FGFR inhibitor for use in the treatment of hypophosphatemic disorders
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
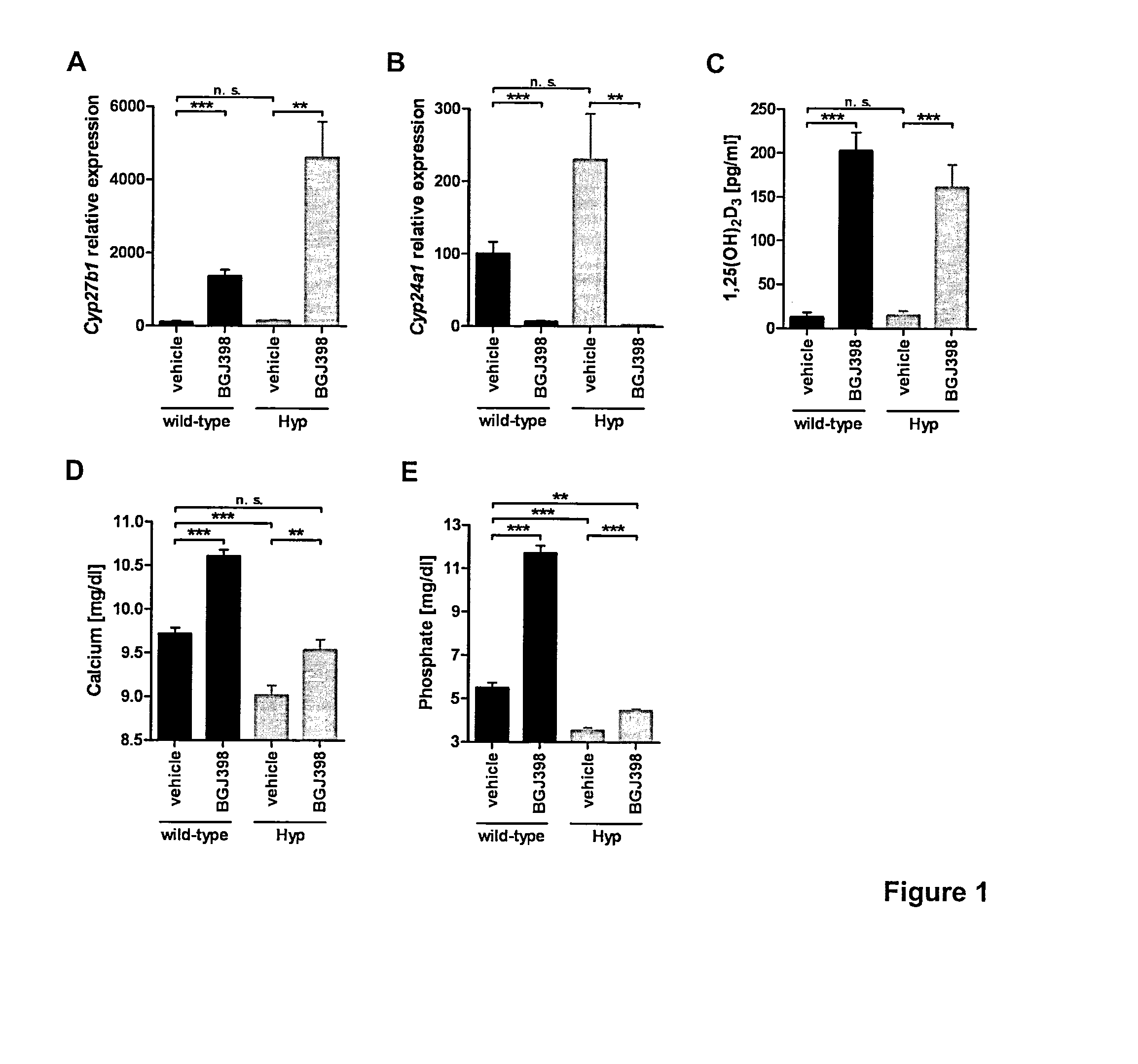
[0036]FGFR inhibitor treatment induces 1,25(OH)2D3 biosynthesis and alleviates hypocalcemia and hypophosphatemia in Hyp mice. Wild-type C57BL / 6 and Hyp (B6.Cg-PhexHyp / J) mice were obtained from The Jackson Laboratory. Dmp1-null mice were generated by Feng et al. (J. Dent. Res. 2003; 82:776-780.). All mice were kept in cages under standard laboratory conditions. Mice were fed on a standard rodent diet with water ad libitum.
[0037]Wild-type or Hyp mice received a single oral dose of the FGFR inhibitor BGJ398 in its free base form (50 mg / kg) or vehicle and were studied 7 h after administration of the compound. BGJ398 or vehicle only (PEG-300 / Glucose 5%, 2:1 mix) was administered by oral gavage. Mice were used at 5-7 weeks of age in the case of single dose administrations. Mice were anesthetized by isoflurane inhalation and blood was collected from the caval vein. Mice were sacrificed by exsanguination and kidney and tibial and femoral bones were obtained. Concentrations of BGJ398 in kid...
example 2
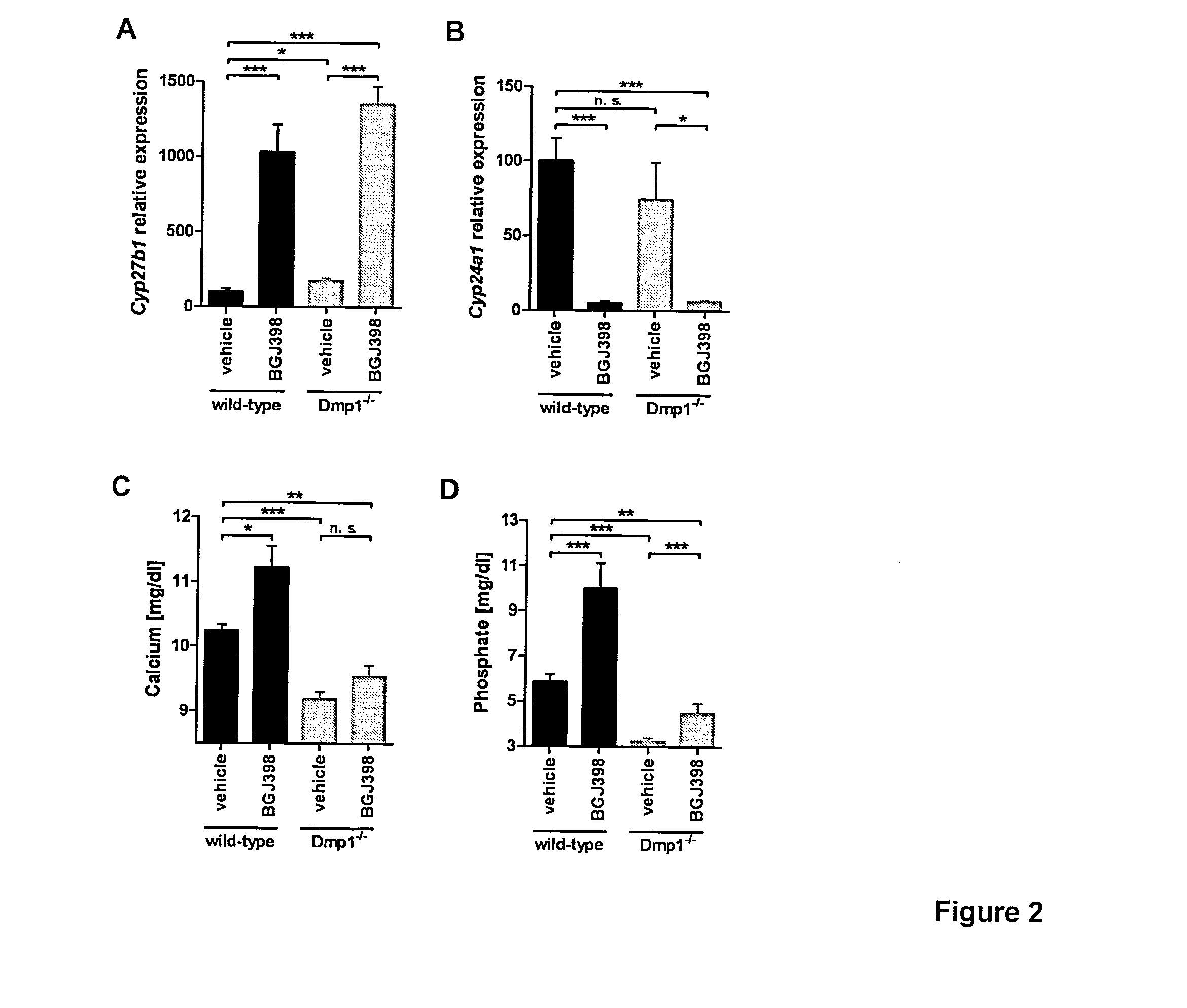
[0045]FGFR inhibitor treatment modulates renal FGF23 target gene expression and alleviates hypocalcemia and hypophosphatemia in Dmp1-null mice. Regulation of the renal FGF23 target genes Cyp27b1 (FIG. 2A) and Cyp24a1 (FIG. 2B) upon FGFR inhibition in vivo is shown on FIG. 2. In addition to our findings in the Phex-deficient Hyp model, we observed a similar regulation of renal Cyp27b1 and Cyp24a1 expression in Dmp1-null mice, another FGF23-related hypophosphatemia model (FIGS. 2A and B). Wild-type or Dmp1-null mice received a single oral dose of the FGFR inhibitor BGJ398 (50 mg / kg) or vehicle and were again studied 7 h after administration of the compound. As before, kidneys were sampled, total RNA was isolated and gene expression was analyzed by qPCR. Expression values were normalized to Gapdh mRNA copies. Data in A and B are shown as relative levels to the wild-type vehicle control group and are given as average with standard errors of the mean (SEM) (n≧6).
[0046]For analysis of cal...
example 3
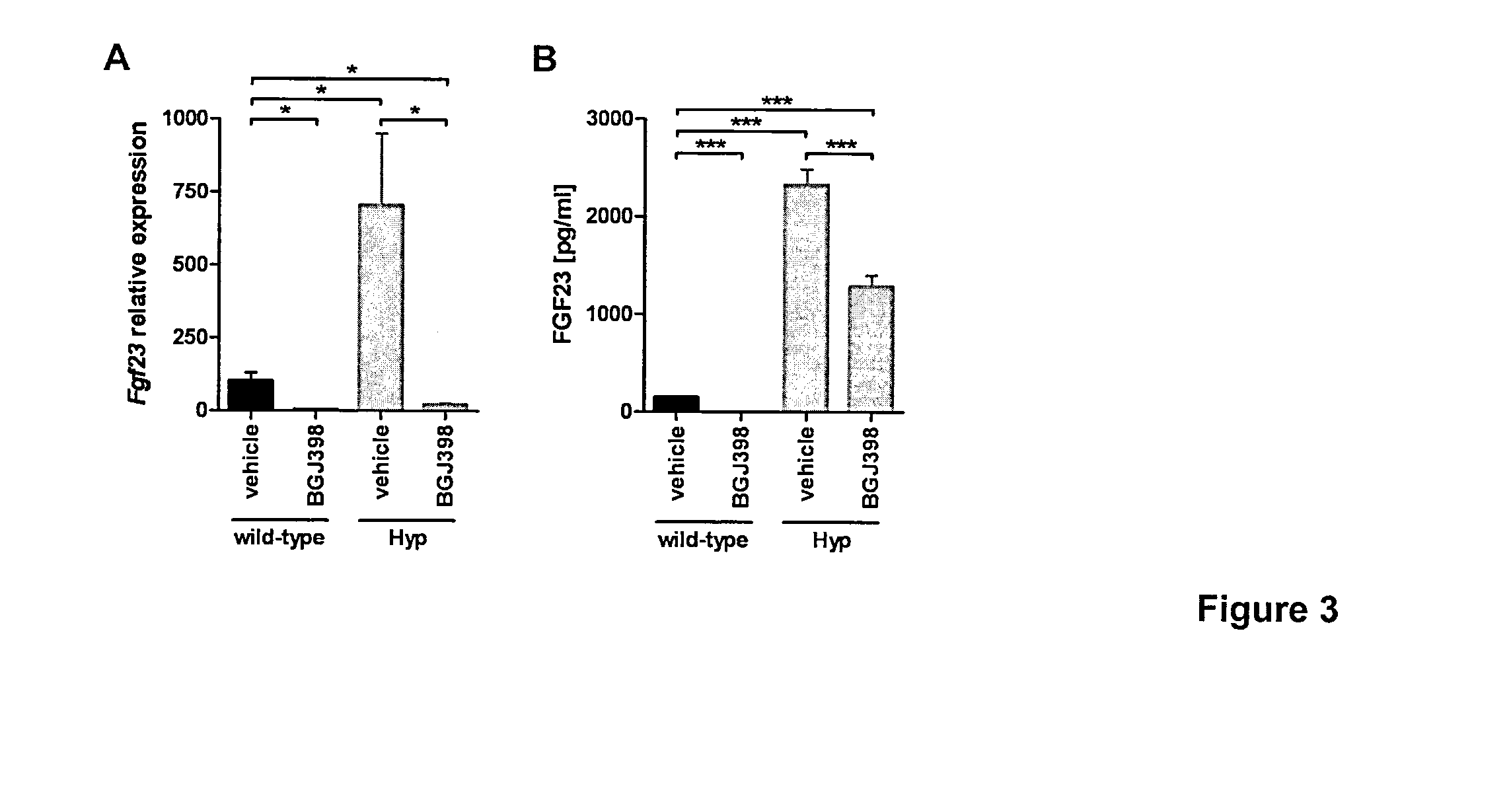
[0047]FIG. 3 shows FGFR-dependent signaling regulates FGF23 expression in bone. Besides the alleviation of the mineral ion deficiency in the two mouse models for FGF23-related hypophosphatemic rickets, we also noticed a repressive effect of FGFR inhibitor treatment on FGF23 levels in BGJ398-treated Hyp mice. Mice received a single oral dose of the FGFR inhibitor BGJ398 (50 mg / kg) or vehicle and were studied 7 h post-administration. FGF23 bone mRNA (FIG. 3A) and serum (FIG. 3B) levels in wild-type and Hyp mice treated with BGJ398 were determined. At 7 h post-dosing of BGJ398 FGF23 expression in bone of both Hyp and wild-type mice was almost abolished (FIG. 2A). The transcriptional repression of FGF23 resulted in undetectable serum FGF23 levels in wild-type mice, while the pathological high FGF23 levels in Hyp mice were reduced by approximately 50% (FIG. 3B). mRNA expression is shown on the figure as relative levels to the wild-type vehicle control group (relative levels of 100) and a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com