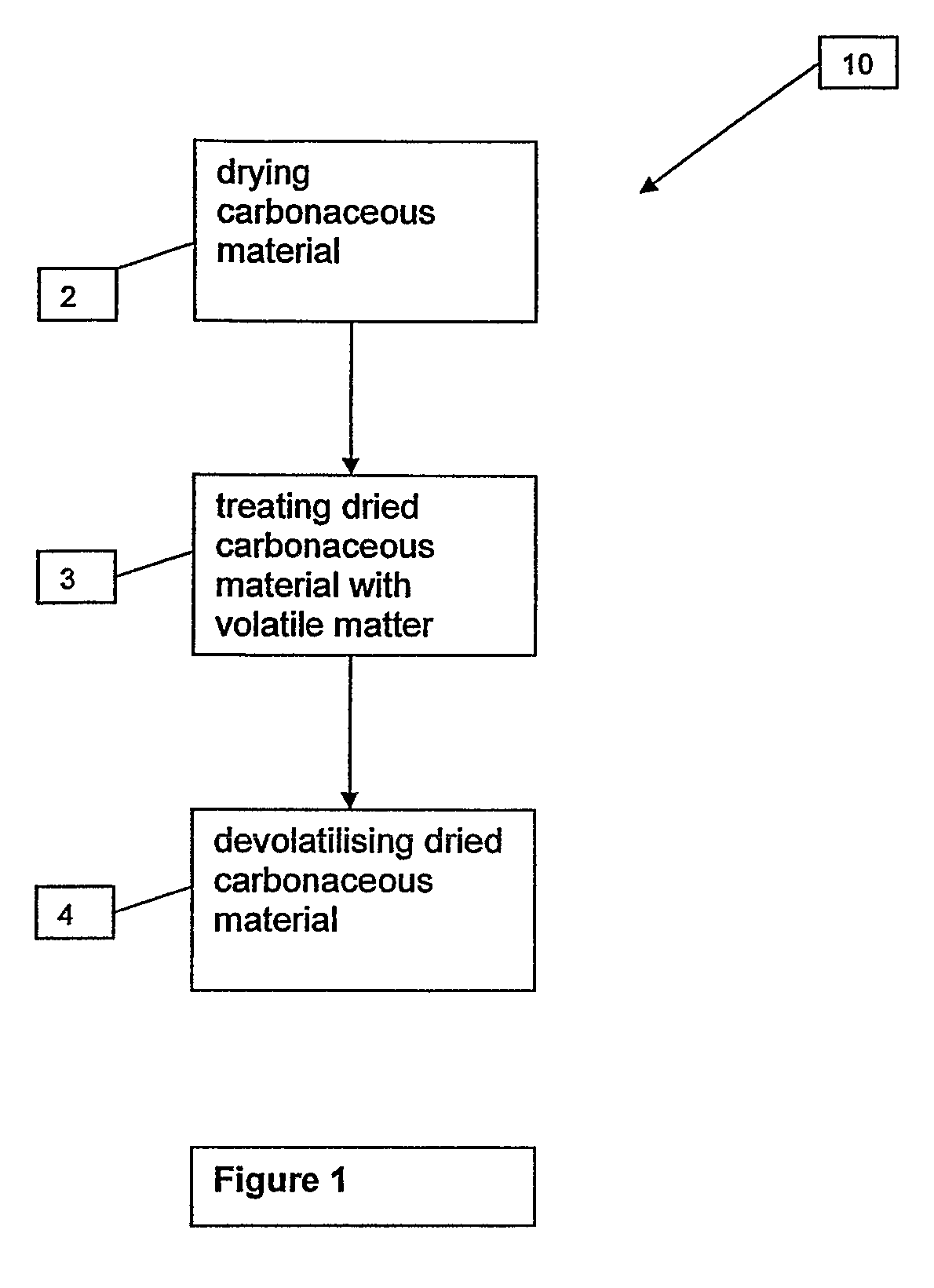
Process, system and apparatus for passivating carbonaceous materials
a carbonaceous material and passivating technology, applied in the direction of chemistry apparatus and processes, combustible gas coke oven heating, fuels, etc., can solve the problems of high cost of coatings, other dried carbonaceous materials, and so as to improve the high calorific content of coal gas. , the effect of high calorific conten
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
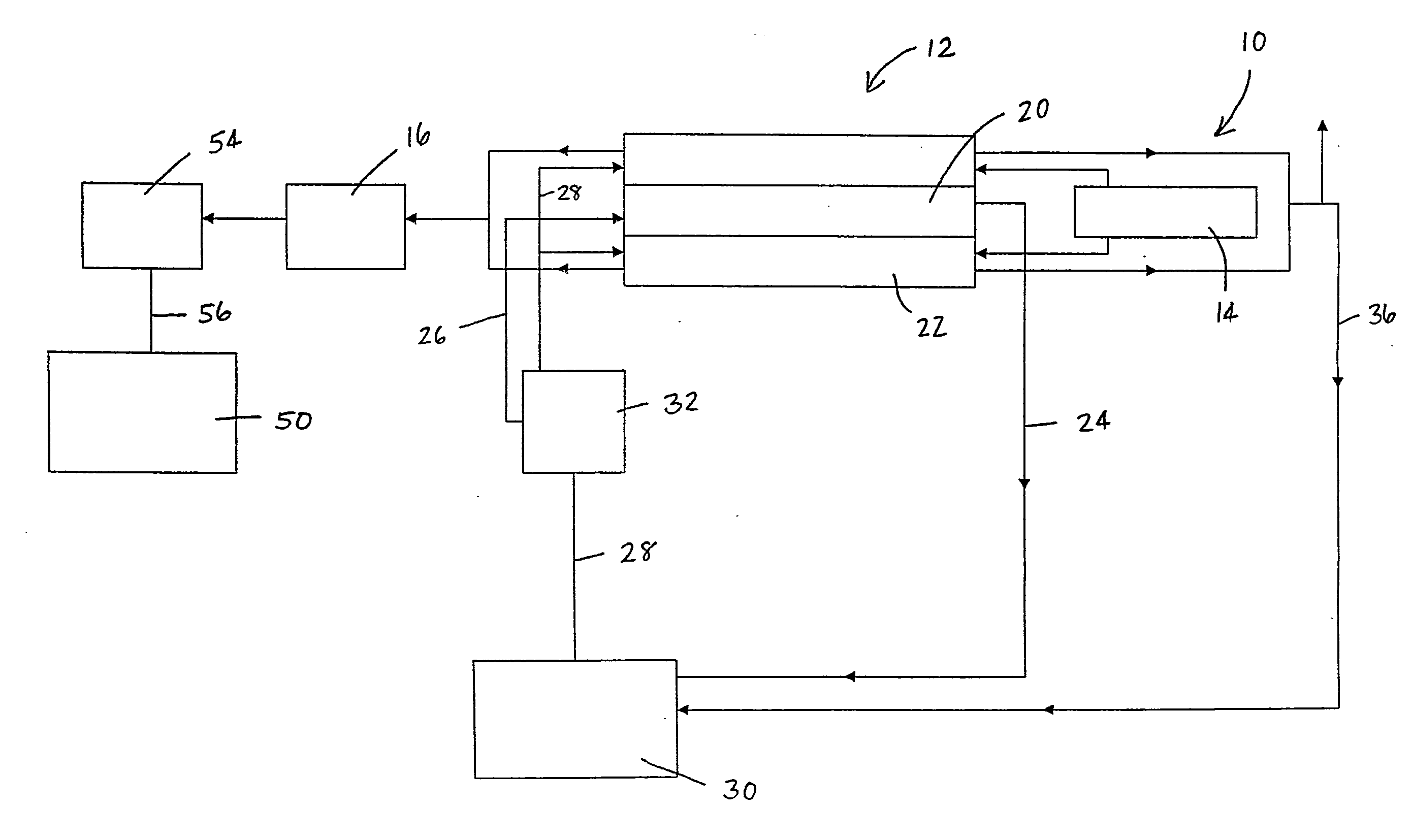
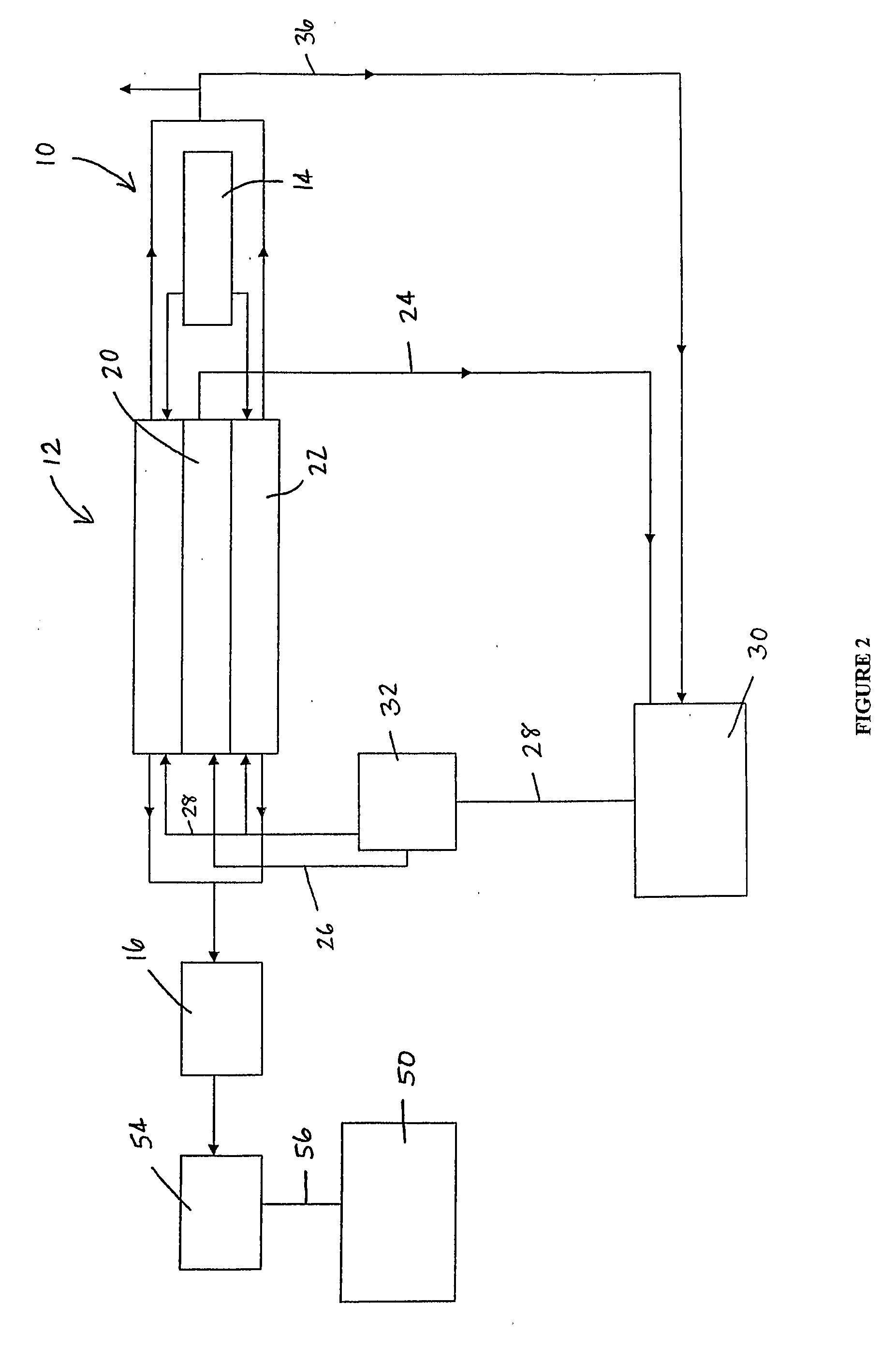
[0152]Crushed coal from the Ewington mine in Western Australia (100%-15 mm) at 28% moisture is fed at 49 tph to a 16.5-m long five cell fluidised bed dryer. The coal in the fluidised bed dryer is heated with a flow (28,500 kg / h) of waste gas containing 1.6% (m / m) O2 at temperatures of 800° C. produced in a 10 MW burner. The coal feed stream has a residence time of 9 to 10 minutes in the dryer. The last cell of the dryer is heated by the off gas generated from the pyrolising means in this system.
[0153]Hot (150° C.) dry coal is fed to a 13.2-m long refractory lined carboniser via a gas lock feeder. The dried coal is heated to 1,300° C. These high temperatures are generated by feeding hot air (800° C.) to the carboniser which combusts with some of the coal gas evolved during pyrolisis. The coal gas flows in a counter-current direction to the flow of the coal / char feed stream. The total residence time of the char feed stream held above 900° C. is between 11 and 12 minutes. Approximately...
example 2
Trial Data
[0156]Collie coal, with 24% moisture, was pre-dried in an oven under nitrogen at 120° C. This coal was then heated at 5° C. / min until it reached 300° C. The mass lost was 0.6% and the equilibrium moisture was 6.5%. The same dried coal was placed in an oven for 10 minutes at 400° C. The resulting mass loss was 2.6% and the equilibrium moisture was 4.5%. The feed coal typically has an equilibrium moisture of about 13%.
[0157]A large scale trial was performed using a rotary kiln with recycled coal gas and air dried coal. The results are presented below in Table 1. The coal residence time was 20 minutes to heat the coal to an average discharge temperature of 266° C.
TABLE 1Low Temperature Carbonized CoalTotalVola-SpecificMois-tileFixedEnergytureLevelAshCarbonSulfurMJ / kgfeed coal (gar)25.5%27.2%3.60%43.7%0.55%21.28feed coal (db)36.5%4.83%58.7%0.74%28.56carbonised 8.5%26.0% 5.5%60.0%0.66%27.4coal (gar)carbonised28.4% 6.0%65.7%0.72%29.2coal (db)
[0158]The overall yield was 65.6% on ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com