Polyamic acids dope composition, preparation method of hollow fiber using the same and hollow fiber prepared therefrom
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0121]As depicted in Reaction Scheme 3 below, a hollow fiber comprising polybenzoxazole represented by Formula 41 are prepared from the polyhydroxyamic acid-containing dope solution.
[0122](1) Preparation of Polyhydroxyamic Acid
[0123]36.6 g (0.1 mol) of 2,2′-bis(3-amino-4-hydroxyphenyl)hexafluoropropane and 44.4 g (0.1 mol) of 4,4′-(hexafluoroisopropylidene)diphthalic anhydride were added to 189 g (70 wt %) of N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP) and were allowed to react at 15° C. for 4 hours to prepare a pale yellow viscous polyamic acid.
[0124](2) Preparation of Dope Solution
[0125]Without removing the solvent, 5% by weight of tetrahydrofurane as an additive was added to the NMP containing polyamic acid and then mixed to prepare a homogeneous dope solution.
[0126](3) Preparation of Hollow Fiber
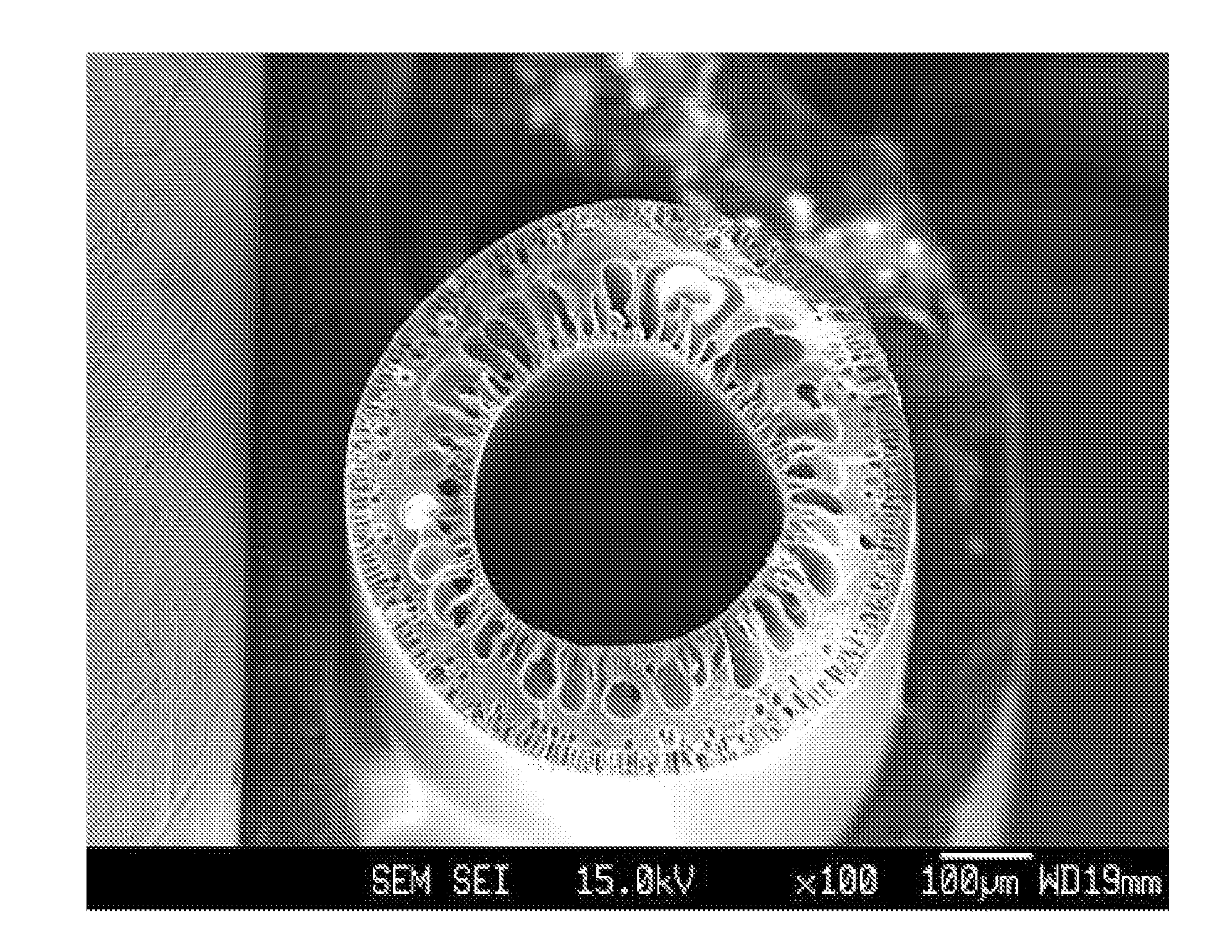
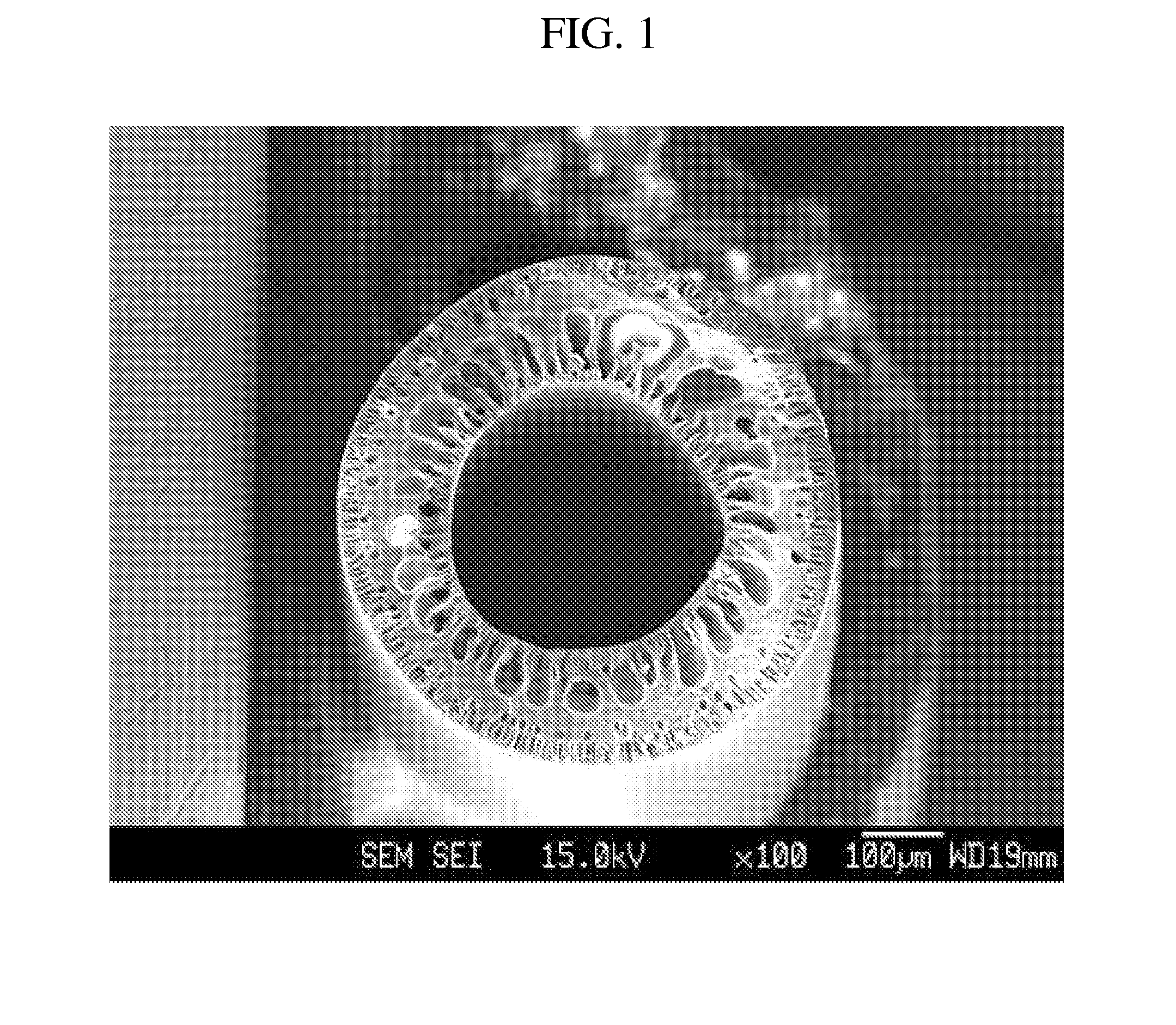
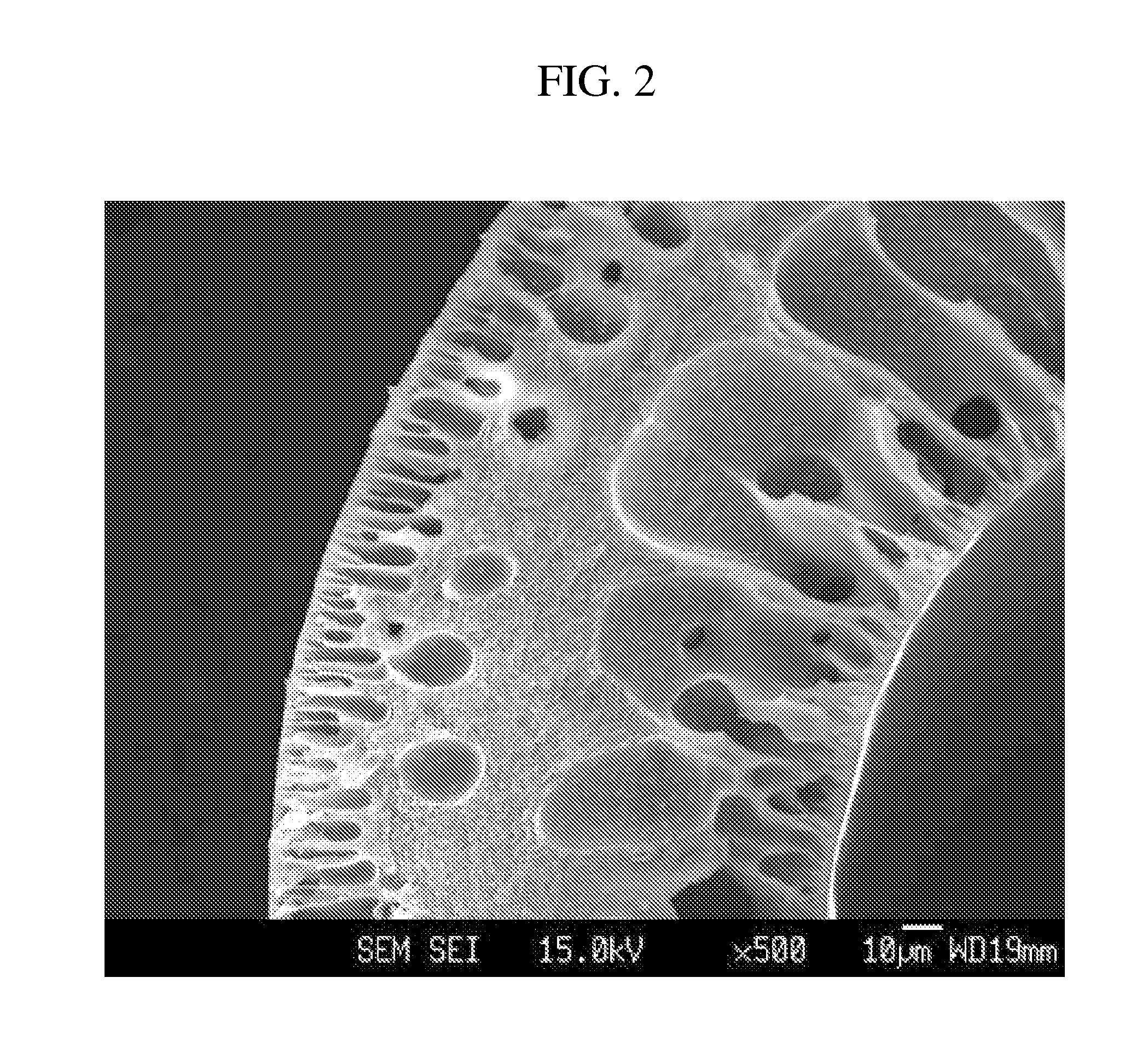
[0127]The dope solution thus prepared was defoamed at ambient temperature under reduced pressure for 24 hours, and foreign materials were removed using a glass filter (pore diameter: 60 μm). Subsequently,...
example 2
[0129]A hollow fiber comprising polybenzothiazole represented by the following Formula 42 was prepared from the polythiolamic acid-containing dope solution through the following reactions.
[0130]A hollow fiber thermally rearranged into polybenzothiazole represented by Formula 42 was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1, except that 20.8 g (0.1 mol) of 2,5-diamino-1,4-benzenedithiol dihydrochloride and 44.4 g (0.1 mol) of 4,4′-(hexafluoroisopropylidene)diphthalic anhydride as starting materials were reacted to prepare thiol group (—SH)-containing polyamic acid.
[0131]The hollow fiber thus prepared had a weight average molecular weight of 14,500 Da. As a result of FT-IR analysis, characteristic bands of polybenzothiazole at 1,484 cm−1 (C—S) and 1,404 cm−1 (C—S) which were not detected in polyimide were confirmed.
example 3
[0132]A hollow fiber comprising polybenzopyrrolone represented by Formula 43 was prepared from the polyaminoamic acid-containing dope solution through the following reactions.
[0133]A hollow fiber thermally rearranged into polybenzopyrrolone represented by Formula 43 was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1, except that 21.4 g (0.1 mol) of 3,3′-diaminobenzidine as a starting material was reacted with 44.4 g (0.1 mol) of 4,4′-(hexafluoroisopropylidene)diphthalic anhydride to prepare an amine group (—NH2)-containing polyamic acid.
[0134]The prepared hollow fiber had a weight average molecular weight of 18,000 Da. As a result of FT-IR analysis, characteristic bands of polybenzopyrrolone at 1,758 cm−1 (C═O) and 1,625 cm−1 (C═N) which were not detected in polyimide were confirmed.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com