Rapid triglyceride assay for use in pulp pitch control
a triglyceride assay and pulp technology, applied in the direction of non-fibrous pulp addition, pulp deposit formation/corrosion prevention, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of not providing an assessment, the known methods of triglyceride analysis of pulp take between 8 and 24 hours to complete, etc., to achieve the effect of low cos
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Enzymatic Colorimetric TG Method Using PC-A / PC-B
[0120] The triglycerides would be reduced to glycerol and fatty acids by a lipase. The glycerol would react with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to form adenosine-5′-diphosphate (ADP) and glycerol-1-phosphate, which would react with oxygen to form dihydroxyacetone phosphate and peroxide. The peroxide would react with 4-aminoantipyrine and sodium-N-ethyl-N-(3-sulfopropyl)m-anisidine (ESPA) to form quinoneimine dye and water. From this series of reactions, the concentration of quinoneimine dye formed as the final product would be directly proportional to the concentration of depositable triglycerides initially present in the sample, which would be detected with a spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 540 nm.
[0121] Reagents
[0122] Three primary reagents (PC-A, PC-B, and triolein standard) would be used. The PC-A would have the following composition:
ATP0.375mMMagnesium salt3.75mM4-Aminoantipyrine0.188mMSodium-N-ethyl-N-(3-sulfopropyl) m-an...
example 2
Enzymatic Colorimetric TG Method Using PC-Y / PC-Z
[0148] The triglycerides would be reduced to glycerol and fatty acids by a lipase. The glycerol would be reacted with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to form adenosine-5′-diphosphate (ADP) and glycerol-1-phosphate which would react with nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) to form dihyroxyacetone phosphate (DAP) and NADH (the reduced form of NAD). The reduction of NAD would be catalyzed by glycerol-1-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-1-PDH). NADH reacts with 2-(p-iodophenyl)-3-p-nitrophenyl-5-phenyltetrazolium chloride (INT) to form formazan dye and NAD. This reaction would be catalyzed by diaphorase. From this series of reactions, the concentration of formazan dye formed as the final product would be directly proportional to the concentration of depositable triglycerides initially present in the sample and would be detected with a spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 500 nm.
[0149] Reagents
[0150] Three primary reagents (PC-Y, PC-Z, and tri...
example 3
Testing the Enzymatic Colorimetric TG Method for Pulp
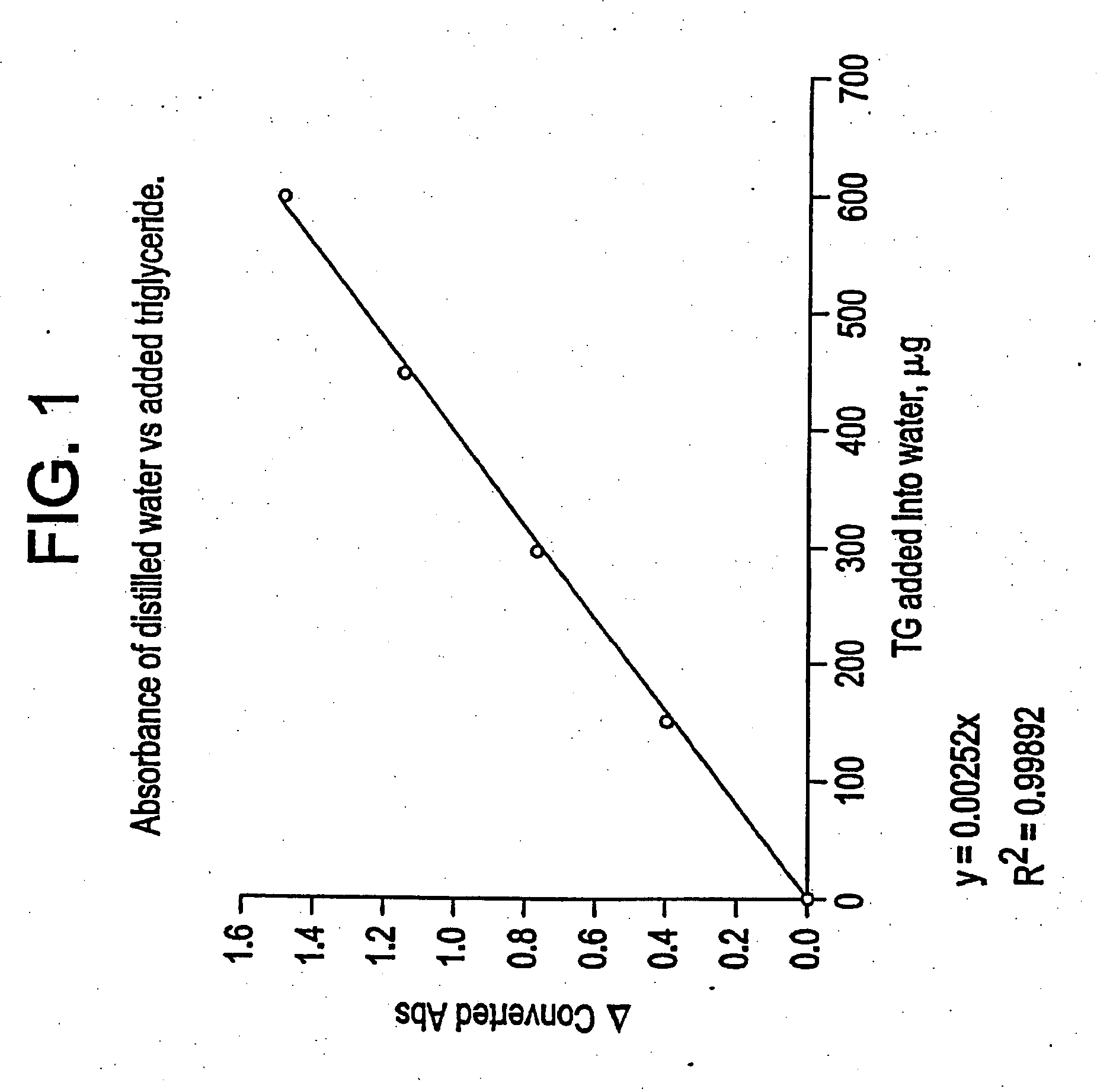
[0178] Test vials were prepared, containing 2 mL of water, to which 2 mL of PC-A was added along with varying amounts of triglycerides (standard concentration of 3000 mg / L) as shown in Table 3. The procedures of Example 1 were used to obtain the results.
[0179] For the sake of clarity, the actual measurement value that is taken when the sample is placed in the spectrophotometer is termed the “absorbance”. “Converted absorbance” is the absorbance of the sample with lipase treatment multiplied by 1.1, the ratio of the total volume of the pulp suspension with and without the addition of lipase, minus the absorbance of the sample without lipase treatment. The “Δ converted absorbance” represents the normalized data values obtained by subtracting the converted absorbance value obtained for the sample with 0 micrograms of added triglycerides from all of the data points.
[0180] Results
[0181] The results shown in Table 3 are illustrated ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelengths | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelengths | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelengths | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com