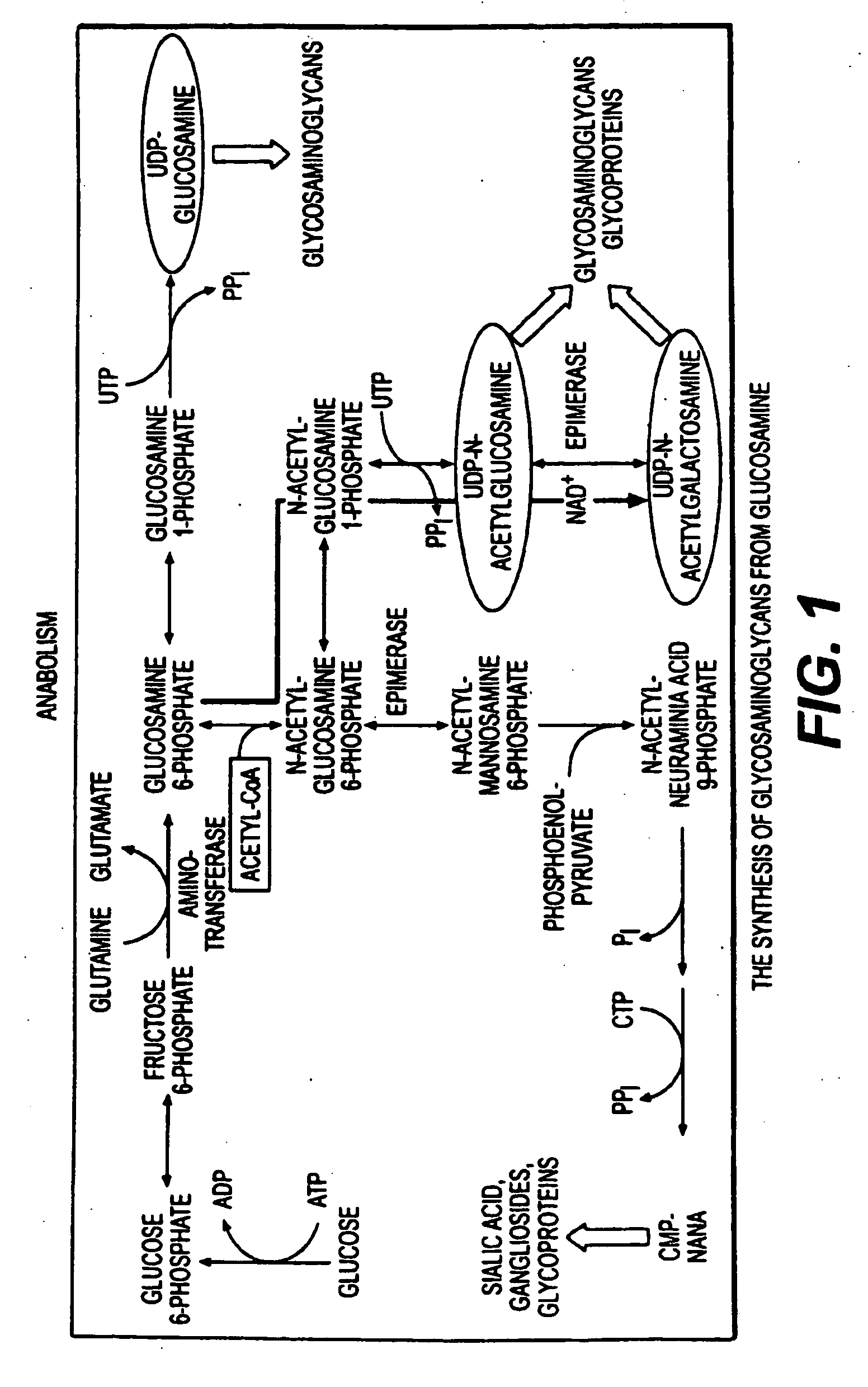
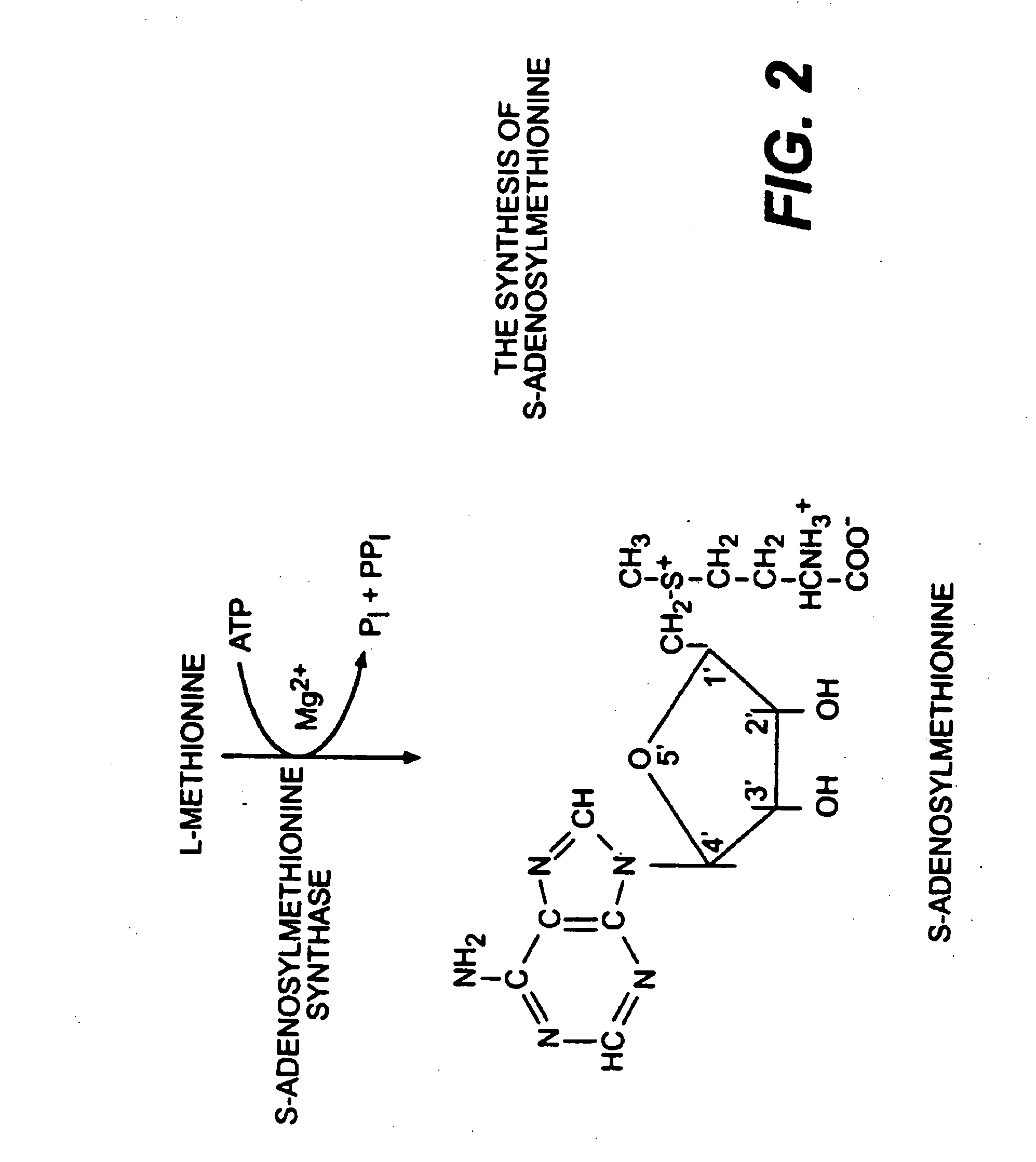
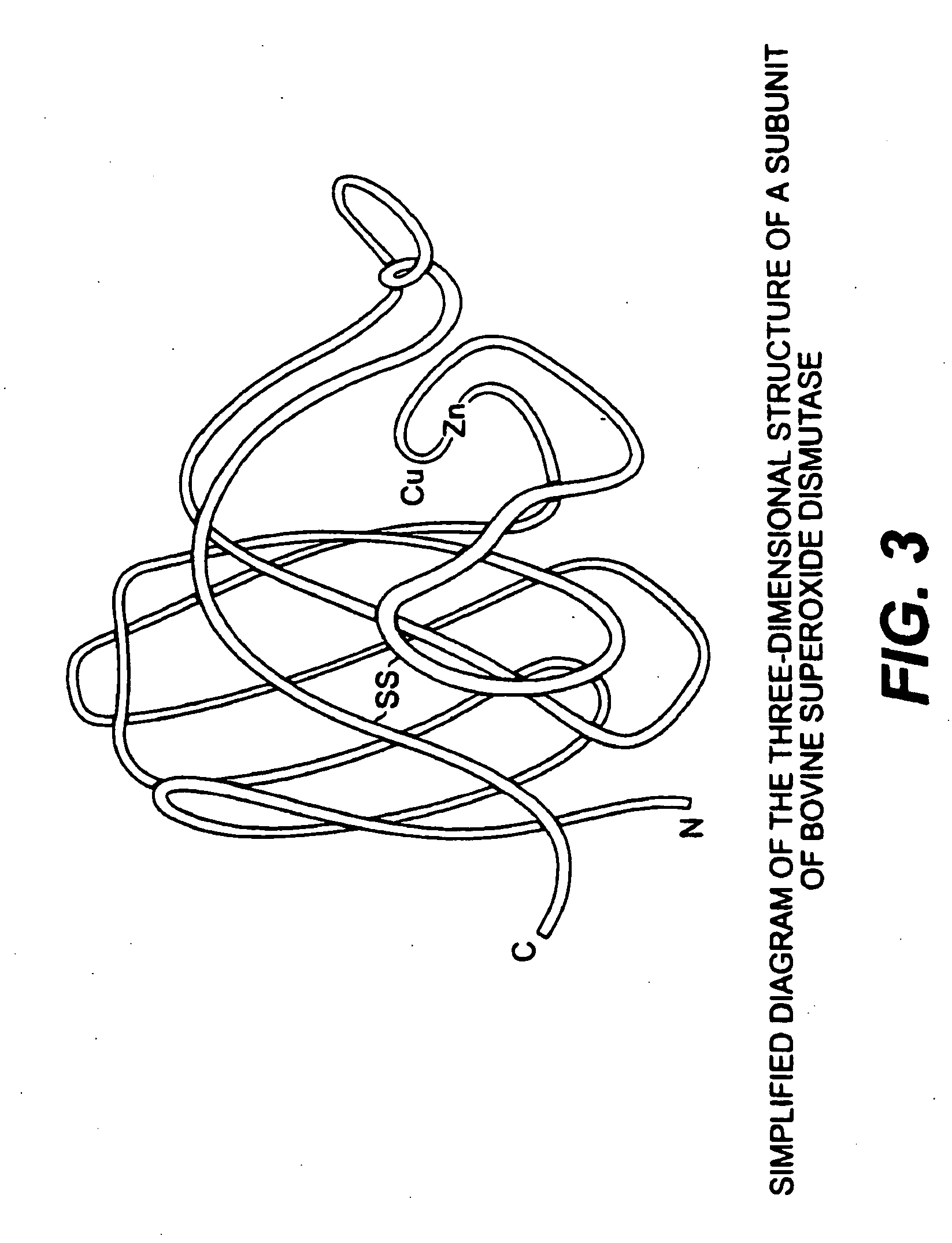
Use of anabolic agents, anti-catabolic agents, antioxidant agents, and analgesics for protection, treatment and repair of connective tissues in humans and animals
an anabolic agent and anti-catabolic agent technology, applied in the field of compositions, can solve the problems of reducing the production of extracellular matrix components, affecting the healing effect, and not easily categorized as strictly anabolic, so as to prevent damage to connective tissue, treat, and repair
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0105] In our preliminary investigations, surgical instability was induced in the stifle joint of New Zealand white rabbits by modification of the Hulth technique. Post-operatively, animals were exercised for 1 hour daily. Experimental dietary formulas were evaluated for their cartilage stabilizing effect. The standard Harland (Teklad) rabbit diet (control); a standard diet also containing a 2% fungal oil containing 40% AA by weight (Arasco); and a standard diet containing also arachidonic acid and glucosamine / chondroitin were investigated. At 16 weeks, the medial femoral condyles of all rabbits were removed and cartilage degeneration quantitatively evaluated with a modified Mankin histological-histochemica-1 grading system with safranin-O stained slides. Cartilage from all joints with surgical instability exhibited varying degrees of macroscopic degenerative lesions. Our preliminary results indicated that adding arachidonic acid to glucosamine / chondroitin sulfate has the potential ...
example 2
[0106] Procedure:
[0107] Articular cartilage was resected from human or animal joints aseptically and placed into a large petri dish in a small amount of DMEM / F-12 or F-12. The tissue was diced to 1-2 mm dimensions and transferred to a small culture flask containing 20 mL DMEM or F-12+400 u / mL collagenase. The flask was placed on the shaker and incubated overnight.
[0108] The cell digest was repeatedly aspirated to increase release of cells. The cell digest was then placed into a 50 mL sterile centrifuge tube and centrifuged in the Beckman at 1000 RPM for 10 minutes. The medium was discarded by pipette and fresh DMEM / F-12 containing 1% FCS added. Depending on the size of the pellet, about 2040 mL medium was added. Cell counts were determined by haemocytometer and the digest made up to a concentration of 100,000 cells / 0.2 mL.
[0109] GAG Synthesis:
[0110] To conduct GAG synthesis, 0.2 mL was aliquoted into each well of a 96 well plate using an 8 channel pipetter and the cells allowed ...
example 3
[0114] A 4 year old child has juvenile rheumatoid arthritis in which the immune system inappropriately targets endogenous connective tissues with antibodies against native collagen type II. The resulting inflammation and degradation of cartilage causes pain and dysfunction in the synovial joints. Present treatments include corticosteroids which non-selectively suppress the immune system, thus leaving the body vulnerable to infectious disease, or methotrexate, which inhibits DNA synthesis, repair, and cellular replication, thus affecting not only the immune system but also intestinal mucosa, and the bone marrow. This child is given 2 mg of collagen type II daily, and SOD 10 mg daily. The collagen decreases the inappropriate immune attack, and the SOD inactivates destructive free radicals that damage cells. By preventing cellular damage, the SOD helps maximize the normal function of joint tissue cells. This combination has no harmful side effects at therapeutic doses and is a benefici...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com