Method of in-situ filling symbiotic iron nanometer wire on thin wall nanometer pipe
A technology of iron nanowires and carbon nanotubes, which is applied in the direction of nanotechnology, nanotechnology, and nanostructure manufacturing, can solve the problems of rough tube walls, low filling rate, and tube wall thickness, and achieve simple and controllable preparation processes. Strong controllability, simple process and controllable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
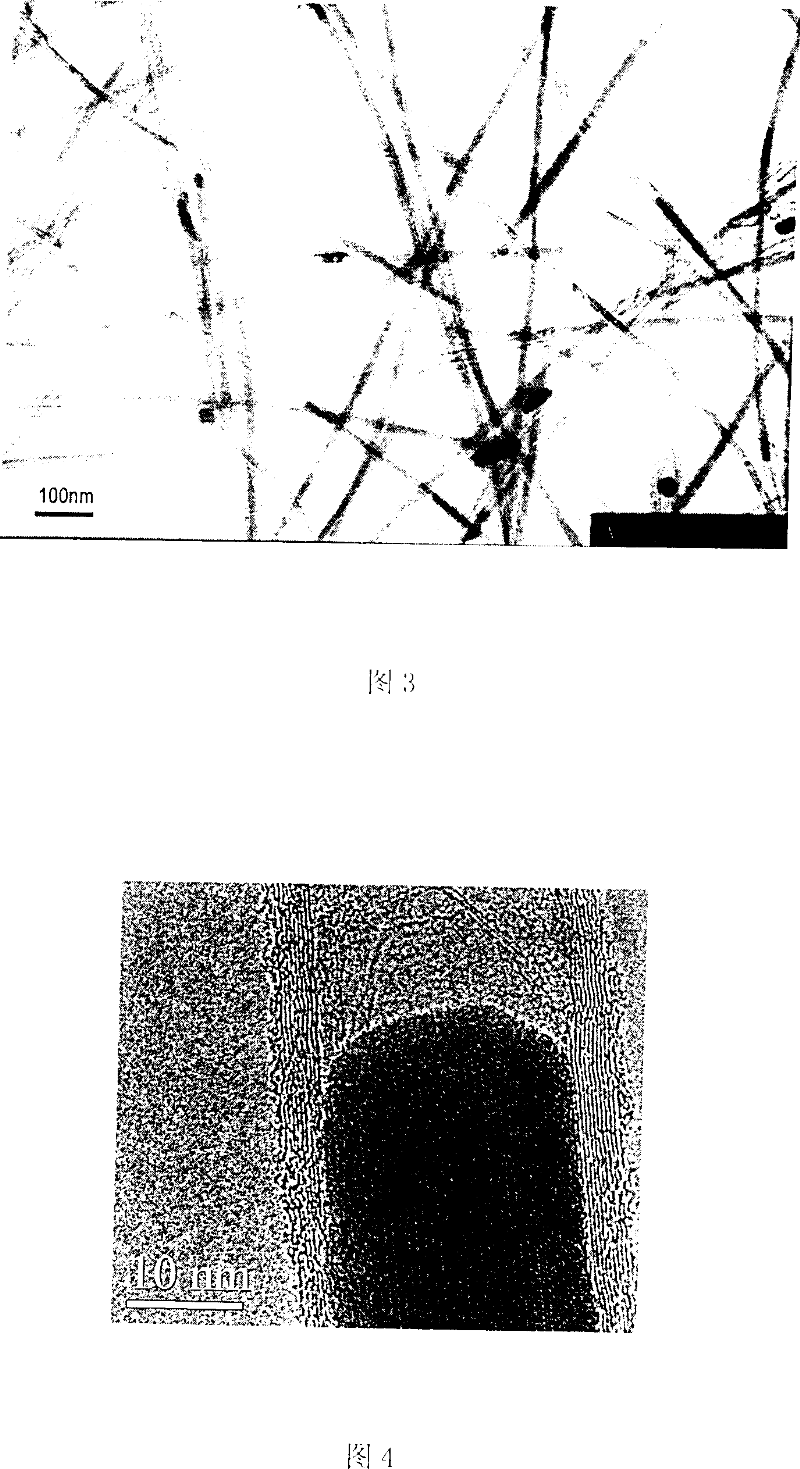
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] 1) Weigh 1.0 g of ferrocene powder, dissolve in 20 mL of dichlorobenzene solution, and mix to form a brown-yellow transparent solution;
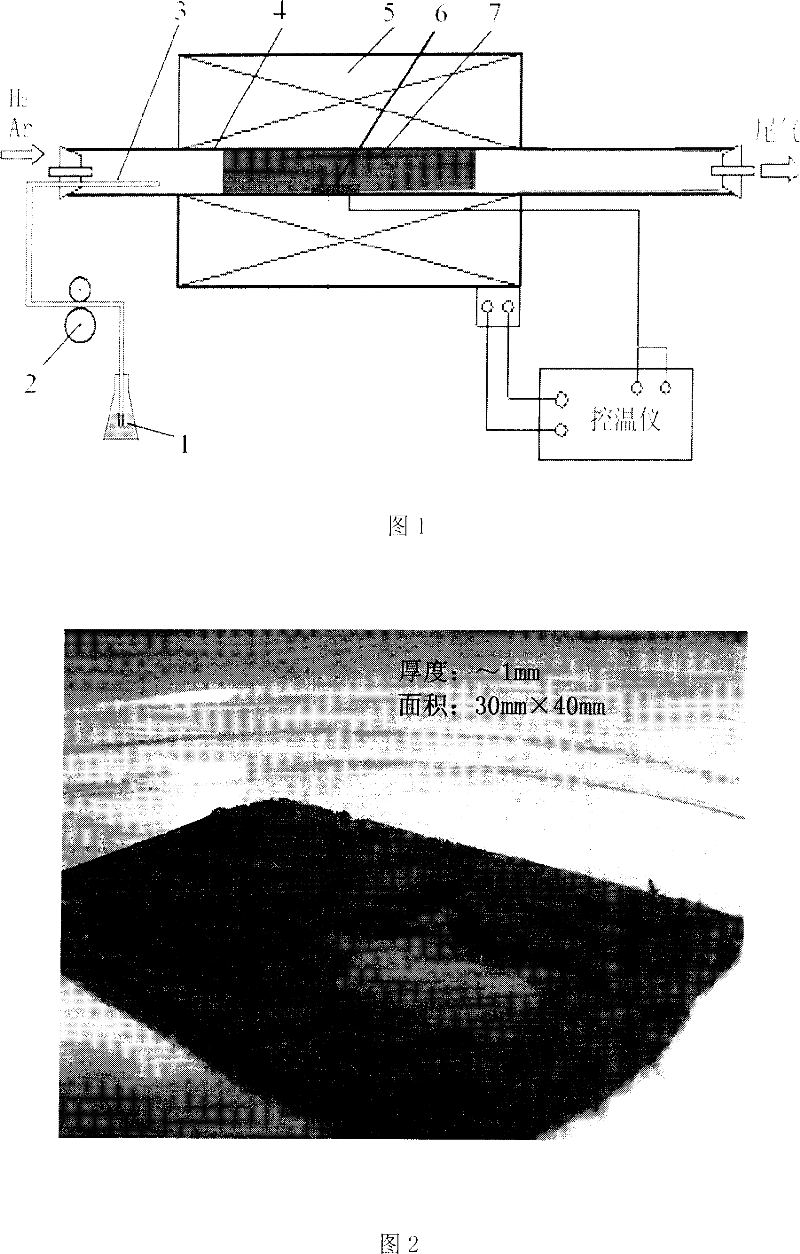
[0040] 2) Put the quartz substrate base on the quartz boat, then slowly push the quartz boat into the middle of the quartz tube, seal both ends of the quartz tube with sealant, and use the method of heating gas expansion to ensure the air tightness of the quartz tube.
[0041] 3) Pass argon gas into the quartz tube, the flow rate is 200mL / min, and heat to the temperature required for the test at 750°C;
[0042] 4) Use a temperature controller to keep the temperature at the capillary port inserted into the quartz tube at 250°C;
[0043] 5) Adjust argon to 3000mL / min, and feed 200mL / min of hydrogen;
[0044] 6) Turn on the precision flow pump, and suck the reaction solution into the quartz tube at a feed rate of 0.4 mL / min;
[0045] 7) After 30min, stop the flow of hydrogen, reduce the flow of argon to 200mL / min, until the furnace tem...
Embodiment 2
[0047] 1) Weigh 1.2 g of ferrocene powder and dissolve it in 20 mL of dichlorobenzene solution, and mix to form a brownish-yellow transparent solution.
[0048] 2) Put the quartz substrate base on the quartz boat, then slowly push the quartz boat into the middle of the quartz tube, seal both ends of the quartz tube with sealant, and use the method of heating gas expansion to ensure the air tightness of the quartz tube.
[0049] 3) Pour argon gas into the quartz tube, the flow rate is 300mL / min, and heat to 900°C required for the test.
[0050] 4) Use a temperature controller to keep the temperature at the capillary port inserted into the quartz tube at 300°C.
[0051] 5) Adjust the argon gas to 3000mL / min, and pass the hydrogen gas of 200mL / min.
[0052] 6) Turn on the precision flow pump, and suck the reaction solution into the quartz tube at a feed rate of 0.6 mL / min.
[0053] 7) After 30min, stop the flow of hydrogen, reduce the flow of argon to 200mL / min, until the furna...
Embodiment 3
[0055] 1) Weigh 1.8 g of ferrocene powder and dissolve it in 20 mL of dichlorobenzene solution, and mix to form a brown-yellow transparent solution.
[0056] 2) Put the quartz substrate base on the quartz boat, then slowly push the quartz boat into the middle of the quartz tube, seal both ends of the quartz tube with sealant, and use the method of heating gas expansion to ensure the air tightness of the quartz tube.
[0057] 3) Pour argon gas into the quartz tube, the flow rate is 300mL / min, and heat to 820°C required for the test.
[0058] 4) Use a temperature controller to keep the temperature at the capillary port inserted into the quartz tube at 300°C.
[0059] 5) Adjust the argon gas to 3000mL / min, and pass the hydrogen gas of 200mL / min.
[0060] 6) Turn on the precision flow pump, and suck the reaction solution into the quartz tube at a feed rate of 0.8 mL / min.
[0061] 7) After 30min, stop the flow of hydrogen, reduce the flow of argon to 200mL / min, until the furnace ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com