Upgrading residues, heavy oils and plastics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
ue Upgrading
Summary
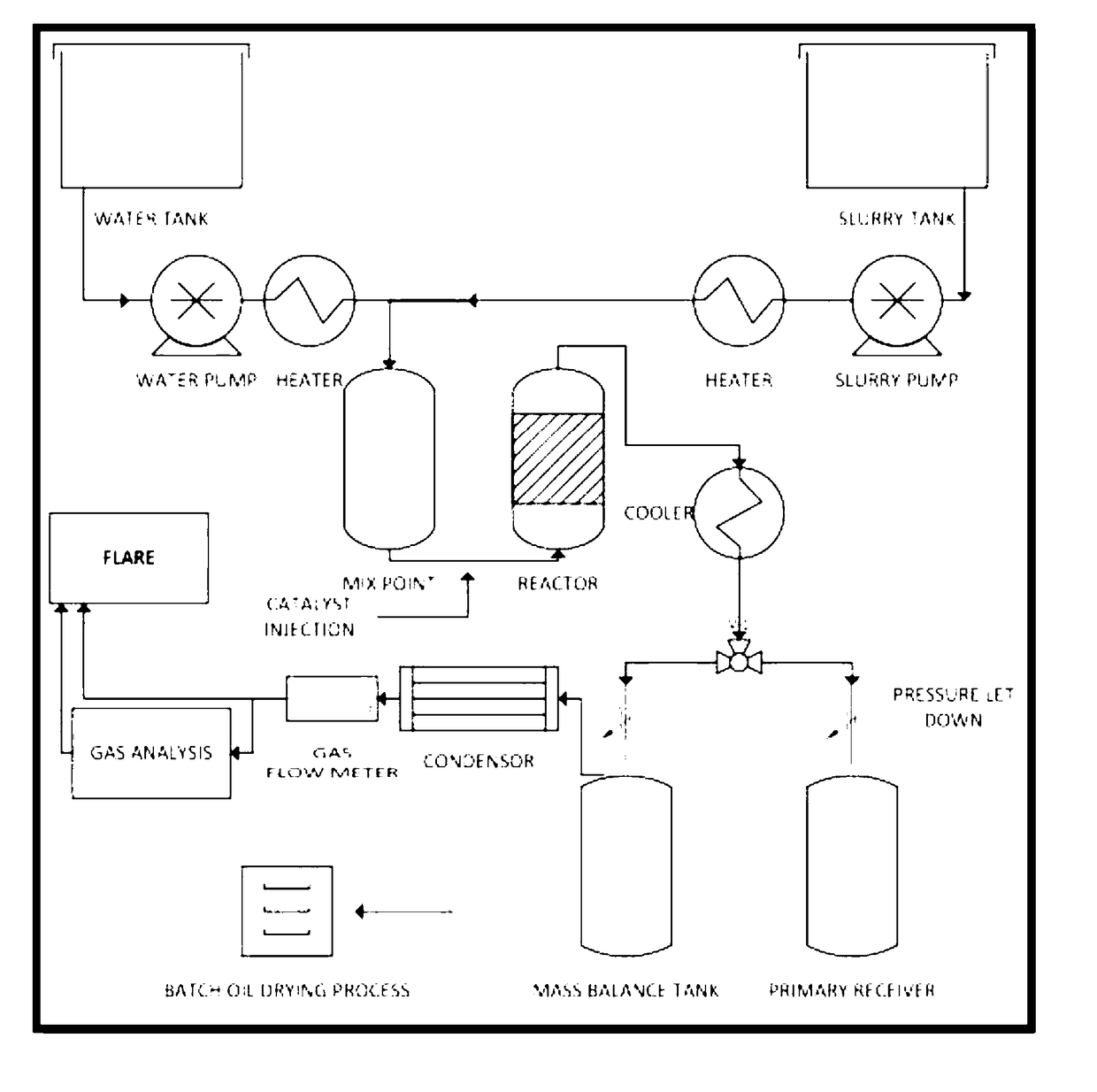
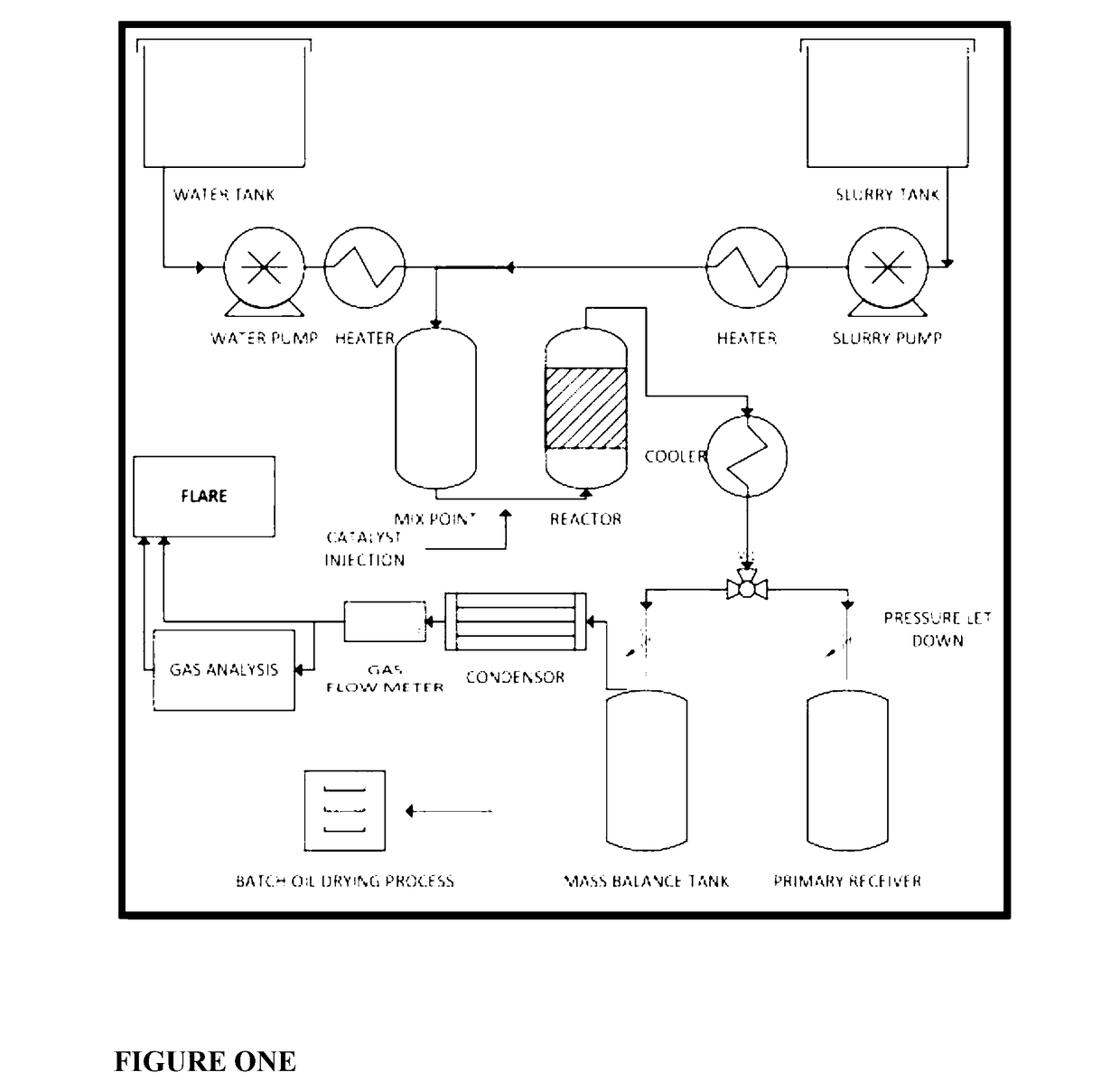
[0275]A technology was developed to upgrade low-value feed stocks to high-value products. One such feed stock is the lube oil residue (LOR) gathered from the bottoms fraction of a vacuum distillation plant for recycling used lube oil. This residue is made up of the non-distillable fraction of the oil and contains contaminating components retained in the oil through use and additive residues.
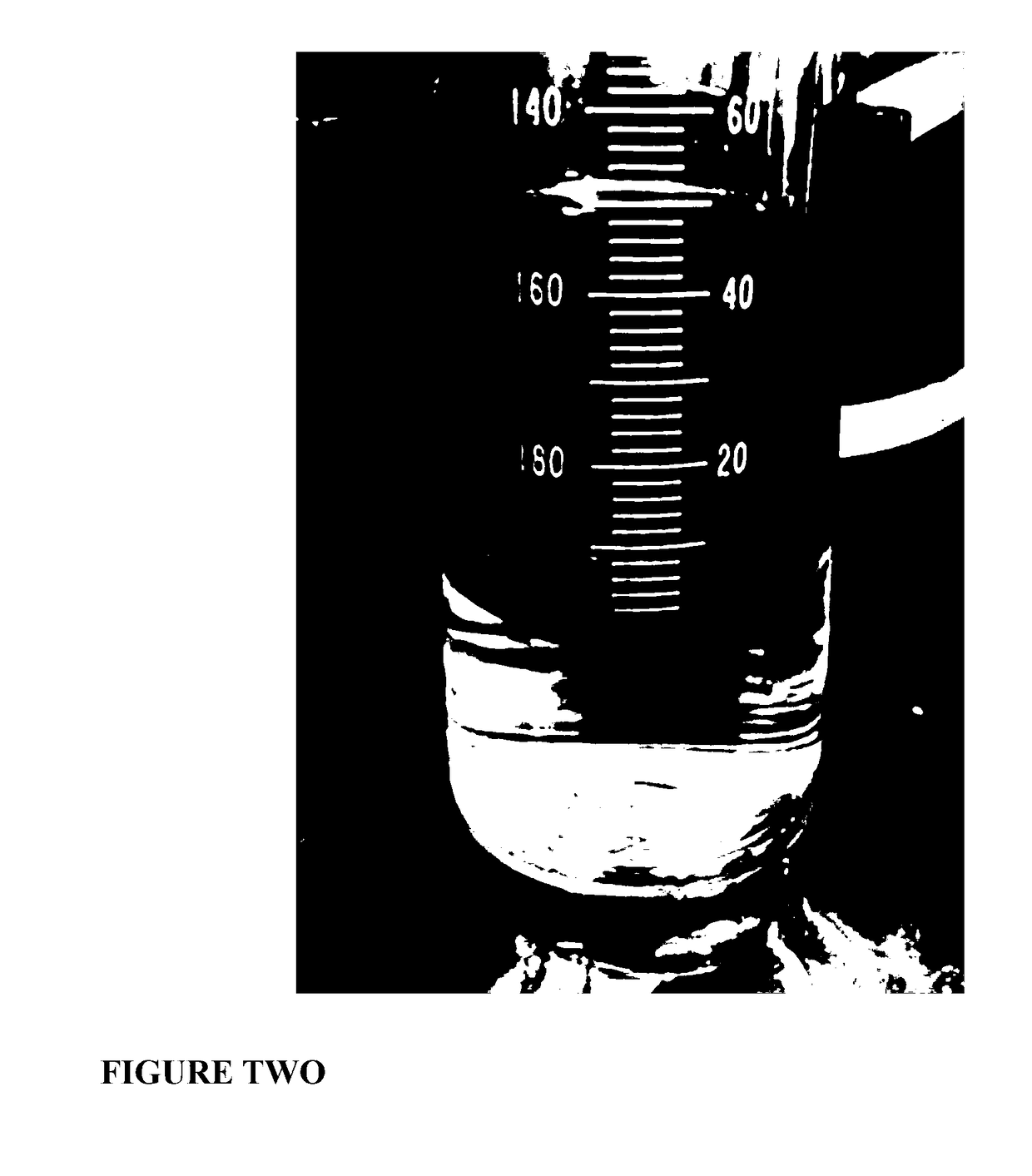
[0276]Lube oil residue was successfully processed. About 70% of the resulting upgraded LOR could be distilled to a strongly upgraded oil product after treatment. By contrast only about 20% of the as received LOR could be distilled under comparable conditions.
[0277]The results confirm that supercritical water upgrading of LOR using the disclosed methods provides substantial benefits:
(i) A large fraction of the LOR is cracked to lighter products, leading to hydrocarbon oils boiling in the diesel and heavy gas oil ranges;
(ii) The residue remaining after upgrading followed by disti...
example 2
ue Upgrading in Combination with Polymers
Introduction
[0311]Example 2 is a prophetic Example.
[0312]Plastic and / or rubber and / or other polymeric material (polymers) may be used in combination with heavy oil components of the feedstock mixture for cracking in the reactor. Accordingly, plastic and / or rubber and / or other polymeric material (polymers) may be added to the feedstock mixture for cracking in the reactor according to the methods described below.
[0313]The polymers may be characterised in part by their glass transition temperatures Tg and / or their melting temperatures Tm in the case of semi-crystalline or crystalline polymers. Above Tg polymers generally exhibit rubbery characteristics. Non-limiting examples of glass transition temperatures and melting temperatures are given below in Table 7.
TABLE 7Tg and Tm temperatures of exemplary polymersPolymerTm ° C.Tg ° C.Polyethylene (PE)135−68Polypropylene (PP)176−8Polystyrene (PS)240100Poly(methyl methacrylate) PMMA200105Poly(vinyl chl...
example 2.1
[0317]PE is ground to a powder and suspended in LOR at a temperature of 70° C. or greater such that the viscosity of the continuous phase is sufficiently low to form a pumpable suspension. At elevated temperatures the PE may begin to dissolve into the oil. For example polyethylene solubility in mineral oil increased from about 20 g / 100 g at 50° C. to about 100 g / 100 g at 65° C. according to Litkovets et al. [Chemistry and Technology of Fuels and Oils, December 1988, Volume 24, Issue 12, pp 556-559, Solubility of polyethylene in a mineral oil, E. A. Litkovets, I. M. Bolyuk, A. M. Zeliznyi]. The melting temperature of LDPE is approximately 110° C. The mixture is pressurized using a high-pressure pump and is subsequently contacted with supercritical steam and raised to the reaction temperature. The contact with the supercritical steam provides water as an aqueous solvent and reactant for the cracking reactions. The mixture is continuously pumped through a reaction vessel to give a resi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com