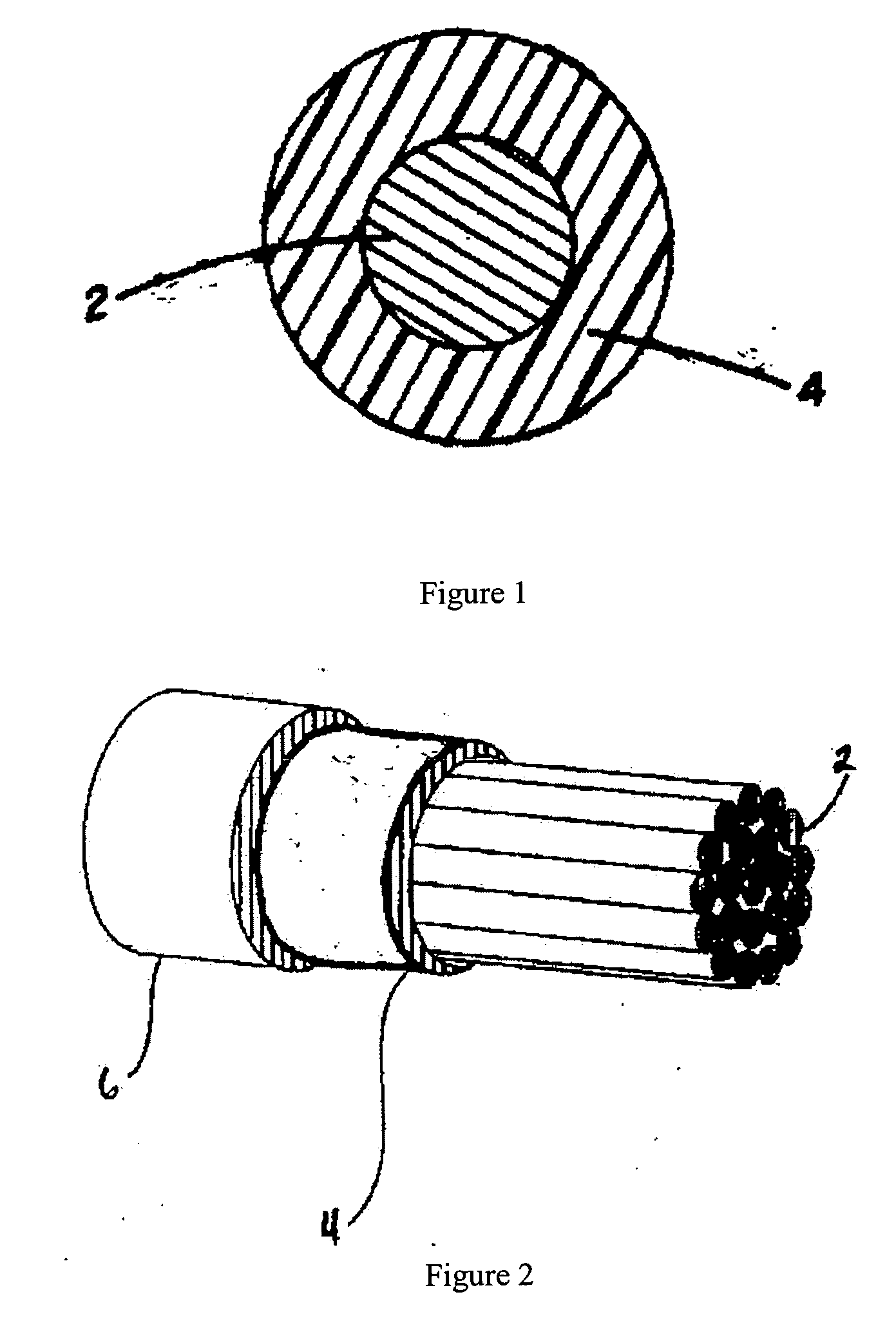
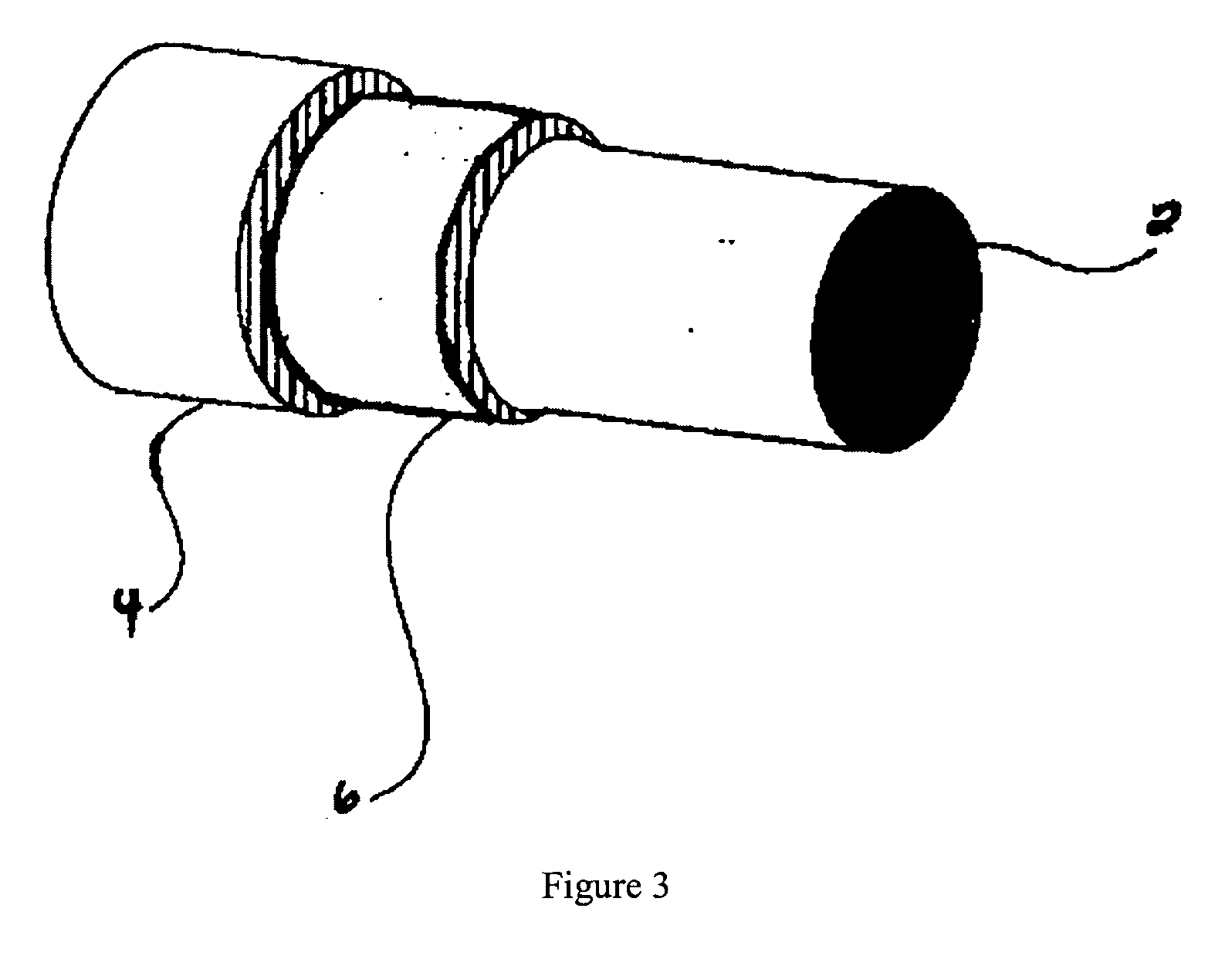
Flame retardant electrical wire
a technology of electrical wires and flame retardants, applied in the direction of insulated conductors, plastic/resin/waxes insulators, insulated cables, etc., can solve the problems of failure prematurely, failure to sustain success, cracking of insulation layers in thermoplastic polyester insulated electrical wires, etc., and achieve the effect of large surface area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0098] The following examples were prepared using the materials listed in Table 1.
TABLE 1ComponentDescriptionPPEA poly(2,6-dimethylphenylene ether) with an intrinsic viscosity of0.46 dl / g as measured in chloroform at 25° C. commerciallyavailable from General Electric under the grade name PPO646.KG1650A polyphenylethylene-poly(ethylene / butylene)-polyphenylethyleneblock copolymer having a phenylethylene content of 30 weightpercent, based on the total weight of the block copolymer andcommercially available from KRATON Polymers under the grade nameG 1650.PPA polypropylene having a melt flow rate of 1.5 g / 10 mindetermined according to ASTM D1238 as described above andcommercially available under the tradename D-105-C SunocoChemicals.Tuftec H1043A polyphenylethylene-poly(ethylene / butylene)-polyphenylethyleneblock copolymer having a phenylethylene content of 67 weightpercent, based on the total weight of the block copolymer andcommercially available from Asahi Chemical.KG1657A mixture of...
examples 1-18
[0099] Examples 1-19 were made by combining the components in a twin screw extruder. The PPE and block copolymers were added at the feedthroat and the PP was added downstream. The organophosphate ester was added by a liquid injector in the second half of the extruder. The material was pelletized at the end of the extruder and the pelletized material was injected molded into test specimens for flexural modulus, heat deflection temperature, and melt flow rate testing.
[0100] Flexural modulus (FM) was determined using ASTM D790-03 at a speed of 1.27 millimeters per minute and is expressed in kilograms per square centimeter (kg / cm2). The values given are the average of three samples. The samples for flexural modulus were formed using an injection pressure of 600-700 kilograms-force per square centimeter and a hold time of 15 to 20 seconds on a Plastar Ti-80G2 from Toyo Machinery & Metal co. LTD. The remaining molding conditions are shown in Table 2.
[0101] Heat distortion temperature (H...
examples 19-26
[0107] Examples 19-26 were made and tested as described above with regard to Examples 1-18. Compositions and results are shown in Table 4.
TABLE 419*20*212223*24*2526*PPE51.449.247.141.853.952.350.646.5PP2727272727272727KG 1650101010101010101071B (A)11.613.815.921.2————RDP (A)————9.110.712.416.5FM1609816658167011376416136163731657315438HDT1201109972127128120103MFR22.1530.641.058.2517.116.3521.0534.9Weighted average3030303030303030aryl alkylene content(B)Phosphorous content0.991.171.351.800.991.171.351.80(C)(A) + (B)41.643.845.951.239.140.742.446.5(B) + (C)30.9931.1731.3531.8030.9931.1731.3531.80Average flame out61.0121.614.22.3115.2114.27.92.3timeFlame out time >70 secYYNNYYNN
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com