Method for detecting disease-associated mutations
a technology for detecting disease-associated mutations and detecting methods, which is applied in the field of detecting disease-associated mutations, can solve the problems of laborious identification of disease-causing mutations, and achieve the effect of prolonging the life of patients and improving the chance of being diagnosed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
The Detection of a Missense Mutation in the β Cardiac Myosin Heavy-Chain Gene in Members from Family A and Family OO
General Methodology
Cell Lines and DNA and RNA Extraction
[0046] Blood was drawn from members of Family A and normal control subjects. The blood samples were used to prepare DNA from red-cell pellets (Gross-Bellard et al., Eur. J. Biochem. 36:32-8 (1973)) and to establish lymphoblastoid cell lines (Holcombe et al., Genomics 1:287-91 (1987)). RNA was prepared from fresh peripheral-blood mononuclear cells or Epstein-Barr virus-transformed cell lines by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction (Chomczynski et al., Anal. Biochem. 162:156-9 (1987)).
PCR and Restriction Enzyme and Sequence Analysis
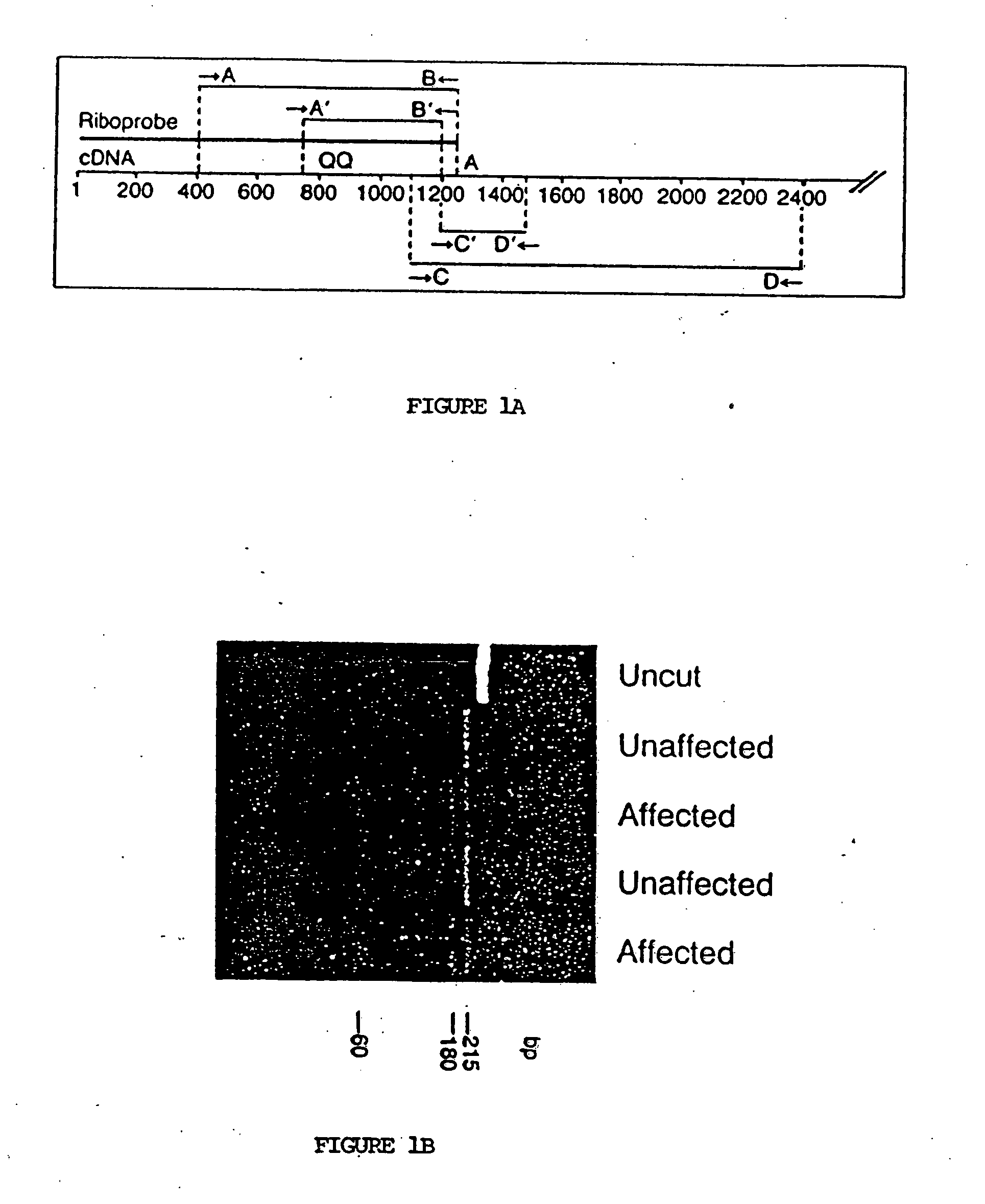
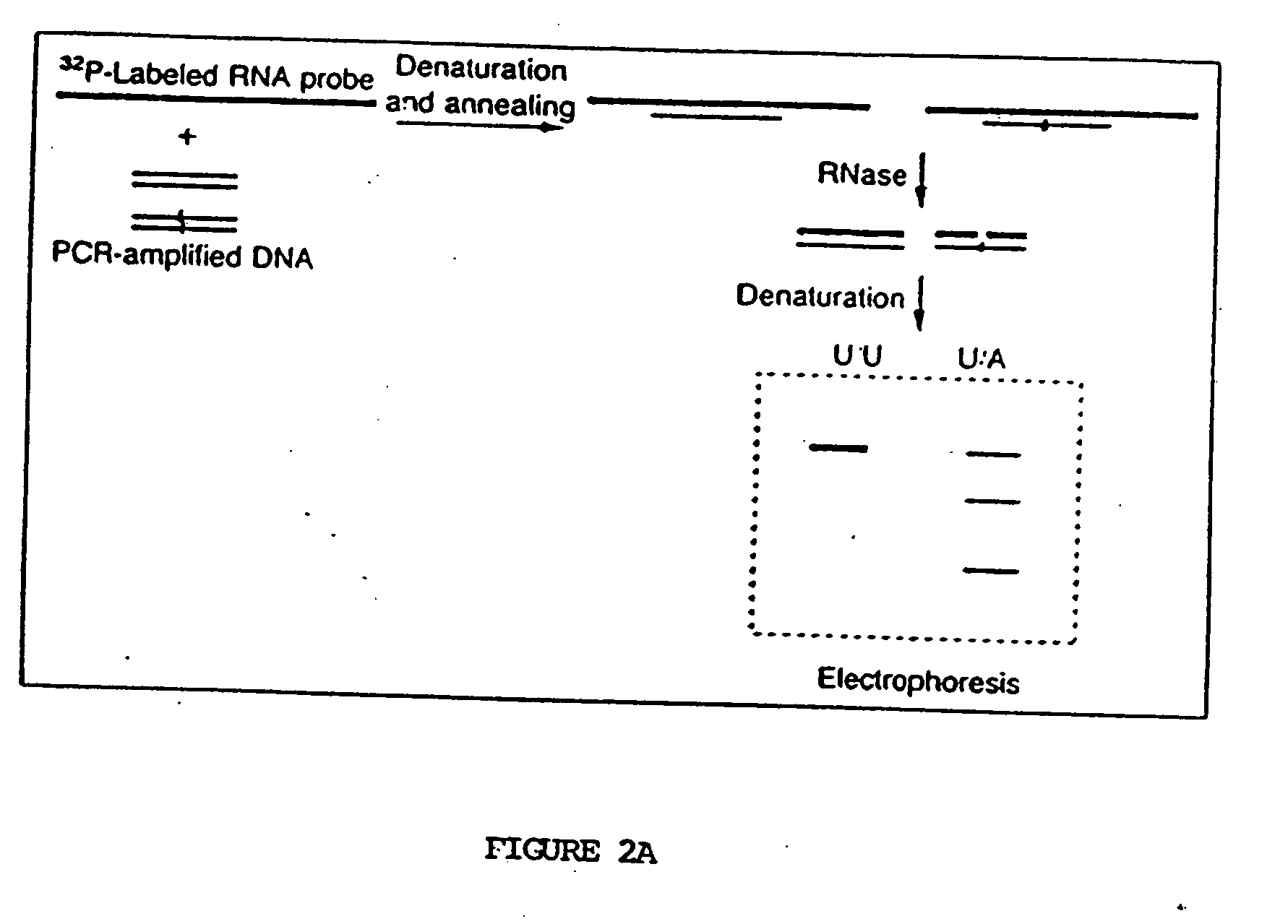
[0047] Nested PCR (Sarkar et al., Science 244:331-4 (1989)) was used to amplify β cardiac myosin heavy-chain RNA from fresh peripheral-blood mononuclear cells and cell lines transformed by Epstein-Barr virus (see FIG. 1A). One to 2 μg of total RNA was reverse-t...
example 2
Determination of the Proportion of Families with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Caused by Myosin Heavy-Chain Mutations
[0066] Twenty-five families were studied whose members have hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Preliminary research had indicated that major structural abnormalities of the α or β cardiac myosin heavy-chain genes are not a common cause of FHC. RNase protection assays therefore were used to screen directly for point mutations or other small alterations in the β cardiac myosin heavy-chain gene which encodes the predominant isoform of myosin expressed in the ventricles of adults (Mahdavi et al., Nature 297:659-64 (1982); Lomprei et al., J. Biol. Chem. 259:6437-46 (1987)). The following general methodology was used in the example below.
[0067] The affected members of these twenty-five families have features typical of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy as assessed by physical examination, two-dimensional Doppler echocardiography and electrocardiography. The disease was inherited as an ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com