Treatment of parkinson's disease
a parkinson's disease and treatment technology, applied in the field of neurodegenerative disorders, can solve the problems of pd), although effective, and cannot stop the progressive loss of substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons, and other limitations of the related ar
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
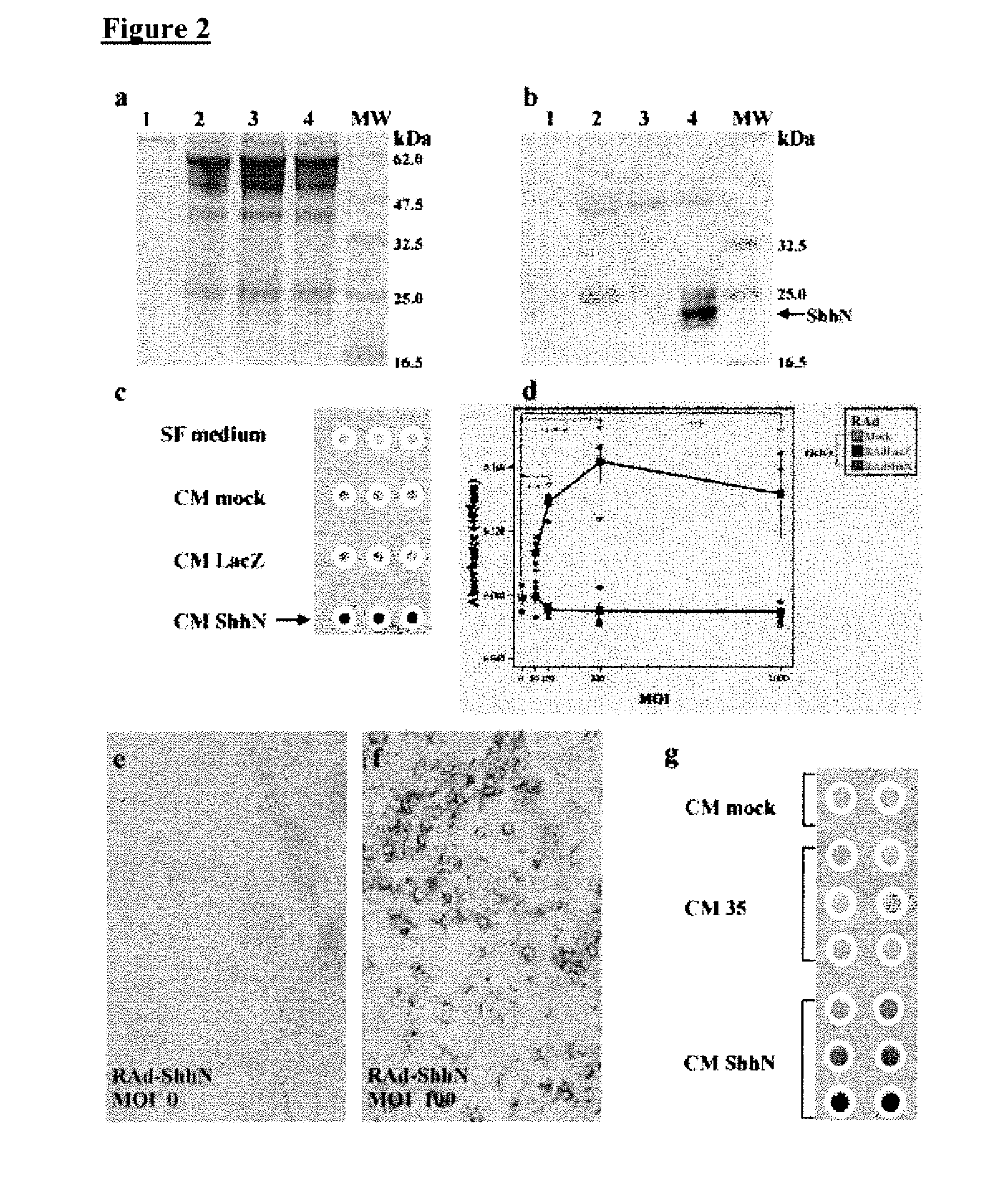
Preparation of Cell Lines
[0084]Human embryonic kidney cells (293 transformed with E1 from Ad5) were obtained from Microbix, Biosystems Inc. (Toronto, Ontario; Canada); HeLa and BHK cells were purchased form the European Collection of Animal Cell Cultures (Porton Down. Salisbury; UK). These cells were grown using complete minimal essential medium Eagle (MEM; fetal bovine serum 10%, penicillin / streptomycin 1%, L-glutamine 1%, MEM nonessential amino acids) and incubated at 37° C. with 5% CO2 [P. Lowenstein et al. Protocols for Gene Transfer in Neuroscience: Towards Gene Therapy of Neurological Disorders, Wiley, Chichester (1996)]. C3H / 10T1 / 2 cells, a mouse embryo mesenchymal cell line that can be differentiated into cartilage and bone, were used to test the bioactivity of ShhN and Gli-1. Differentiation induces alkaline phosphatase expression detected histochemically. C3H / 10T1 / 2 cells were grown in basal Eagle medium with Earle's BSS 90%, supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bo...
example 2
Preparation of Ventral-Mesencephalic Primary Cultures
[0085]Pregnant Sprague-Dawley rats were killed by neck dislocation on day E14.5 [K. Shimoda et al., A high percentage yield of tyrosine hydroxylase-positive cells from rat E14 mesencephalic cell culture, Brain Res., 586:319-331 (1992)]. The uterus was removed and transferred to ice-cold buffer, where fetuses were removed until dissection under a stereomicroscope as described in detail elsewhere [K. Shimoda et al., A high percentage yield of tyrosine hydroxylase-positive cells from rat E14 mesencephalic cell culture, Brain Res., 586:319-331 (1992); A. F. Shering et al., Cell type-specific expression in brain cell cultures from a short human cytomegalovirus major immediate early promoter depends on whether it is inserted into herpesvirus or adenovirus vectors. J. Gen. Viral., 78:445-459 (1997)]. Neocortical cultures were prepared as described earlier [A. F. Shering et al., Cell type-specific expression in brain cell cultures from a ...
example 3
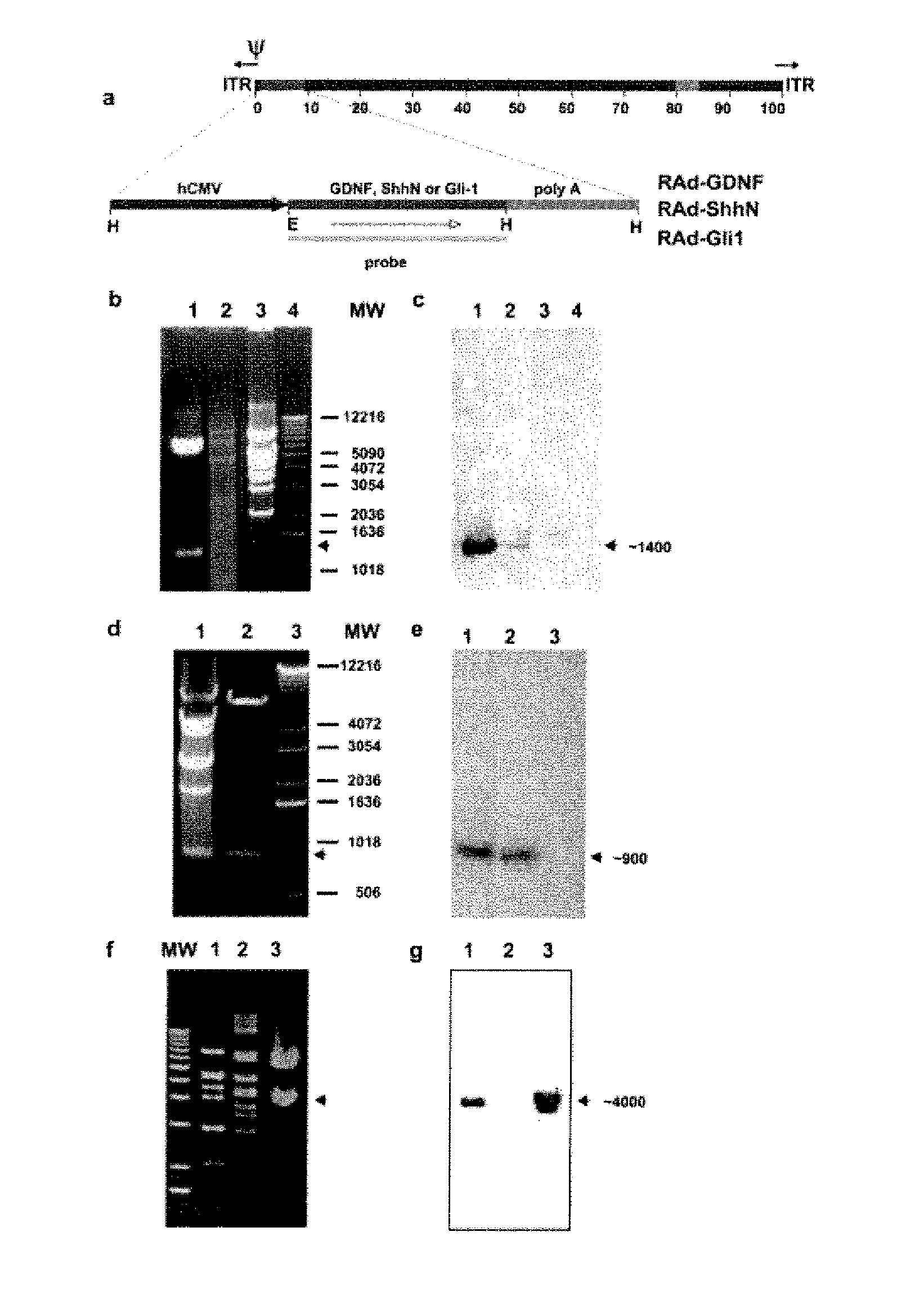
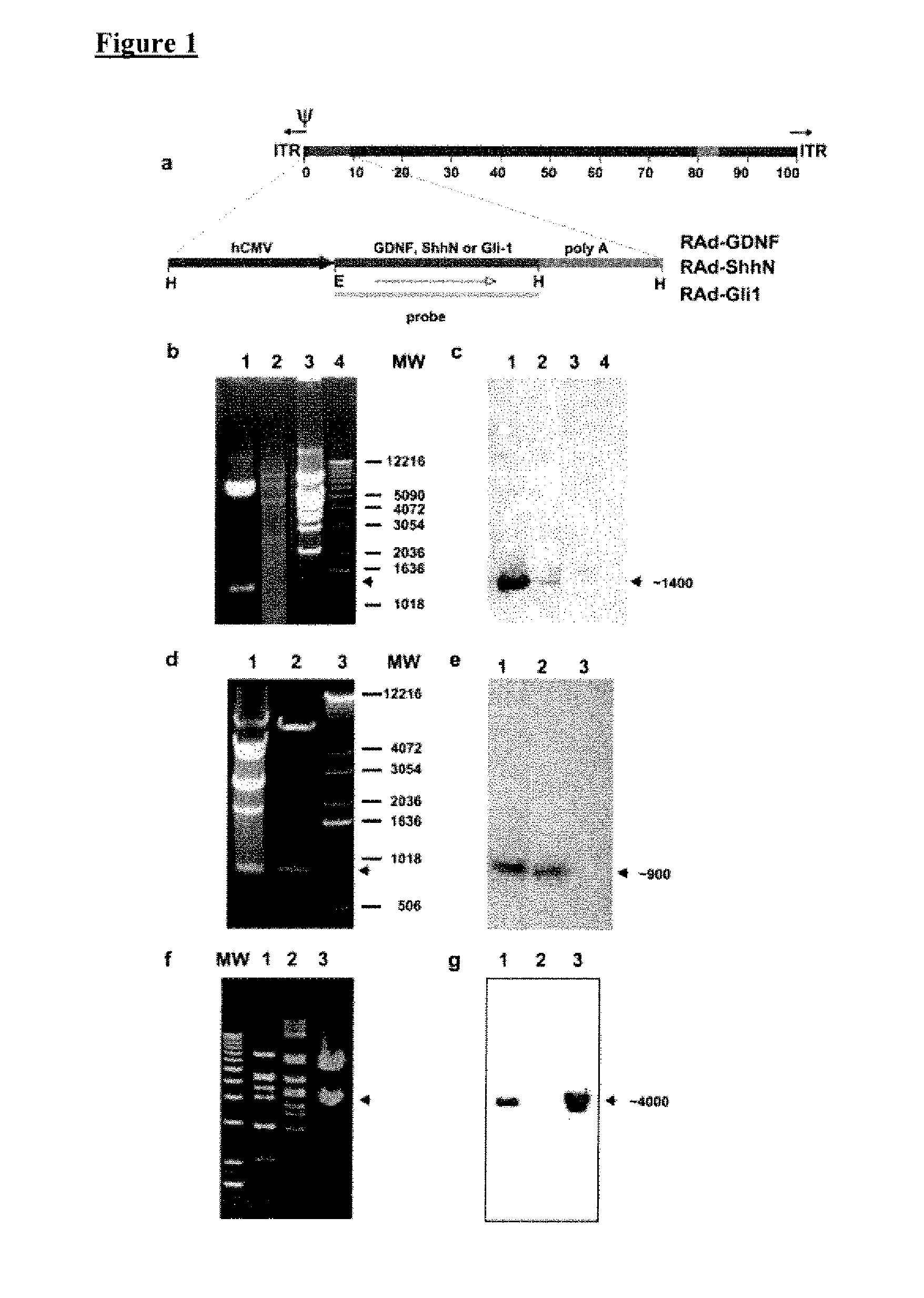
Construction of Recombinant Adenovirus
[0087]The cDNA encoding Shh amino-terminal gene product was excised by enzymatic digestion with EcoRI / HindIII from a recombinant pBluescript II plasmid provided by Dr. P. Beachy, John Hopkins University (Baltimore, Md.). The full-length (3.6 kb) HindIII / XbaI insert of human (Homo sapiens) Gli-1 cDNA clone pGLIK12 was kindly provided by Dr. Bert Volgestein, Johns Hopkins University. and the full-length (0.7 kb) BamHI / XhoI insert of rat GDNF cDNA clone pCDNA-GDNF was made available by Dr. Ira Black (UMDNJ, NJ). These inserts were then cloned into the shuttle vector pAL119, yielding pALShhN, pALGIi-1, and pALGDNF containing the ShhN, the Gli-1, or the GDNF coding region, respectively, in the sense orientation with respect to the major immediate early hCMV promoter of pAL119 [A. F. Shering et al., Cell type-specific expression in brain cell cultures from a short human cytomegalovirus major immediate early promoter depends on whether it is inserted i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| body weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com