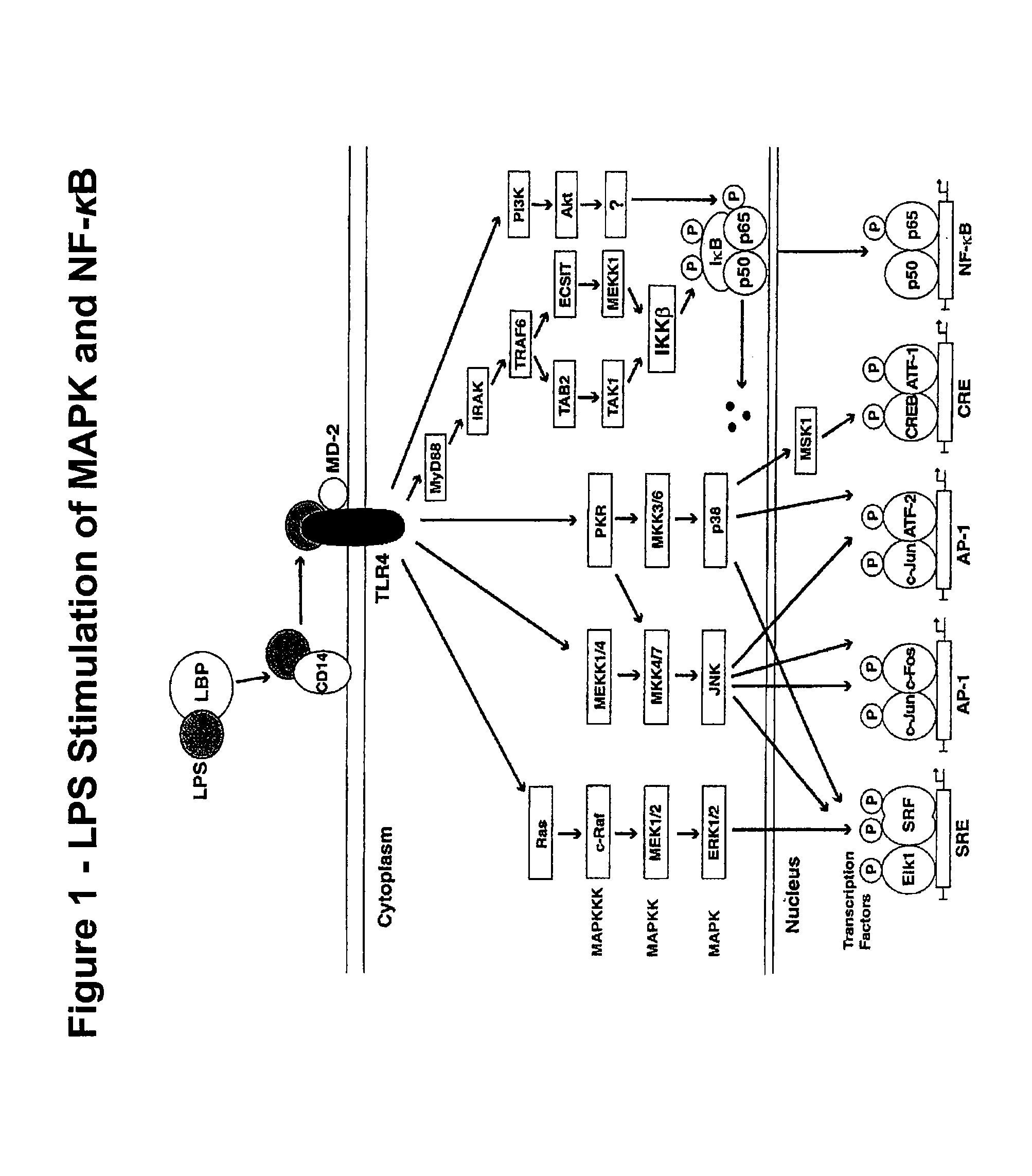
Pan-Kinase Activation and Evaluation of Signaling Pathways
a signaling pathway and activation technology, applied in the field of pankinase activation and evaluation of signaling pathways, can solve the problems of cumbersome assays and lack of sensitivity, and achieve the effect of small sample size and increased specificity and sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Protocol for LPS Activation of MAPK Signaling in Whole Blood Samples
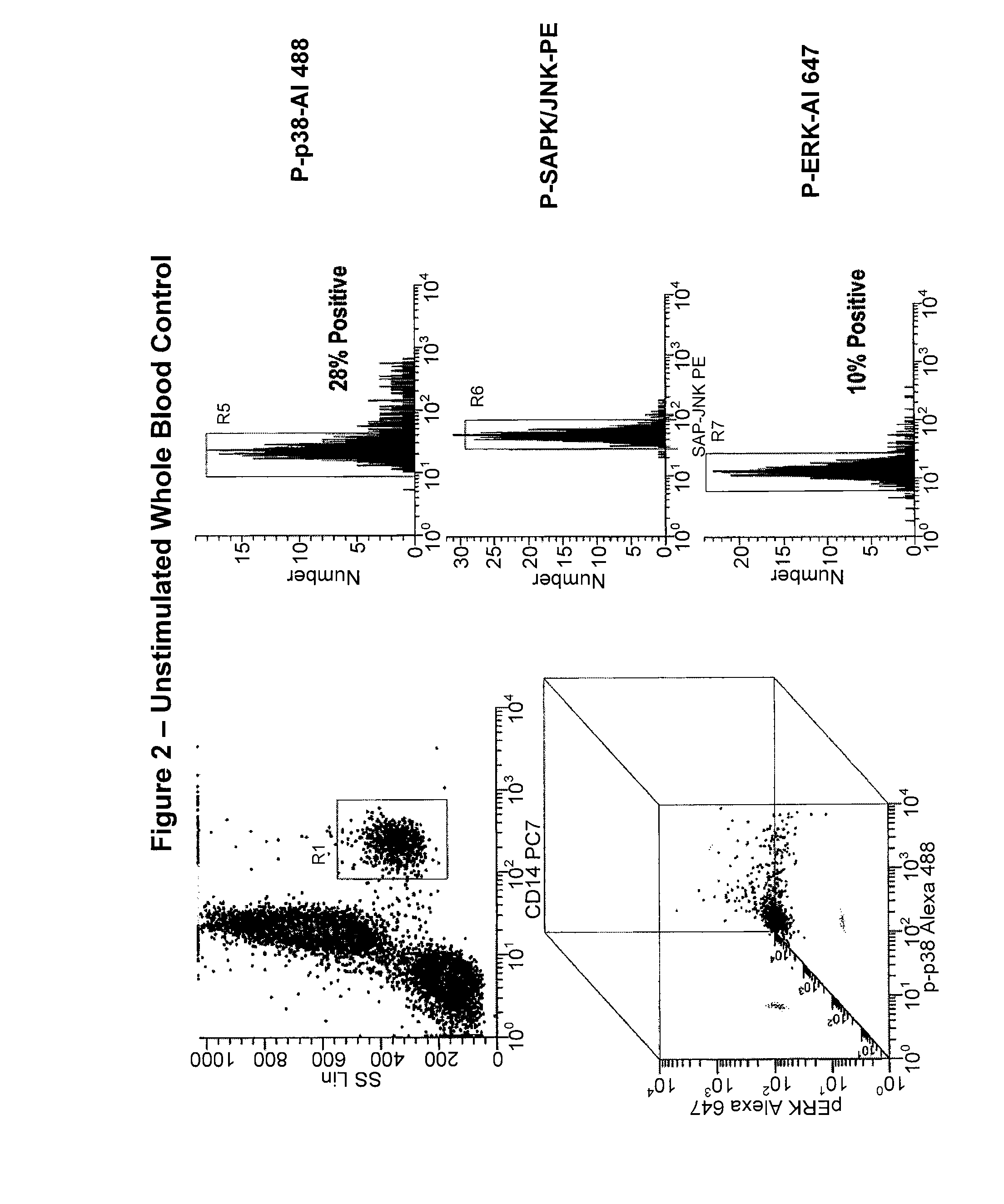
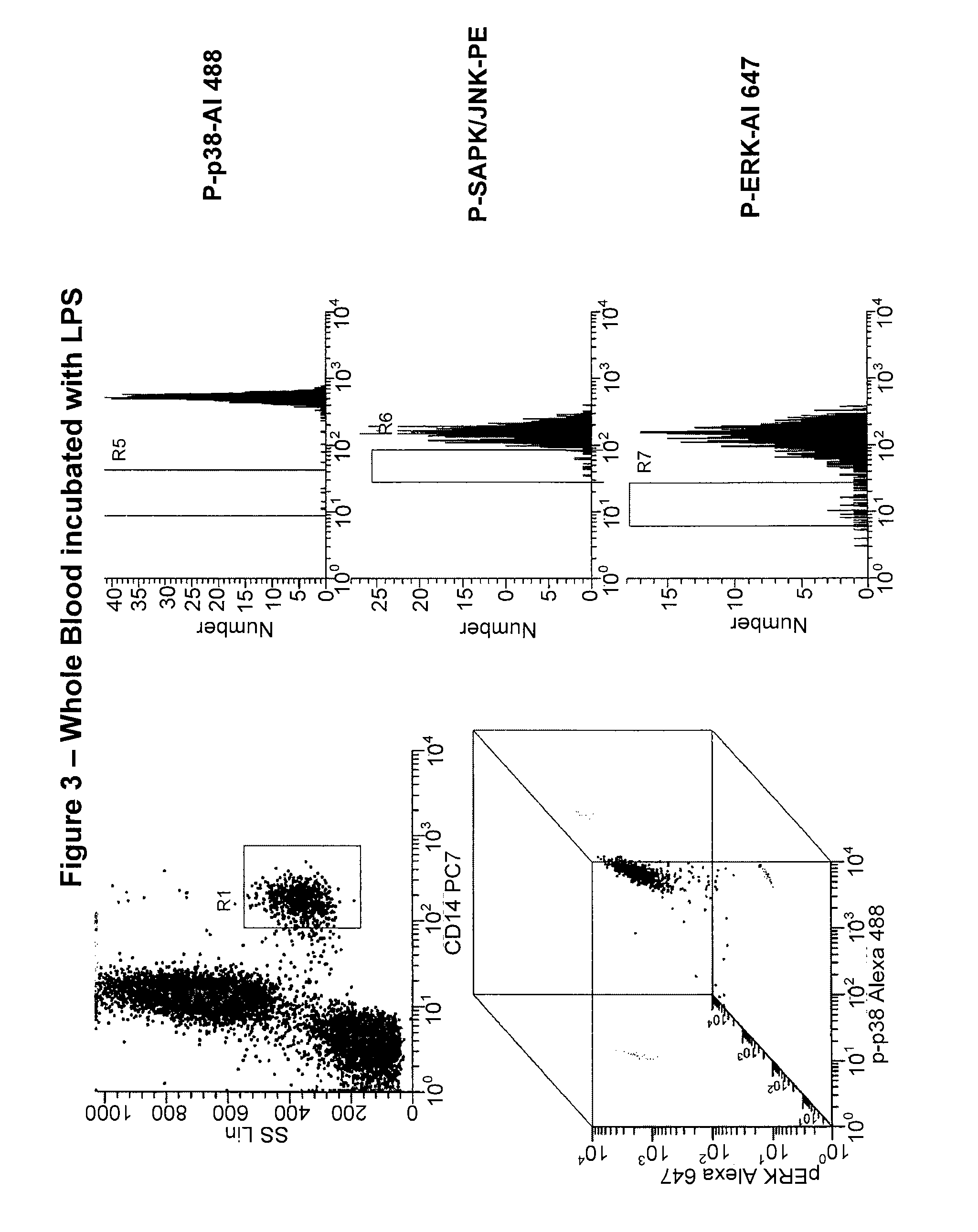
[0178]100 μl of blood was inserted into the bottom of 12×75 mm tubes. Blood was removed from the side of tube with cotton swab to eliminate potential contamination of the sample with unfixed cells. 100 ng lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was added to activation tubes (or equal volume of phosphate buffered saline (PBS) to control tubes) and the tubes were placed in a 37° C. water bath.
[0179]After various incubation times (e.g. 1 minute to 60 minutes, the first tube was removed from the incubator and 65 ul 10% formaldehyde was added into tube. The tubes were mixed and placed in a rack and incubated at room temperature. After exactly a 10 minute incubation with formaldehyde, 1 ml Lyse / Permeabilization Buffer (585 μl Triton X-100 10% stock solution to 500 ml with PBS. 0.1165% Triton X-100 solution at room temperature in the dark and pre-heated to 37° C. immediately prior to use.) was added to each tube, vortexed vigorously and ...
example 2
Flow Cytometry Based Sepsis Assay
[0185]In this study, a simultaneous measurement of four different signaling phospho-epitopes, which include P-ERK, P-p38 MAP Kinase, P-SAPK (Stress-Activated Protein Kinase), and P-S6 ribosomal protein (a measurement of new polypeptide synthesis), was conducted. This assay employed a measurement of the time course of LPS activation, in both “naïve” whole blood, and whole blood samples previously exposed to LPS activation (“re-activated”). This assay also employed the fixation and permeabilization approach described above to measure both cell surface (CD14 to identify monocytes) and cytoplasmic or nuclear localized phospho-epitopes (P-ERK, P-p38, P-SAPK, and P-S6). This assay also employed an internal negative control to analyzing the data, relying on populations, rather than isotype controls, and measuring changes in MFI (mean fluorescence intensity) rather than percent positive.
[0186]The results from this study for each individual marker is presente...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com