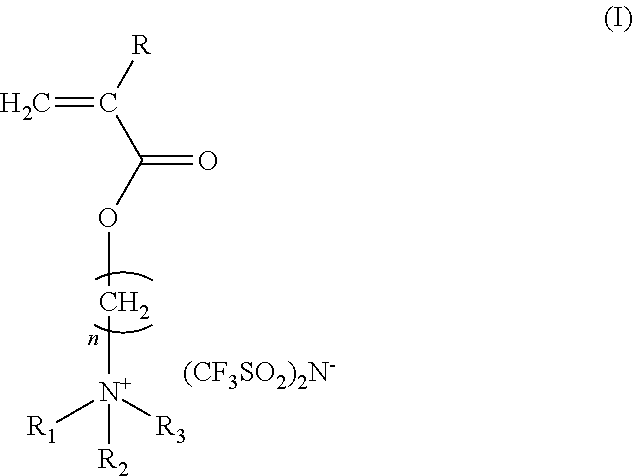
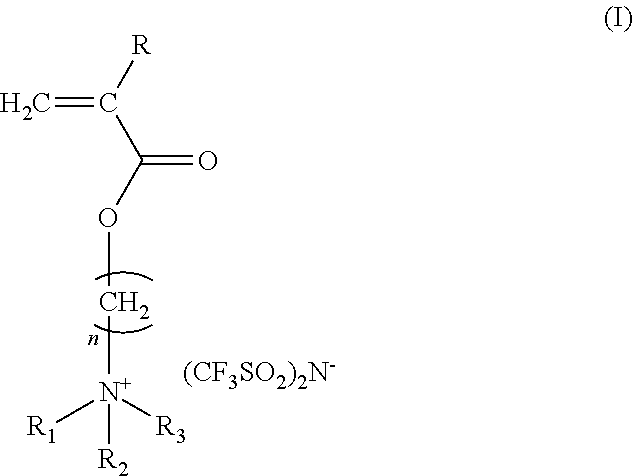
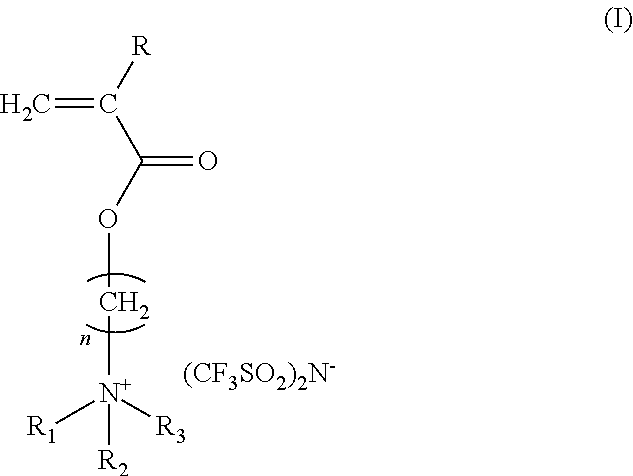
Antistatic ionic compound, oligomer thereof, copolymer thereof, and pressure-sensitive adhesive composition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
synthesis example 1
Synthesis of the Ionic Compound (a)
[0041]45 parts by weight of 2-(acryloyloxy)ethyl trimethyl ammonium chloride aqueous solution in a concentration of 80% by weight was loaded in a stirring tank and was diluted with 45 parts by weight of pure water, followed by adding 10 parts by weight of acetone and 0.01 parts by weight of p-hydroxyl anisole. The temperature was controlled at from 4 to 8° C. 60 parts by weight of lithium bis(trifluoromethane-sulfonyl)imide dissolved in 60 parts by weight of pure water was dropped slowly into the stirring tank, and acetone was added in the same time for keeping the solution clear. Thereafter, the stirring was continued for about 3 hours. The acetone was evacuated by rotary concentration at room temperature. Then, extraction was performed twice by adding ethyl acetate and the organic phase was collected. The organic phase was added with a little amount of acetone and dewatered by anhydrous magnesium sulfate. After the magnesium sulfate was filtered ...
synthesis example 2
Synthesis of the Ionic Compound (b)
A magnetic Stirrer, 100 Parts by Weight of Ionic Compound (a),
[0042]400 parts by weight of ethyl acetate as a solvent, and 2 parts by weight of 2,2′-azobisisobutyronitrile as a polymerization initiator were loaded in a two-necked flask equipped with a nitrogen inlet and a condenser. Nitrogen was introduced into the flask for 30 minutes under mild stirring and the flask was heated to reach a temperature of 70° C. to carry out the polymerization for about 6 hours and then cooled down to room temperature, obtaining a light yellow transparent liquid as a solution of the ionic compound (b) with a solid content of 20%. The ionic compound (b) is an oligomer of the ionic compound (a) and has a glass transition point at 33° C. as determined by a differential scanning calorimeter.
synthesis example 3
Synthesis of the Ionic Compound (c)
A Magnetic stirrer, 50 Parts by Weight of Ionic Compound (a),
[0043]50 parts by weight of butyl acrylate, 400 parts by weight of ethyl methyl ketone as a solvent, and 2 parts by weight of 2,2′-azobisisobutyronitrile as a polymerization initiator were loaded in a two-necked flask equipped with a nitrogen inlet and a condenser. Nitrogen was introduced into the flask for 30 minutes under mild stirring and the flask was heated to reach a temperature of 80° C. to carry out the polymerization for about 6 hours and then cooled down to room temperature, obtaining a solution of the ionic compound (c) with a solid content of 20%. The ionic compound (c) is a copolymer of the ionic compound (a) and butyl acrylate.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com