Convective earrh coil
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
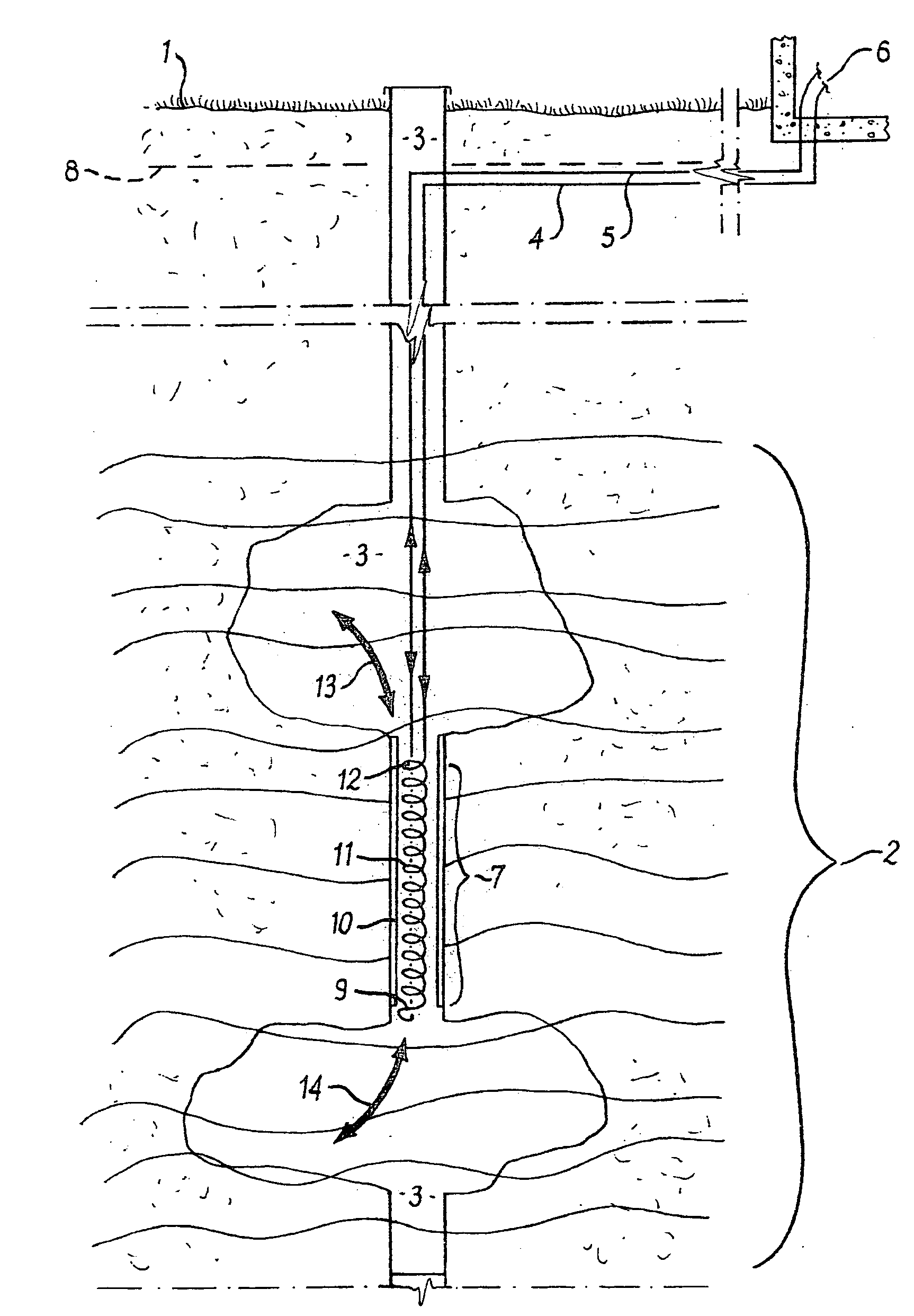
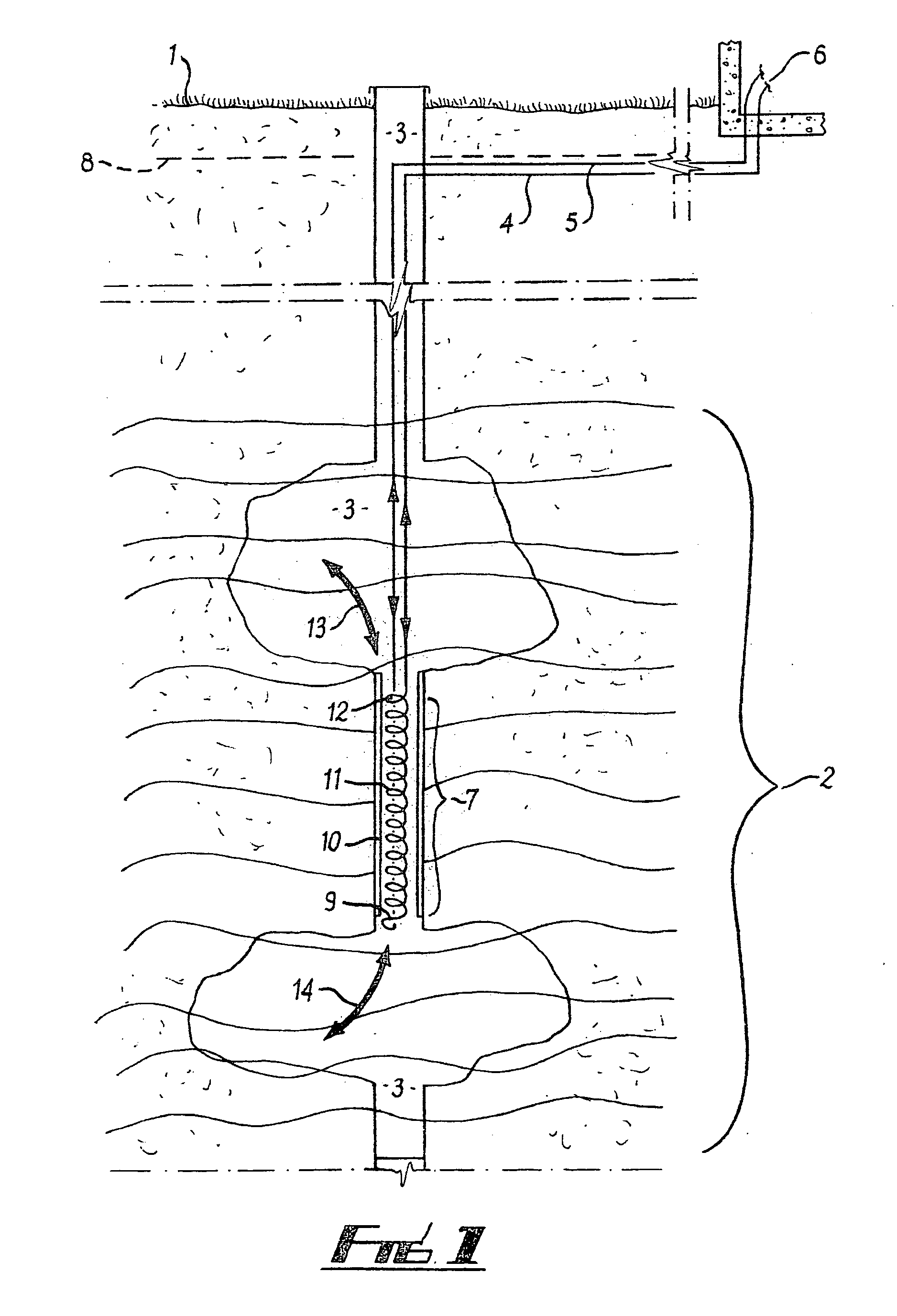
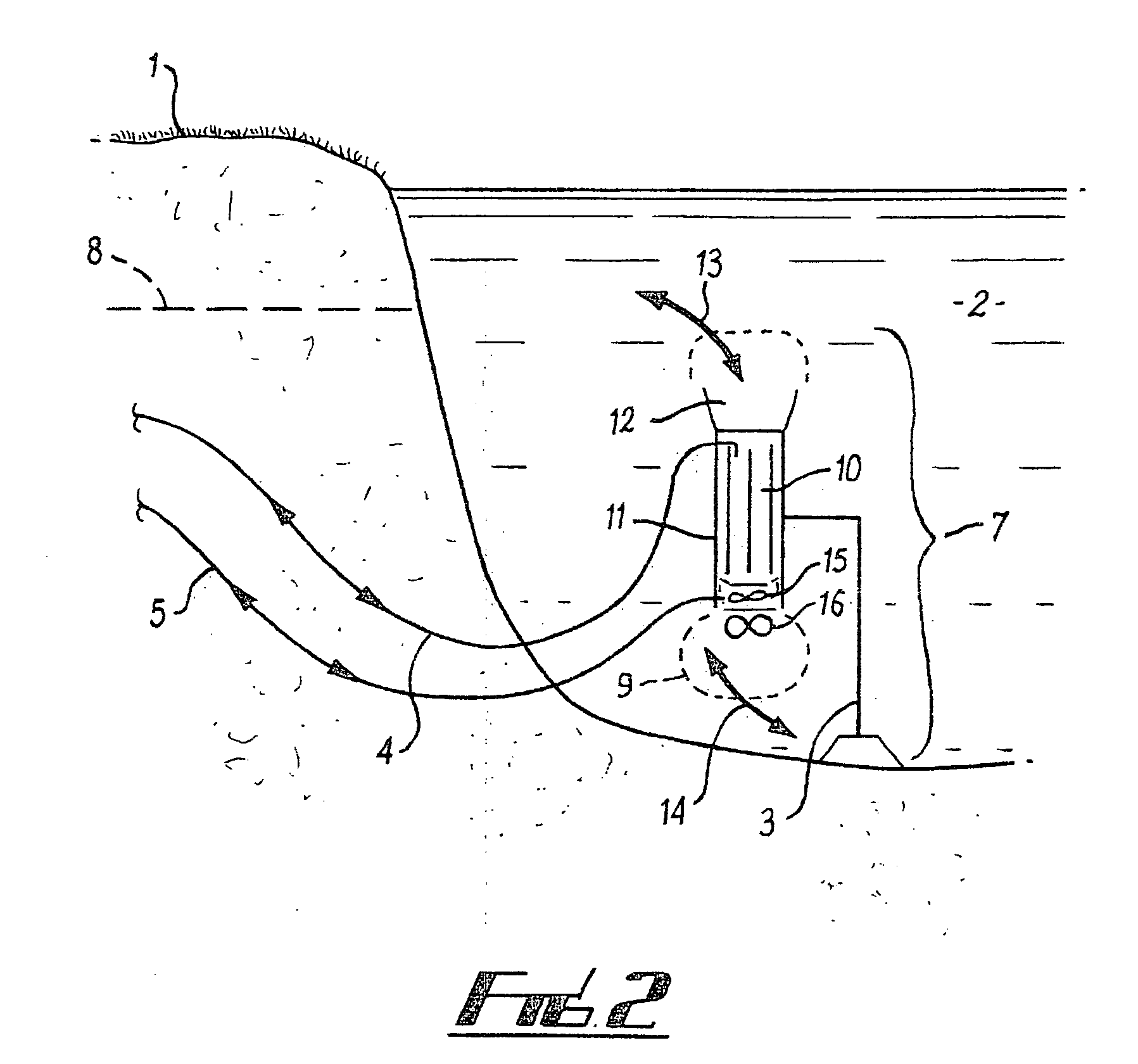
[0040]Referring to FIG. 1, a portion of an aquifer some depths below the earth surface 1 is generally shown by reference numeral 2. A well 3 is drilled from the earth surface 1 until it reaches the desired aquifer 2. Pipes 4 and 5 for supplying and returning the heat transfer fluid from the thermal load 6 to the convective earth coil 7 are run below the earth's surface 1 (preferably below the frost line 8) to the well 3, and down the well 3 to the convective earth coil 7. In FIG. 1, the convective earth coil 7 is generally comprised of inlet 9, a vertical chamber 10, a convective heat exchanger 11, and a discharge outlet 12. In FIG. 1 the convective heat exchanger 11 is represented as a spiral tube within a tube.
[0041]The convective earth coil can be used to inject heat into the ground or extract heat energy from the ground. In the illustrated embodiment, in operation in the heat injection mode, warm heat transfer fluid flows from the thermal load 6 through pipe 4 into the top porti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com