projection lithographic method includes providing an illumination sub-system for producing and directing an extreme ultraviolet soft x-ray radiation lambd from an extreme ultraviolet soft x-ray source; providing a mask sub-system illuminated by the extreme ultraviolet soft x-ray radiation lambd produced by the illumination sub-system and providing the mask sub-system includes providing a patterned reflective mask for forming a projected mask pattern when illuminated by radiation lambd. Providing the patterned reflective mask includes providing a Ti doped high purity SiO2 glass wafer with a patterned absorbing overlay overlaying the reflective multilayer coated Ti doped high purity SiO2 glass defect free wafer surface that has an Ra roughness<=0.15 nm. The method includes providing a projection sub-system and a print media subject wafer which has a radiation sensitive wafer surface wherein the projection sub-system projects the projected mask pattern from the patterned reflective mask onto the radiation sensitive wafer surface.
Owner:CORNING INC
Radiation window and method of manufacture
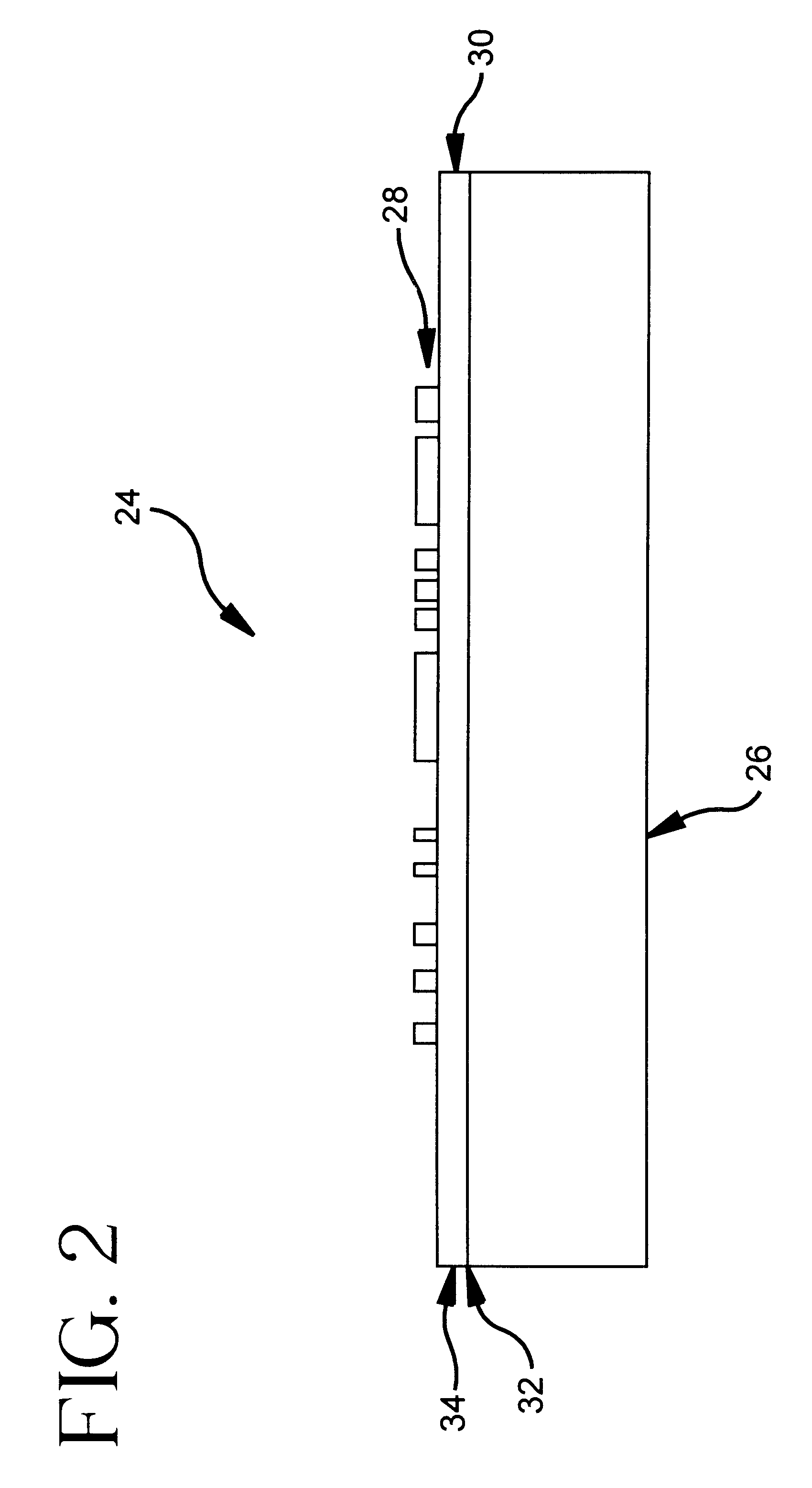
A radiation window device to transmit radiation as part of an x-ray source or detector includes a support to be subject to a substantial vacuum, and an opening configured to transmit radiation. A film is mounted directly on the support across the opening, and has a material and a thickness selected to transmit soft x-rays. An adhesive directly adheres the film to the support. A coating covers exposed portions of at least one of the evacuated or ambient sides of the film, and covers a portion of the support surrounding the film. The support, film and adhesive form a vacuum tight assembly capable of maintaining the substantial vacuum when one side is subject to the substantial vacuum. In addition, the vacuum tight assembly can withstand a temperature of greater than approximately 250 degrees Celsius.
Owner:MOXTEK INC
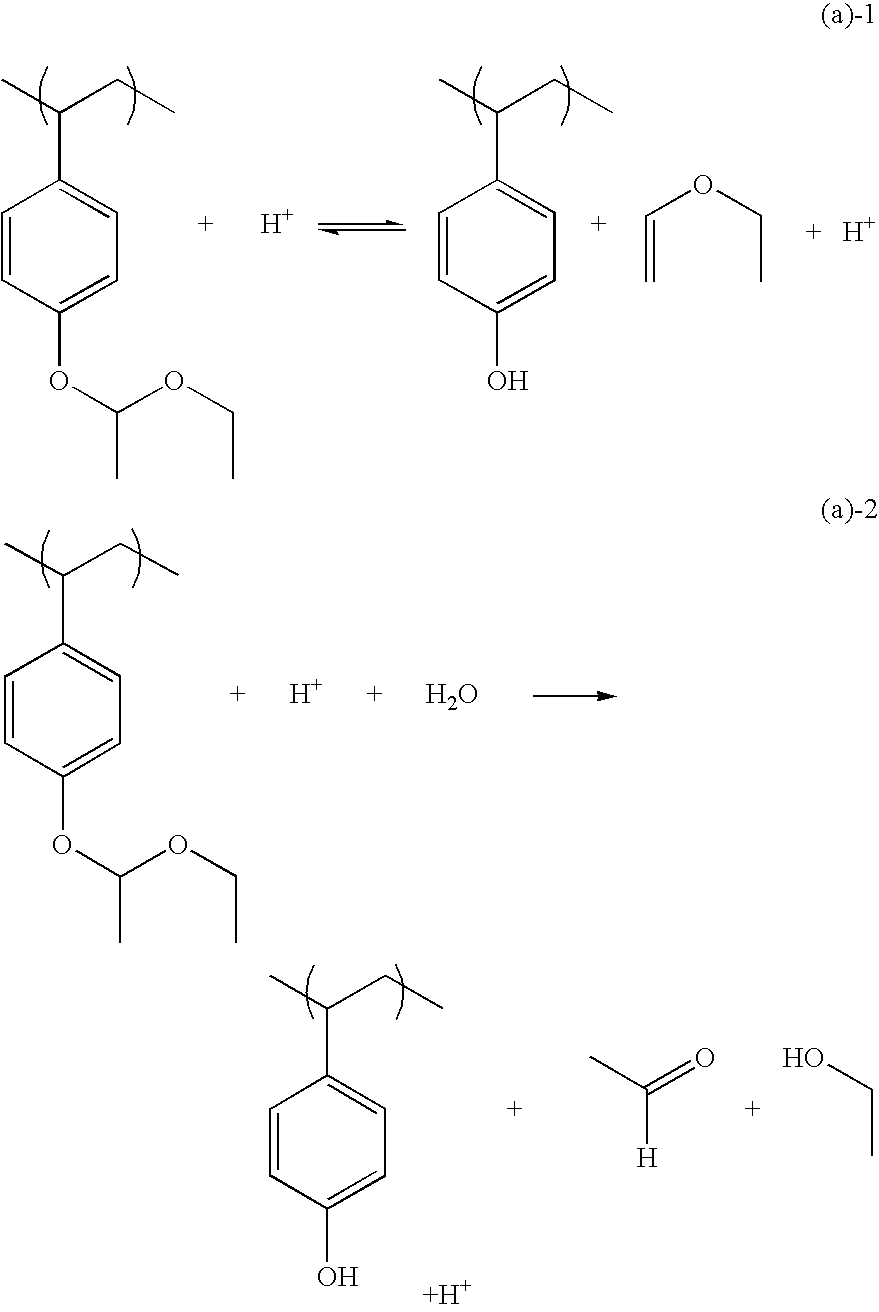
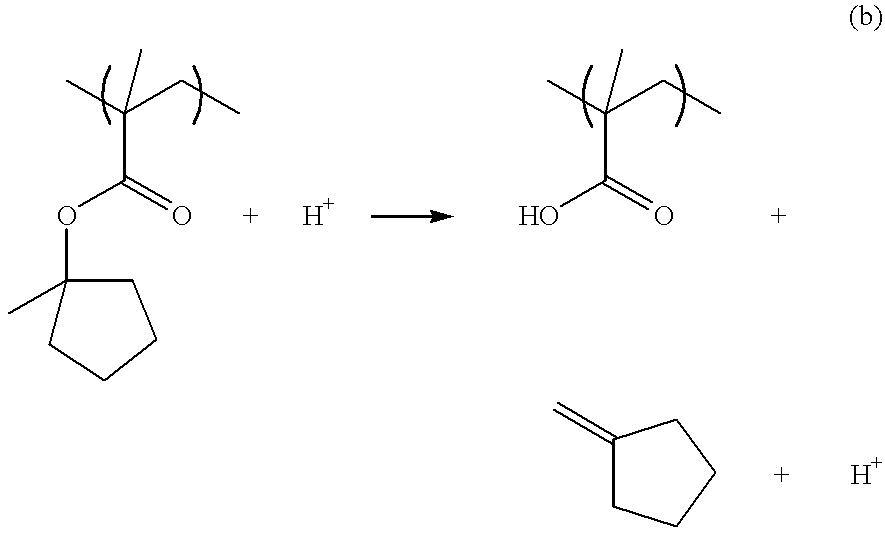
Chemically amplified positive resist composition
InactiveUS6869744B2Minimized change of sensitivityMinimize changesElectric discharge tubesPhotosensitive materialsResistCarboxylic group
A chemically amplified positive resist composition contains as a base a carboxyl or phenolic hydroxyl group-containing resin soluble in aqueous alkaline solution, in which acid labile groups are incorporated into at least some of the hydrogen atoms on the carboxyl or phenolic hydroxyl groups so that the resin becomes insoluble or substantially insoluble in alkali, wherein the resin contains acid labile groups of at least two types, acid labile groups of one type are acetal or ketal groups, and acid labile groups of the other type are tertiary hydrocarbon groups or tertiary hydrocarbon group-containing substituents. The resist composition remains stable during vacuum standing after exposure to electron beams or soft x-rays, leaves minimal footings on chromium substrates, has an excellent sensitivity and resolution, and is thus suited as a micropatterning material for use in the processing of mask substrates.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
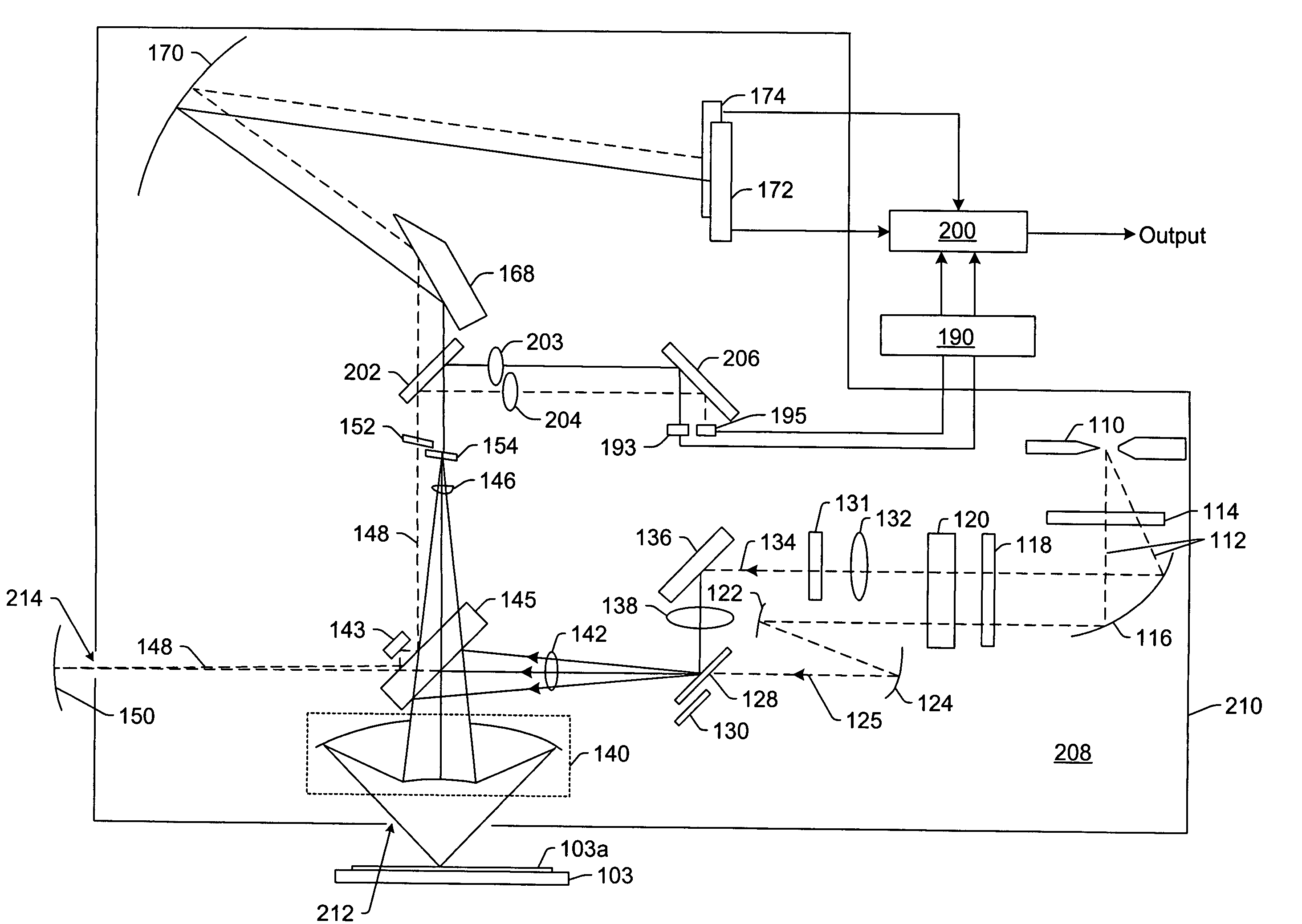
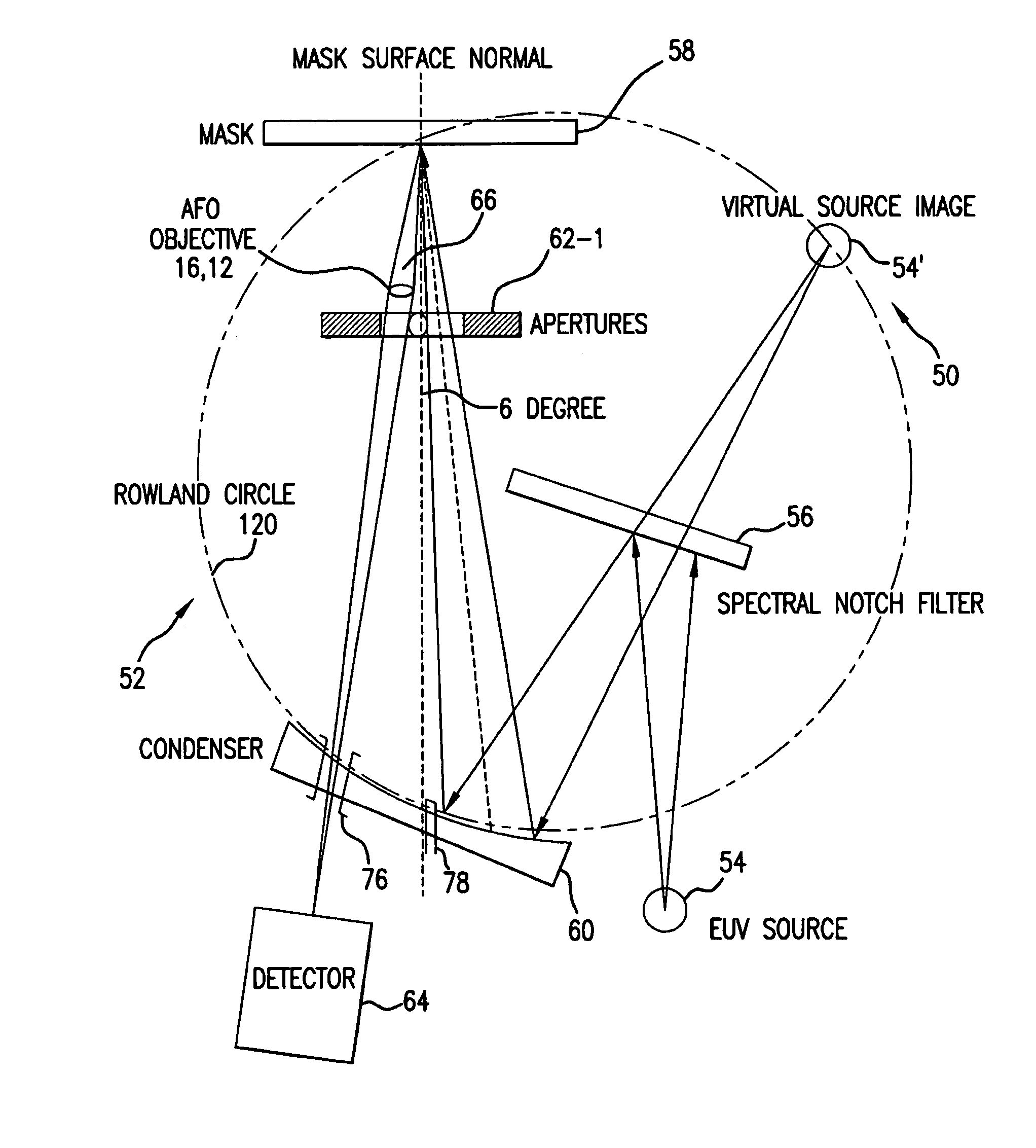
Short wavelength metrology imaging system
ActiveUS7268945B2Easy to implementEasy to switchImaging devicesNanoinformaticsHigh resolution imagingSystems design
An extreme ultraviolet (EUV) AIM tool for both the EUV actinic lithography and high-resolution imaging or inspection is described. This tool can be extended to lithography nodes beyond the 32 nanometer (nm) node covering other short wavelength radiation such as soft X-rays. The metrology tool is preferably based on an imaging optic referred to as an Achromatic Fresnel Optic (AFO). The AFO is a transmissive optic that includes a diffractive Fresnel zone plate lens component and a dispersion-correcting refractive lens component. It retains all of the imaging properties of a Fresnel zone plate lens, including a demonstrated resolution capability of better than 25 nanometers and freedom from image distortion. It overcomes the chromatic aberration of the Fresnel zone plate lens and has a larger usable spectral bandwidth. These optical properties and optical system designs enable the development of the AFO-based AIM tool with improved performance that has advantages compared with an AIM tool based on multilayer reflective mirror optics in both performance and cost.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
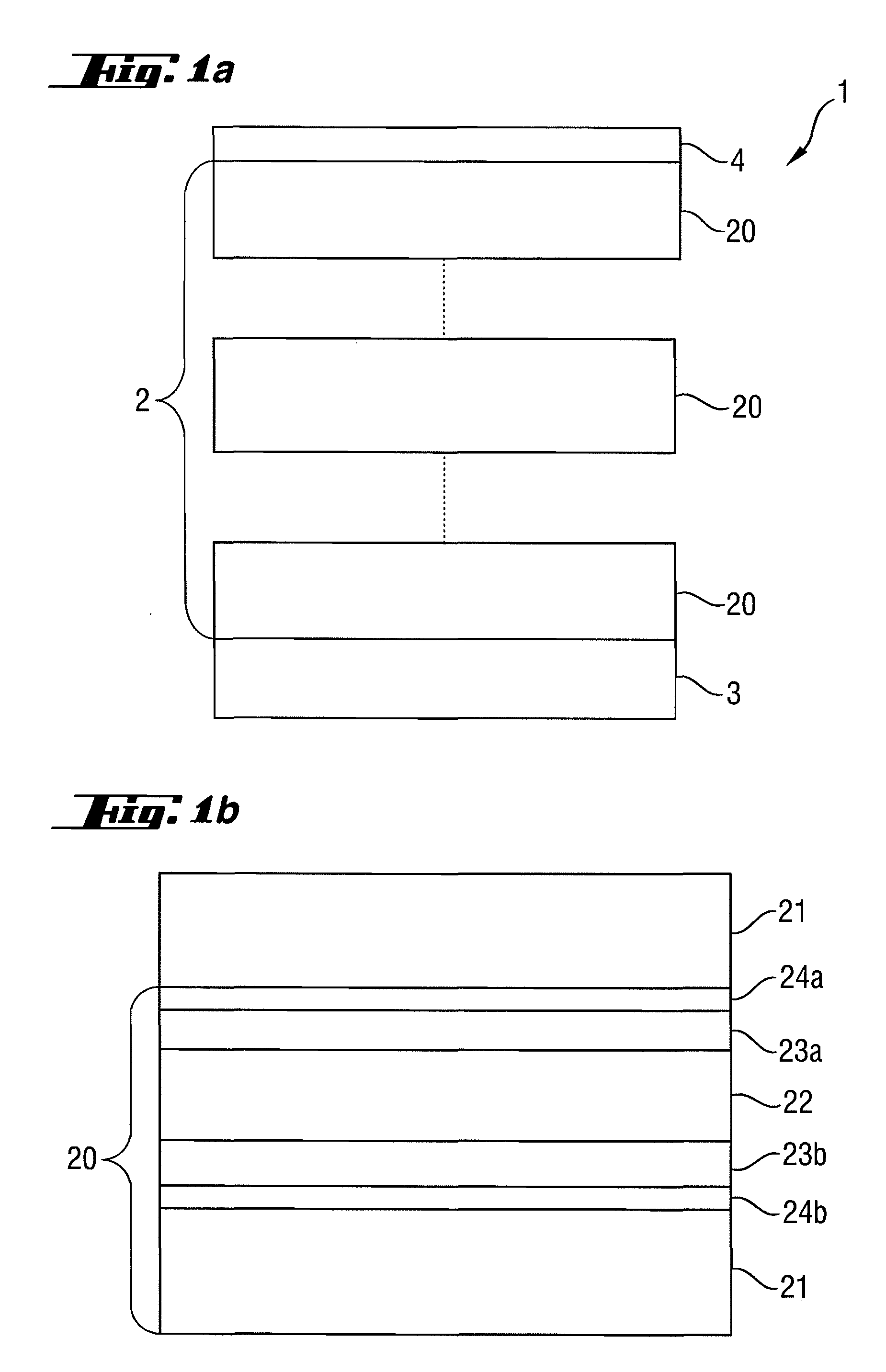
Reflective optical element for EUV lithography device
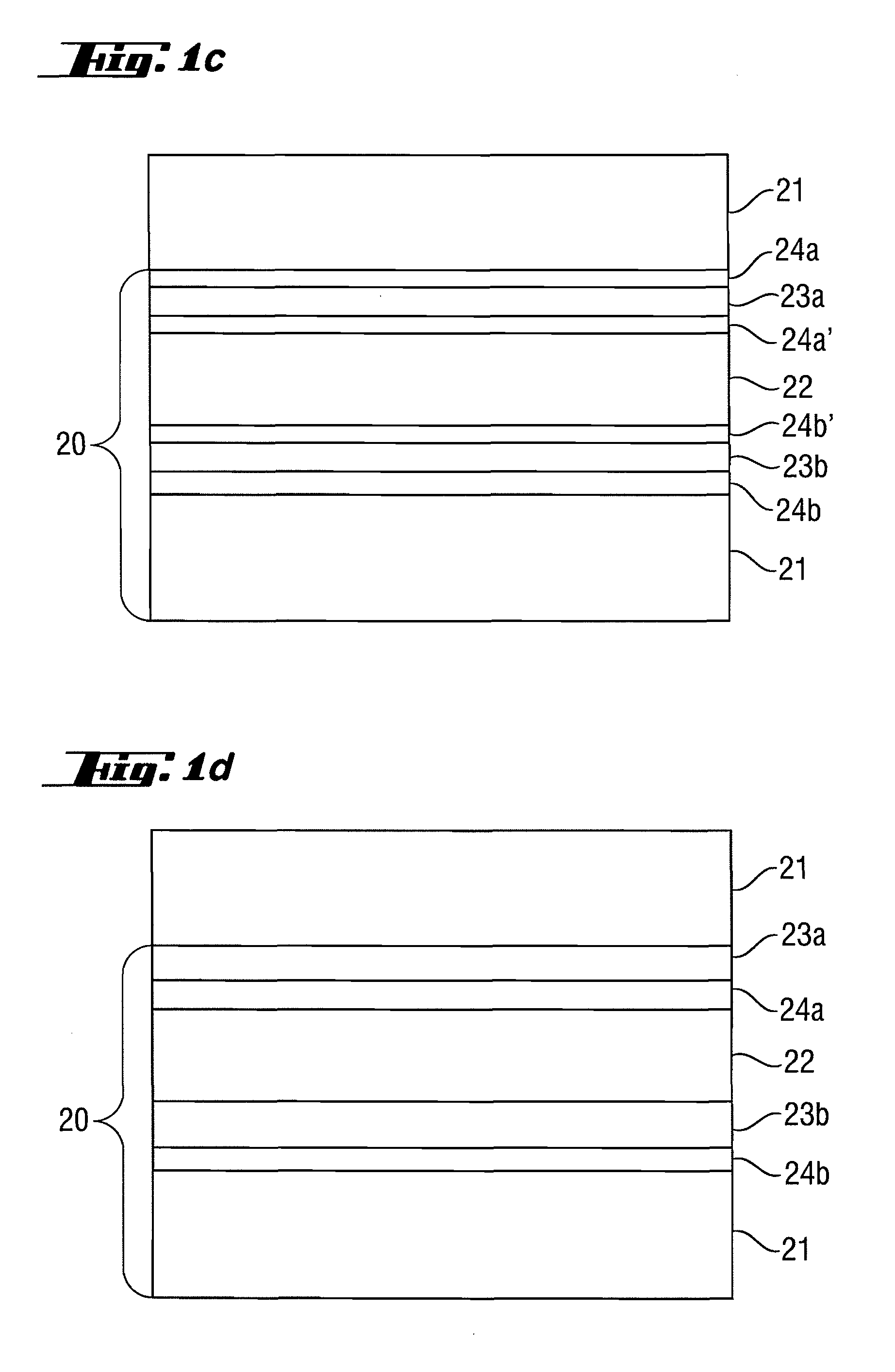
ActiveUS20100027107A1Improve reflectivityIncrease of maximum reflectivityMirrorsNanoinformaticsCatoptricsComputational physics
A reflective optical element exhibits an increase in the maximum reflectivity at operating wavelengths in the extreme ultraviolet or soft x-ray wavelength range. A first additional intermediate layer (23a, 23b) and a second additional intermediate layer (24a, 24b) are provided between the absorber layer (22) and the spacer layer (21), wherein the first additional intermediate layer increases the reflectivity and the second additional intermediate layer (24a,b) prevents chemical interaction between the first additional intermediate layer (23a,b) and the adjoining spacer layer (21) and / or the absorber layer (22).
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
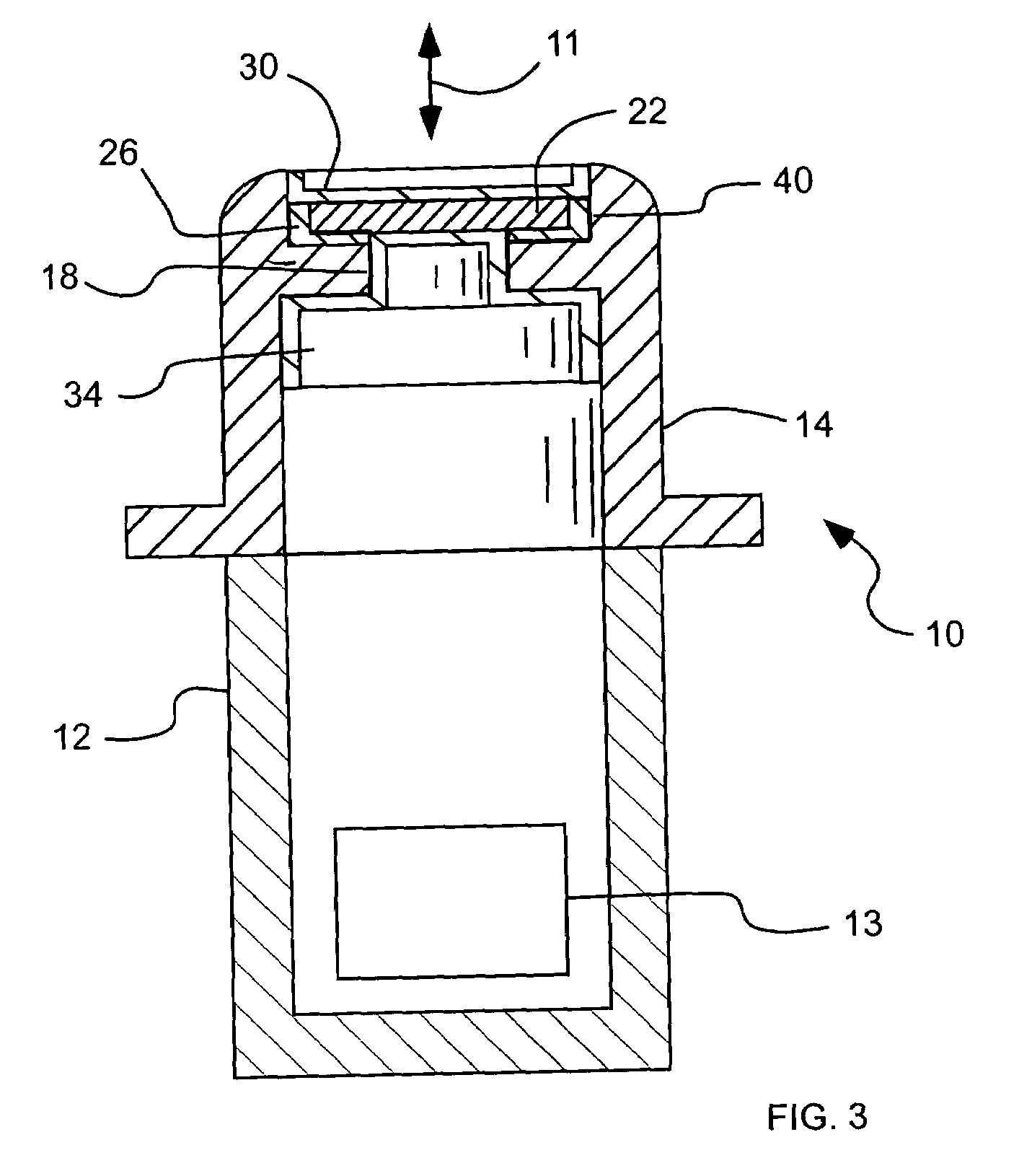
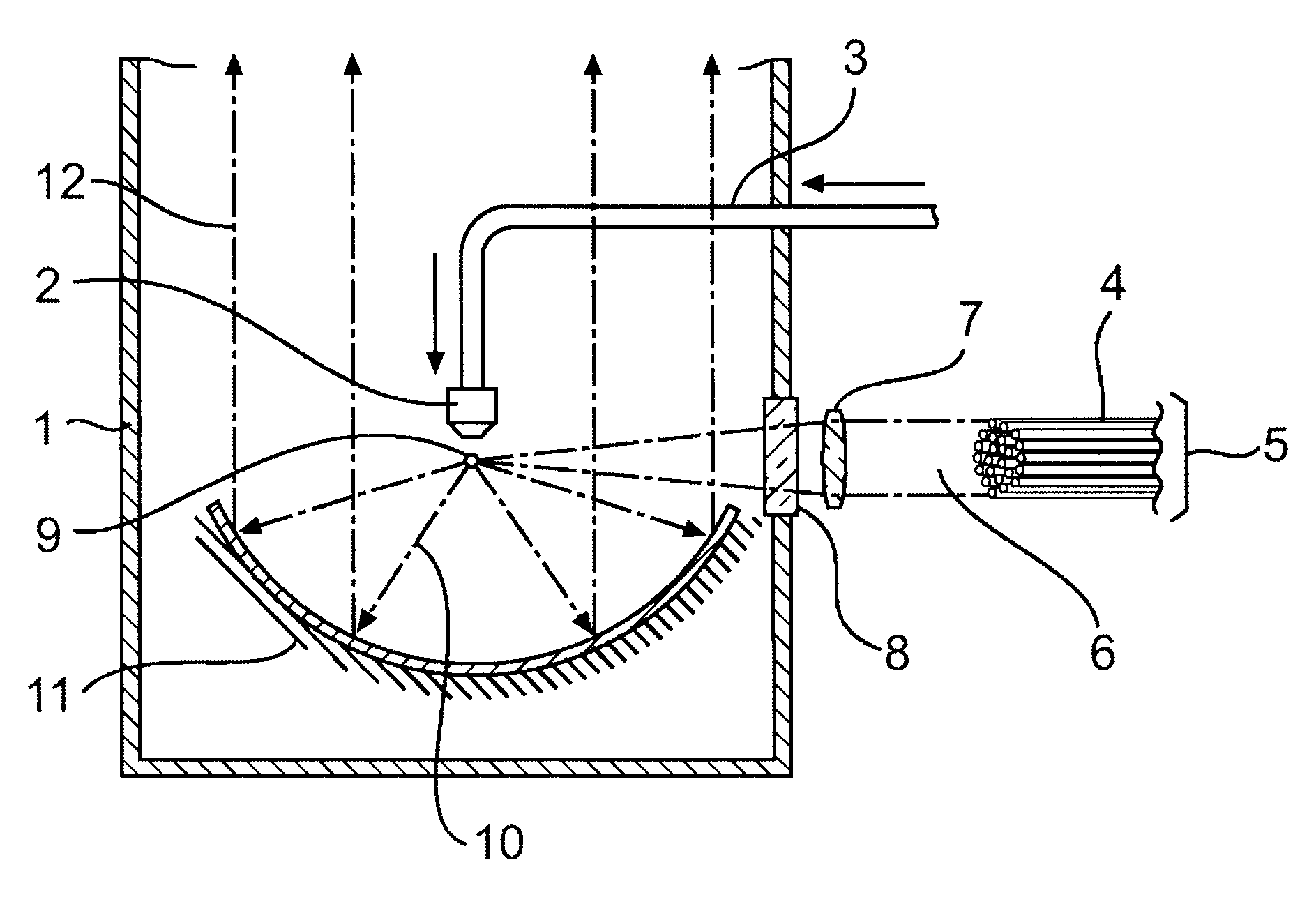
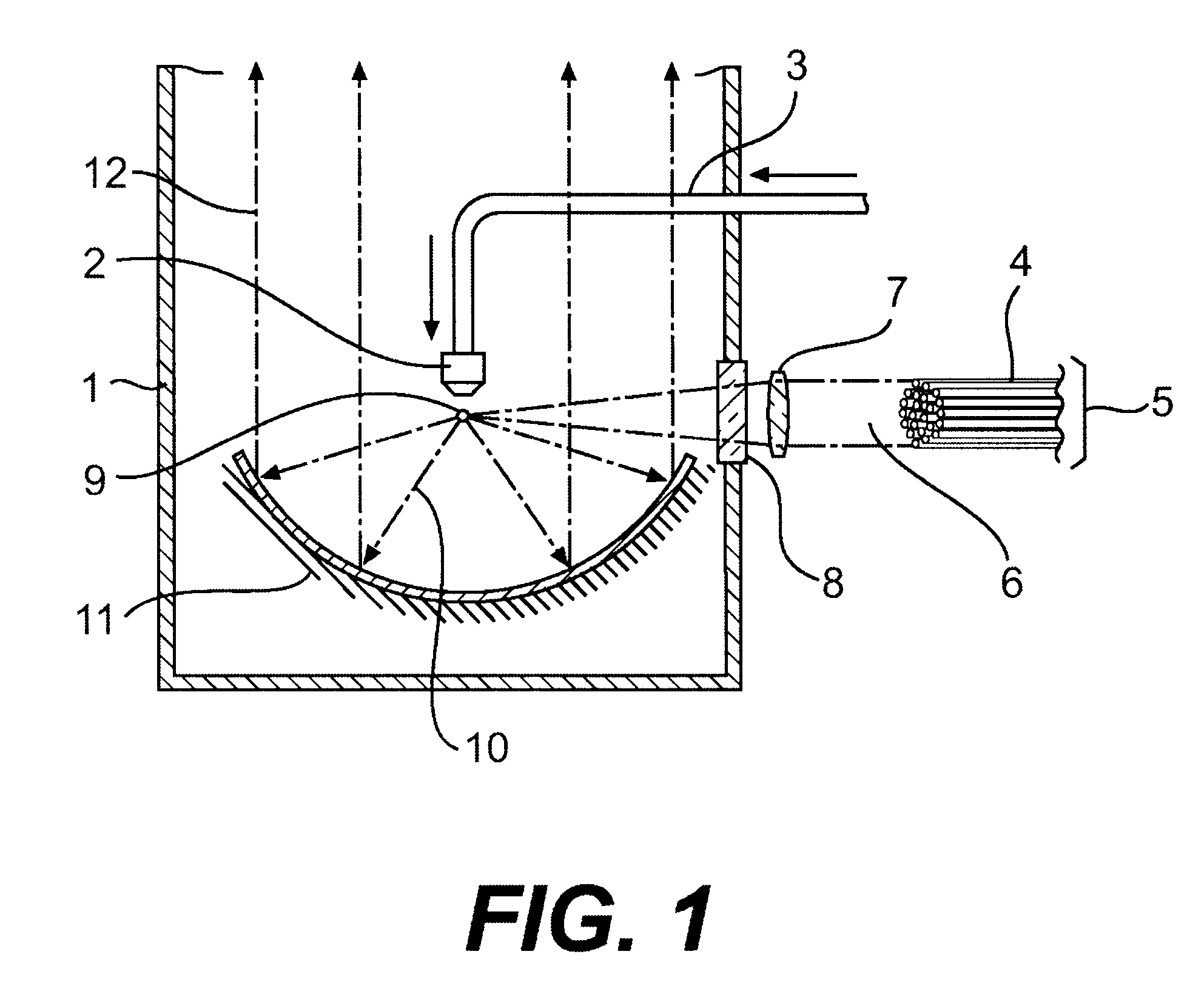
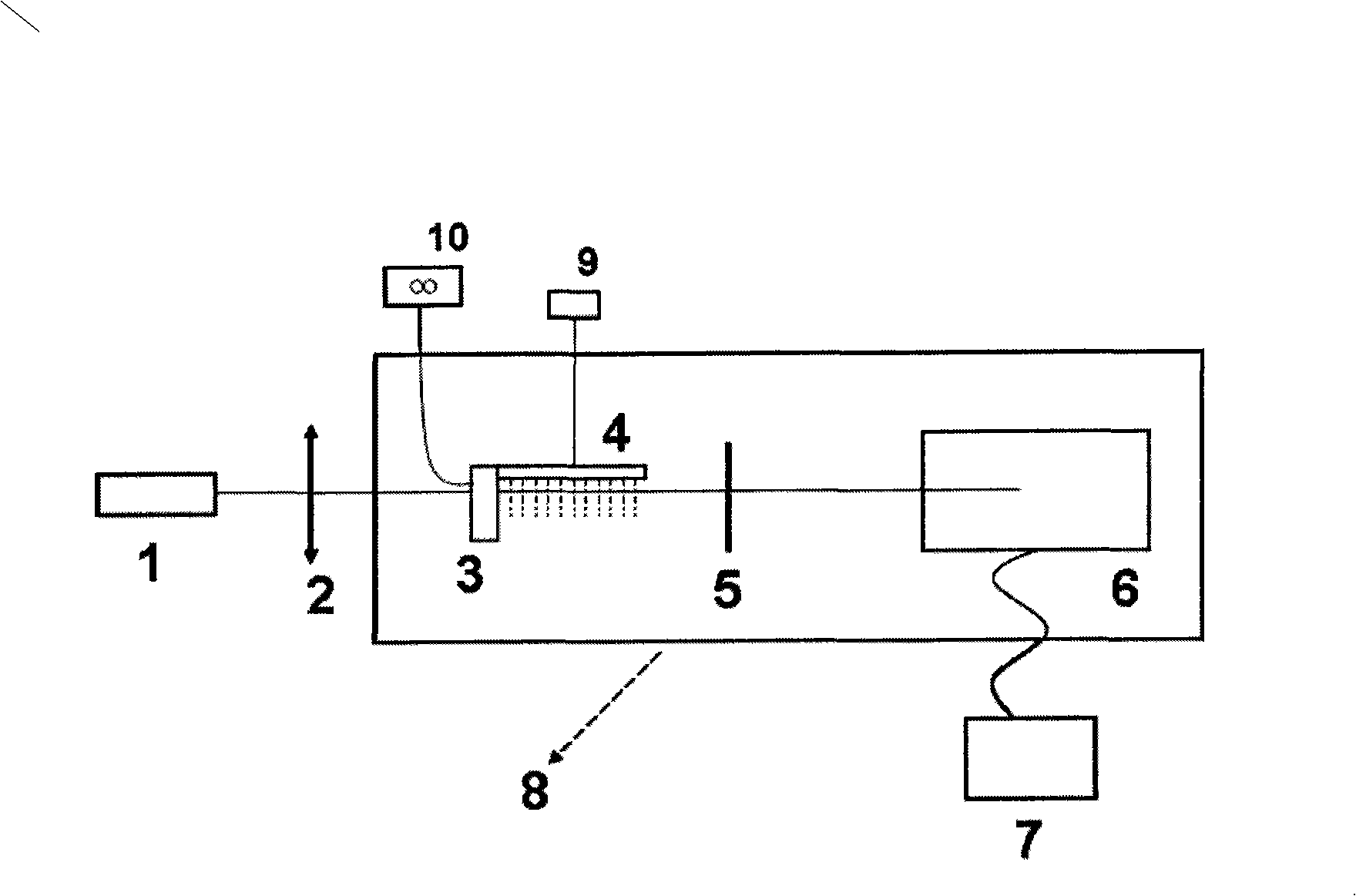
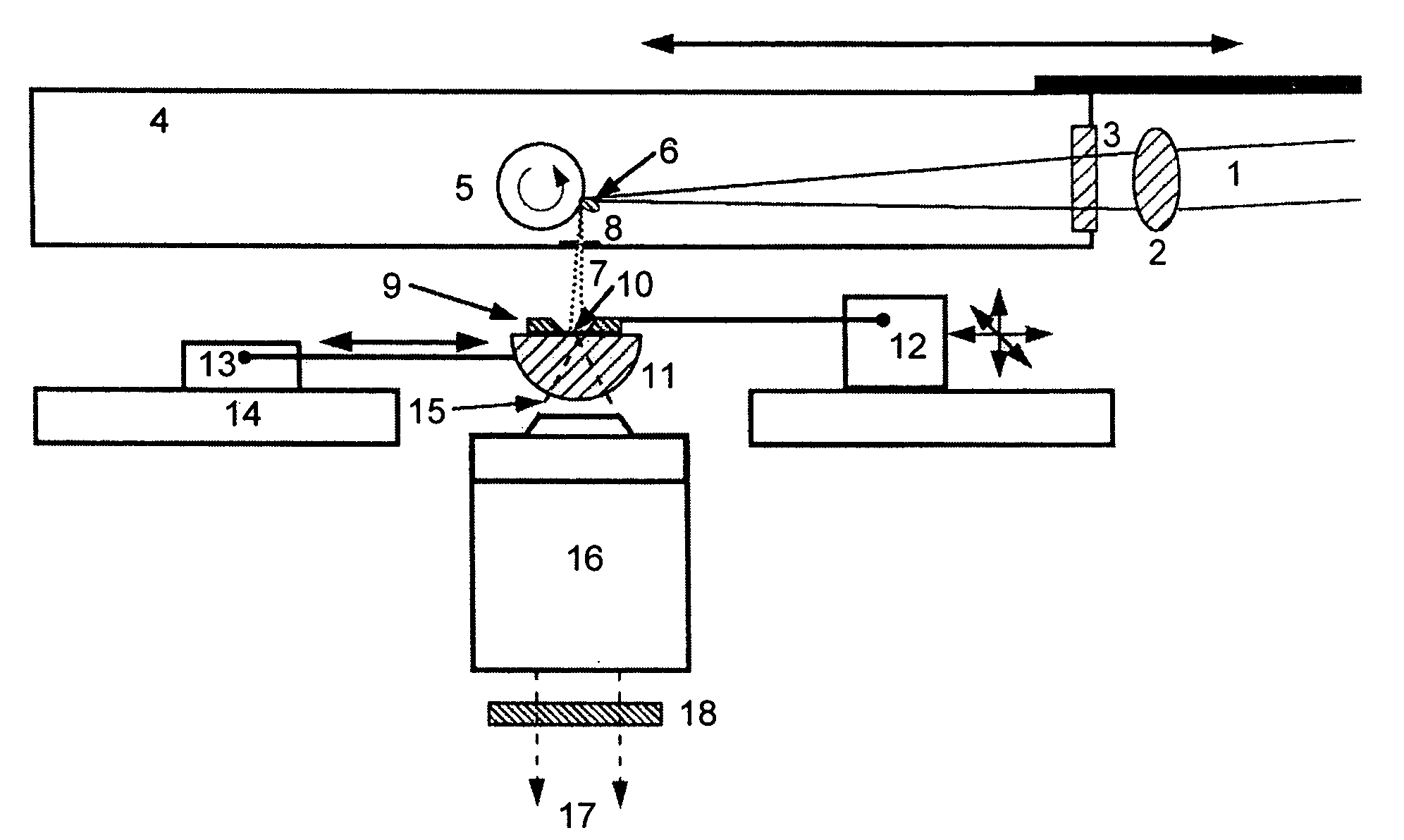
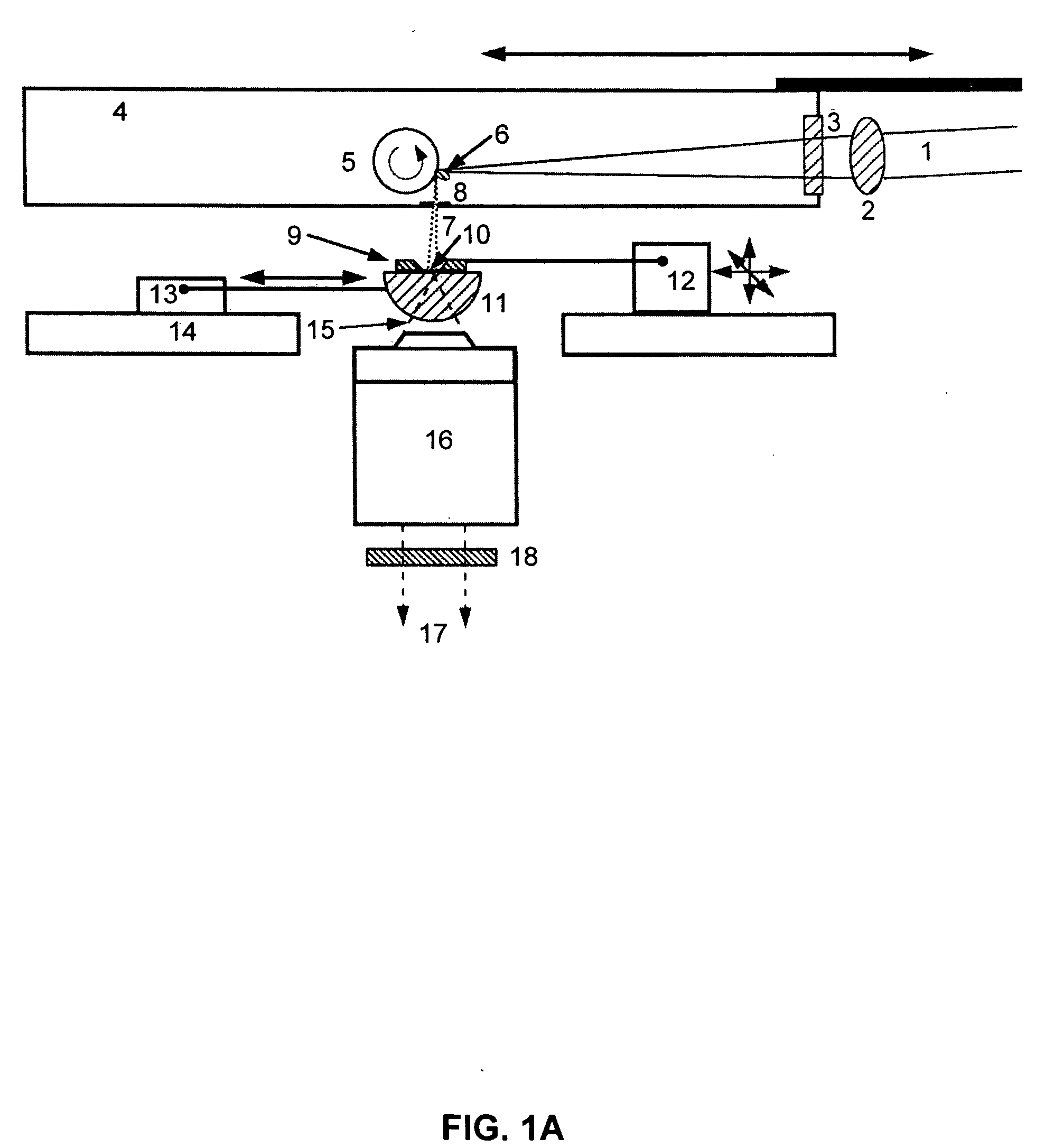
Soft x-ray light source device
A high-pressure krypton gas is supplied to the interior of a vessel from a gas introduction pipe. Light emitted from an optical fiber group formed by bundling together optical fibers constituting the output ends of fiber amplifiers or fiber lasers passes through a lens and exciting laser light introduction window, and is focused on the krypton gas jetting from the tip end of the nozzle. As a result, the krypton gas is excited as a plasma and soft X-rays are generated. The soft X-rays are reflected by a rotating multi-layer coat parabolic mirror and are emitted to the outside as a parallel beam of soft X-rays. Since light from fiber amplifiers is used as exciting light, and since numerous optical fibers are bundled together to form a light source, a large quantity of soft X-rays can easily be obtained.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Methods And Systems For Semiconductor Metrology Based On Polychromatic Soft X-Ray Diffraction
ActiveUS20190017946A1Increase measurement throughputSimultaneous measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMetrologyAngle of incidence
Methods and systems for performing measurements of semiconductor structures based on high-brightness, polychromatic, reflective small angle x-ray scatterometry (RSAXS) metrology are presented herein. RSAXS measurements are performed over a range of wavelengths, angles of incidence, and azimuth angles with small illumination beam spot size, simultaneously or sequentially. In some embodiments, RSAXS measurements are performed with x-ray radiation in the soft x-ray (SXR) region at grazing angles of incidence in the range of 5-20 degrees. In some embodiments, the x-ray illumination source size is 10 micrometers or less, and focusing optics project the source area onto a wafer with a demagnification factor of 0.2 or less, enabling an incident x-ray illumination spot size of less than two micrometers. In another aspect, active focusing optics project programmed ranges of illumination wavelengths, angles of incidence, and azimuth angles, or any combination thereof, onto a metrology area, either simultaneously or sequentially.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Internal and external quality inspecting method and device for agricultural products
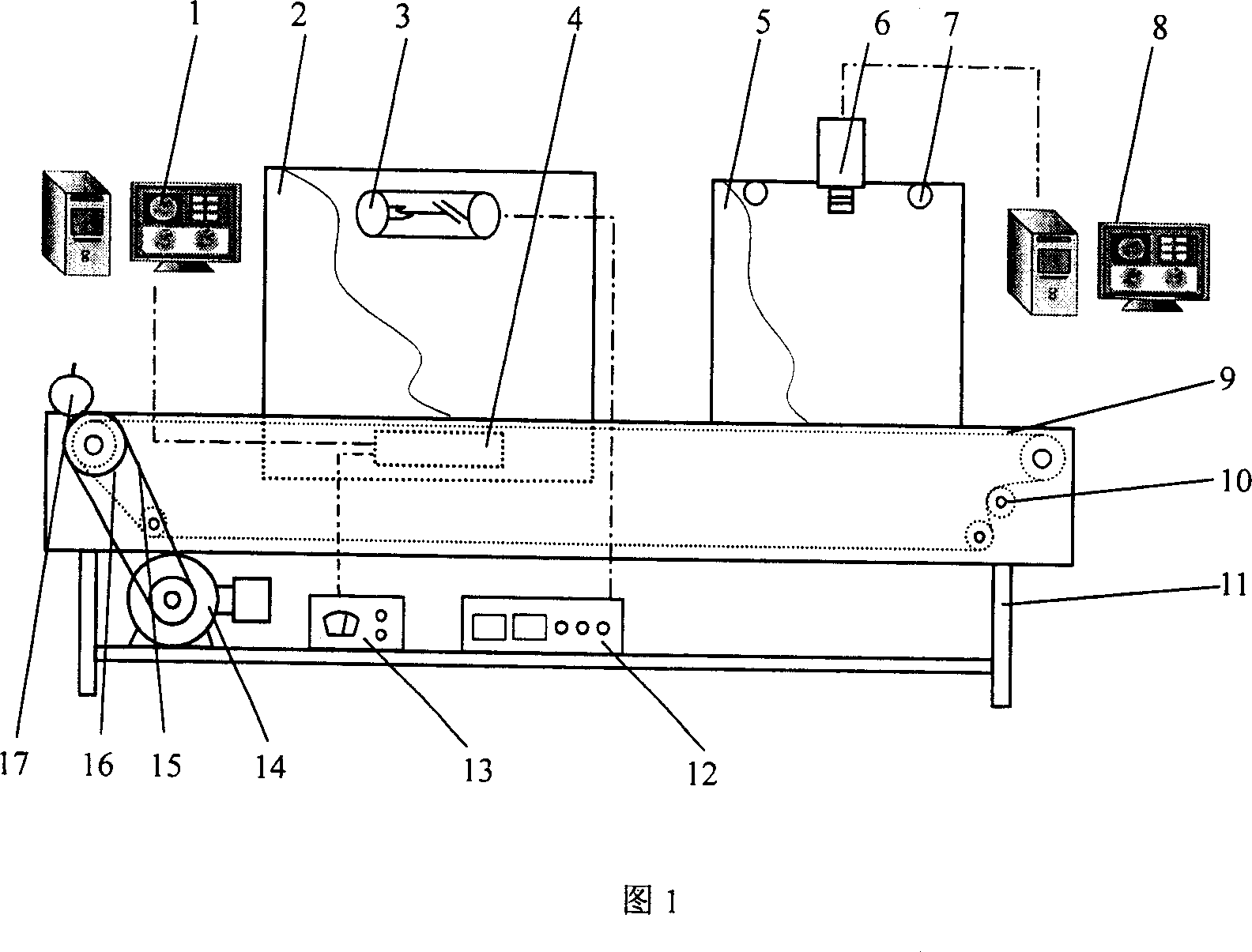
InactiveCN1940555ARealize online detectionOvercome the bottleneck of undetectable internal qualityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by optical meansColor imageSoft x ray
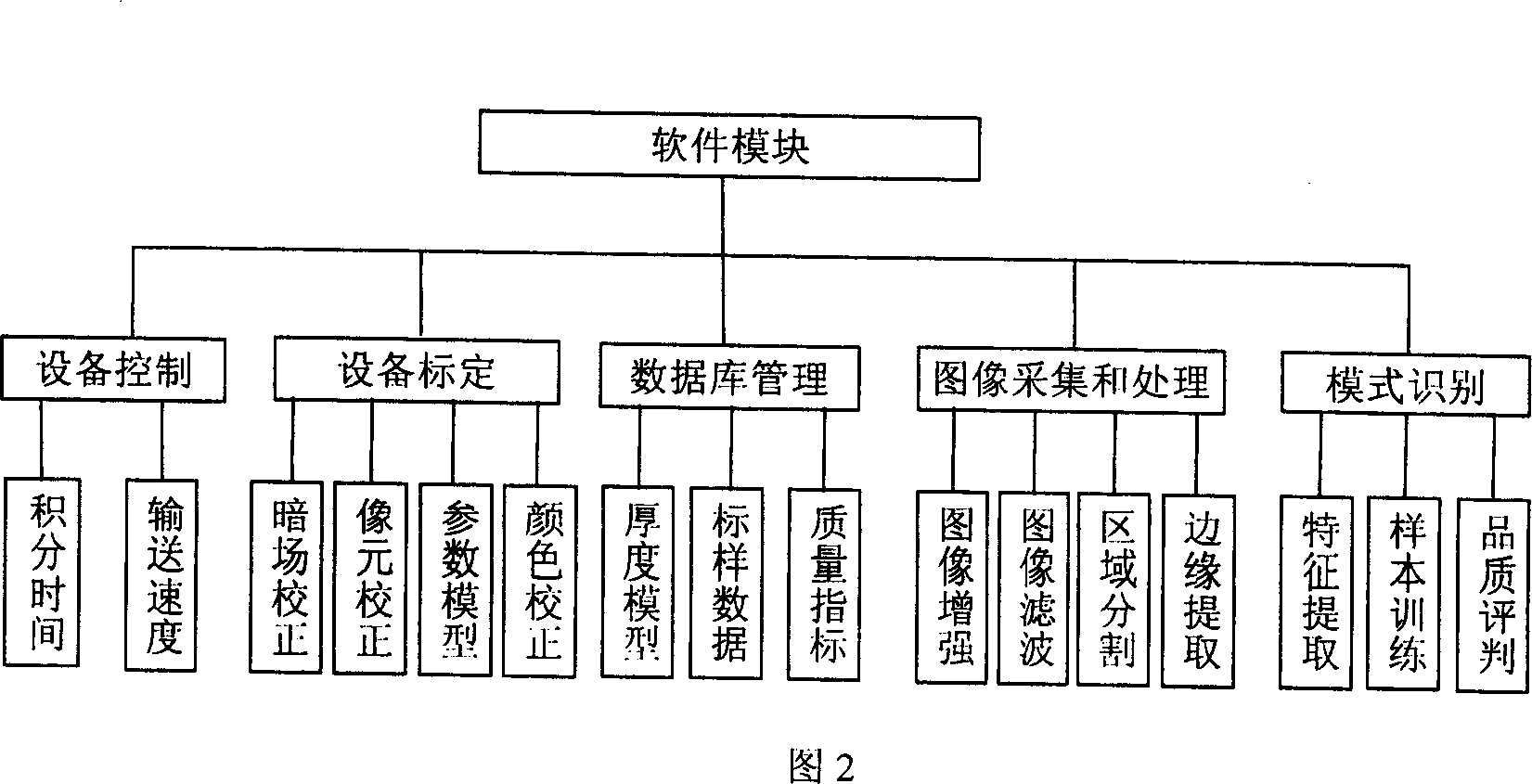
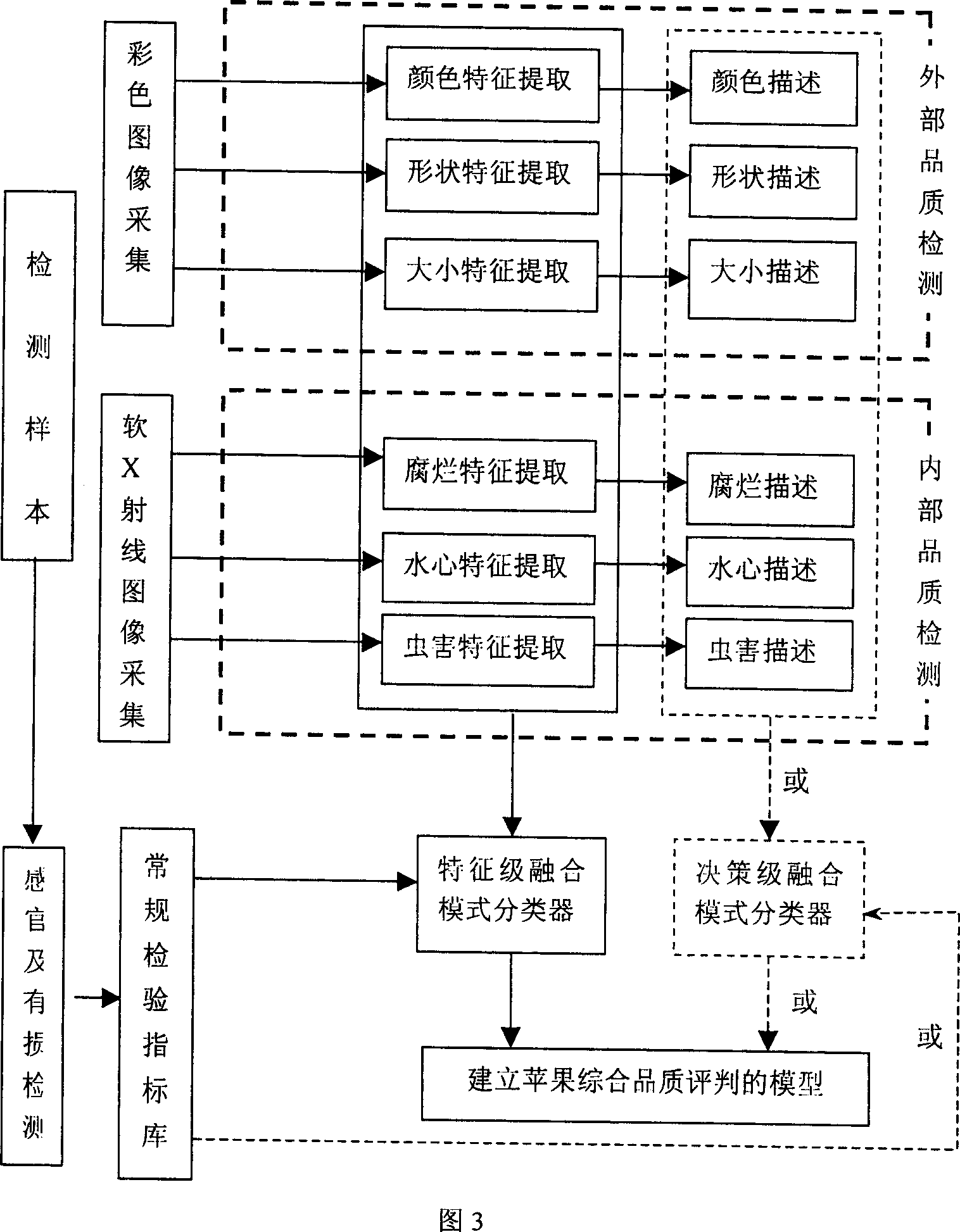
A device used for detecting internal and external quality of agricultural products consists hardware unit including material conveying unit, soft x-ray emission and detection unit, color picture collection unit and computer system; software system including device control, device calibration, sample databank, image collection-treatment and mode identification. It is featured as utilizing soft x-ray image technique and color image collection system to separately obtain x-ray image and external character information of agricultural products.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method For Manufacturing Reflective Optical Element, Reflective Optical Elements, Euv-Lithography Apparatus And Methods For Operating Optical Elements And Euv-Lithography Apparatus, Methods For Determining The Phase Shift, Methods For Determining The Layer Thickness, And Apparatuses For Carrying Out The Methods
InactiveUS20070285643A1Large intensityPhotomechanical apparatusUsing optical meansCatoptricsLayer thickness
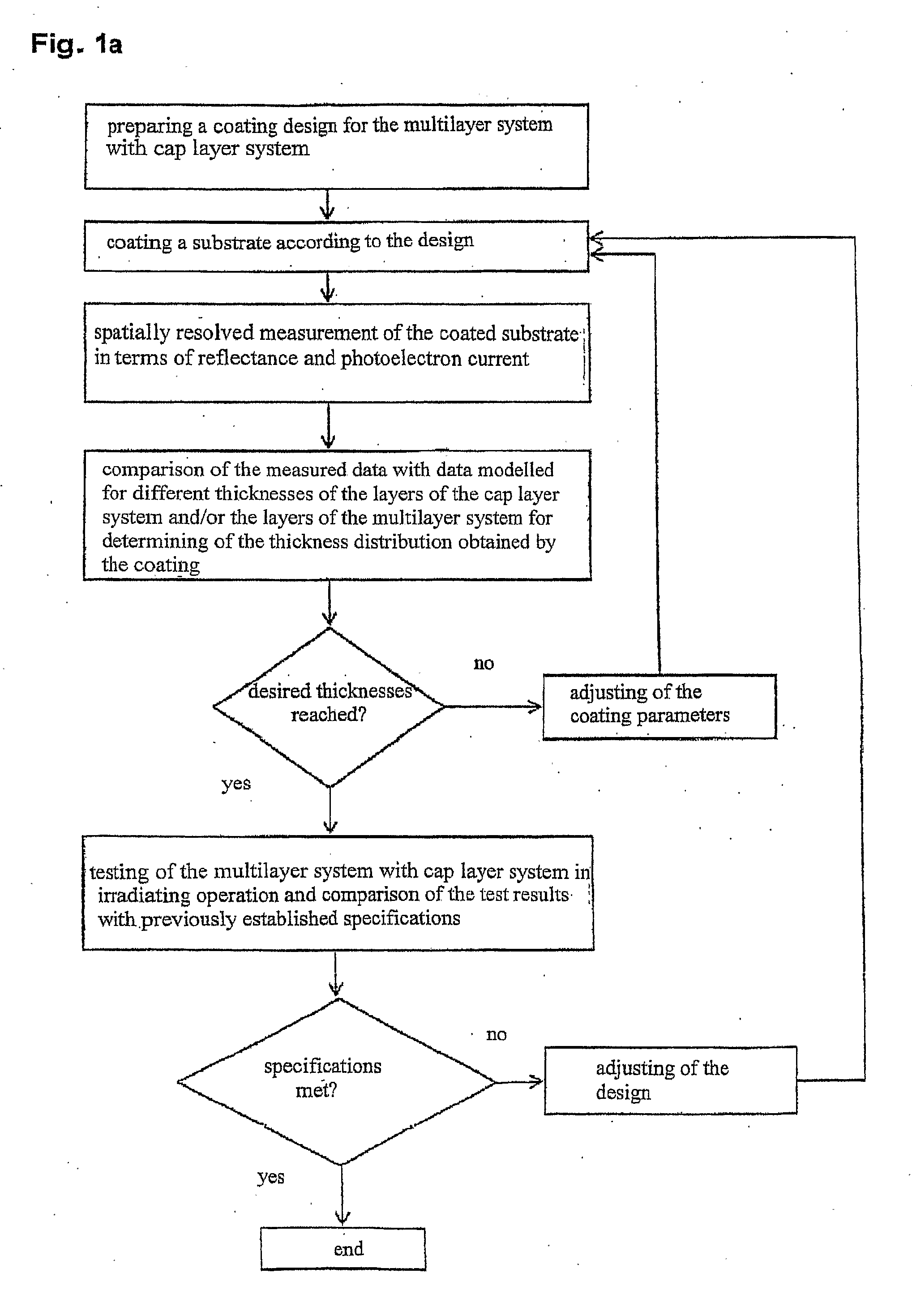
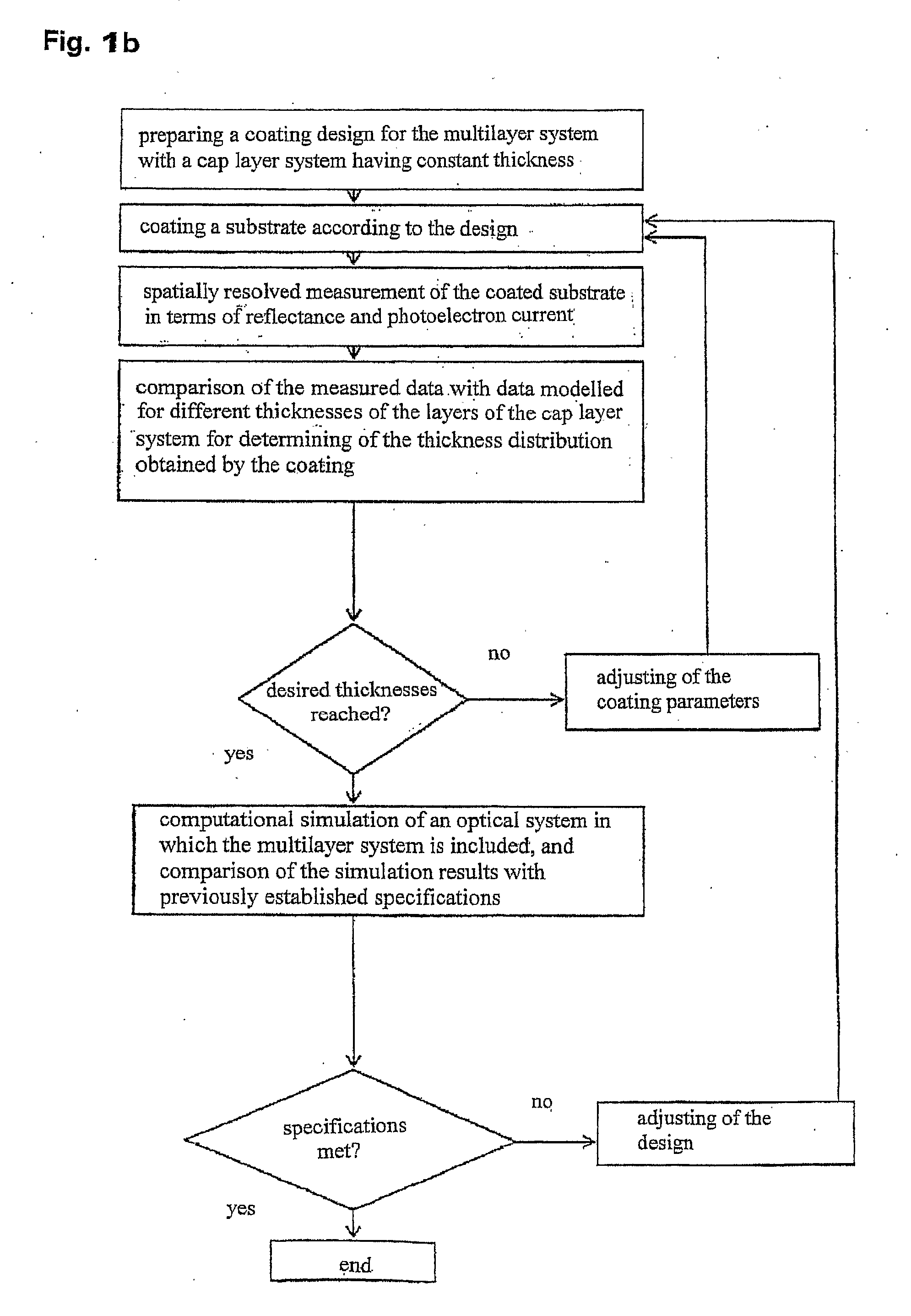
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing of a multilayer system (25) with a cap layer system (30), in particular for a reflective optical element for the extreme ultraviolet up to the soft x-ray wavelength range, comprising the steps of: 1. preparing a coating design for the multilayer system (25) with cap layer system (30); 2. coating a substrate (20) with the multilayer system (25) with cap layer system (30); 3. spatially resolved measurement of the coated substrate in terms of reflectance and photoelectron current in at least one surface point; 4. comparison of the measured data with data modelled for different thicknesses of the layers (31, 32, 33) of the cap layer system (30) and / or the layers (21, 22, 23, 24) of the multilayer system (25) for determining of the thickness distribution obtained by the coating; 5. if necessary, adjusting of the coating parameters and repeating steps 2 to 5 until the coated thickness distribution coincides with the design. The invention also relates to further manufacturing methods, reflective optical elements, EUV-lithography apparatuses, and methods for operating optical elements and EUV-lithography apparatuses as well as methods for determining the phase shift, methods for determining the layer thickness, and apparatuses for carrying out the methods.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
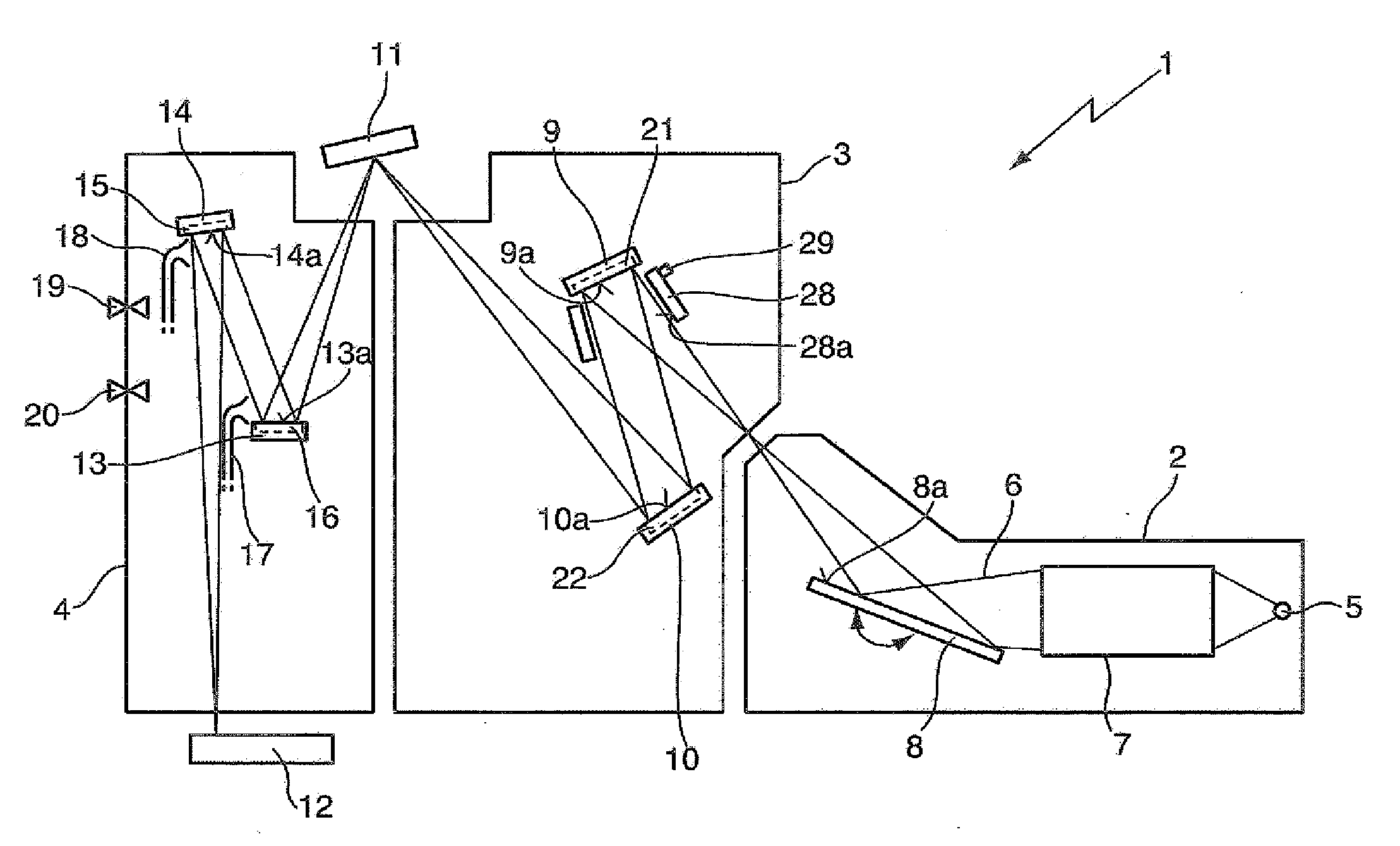
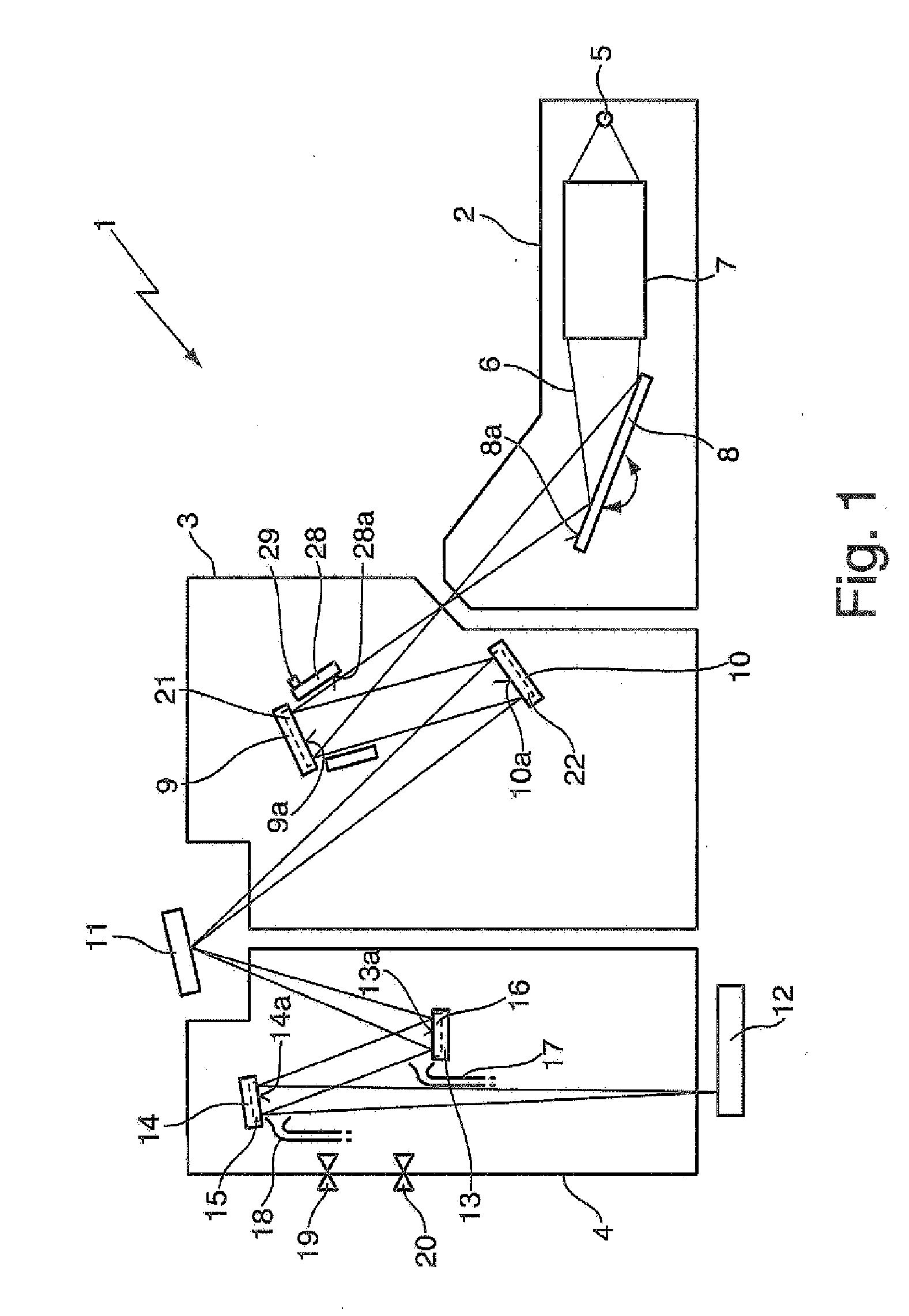
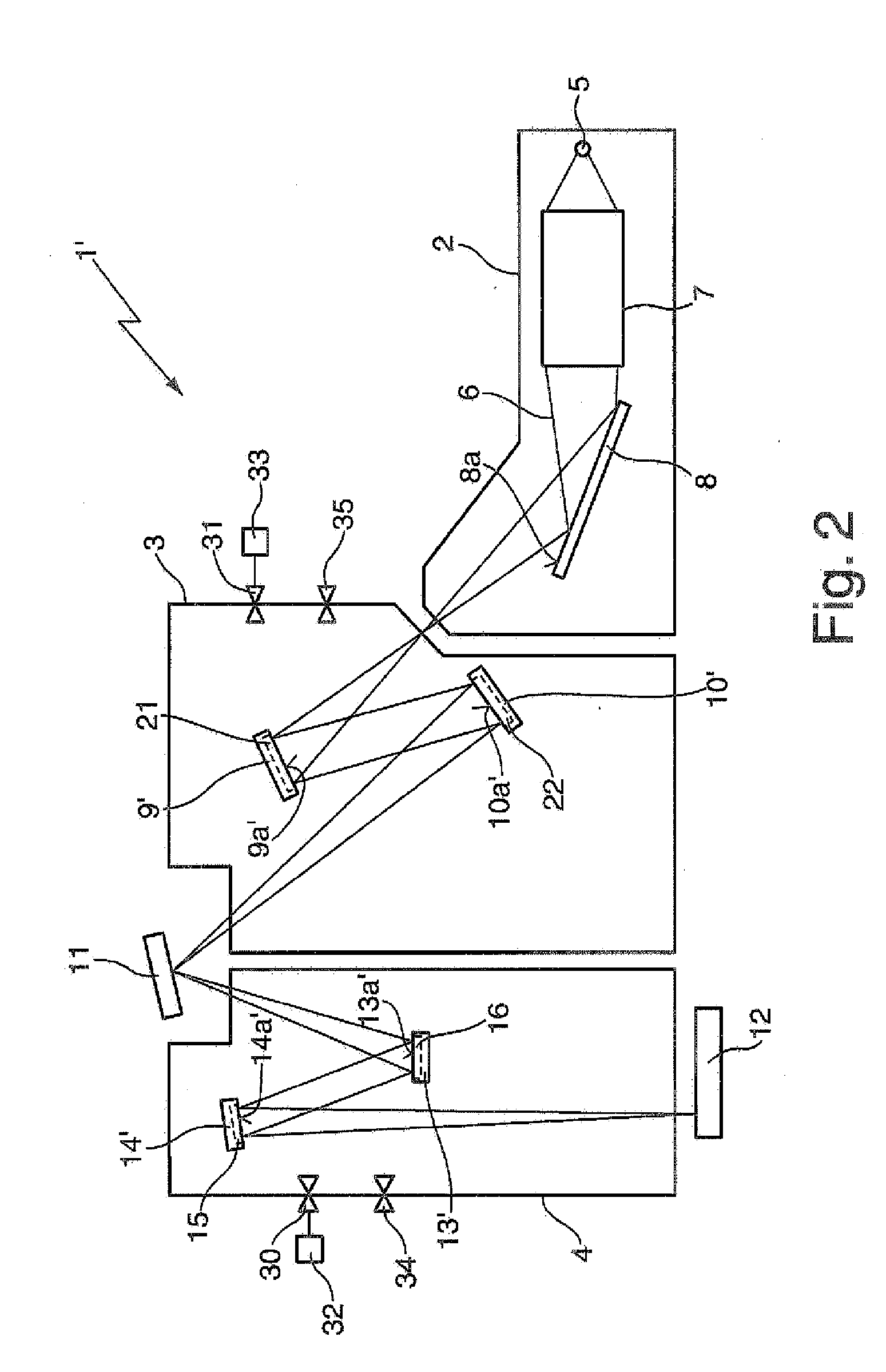
Optical arrangement and EUV lithography device with at least one heated optical element, operating methods, and methods for cleaning as well as for providing an optical element
InactiveUS20080143981A1Improve optical characteristic of optical and of opticalAvoid optical distortionMirrorsRadiation/particle handlingCatoptricsProjection system
An optical arrangement, in particular a projection system, illumination system or beam shaping system for EUV lithography, including at least one optical element that is arranged in a beam path of the optical arrangement and that reflects radiation in the soft X-ray- or EUV wavelength range, wherein at least during operation of the optical arrangement at least one of, preferably each of, the reflective optical elements in the beam path, at least at the optical surface, has an operating temperature of approximately 30° C. or more, preferably of approximately 100° C. or more, particularly preferably of approximately 150° C. or more, and even more preferably of approximately 250° C. or more, and wherein the optical design of the at least one reflective optical element is selected such that its optical characteristics are optimised for operation at the operating temperature. Also presented is a method for providing a reflective optical element with such an optical design.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH +1
Radiation window and method of manufacture
A radiation window device to transmit radiation as part of an x-ray source or detector includes a support to be subject to a substantial vacuum, and an opening configured to transmit radiation. A film is mounted directly on the support across the opening, and has a material and a thickness selected to transmit soft x-rays. An adhesive directly adheres the film to the support. A coating covers exposed portions of at least one of the evacuated or ambient sides of the film, and covers a portion of the support surrounding the film. The support, film and adhesive form a vacuum tight assembly capable of maintaining the substantial vacuum when one side is subject to the substantial vacuum. In addition, the vacuum tight assembly can withstand a temperature of greater than approximately 250 degrees Celsius.
Owner:MOXTEK INC
Self-supporting transmission metal grating based on nanometer stamping technology and its preparation method
InactiveCN101261331ASimple processLow costPhotomechanical apparatusDiffraction gratingsMetallic materialsReactive-ion etching
The invention relates to a high-intensity, self-supporting transmission metal grating which is made based on nanometer imprinting technique, and is used for diffraction of deep ultraviolet ray, soft X ray and material particle; the line density of the metal grating is larger than 2000 bars per millimeter, the grating is not supported by any substrate, a gap between the metal lines of the grating is hollow, the metal lines are supported by metal network structure with enough intensity and relatively larger cycle (1 to 40 micrometer), the metal material of the grating is made by gold. The manufacturing steps: (1) high density metal grating is prepared on the substrate through nanometer imprinting technique, reactive ion etching technique and electrochemical filming technique; (2) metallic network supporting structure with major cycle is prepared through photo-etching technique and electrochemical filming technique; (3) the substrate is removed by a chemical etching method to lead the grating to be hollow; (4) focused ion beam technology is used for repairing local defects generated during the manufacturing process of the transmission grating. The metal grating of the invention has the advantages that the manufacture method for the nanometer imprinting technique preparation grating structure is convenient and reliable, which greatly reduces the manufacture cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Window membrane for detector and analyser devices, and a method for manufacturing a window membrane
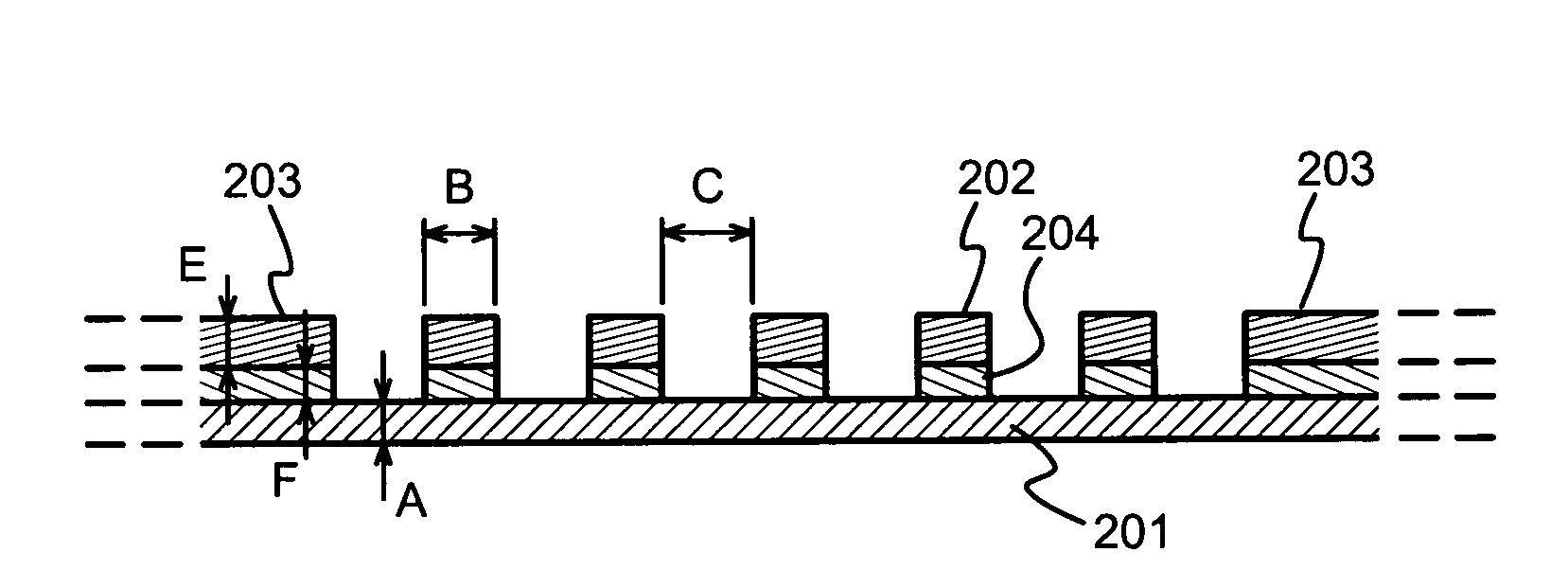
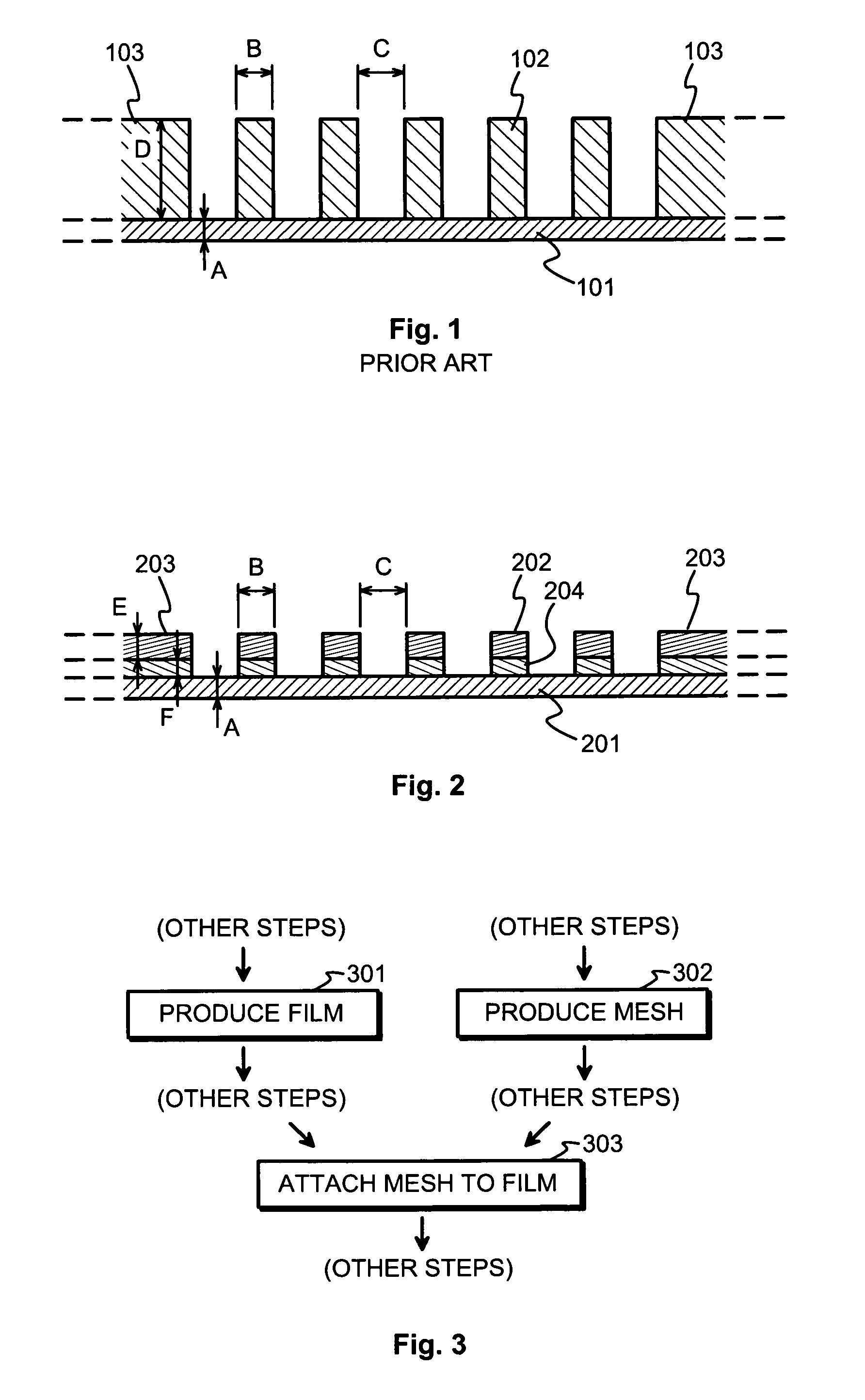
InactiveUS20070111617A1Advantageous mechanical characteristicLower unit costLiquid surface applicatorsWarp knittingSoft x rayEngineering
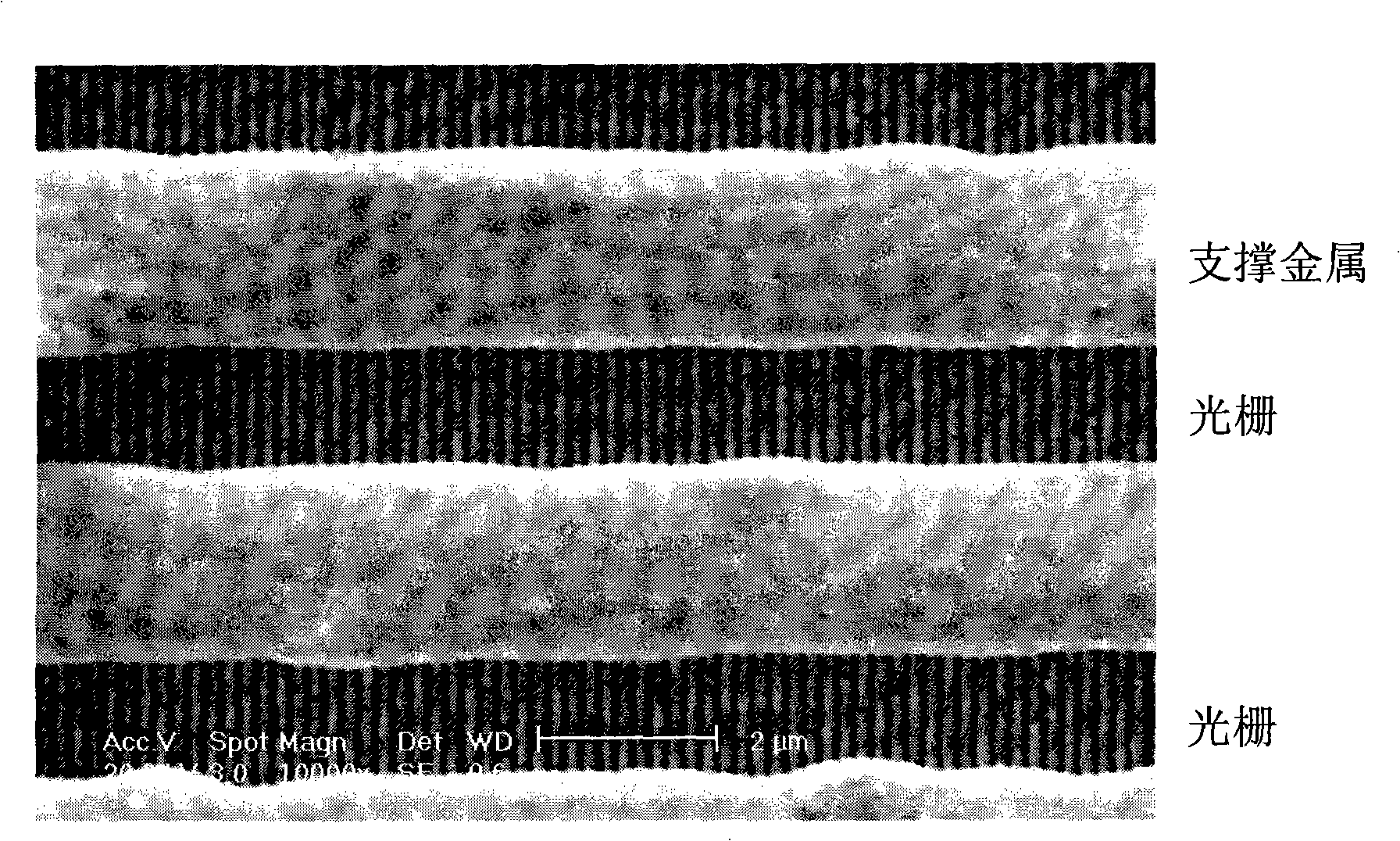
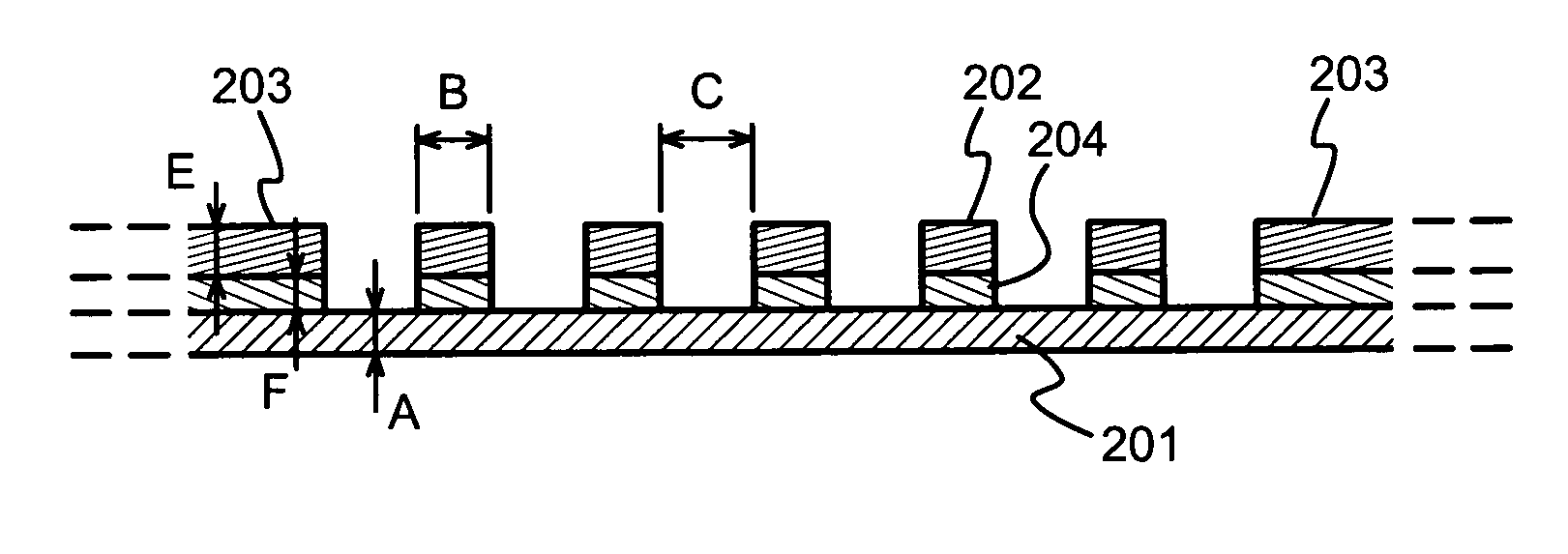
A window membrane is permeable to electromagnetic radiation, especially soft X-rays. It comprises a film (201) and a metallic reinforcement mesh (202) attached to the film (201). A preferable way of attaching the metallic reinforcement mesh (202) to the film is to use a positive-working photosensitive glue (204) and allow the reinforcement mesh (202) to act as the exposure mask.
Owner:OXFORD INSTUMENTS ANALYTICAL LIMITED
Systems and methods for measurement or analysis of a specimen using separated spectral peaks in light
ActiveUS20050253080A1Improve accuracyMaintain calibrationRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSoft x rayProgram instruction
A system configured for measurement of a specimen is provided. The system includes an optical subsystem configured to perform measurements of the specimen. The optical subsystem includes a light source that is configured to generate light having a relatively large number of separated spectral peaks with substantially no continuous background. In some embodiments, the light may include vacuum ultraviolet light, extreme ultraviolet light, and / or soft x-rays. A carrier medium is also provided that includes program instructions executable on a computer system to analyze data generated by a detector of an optical subsystem by partitioning the data into individual peaks spaced apart across a wavelength spectrum. Partitioning the data preferably corrects for spectrum shift, drift, stretching, shrinking, or a combination thereof at the detector. The individual peaks correspond to separated spectral peaks in light generated by a light source of the optical subsystem.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
A method for pattern recognition of cancer cells using soft x-ray microscopic imaging
InactiveCN102297873APreparing sample for investigationBiological neural network modelsMicroscopic imageSoft x ray
This invention discloses a method for utilizing soft X-ray microimaging for cancer cell image recognition. The method comprises the steps of 1) sample preparation; 2) pathological examination; 3) soft X-ray imaging; and 4) analysis and recognition. This invention applies soft X-ray microimaging for cancer cell image recognition, successfully obtains the soft X-ray microscopic image of a cancer cell by scanning the cancer cell with synchrotron radiation soft X-ray microimaging, provides recognition steps and experimental data, and establishes a method for utilizing soft X-ray microimaging for cancer cell image recognition. This invention creates a method for analyzing soft X-ray microscopic images, provides a novel synchrotron radiation soft X-ray pathological diagnosis method for cancer diagnosis, and provides an extremely valuable basis for the creation and clinical application of soft X-ray pathology in the 21st century.
Owner:NO 128 HOSPITAL OF HANGZHOU
Arrangement for the generation of intensive short-wave radiation based on a plasma
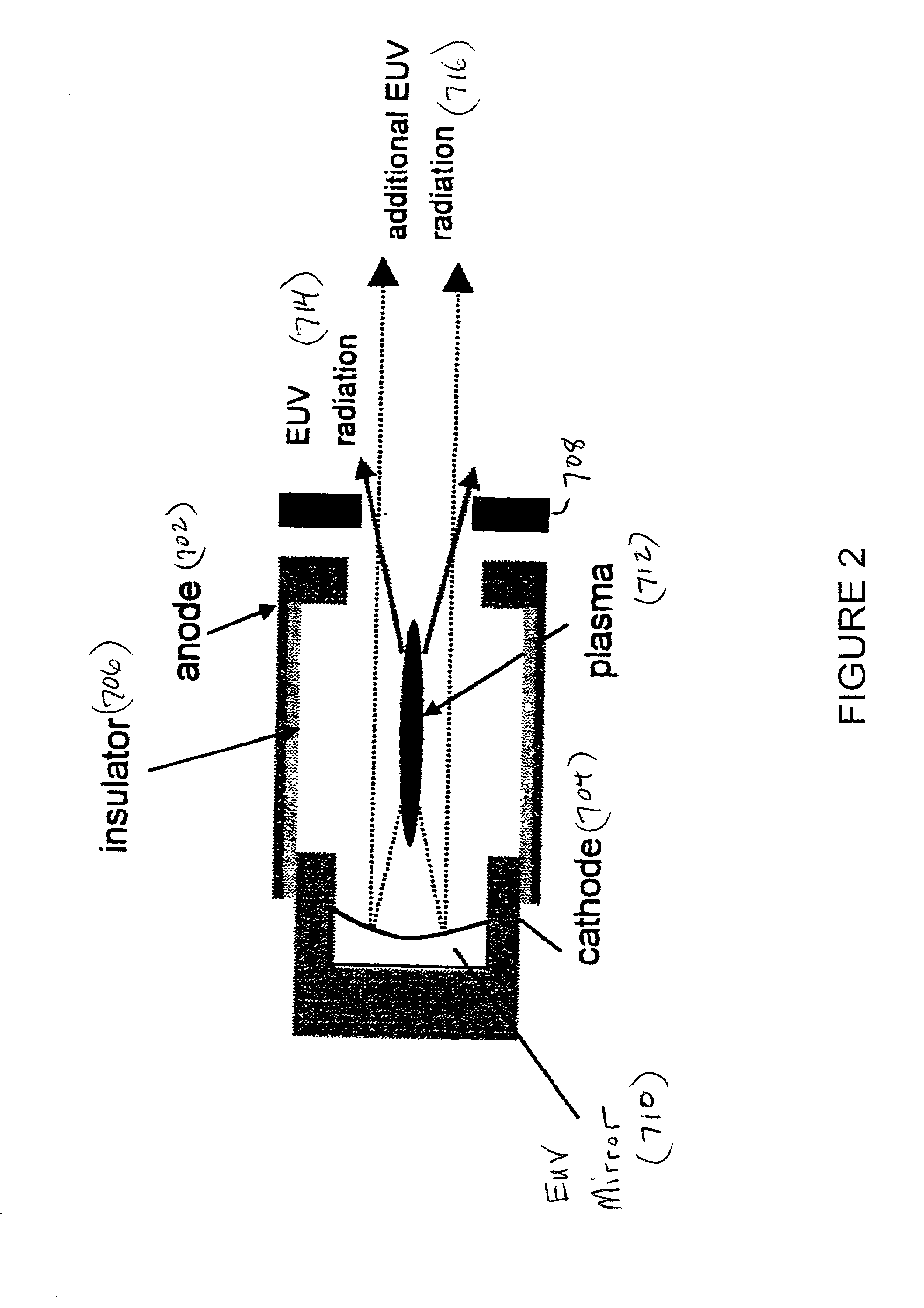
InactiveUS6995382B2Increased radiation outputHigh outputRadiation pyrometryRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayPulse energy
The invention is directed to an arrangement for generating intensive radiation based on a plasma, particularly short-wavelength radiation from soft x-ray radiation to extreme ultraviolet (EUV) radiation. The object of the invention is to find a novel possibility for generating radiation generated from plasma in which the individual pulse energy coupled into the plasma and, therefore, the usable radiation output are appreciably increased while retaining the advantages of mass-limited targets. According to the invention, this object is met in that the target generator has a multiple-channel nozzle with a plurality of separate orifices, wherein the orifices generate a plurality of target jets, the excitation radiation for generating plasma being directed simultaneously portion by portion to the target jets.
Owner:XTREME TECH
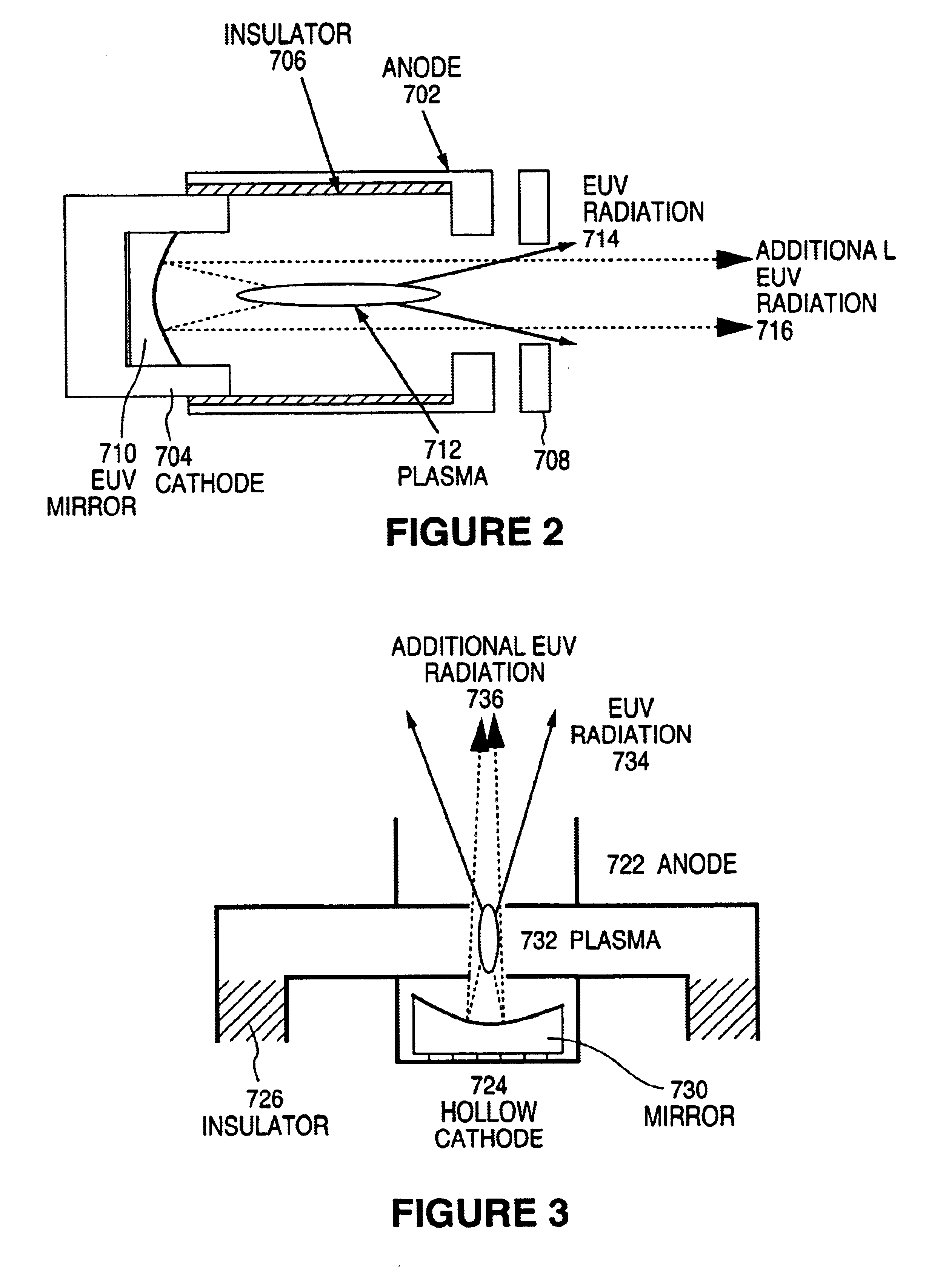
High-luminosity EUV-source devices for use in extreme ultraviolet (soft X-ray) lithography systems and other EUV optical systems
InactiveUS6861656B2NanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSoft x rayPoint light
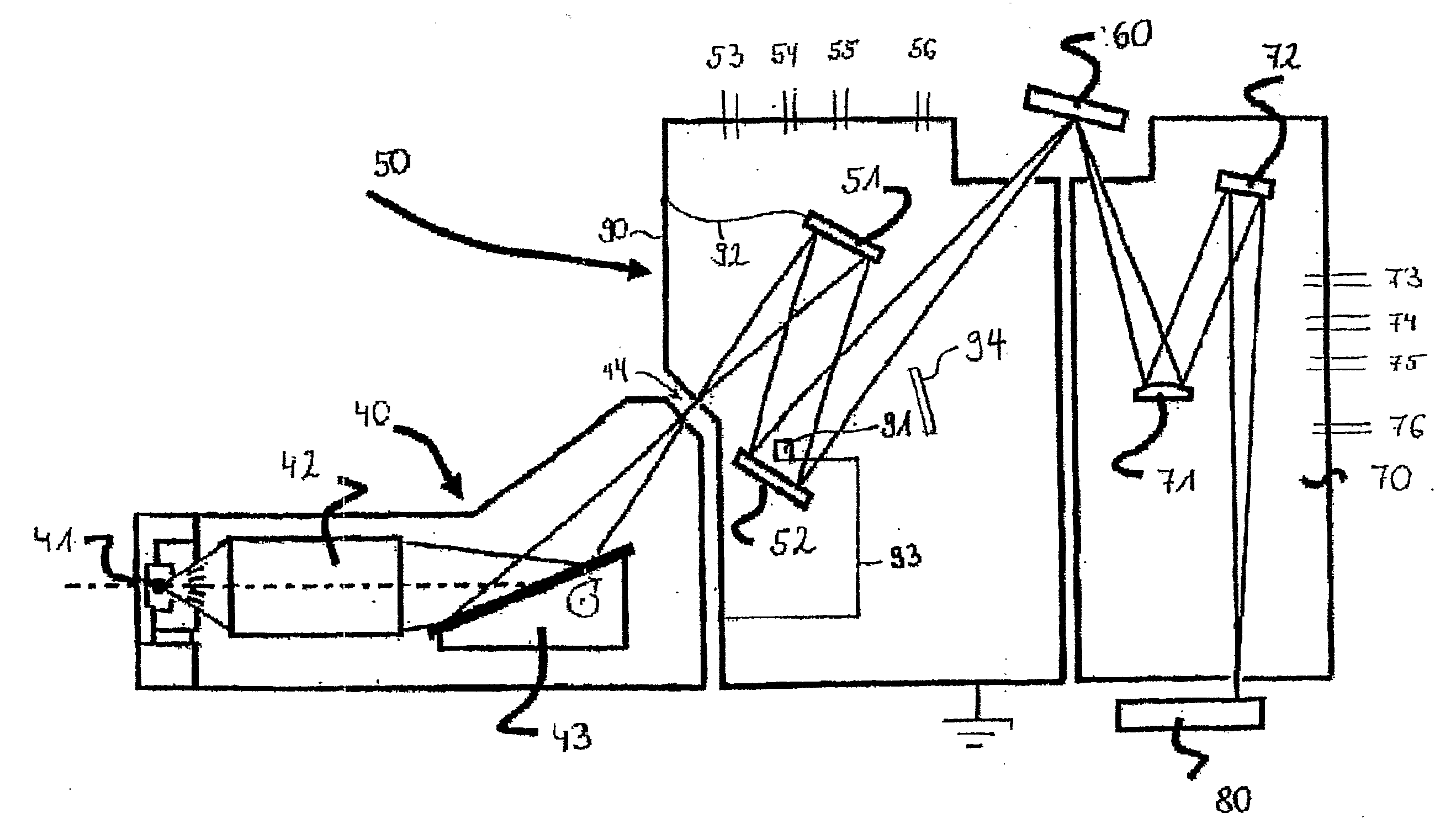
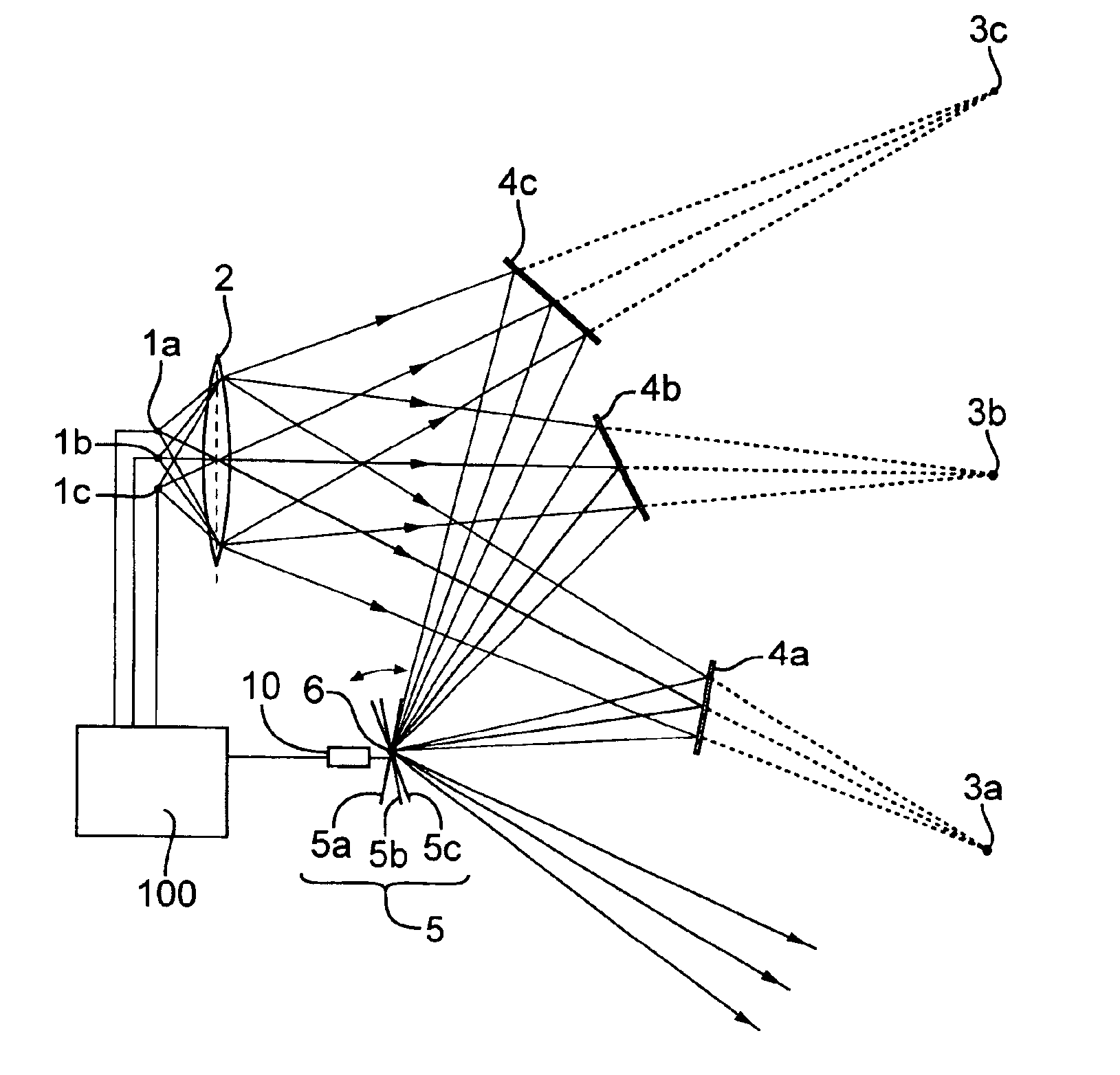
Devices and methods are disclosed that provide effective utilization of light beams produced from multiple EUV-light sources, especially such sources that have been bundled. An embodiment of an EUV-source device comprises multiple individual EUV-light sources each providing a respective point-light source of EUV radiation propagating as a respective beam from each point-light source. A reflective focusing-optical system is situated downstream of the EUV-light sources, and is configured to focus the beams from the point-light sources at a focus point. A variable-angle mirror is situated downstream of the focusing-optical system and is configured to reflect light of the respective beams from the point-light sources that has been reflected by the focusing-optical system. A mirror-tilting mechanism is coupled to the variable-angle mirror. The mechanism, when activated, tilts the mirror by a respective angle corresponding to the particular beam from one of the point-light sources that is incident on the mirror. This produces a composite beam propagating in a constant direction from the variable-angle mirror.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Quasi-phase-matching higher harmonic device based on ultrasonic modulation
InactiveCN101515105AExpand the adjustment rangeLarge adjustment rangeNon-linear opticsUltrasonic sensorFemto second laser
The invention relates to a quasi-phase-matching higher harmonic device based on ultrasonic modulation in the laser technical field, which comprises a femto-second laser, a focusing lens, an ultrasonic transducer, a bar type nozzle, a metallic film, an X ray spectrometer, a computer, a vacuum chamber, a decompression gas valve and a control panel. The output light path of the femto-second laser is sequentially provided with the focusing lens, the ultrasonic transducer, inert gases, the metallic film and the X ray spectrometer. Lasers emitted by the femto-second laser is focused below the bar type nozzle by the lens and interact with the inert gases with density periodic variation which is spouted by the nozzle and modulated by an ultrasonic field to radiate higher harmonics which are reflected into the X ray spectrometer after being filtered by the metallic film and then are sent into the computer. The device meets the quasi-phase-matching condition of the higher harmonics by using ultrasonic modulation gas density, is convenient to be operated and simple and easy, can propel the coherent light source of the higher harmonics soft X ray to shorter waver.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Window membrane for detector and analyser devices, and a method for manufacturing a window membrane
InactiveUS7618906B2Excellent characteristicsImprove permeabilityLiquid surface applicatorsWarp knittingSoft x rayEngineering
A window membrane is permeable to electromagnetic radiation, especially soft X-rays. It comprises a film (201) and a metallic reinforcement mesh (202) attached to the film (201). A preferable way of attaching the metallic reinforcement mesh (202) to the film is to use a positive-working photosensitive glue (204) and allow the reinforcement mesh (202) to act as the exposure mask.
Owner:OXFORD INSTUMENTS ANALYTICAL LIMITED
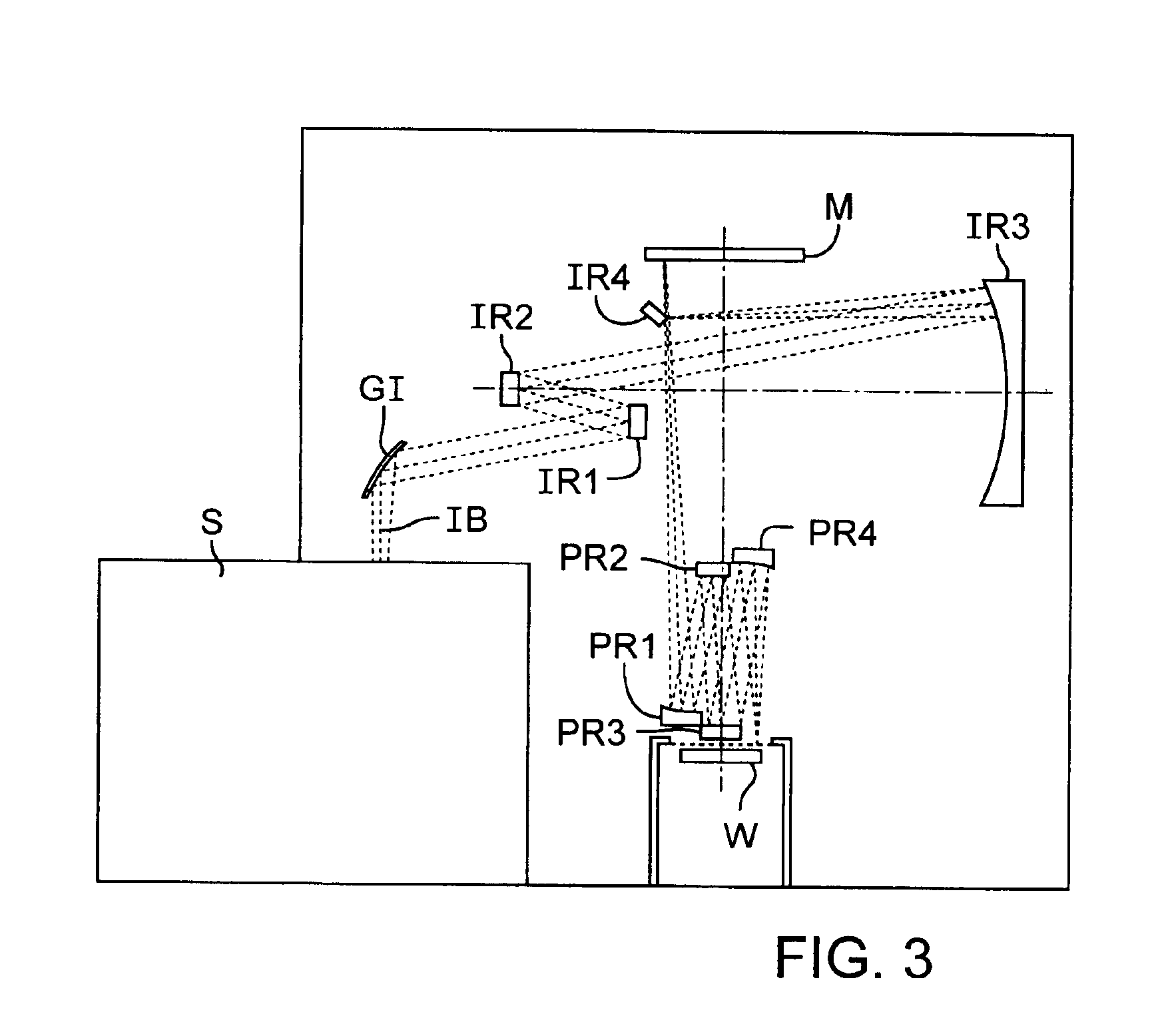
Methods for achieving high resolution microfluoroscopy
A microfluoroscope has a source of soft x-rays and a solid immersion lens including a plano surface. There is means for placing a sample in close proximity to the plano surface so that an x-ray absorption shadowgraph of the sample is projected onto the plano surface by the source of soft x-rays. A scintillator on the solid immersion lens plano surface produces fluorescent light from soft x-rays passing through the sample. An optical microscope is used for viewing through the solid immersion lens the fluorescent light from the scintillator corresponding to the x-ray absorption shadowgraph of the sample. A microfluoroscope is also disclosed which includes a source of soft x-rays, a fluorescent screen placed at a plane to receive x-rays and means for placing a sample in close proximity to the plane so that an x-ray absorption shadowgraph of the sample is projected onto the fluorescent screen. A nanochannel mask placed between the fluorescent screen and the sample for limiting x-rays reaching the fluorescent screen to a periodic matrix of nanochanneled beams. A computer system combines all the discrete images at each raster position into a composite image representing the x-ray absorption shadowgraph of the entire sample.
Owner:HIRSCH GREGORY
Soft x-ray imager with ten micrometer resolution
InactiveUS20060261278A1Reduce penetrationImprove detection efficiencyMaterial analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentSoft x rayPhoton emission
The method of imaging a spatial distribution of photon emitters, the method includes producing an image with a resolution of at most about 180 microns using an imaging device including a detector and a coded aperture, wherein a photon emitted from the photon emitter has an energy of at most about 35 keV (5.6×10−15 J). Further provided is an imaging device for imaging a distribution of photons having energies of at most about 35 keV (5.6×10−15 J), which includes a coded aperture comprising a mask pattern having a plurality of holes, wherein the coded aperture is adapted to provide a resolution of at most about 180 micron, a detector on which a raw image is projected through the coded aperture; and a decoder that receives the raw image from the detector and produces an image having a resolution of at most about 180 micron.
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
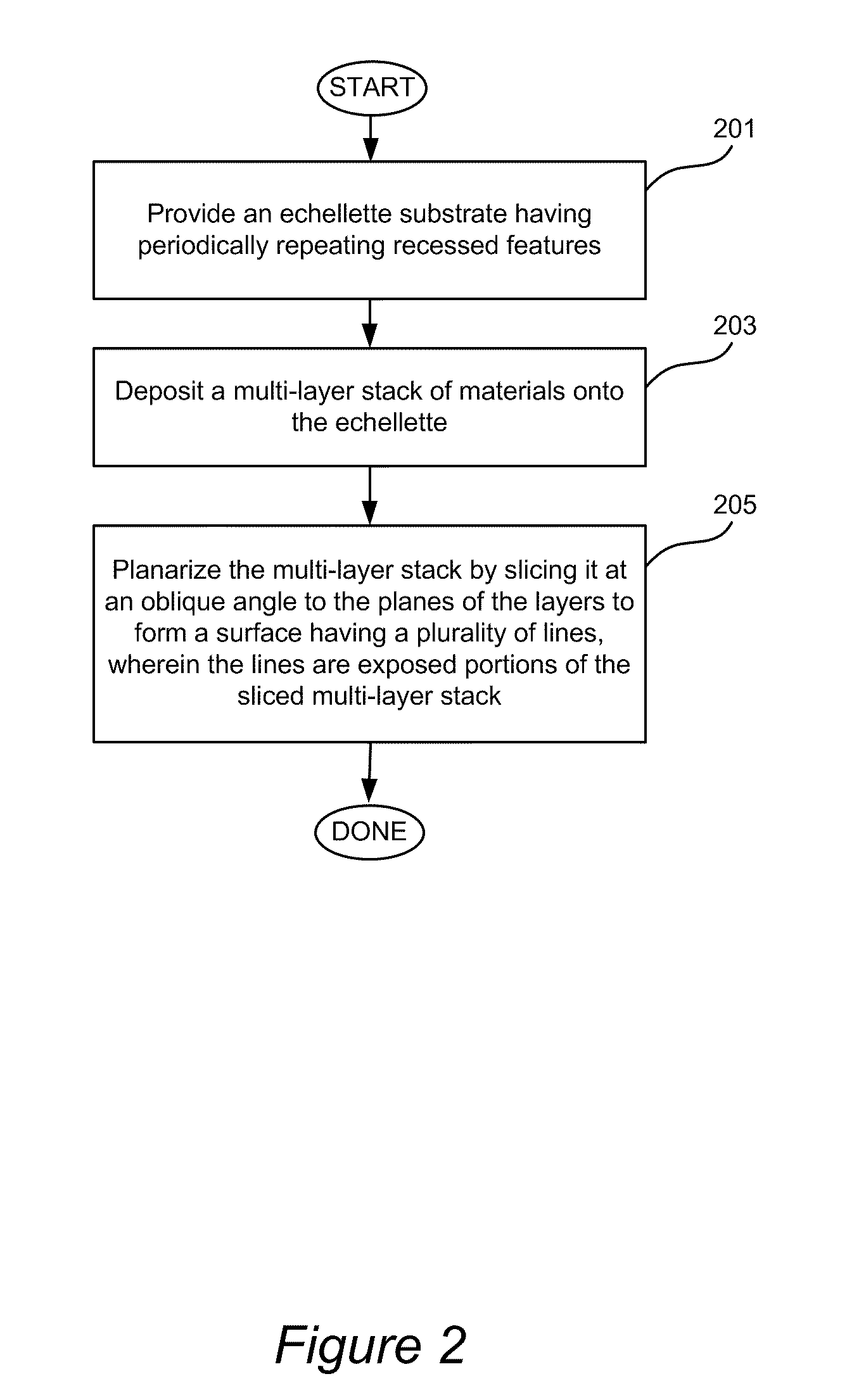
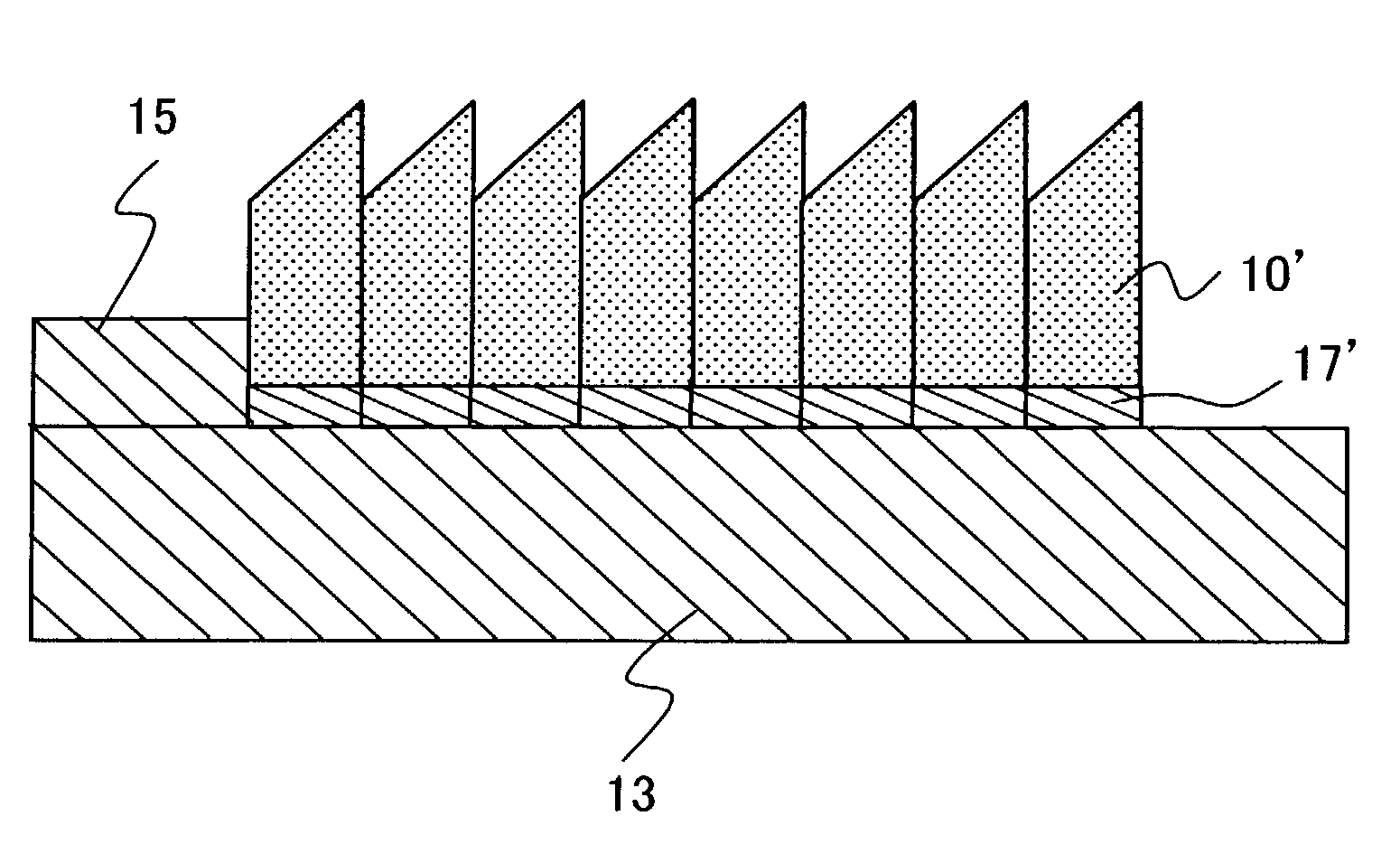
Ultra-high Density Diffraction Grating
InactiveUS20100053611A1High resolutionUltra-high density diffractionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSoft x rayVolumetric Mass Density
A diffraction grating structure having ultra-high density of grooves comprises an echellette substrate having periodically repeating recessed features, and a multi-layer stack of materials disposed on the echellette substrate. The surface of the diffraction grating is planarized, such that layers of the multi-layer stack form a plurality of lines disposed on the planarized surface of the structure in a periodical fashion, wherein lines having a first property alternate with lines having a dissimilar property on the surface of the substrate. For example, in one embodiment, lines comprising high-Z and low-Z materials alternate on the planarized surface providing a structure that is suitable as a diffraction grating for EUV and soft X-rays. In some embodiments, line density of between about 10,000 lines / mm to about 100,000 lines / mm is provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
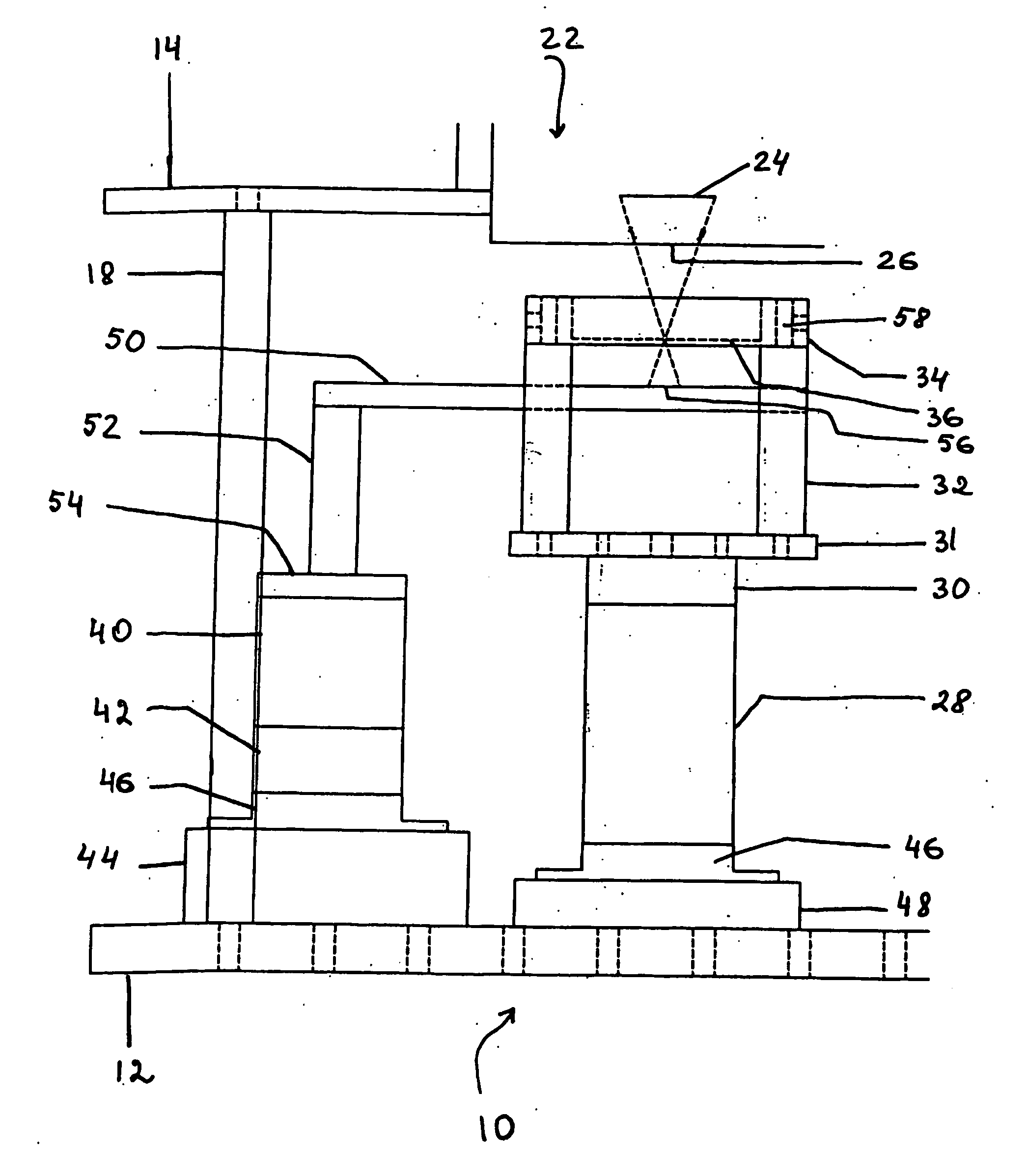
Multifaceted reflecting mirror, illumination optical system based on use of the same, and semiconductor exposure apparatus
InactiveUS6984051B2Precise positioningEasy to adjustMirrorsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionSoft x rayLight beam
A multifaceted reflecting mirror is provided with a plurality of reflecting mirror elements 10 and a base plate 13 for magnet, each of the plurality of reflecting mirror elements 10 comprising a reflecting surface 19 and a magnetic film 17 formed on a bottom surface. The respective reflecting mirror elements 10 can be positioned highly accurately on the base plate 13 by using a positioning guide 15. The maintenance operation is easily performed as well, because the respective reflecting mirror elements 10 are detachable. When the multifaceted reflecting mirror is used in combination with another multifaceted reflecting mirror for an illumination optical system of a reflection type exposure apparatus which uses, as an exposure light beam, a light beam having a short wavelength such as soft X-ray, it is possible to illuminate an exposure area on a substrate with the light beam having an extremely uniform illumination intensity.
Owner:NIKON CORP
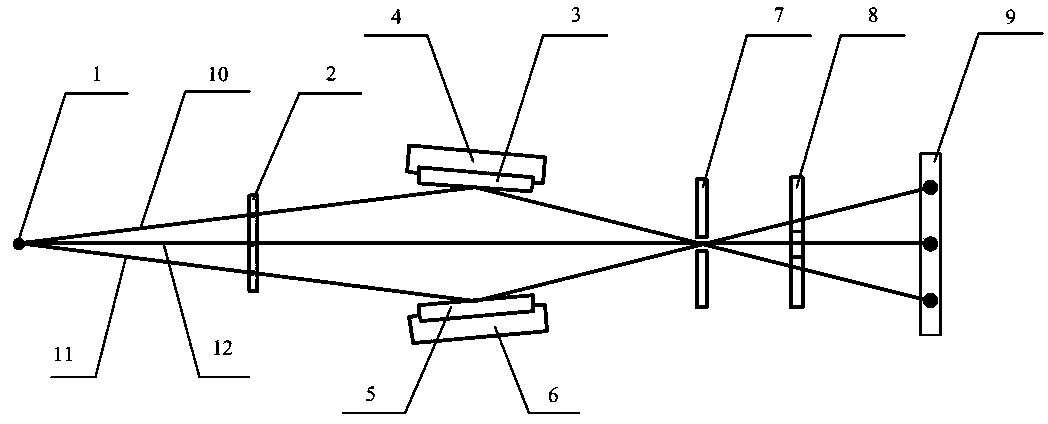
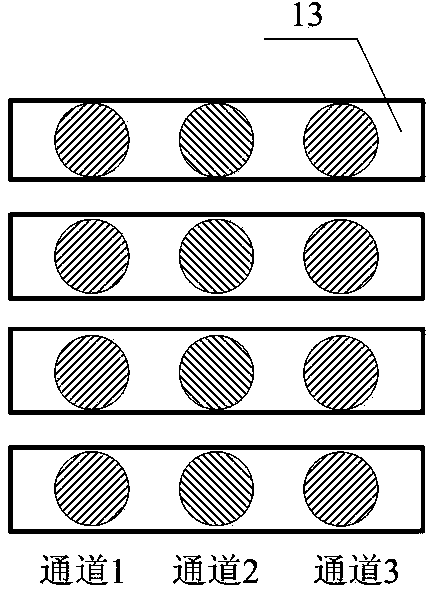
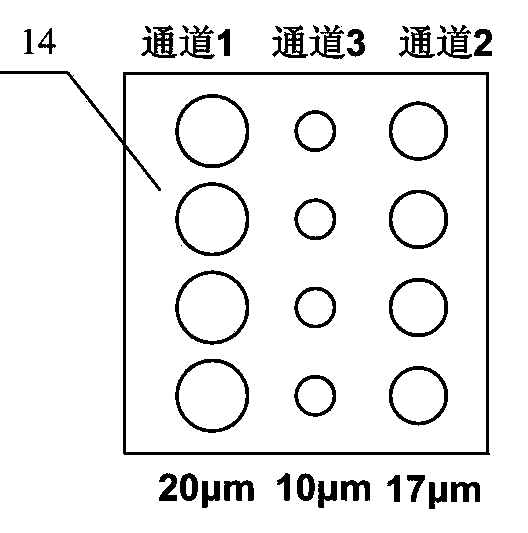
Multiple-energy-point spectrum resolution soft-X-ray framing imaging system
InactiveCN103955108AImprove diagnostic capabilitiesHave timeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotographyPlane mirrorX-ray
The invention provides a multiple-energy-point spectrum resolution soft-X-ray framing imaging system. The imaging system mainly comprises a pin hole array plate, glancing incidence plane mirrors, an optical adjusting mechanism, a filter disc, a light limiting slit, a recording medium and the like. The glancing incidence plane mirrors and the filter disc form an X-ray enable element, each glancing incidence plane mirror and one row of pin holes form an imaging channel, the diameter of each row of pin holes is subjected to optimum design according to observation energy points so as to obtain optimum spatial resolution, and an imaging result is recorded by finally utilizing a time-resolved framing camera or a time-integrated X-ray imaging plate and the like. The imaging system is mainly used for observing laser fusion, Z-hoop condensation polymerization or a high-temperature high-density plasma in a laboratory astrophysical experiment and can obtain plasma evolution images having time resolution, two-dimensional space resolution and spectrum resolution through one-time experiment. Compared with the prior art, the multiple-energy-point spectrum resolution soft-X-ray framing imaging system has the advantages of being low in implementation difficulty, wide in application range, flexible in energy area configuration and good in imaging signal to noise ratio and having a multiple-energy-point imaging characteristic and the like.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
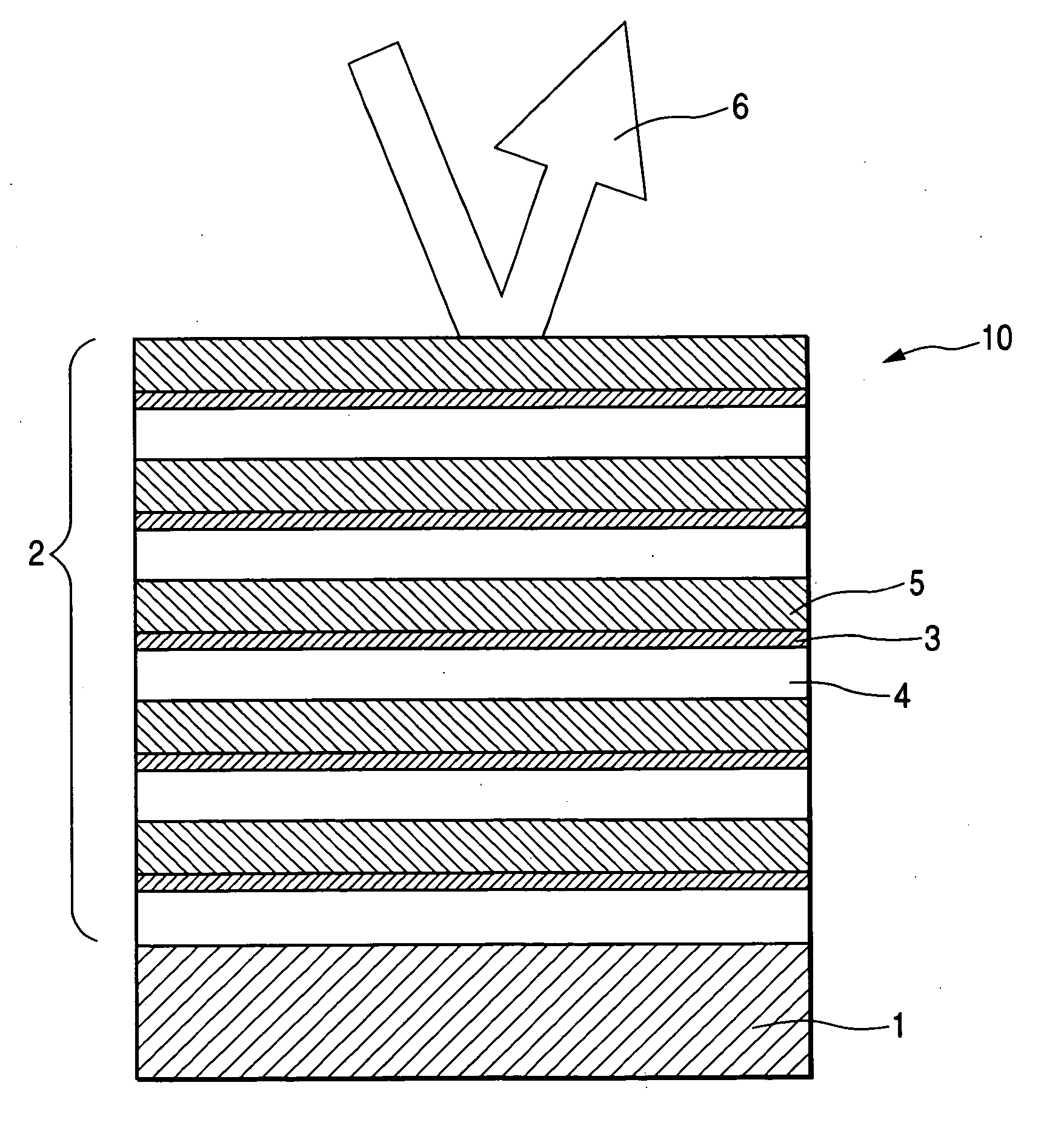
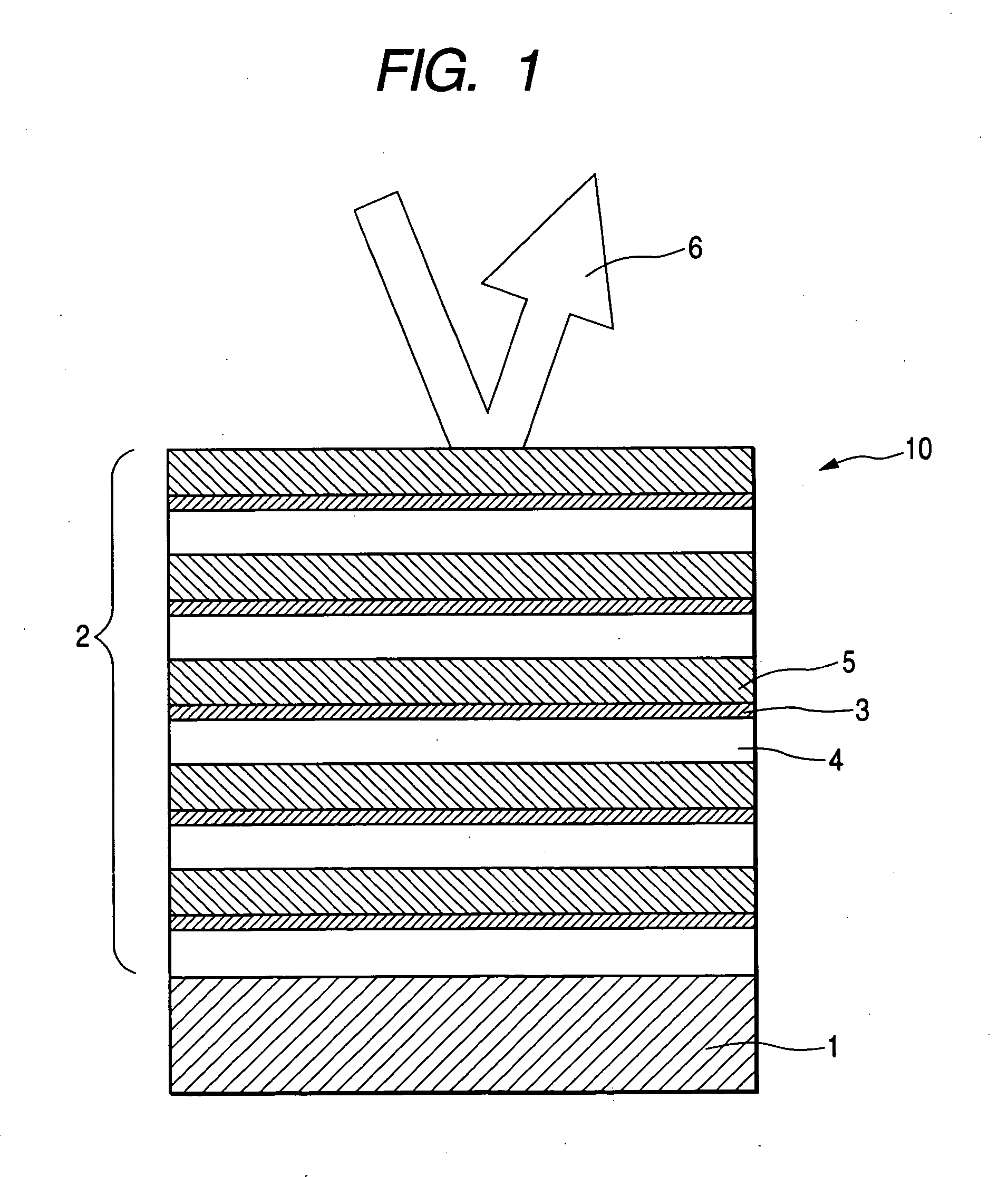
Reflective optical element, optical system and EUV lithography device
InactiveUS20060076516A1Improve reflectivityLess effectMirrorsNanoinformaticsSoft x rayLithographic artist
In order to obtain optimal reflectivity on optical elements for the EUV and the soft X-ray range, multilayers constructed of a number of layers are used. Contamination or degradation of the surface leads to imaging defects and transmission losses. In the prior art, it has been attempted to counter a negative change in the surface by providing a cover layer system on the surface of the reflective optical element that should protect the surface. The invention renders the influence of the surface degradation manageable by a targeted selection of the distribution of thickness of the cover layer system, whereby at least one layer of the cover layer system has a gradient that is not equal to zero.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
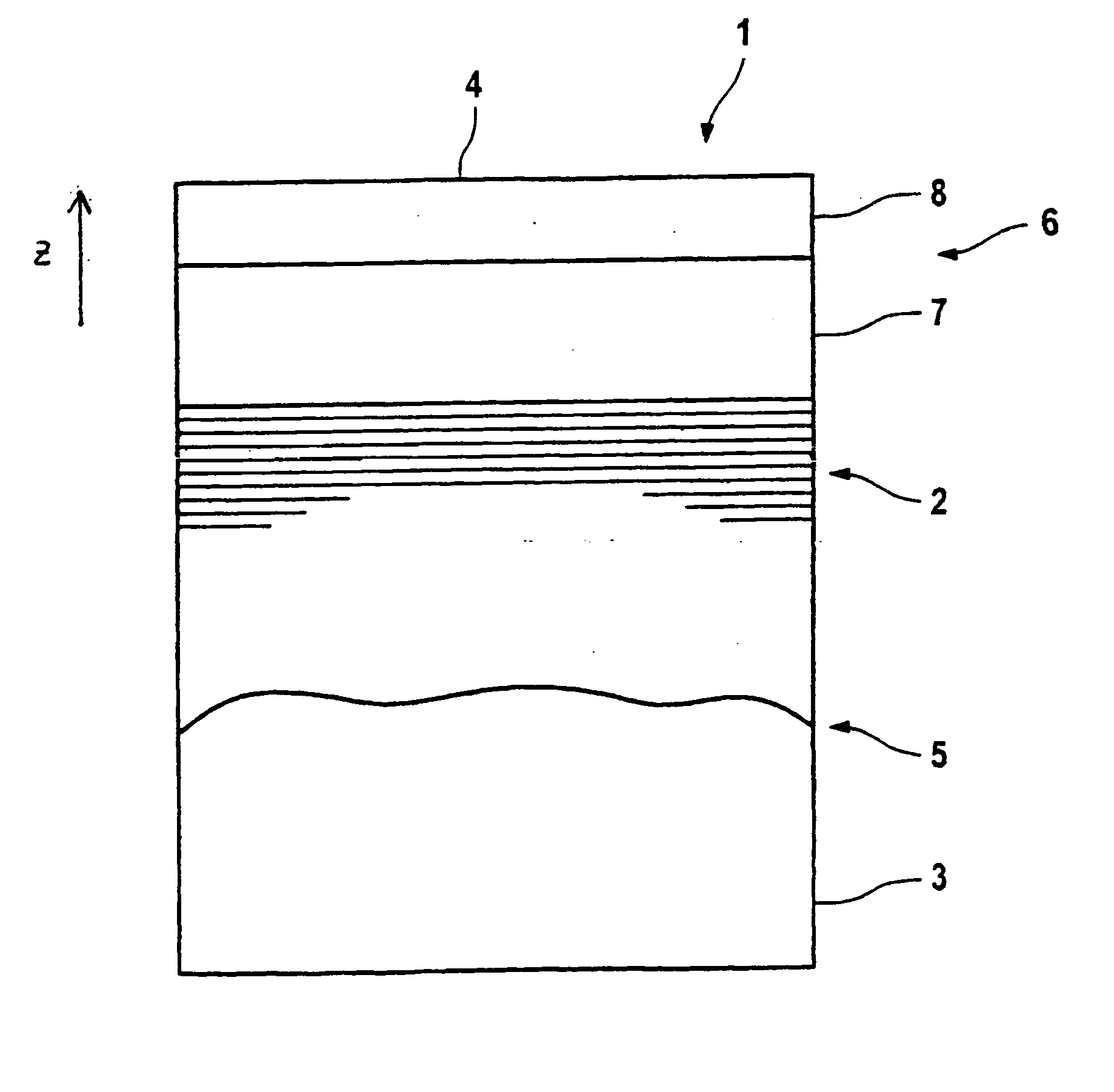
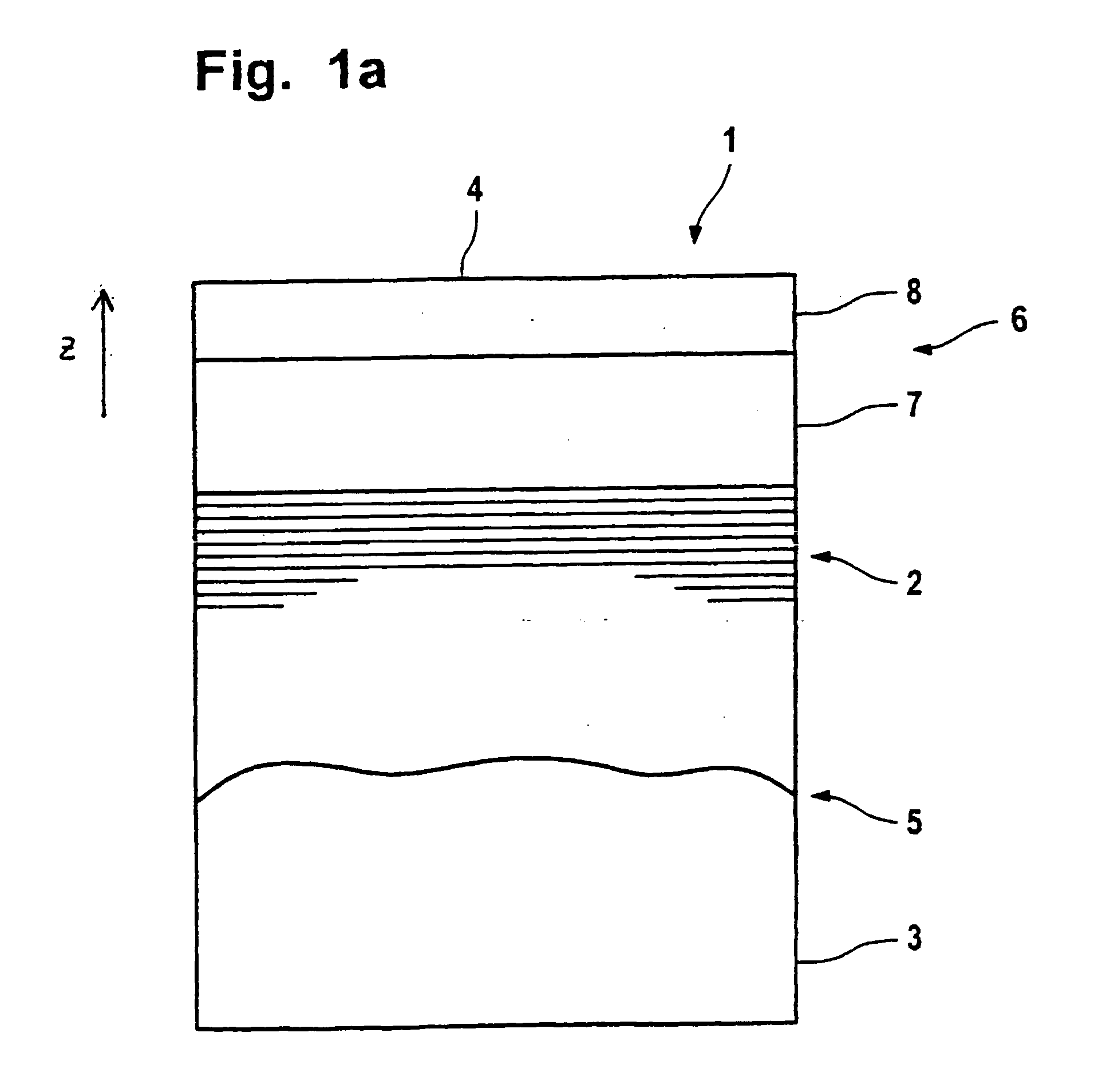
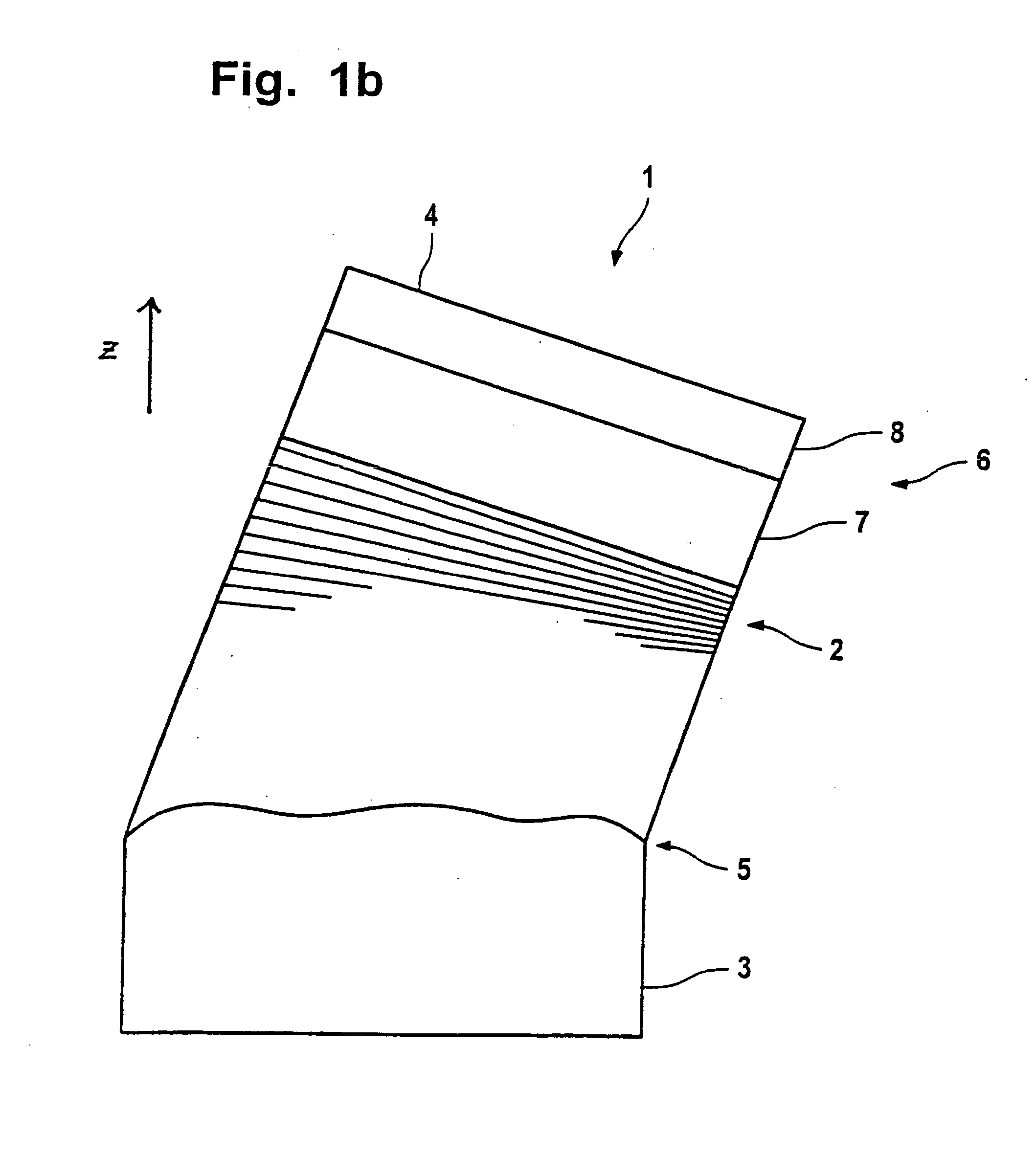
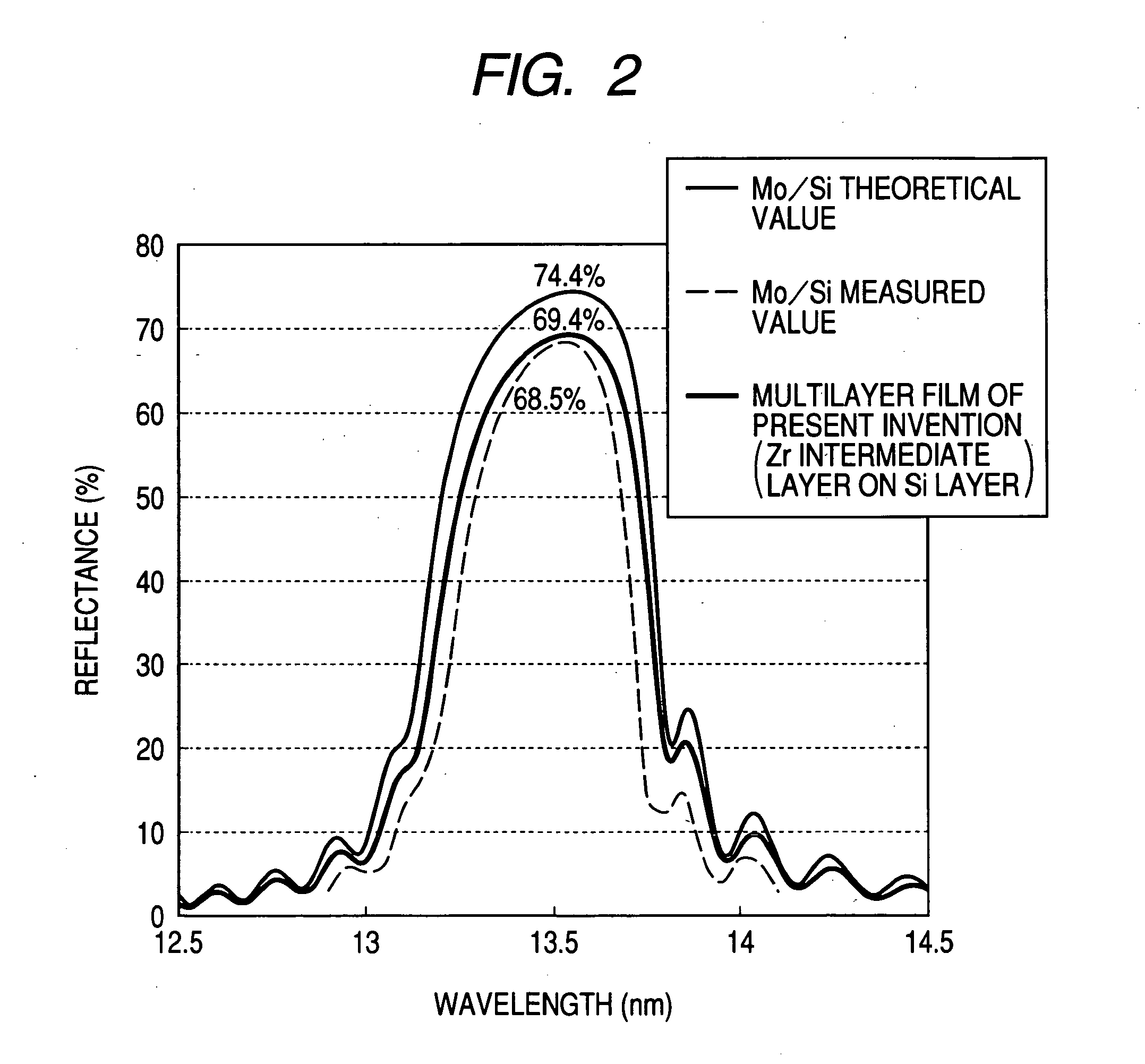
Multilayer film reflector for soft X-rays and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20050213199A1Good reflective propertiesPromote crystallizationMirrorsOptical filtersSoft x rayRefractive index
A multilayer film reflector for X-rays has alternately stacked layers formed on a substrate and comprising a layer (high refractive index layer) comprising a material having a large difference between a refractive index to soft X-ray and a refractive index in vacuum, and a layer (low refractive index layer) comprising a material having a small difference between a refractive index to soft X-ray and a refractive index in vacuum, wherein at least one intermediate layer having a crystalline structure is provided between the low refractive index layer and the high refractive index layer. Thereby, the crystallization of the low refractive index layer is promoted, the refractive index of the low refractive index layer is lowered, so that the reflectance of the multilayer film reflector is improved.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com