Hydrometallurgical process for the recovery of copper, lead or zinc
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Hydrometallurgical Process for Treating Matte-Speiss Material (Cu2S Cu3As) from a Lead Foundry, and Copper Cements from an Electrolytic Zinc Plant
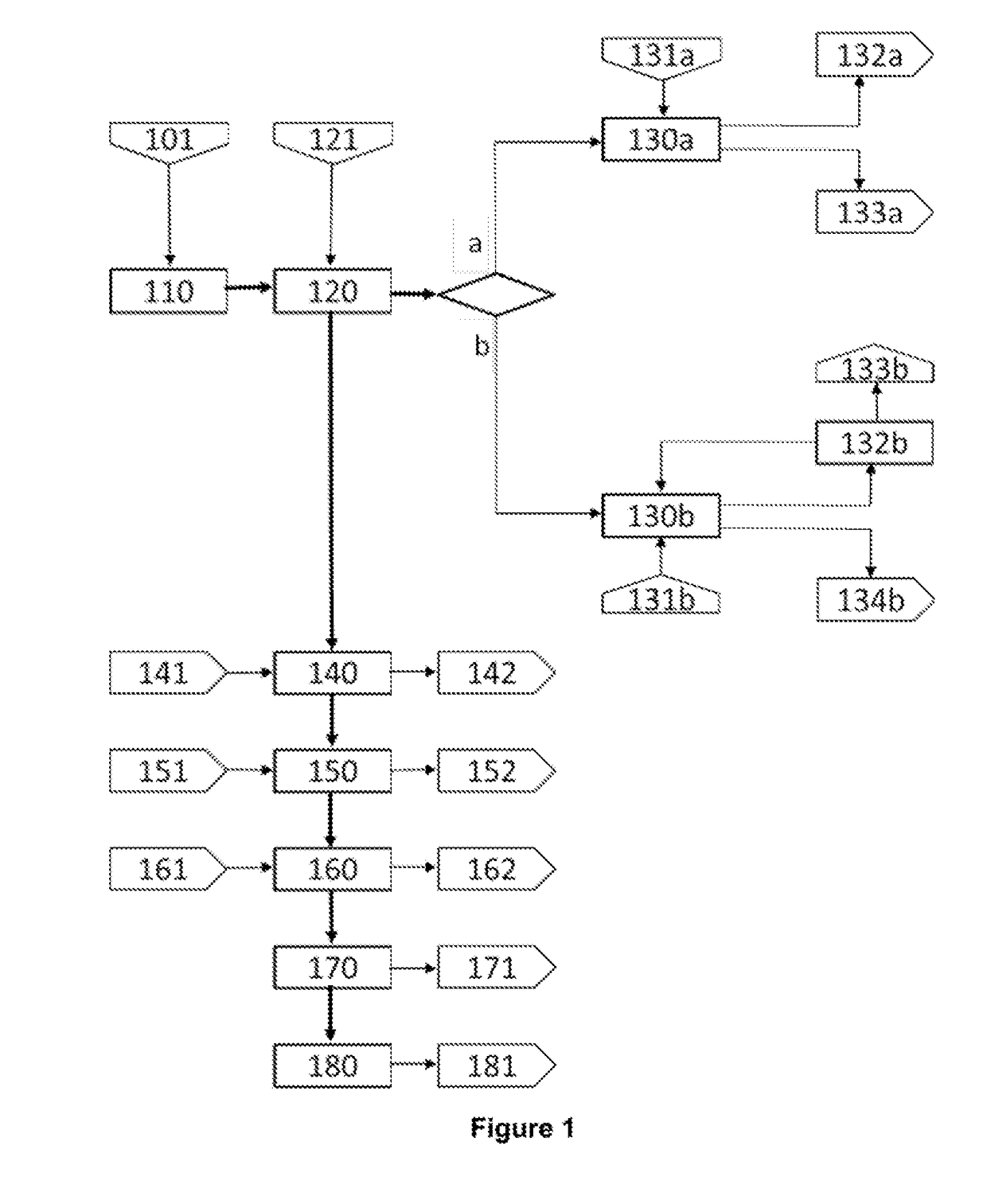
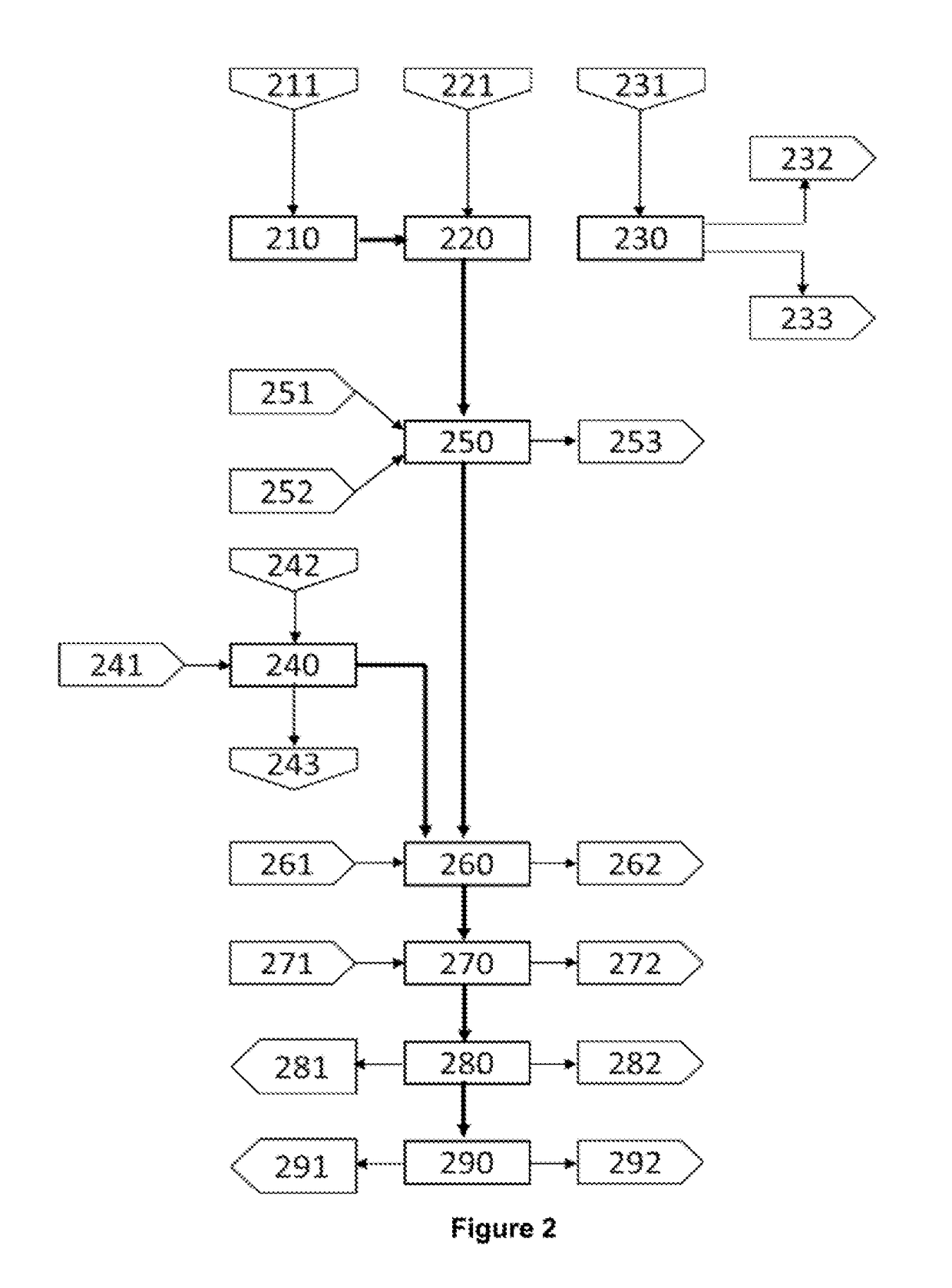
[0041]FIG. 2 shows the schematic block diagram of the hydrometallurgical treatment process of matte-speiss material (Cu2S—Cu3As) from a lead foundry, and copper cements from an electrolytic zinc plant, where each stage of the invention's hydrometallurgical process (FIG. 1) is renumbered for the specific application conditions of this example, as follows:
Stage 1. Grinding (210)
[0042]Matte-speiss material (211) containing 40.13% copper, 20.40% lead, 10.5% total sulphur, 6.73% iron and 4.22% arsenic is subjected to (210) dry grinding until obtaining a particle size P90 of 45 microns. Then, the resulting matte-speiss material is sent for leaching (220).
Stage 2a. Leaching of the Matte-Speiss Material (220)
[0043]A sample of 4.310 g of matte-speiss material from the grinding (210), with a particle size P90 of 46 microns, is mixed with an acid sol...
example 2
Leaching Stage of the Hydrometallurgical Process for Treating Chalcopyrite-Based Copper Concentrates
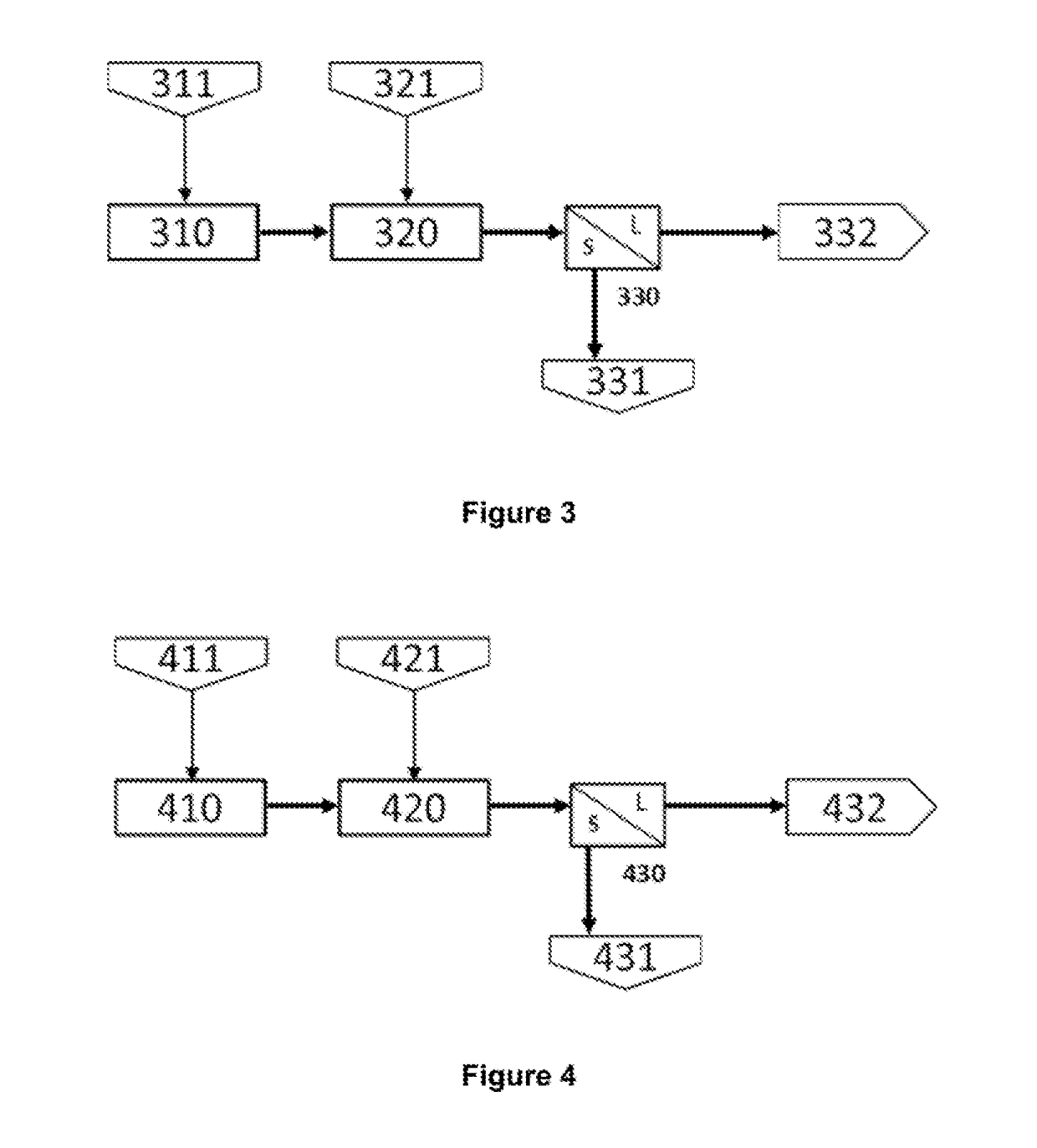
[0056]FIG. 3 shows a block diagram of the grinding and leaching stages of the hydrometallurgical process for treating chalcopyrite-based copper concentrates, where:
[0057]A sample of 999 g of a chalcopyrite concentrate (311) containing 19.80% copper, 10.20% zinc, 20.30% iron and 28.60% of total sulphur, is subjected to grinding (310) to obtain a particle size P80 of 15 microns, the resulting material is sent to leaching (320) where the sample is mixed with 16.5 l of a solution (321) containing 11.50 g / l iron as ferrous sulphate and 64.7 g / l free sulphuric acid. The reactor (321) is closed and kept at a partial oxygen pressure of 12 lb / in2, the reaction temperature is 80° C. and it is allowed to react for 8 hours, the redox potential during this reaction time is maintained between 400 and 500 my with respect to the Ag / AgCl electrode.
[0058]Subsequently, the suspension is filtered (330) a...
example 3
Leaching Stage of the Hydrometallurgical Process for Treating Sphalerite-Based Zinc Concentrates
[0059]FIG. 4 shows a block diagram of the leaching stages of the hydrometallurgical process for treating sphalerite-based zinc concentrates, where:
[0060]A sample of 262 g of a concentrate of zinc (411) containing 48.5% zinc, 12.39% iron and 34.6% of total sulphur, is subjected to grinding (410) to obtain a particle size P90 of 45 microns, the material retrieved is sent to leaching (420) where the sample is mixed with 239 g zinc ferrite (421) containing 19.8% zinc, 25% of total iron and 21.6% as iron (+3). This material mixture is added to a solution (421) composed of 0.4 l water, 0.043 l sulphuric acid at 98% purity and 3.070 l zinc sulphate solution containing 36.50 g / l zinc as zinc sulphate and 165.6 g / l free sulphuric acid.
[0061]The reactor (421) is closed and kept at a partial oxygen pressure of 12 lb / in2, the reaction temperature is 90° C. and it is allowed to react for 14 hours, the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com