Optical film, method for producing the same and polarizing plate using the same
a technology of optical film and polarizing plate, applied in the field of optical film, can solve the problems of large equipment required for drying solvent, insufficient uniformity of film thickness and retardation value, and insufficient uniformity of observing field,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0136]
Cellulose acetate propionate (Acetyl group100parts by weightsubstitution degree: 1.95, propionyl groupsubstitution degree: 0.7, Number average molecular weight: 75,000, Dried in vacuum for 24hours at 60° C.)Triphenyl phosphate10parts by weightEthylphthalylethyl glycol2parts by weightTinuvin 109 (Ciba Specialty Chemicals0.5parts by weightCO., Ltd.)Tinuvin 171 (Ciba Specialty Chemicals 0.5parts by weightCO., Ltd.)Tinuvin 326 (Ciba Specialty Chemicals 0.3parts by weightCO., Ltd.)Antioxidant: 2.6-di-t-butyl-p-cresol +0.01parts by weightpentaerythrytol-tetrakis[3-(3,5-di-t-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl) propionate]
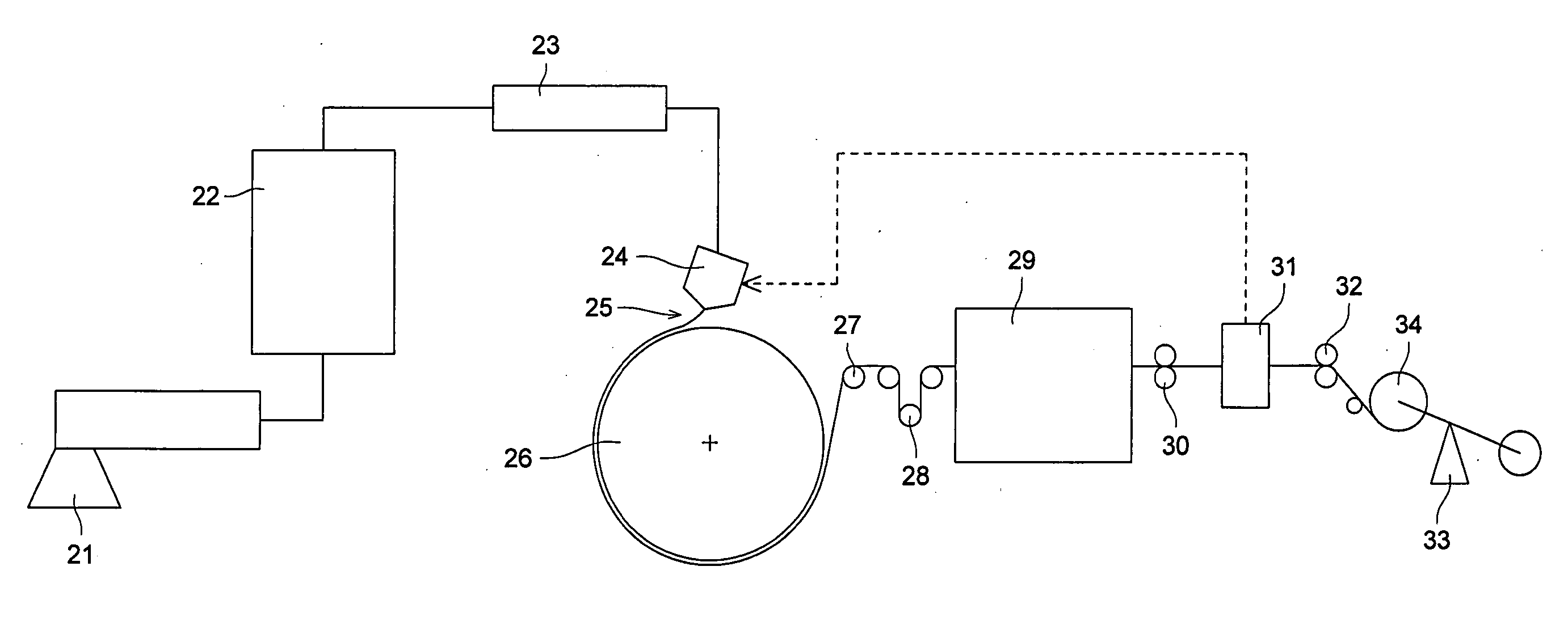
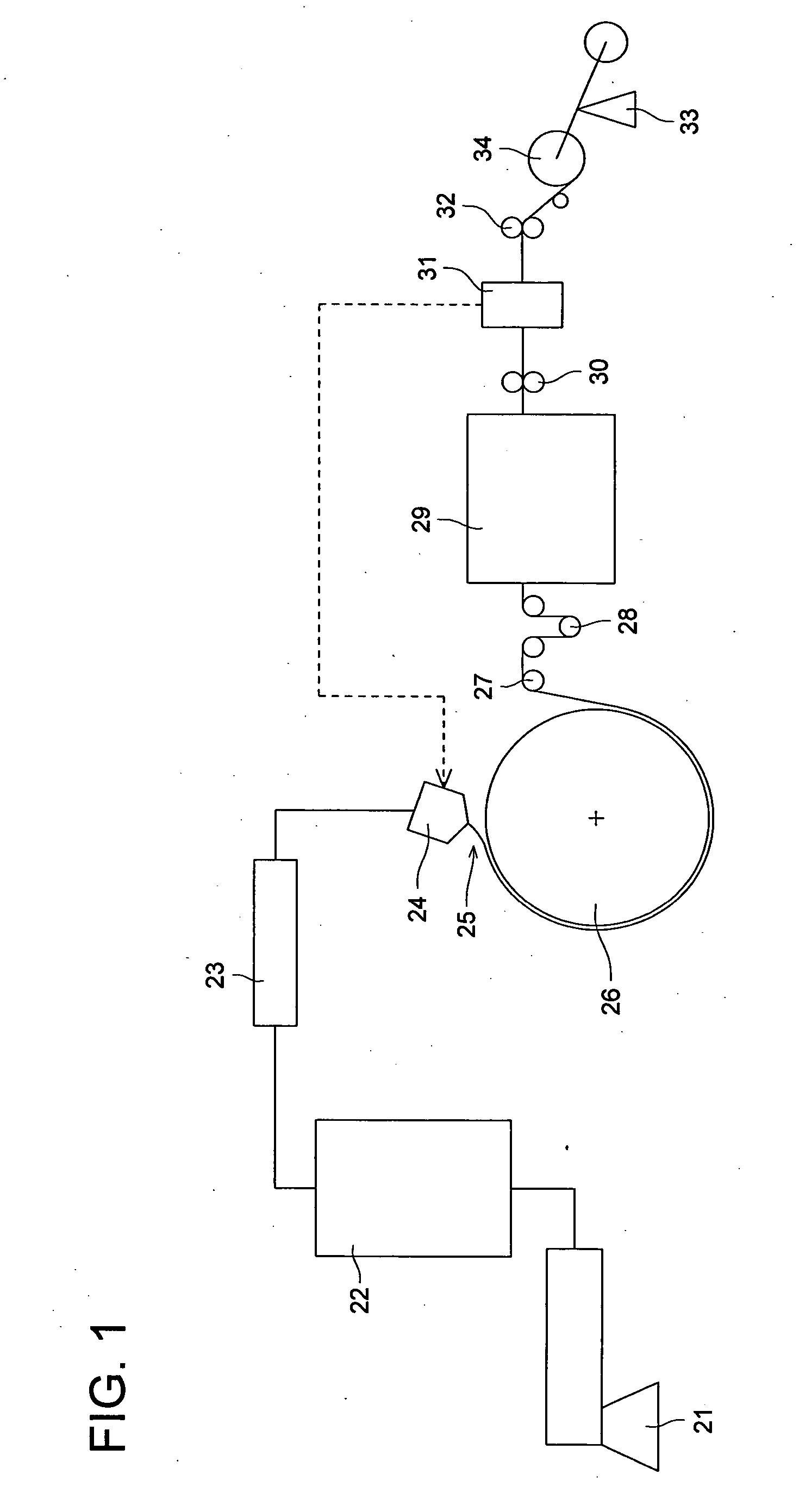
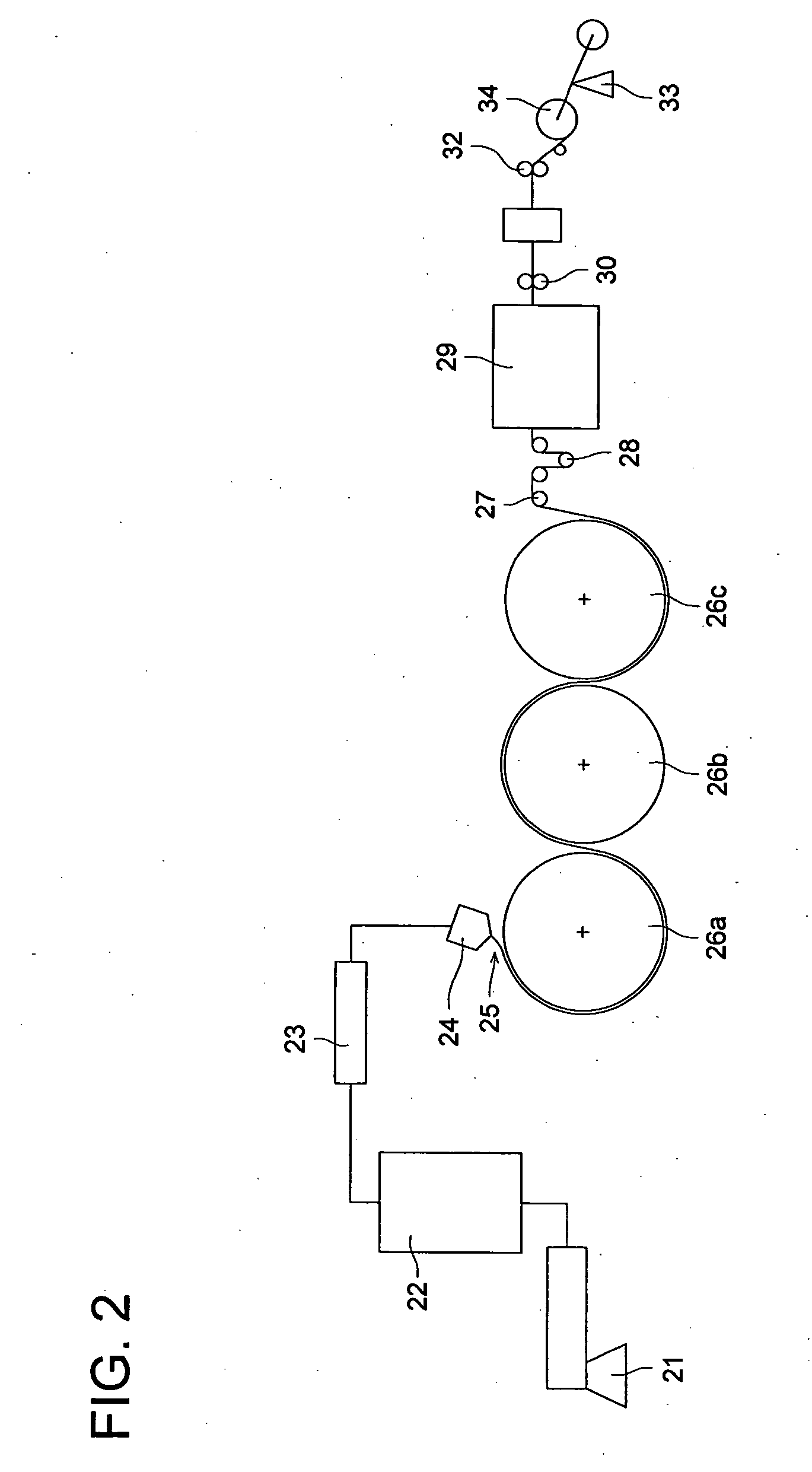
[0137] The above mixture was molten and mixed using the two-axis extruder 21 in FIG. 1 to form pellets. The pellets were molten at 250° C. and extruded through the T-die 24 into a form of film onto the cooling drum 26 held at 30° C. The width of the cooling drum 26 was 1950 mm.
[0138] The cooling drum 26 was divided into regions of: (i) each ⅕ of the width from each of the side e...
example 2
[0159] Poly vinyl alcohol having a thickness of 120 μm was immersed in 100 parts by weight of an aqueous solution containing l part by weight of iodine-and 4 parts by weight of boric acid and stretched for 4 times at 40° C. to prepare a polarization film.
[0160] Besides, Konica Minolta TAC having a thickness 80 μm, cellulose triacetate film manufactured by Konica Minolta Opto Inc., was immersed in an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide having a concentration of 2 moles / liter for 2 minutes at 60° C. and dried for 10 minutes at 100° C. to prepare alkali saponified cellulose triacetate film for the protective film.
[0161] Thus obtained polarization film was pasted with the above triacetate film by an adhesive of 5% aqueous solution of completely saponified poly vinyl alcohol so as to prepare a polarizing plate having the protective film on one side thereof.
[0162] The optical films obtained in Example 1 were each subjected to corona treatment of 50 dyn / cm and pasted onto the side with...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com