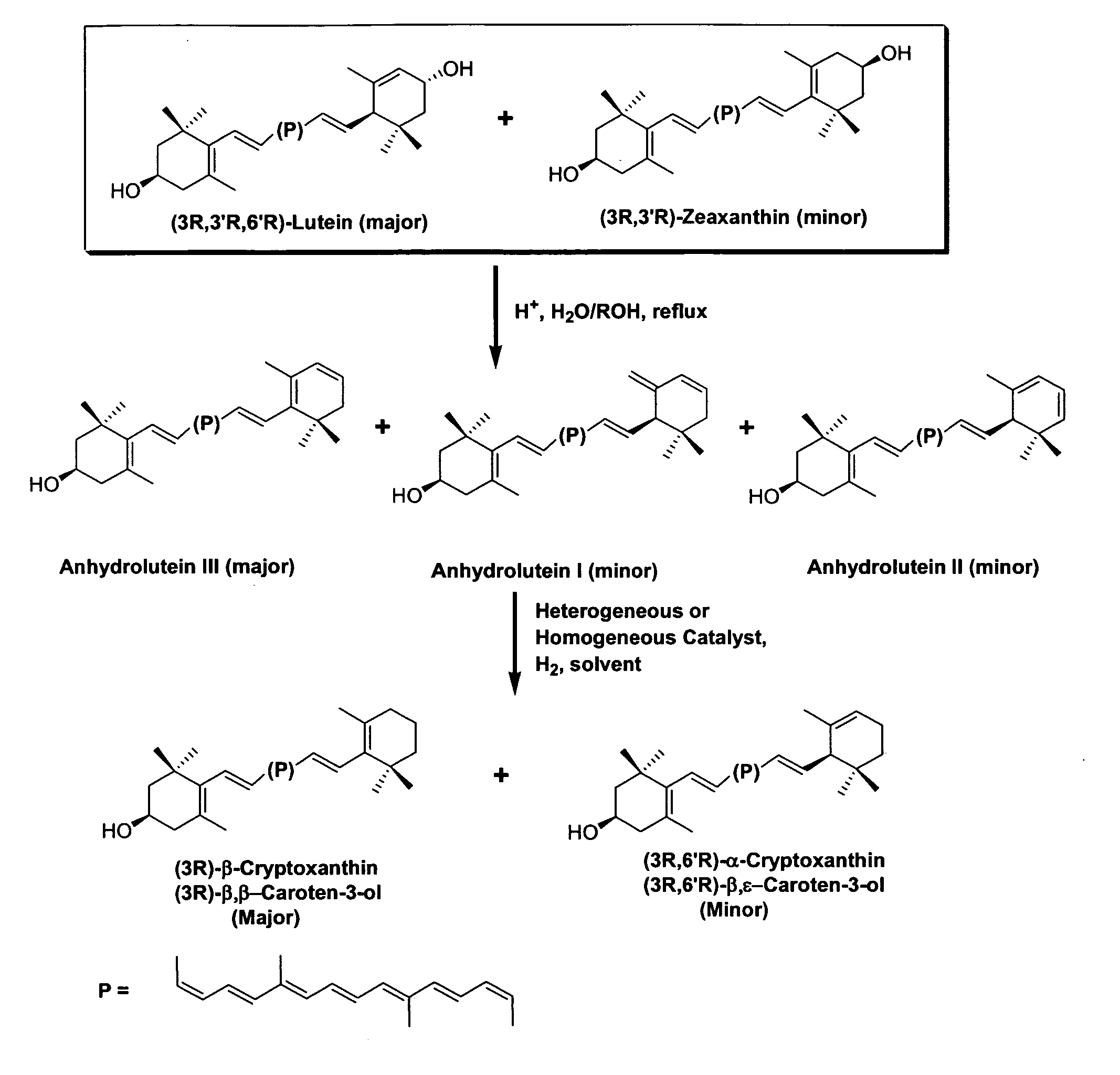
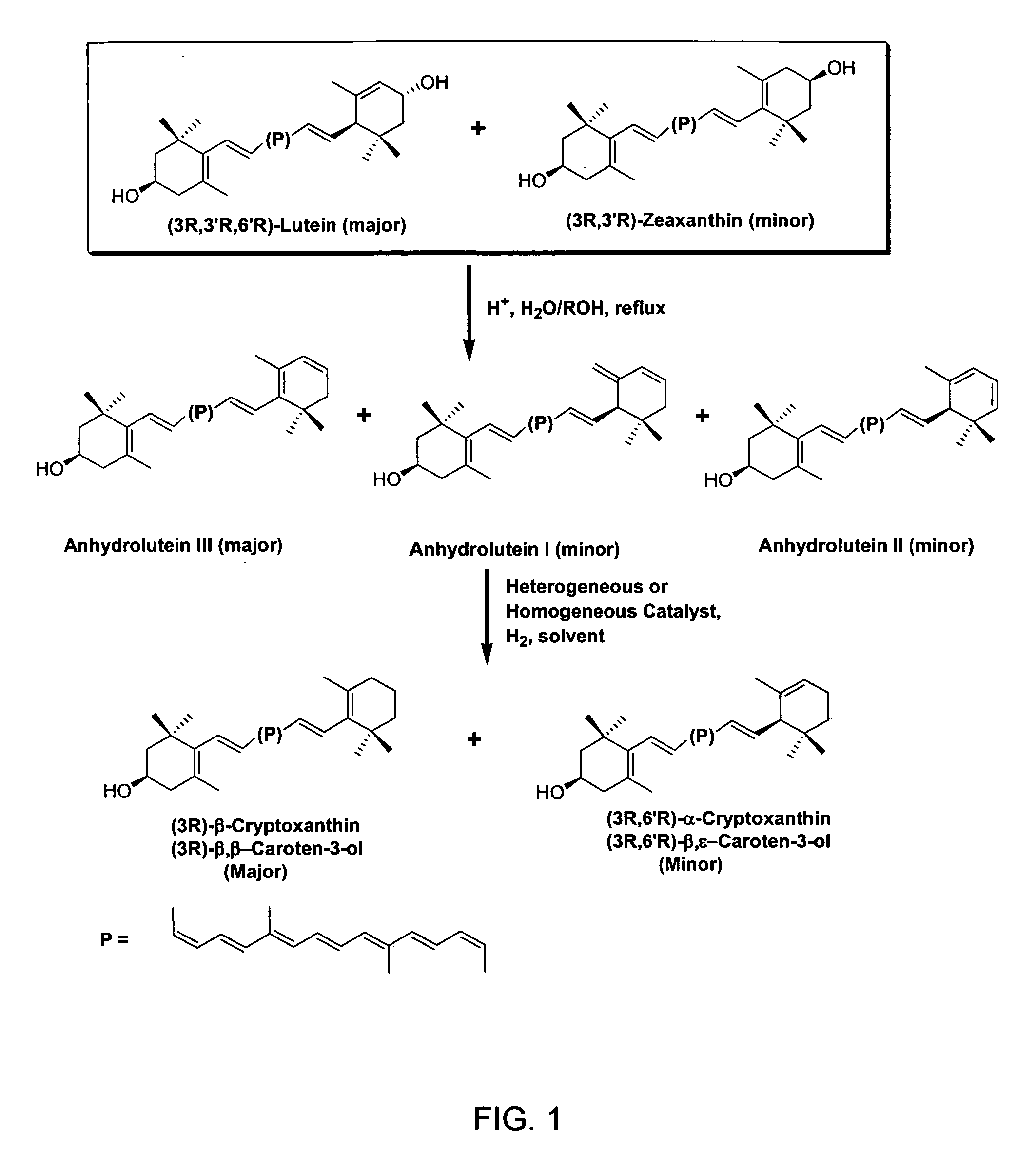
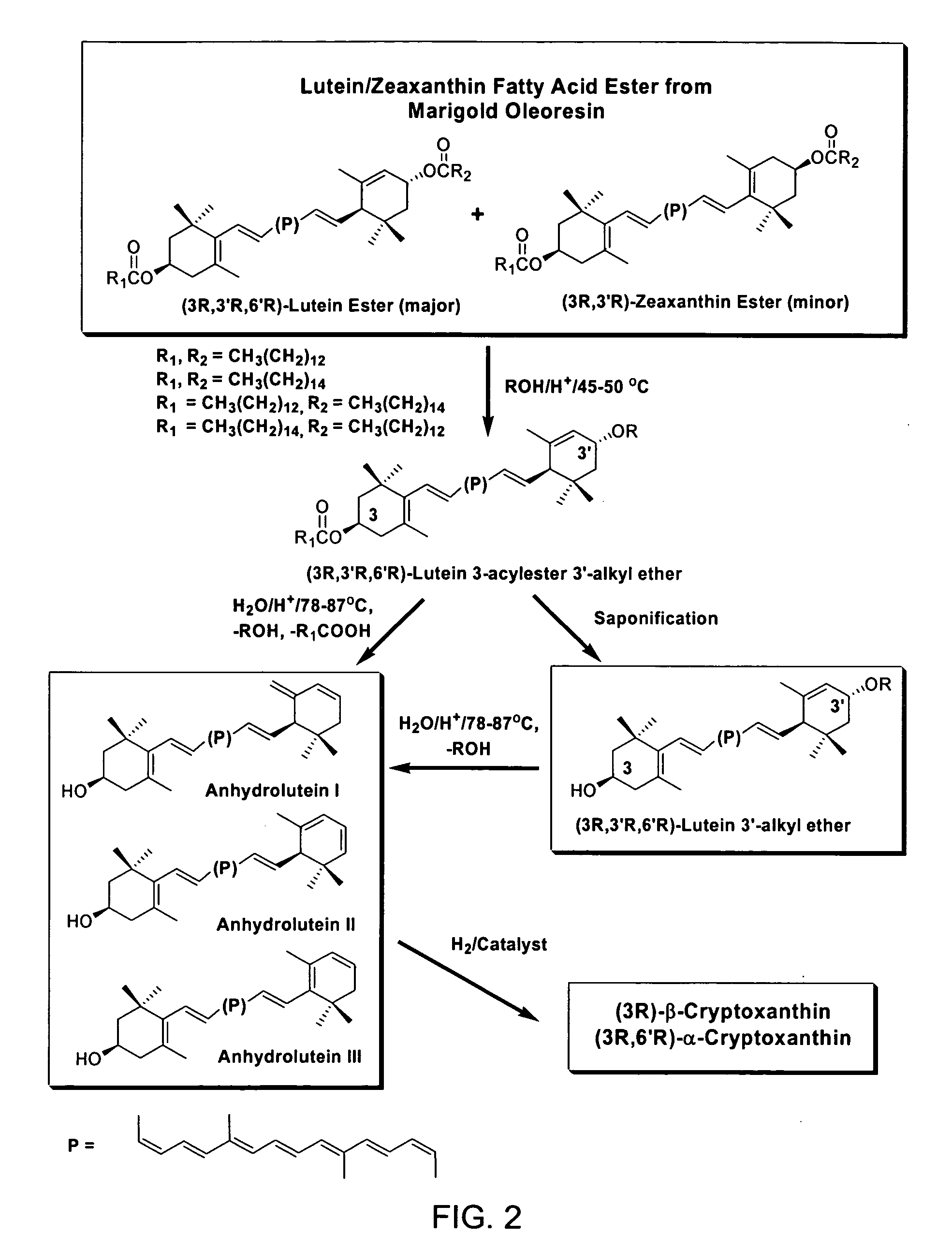
Process for the preparation of alpha- and beta-cryptoxanthin
a technology process, which is applied in the field of process for the preparation of alpha- and beta-cryptoxanthin, can solve the problems of difficult control of the no literature report on regioselective catalytic hydrogenation of carotenoids, etc., and achieves moderate to excellent selectivity and yield. , the effect of safe use by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example e
Catalytic Hydrogenation of Anhydroluteins I, II, III (49% total carotenoids) with Platinum (5%) Supported on Alumina in Ethyl Acetate at 40° C.
[0082] A three-neck round bottom flask is equipped with a mechanical stirrer, a thermometer, and a gas inlet. The flask is charged with a mixture of anhydroluteins (20.0 g, 49% total carotenoids, 27% anhydrolutein III), platinum (5%) supported on alumina (1.5 g), and ethyl acetate (700 ml). The air is displaced with argon and the mixture is heated to 40° C. with mechanical stirring at 500 rpm. Hydrogen is bubbled into the solution and the mixture is stirred at 40° C. After 10 hours, the reaction mixture is allowed to cool down to ambient temperature, diluted with 200 ml of ethyl acetate, and filtered through celite. The filtrate is concentrated under reduced pressure below 40° C. and the residue is crystallized from a solution of ethyl acetate / ethanol / water. The dark orange crystals are collected by filtration, and dried under high vacuum be...
example f
Catalytic Hydrogenation of Anhydroluteins I, II III (75% total carotenoids) with Palladium (5%) Supported on Carbon in Ethyl Acetate at −15° C.
[0083] To a mixture of 75% total carotenoids (0.3 g≈0.225 g) and palladium (5%) supported on carbon (26 mg≈1.3 mg Pd) in a 60 ml glass reaction tube is added 20 ml of ethyl acetate and the mixture is cooled down to −15° C. in a low temperature freezer. The tube is evacuated and filled with hydrogen several times and then sealed. The mixture is stirred at −15° C. and the course of the reaction is followed by HPLC. After nearly 24 h, HPLC shows nearly the complete conversion of anhydroluteins to the desired products. The product is allowed to warm up to ambient temperature and is filtered through celite to remove the catalyst. The filtrate is concentrated under reduced pressure below 40° C. and the residue is crystallized from 10 ml of a 1 / 1 solution of ethanol / water. The dark orange crystals are collected by filtration, washed with 5 ml of co...
example a
Catalytic Hydrogenation of Anhydroluteins I, II, III (75% total carotenoids) with Palladium Acetylacetonate in Tetrahydrofuran (THF) at 45-50° C.
[0084] To a mixture of 75% total carotenoids (0.3 g≈0.225 g) and palladium acetylacetonate (12 mg) in a 40 ml glass reaction tube is added 10 ml of THF and the mixture is cooled down to 0° C. in an ice bath. The tube is evacuated and filled with hydrogen several times and then sealed. The ice bath is removed and the mixture is stirred at 45-50° C. The progress of the reaction is monitored by HPLC. After nearly 15 h, HPLC shows that no additional amounts of β-cryptoxanthin and α-cryptoxanthin can be formed while considerable amounts of anhydroluteins remain unreacted. The product is allowed to cool down to ambient temperature and is filtered through celite to remove the catalyst. The solids are washed with THF (5 ml), and the filtrate is concentrated under reduced pressure below 40° C. The concentrated residue is crystallized from 10 ml of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com