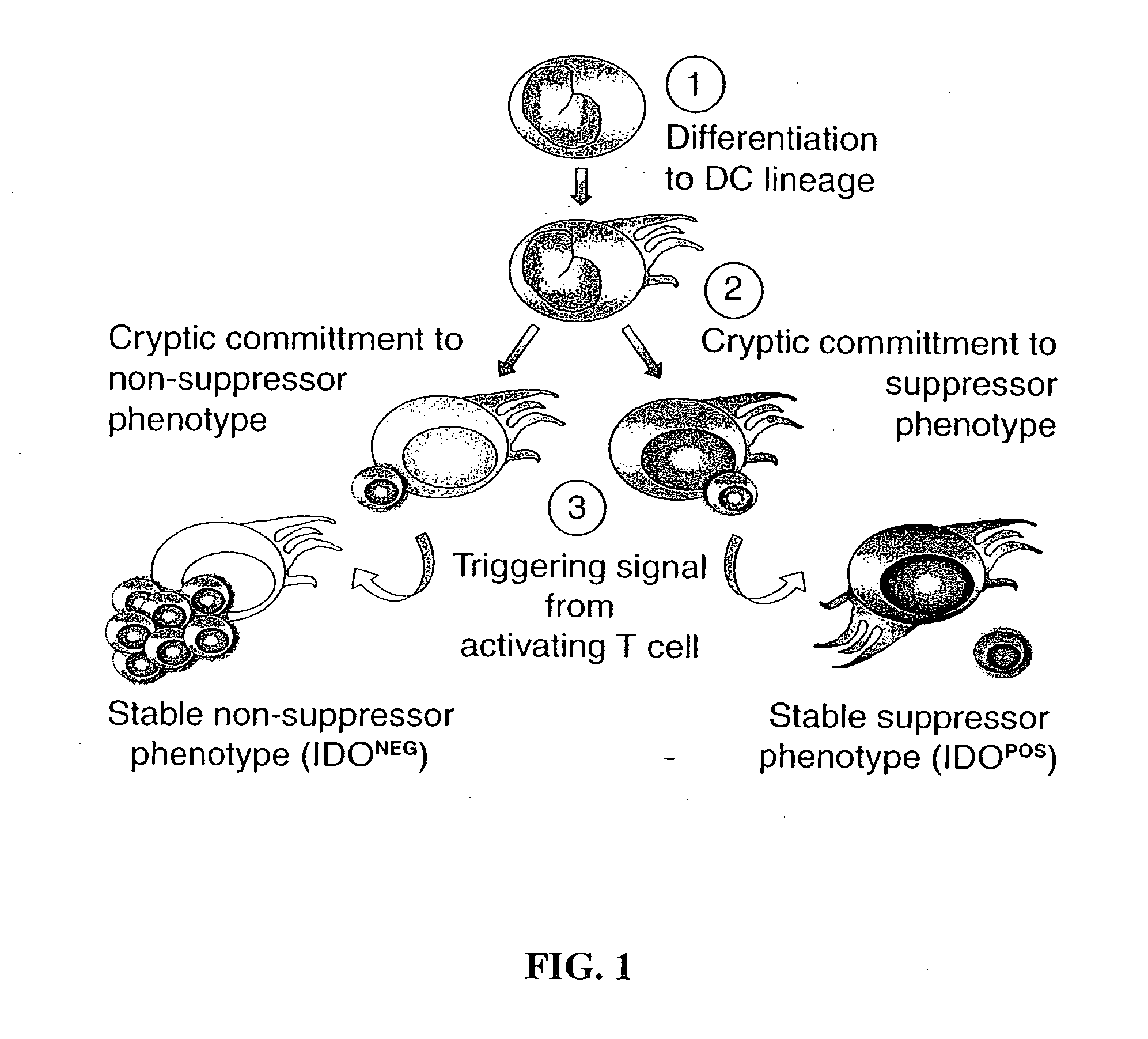
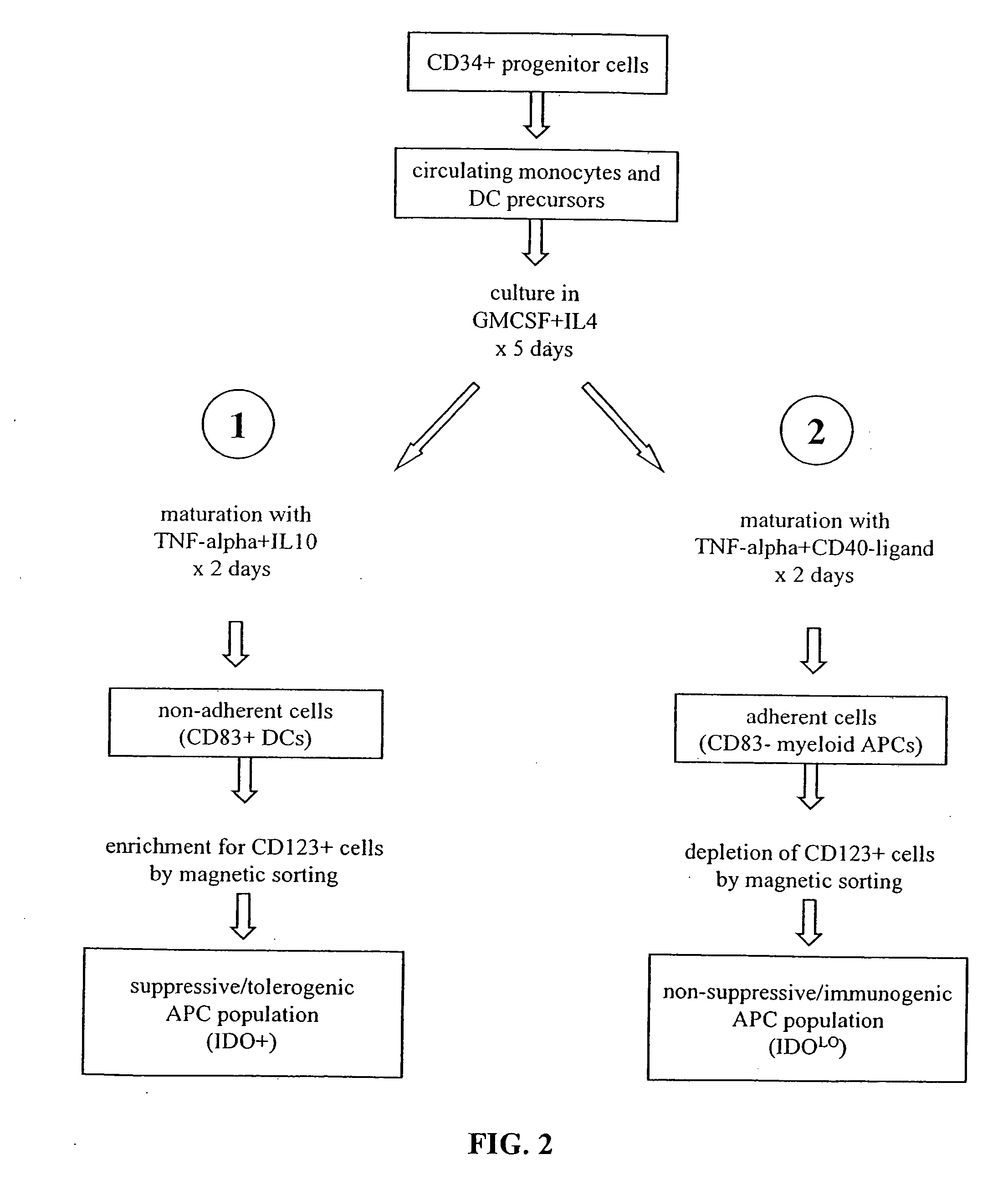
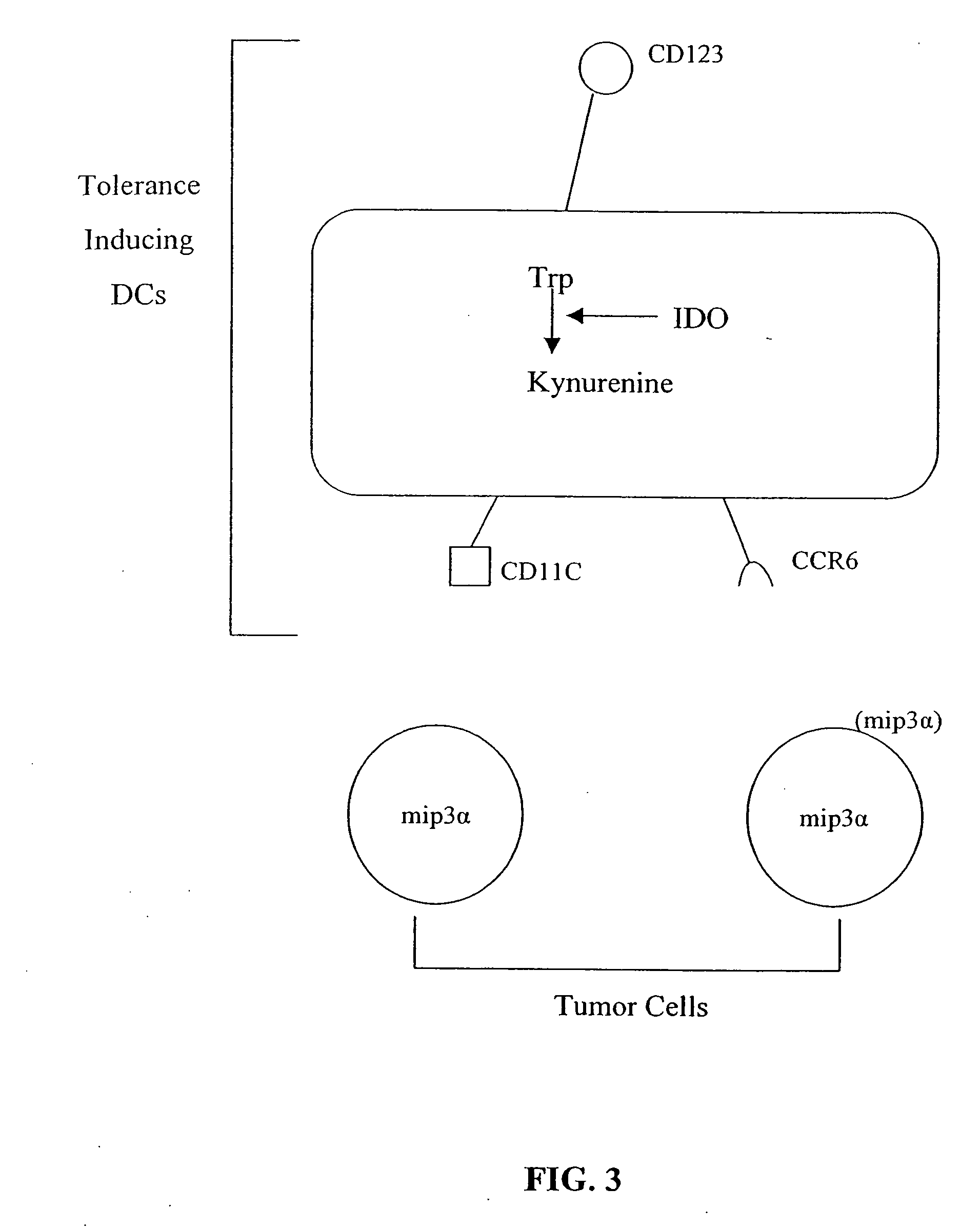
Antigen-presenting cell populations and their use as reagents for enhancing or reducing immune tolerance
a technology of immune tolerance and antigen-presenting cells, which is applied in the field of cell-based pharmaceuticals, can solve the problems of inability to identify these apcs, and the mechanisms they use to induce tolerance, and the molecular mechanism used by immature dcs or other putative tolerogenic apcs to suppress t cell responses, and achieves low expression levels, high expression levels, and low expression levels. ido
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Cell Culture
[0219] Human monocytes and lymphocytes were isolated as separate fractions by leukocytapheresis and counterflow elutriation (D. H. Munn et al., J. Exp. Med. 189, 1363-1372 (1999)). Monocytes (typically >95% purity) were cultured in 100 mm tissue culture petri dishes in RPMI-1640 medium with 10% newborn calf serum (Hyclone) and including penicillin / streptomycin and glutamine. Cultures received either MCSF (200 U / ml, Genetics Institute) on day 0, or GMCSF (50 ng / ml, R&D Systems)+IL4 (50 ng / ml, R&D Systems) on days 0, 2 and 4. For experiments where CCR6 expression was of interest, cultures received a single dose of GMCSF+IL4 (100 ng / ml each) on day 0, with no further supplementation. Loosely adherent dendritic cells (GMCSF+IL4) were harvested by gentle aspiration; adherent macrophages (MCSF) and non-dendritic APCs (GMCSF+IL4) were harvested with EDTA. Other cultures were conducted in serum-free medium (X-vivo 15; BioWhitaker, Walkersville, Md.) plus cytokines.
example 2
Production of Antibodies
[0220] All antibodies were obtained commercially except for polyclonal antiserum against human IDO which was manufactured as a work for hire by ZCB Inc., Hopkinton, Mass. All commercial antibodies and reagents were from BD Biosciences-Pharmingen (San Jose, Calif.) unless specified otherwise. For detection of cell surface antigens, DCs were triple-stained with anti-CD123-biotin (clone 7G3; it was found that clone 9F5 gave suboptimal results with dendritic cells) followed by streptavidin-perCP, plus anti-CD11c-allophycocyanin (clone S-HCL-3) or anti-CCR6-fluorescein (clone 53103.111, R&D systems, Minneapolis, Minn.). CCR6 results were also confirmed using a second anti-CCR6 antibody (clone 11A9; Pharmingen). For detection of IDO, cells were fixed and permeablized (Cytofix / Cytoperm), and then stained with rabbit anti-IDO antibody prepared against the peptide followed by polyerythrin-labeled anti-rabbit secondary antibody (Jackson Immunoresearch, West Grove Pa.)...
example 3
Regulation of IDO Expression During DC Maturation
[0222] In humans DCs, maturation has been associated with loss of tolerogenic activity (Dhodapkar, M. V., et al., J. Exp. Med., 193: 233-238 (2001)). The experiments described in FIG. 4 addressed the issue of whether DC maturation down-regulates IDO mediated suppressor activity. Monocyte-derived DCs were cultured for 7 days in X-vivo 15 medium with GMCSF+IL4 (non-adherent cell population,>95% IDO+, >95% CD123+). During the final two days, the cells were either (A) left as immature DCs (no additions); (B) matured using a cytokine cocktail comprising TNFα, IL1β, IL6 and PGE2 (Jonuleit, H. et al., Eur. J. Immunol., 27: 3135-3142 (1997)); or (C) matured using monocyte-conditioned medium (Reddy, A., et al., Blood 90: 3640-3546 (1997)). Each group was harvested and added to 5×105 allogeneic T cells in V-bottom 96 well microtiter wells in 200 μl medium (10% fetal calf serum in RPMI)). Differing numbers of DCs were added to a fixed number of...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| cell surface | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com