Synthetic Surfaces for Differentiating Stem Cells into Cardiomyocytes
a stem cell and cardiomyocyte technology, applied in the field of cell culture articles, can solve the problems of immune response, hesc-based treatment development is hindered, biological products are vulnerable to batch variation, etc., and achieve the effects of improving shelf life, and reducing potential contamination issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Coating Preparation
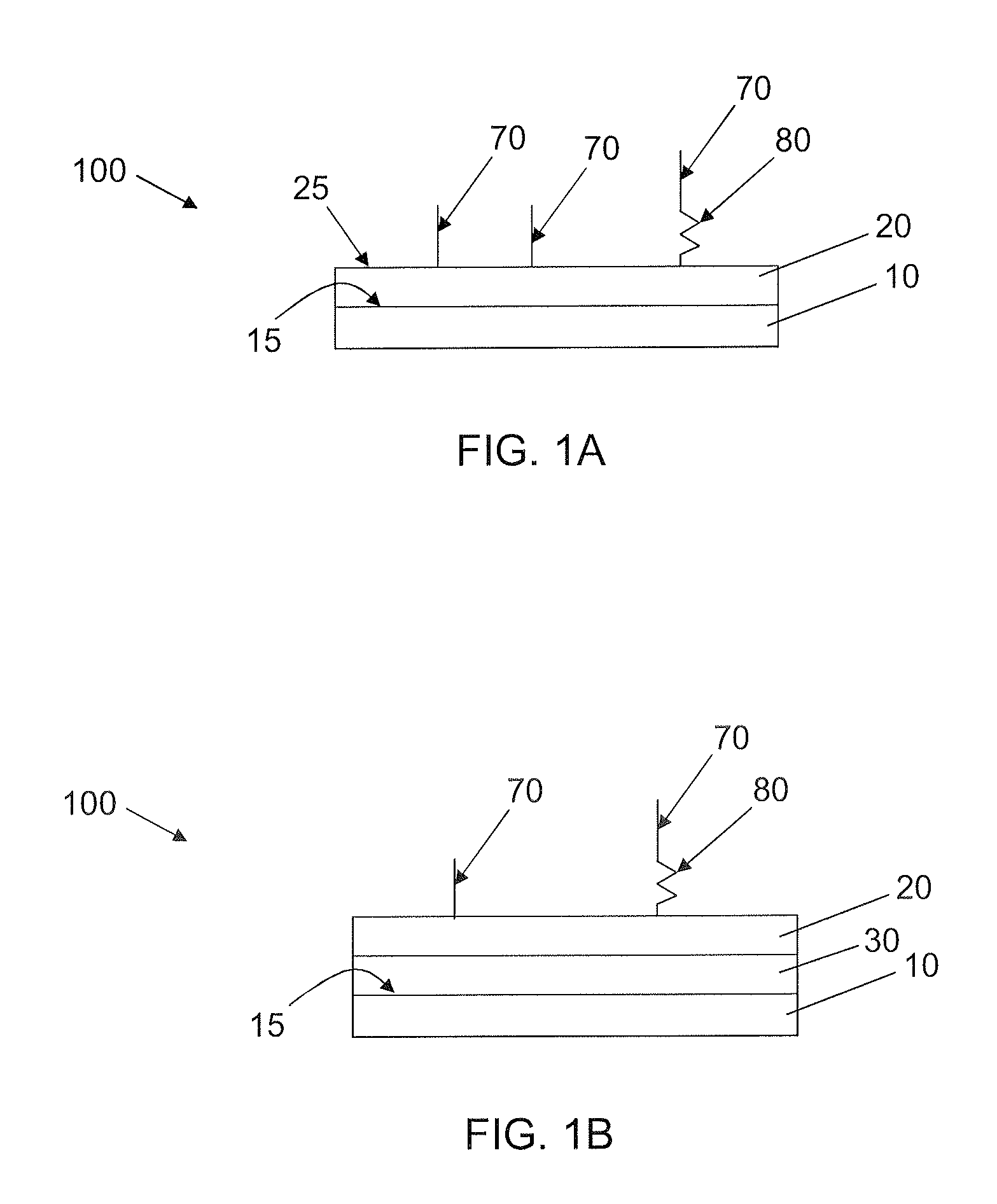
[0109]Swellable (meth)acrylate coating surfaces were prepared from UV polymerizable monomers and include a hydrophilic monomer, a carboxyl group containing monomer, and a crosslinking monomer. Table 1 shows the combination of swellable (meth)acrylate monomers employed. As shown in Table 1, formulations SA1A and SA1 have the same monomer composition. They differ from each other in that SA1A is diluted in ethanol in a 0.1% concentration v / v while SA1 is diluted in ethanol in a 0.25% v / v concentration or higher. The dilutions of monomers diluted in ethanol are shown in Table 3. Table 2 shows the chemical structures of the monomers used.
TABLE 1Swellable (meth)acrylate formulations employedCarboxyl groupFormulationHydrophilic MonomercontainingCrosslinkingNo.(vol. %)monomer (vol. %)monomer (vol. %)SA1A orhydroxyethyl2-carboxyethylTetra(ethyleneSA1methacrylate (80)acrylate (20)glycol)dimethacrylate (3)SA3hydroxyethyl2-carboxyethylTetra(ethylenemethacrylate (60)acrylate (...
example 2
Polypeptide Conjugation to Swellable (Meth)Acrylate Surface
[0113]In a series of experiments designed to evaluate polypeptide conjugation to the swellable (meth)acrylate coatings prepared as described above, a mixture of polypeptides (Ac-ArgGlyGlySerAspProlleTyrLys-NH2 (SEQ ID NO:3) / Rhod-GlyArgGlyAspSerProIleIleLys-NH2 (SEQ ID NO:4)) was conjugated to a swellable (meth)acrylate coating of Formulation SA1A (see Tables 1, 2 and 3) comprising 1-ethyl-3-[3-dimethylaminopropyl]carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) / N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) chemistry. Briefly, 50 μL of 0.1 mM EDC and 0.05 mM NHS solution in DMF were dispensed into a well of 96-well cyclic olefin copolymer plate coated with swellable (meth)acrylate formulation. The activation of carboxyl groups was allowed to proceed for 1-1.5 h, and then the activating solution was aspirated. Immediately after that, 50 μL of polypeptide solution in 25 mM phosphate buffer pH 7.4 were dispensed into the well and the reaction between well surface...
example 3
HT-1080 Cell Adhesion and Proliferation Assays
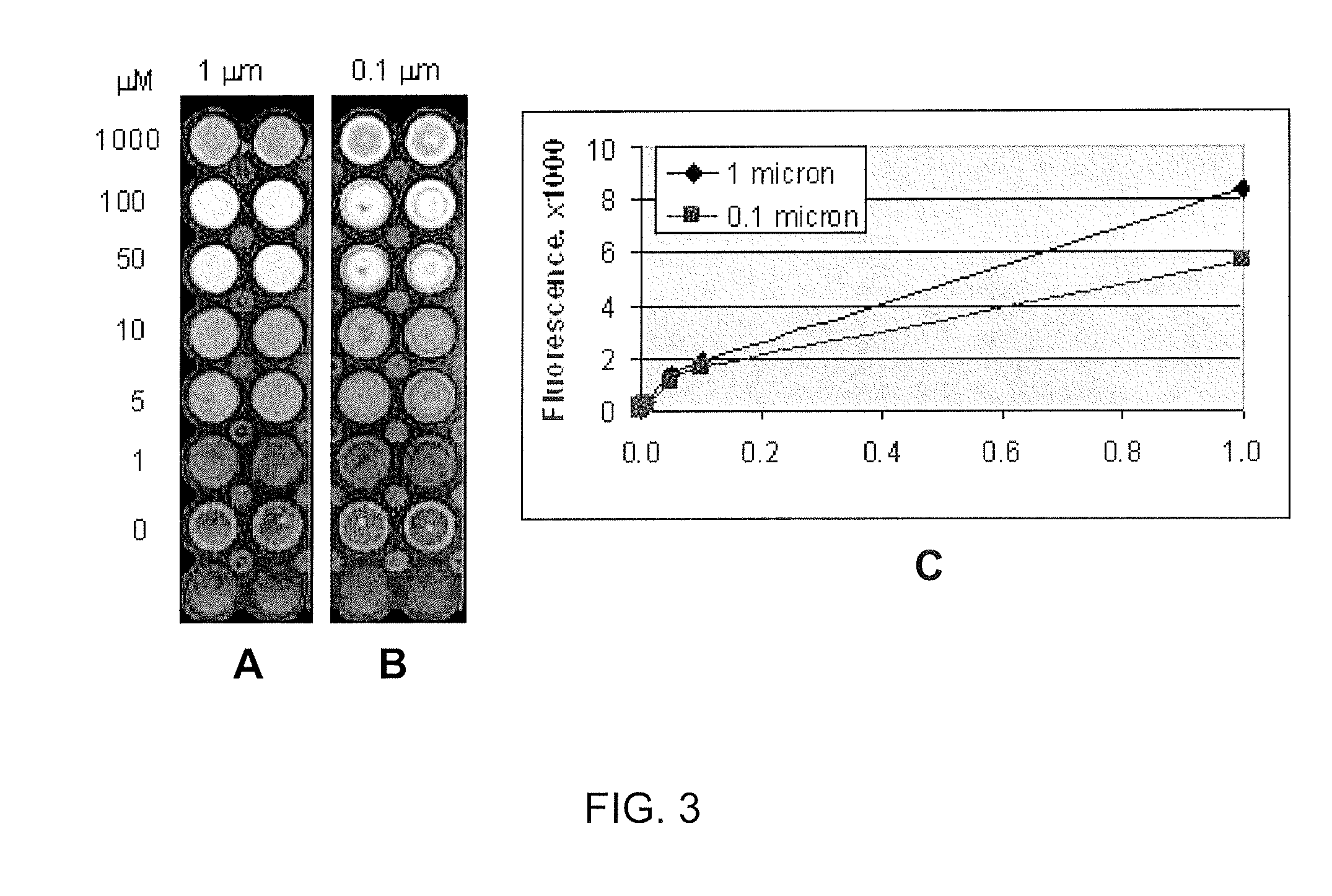
[0117]To evaluate ability of a polypeptide conjugated to embodiments of swellable (meth)acrylate using these conjugation methods to enable cell adhesion and proliferation, peptides Ac-LysTyrGlyArgLysArgLeuGlnValGlnLeuSerlleArgThr-NH2 (SEQ ID NO:22) (AG-73, an adhesive peptide) and Ac—Ac-GlyArgGlyGluSerProIleTyrLys-NH2 (SEQ ID NO:30) (RGE, a negative control) were conjugated to swellable (meth)acrylate (as described above) and adhesion of HT-1080 human fibrosarcoma cells to the swellable (meth)acrylate was evaluated. Briefly, Laminin (5 μg / mL, Sigma-Aldrich) control wells were coated for 1 hour at room temperature. All wells were blocked with 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for 1 hour at 37° C. Wells were washed briefly with PBS before incubation with 0.1% BSA in Iscove's Modified Dulbecco's Medium (IMDM) prior to cell seeding. HT-1080 human fibrosarcoma cells (ATCC number: CCL-121) were grown in IMDM (Lon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com