Methods and compositions for reducing neurodegeneration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
A technology for lateral sclerosis, a neurodegenerative disease, applied in the field of composition of at least one symptom, able to solve the problem that no effective treatment exists
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
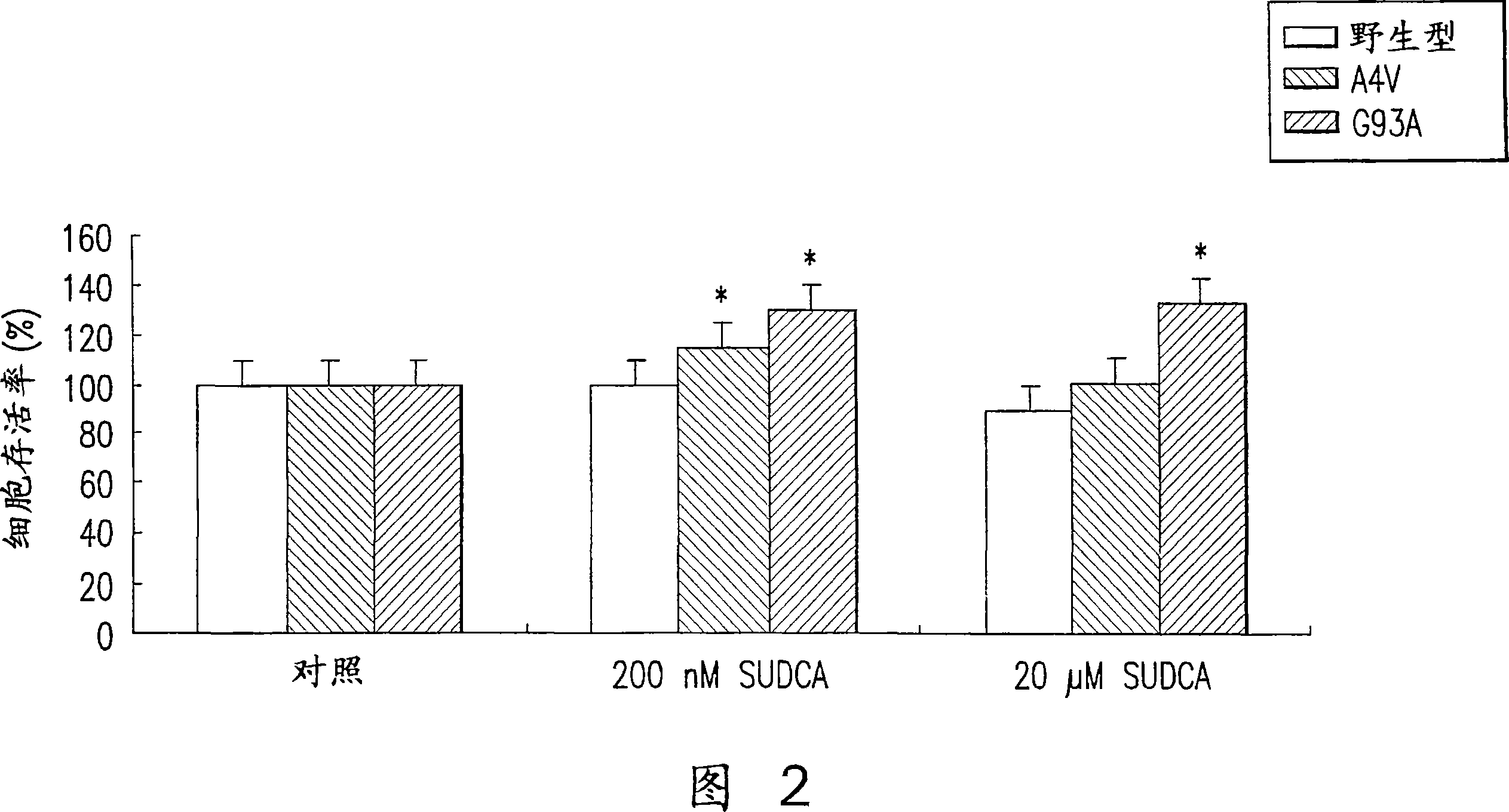
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0076] Embodiment 1: the preparation of bile acid solution
[0077] A stock solution of bile acids was first prepared by dissolving UDCA (60 g) in 500 mL NaOH (6.7 g) solution. Next, 375 g of maltodextrin were added to the resulting clear solution with vigorous stirring in stages. The pH was then adjusted to 7.0-7.2 by dropwise addition of HCl and high-throughput ultrasound (750 W, 20 kHz). Then adjust the volume to 1.0 L with distilled water for injection. Finally, the resulting clear solution was filtered and sterilized under aseptic conditions with a 0.22 μGP express plus filter. (This filtration is important for sterilization, but not for removal of particulate matter since the solution is already clear). Dilutions of this solution at the desired concentration of UDCA are prepared according to standard pharmacy practice.
Embodiment 2
[0078] Embodiment 2: the preparation of bile acid solution
[0079] A stock solution of bile acids was first prepared by dissolving UDCA (25 g) in 400 mL NaOH (2.7 g) solution. Next, 745 g of maltodextrin were added to the resulting clear solution with vigorous stirring in stages. To the resulting solution was added 100 mL of a preservation solution containing 0.95 g of methylparaben and 0.3 g of sodium bisulfite, followed by stirring. The volume was then adjusted to 1.0 L with pharmaceutical grade water. Finally, filter the resulting clear solution with a suitable filter device. (This filtration was not done to remove particulate matter since the solution was already clear). Dilutions of this solution at the desired concentration of UDCA are prepared according to standard pharmacy practice.
Embodiment 3
[0080] Embodiment 3: animal test
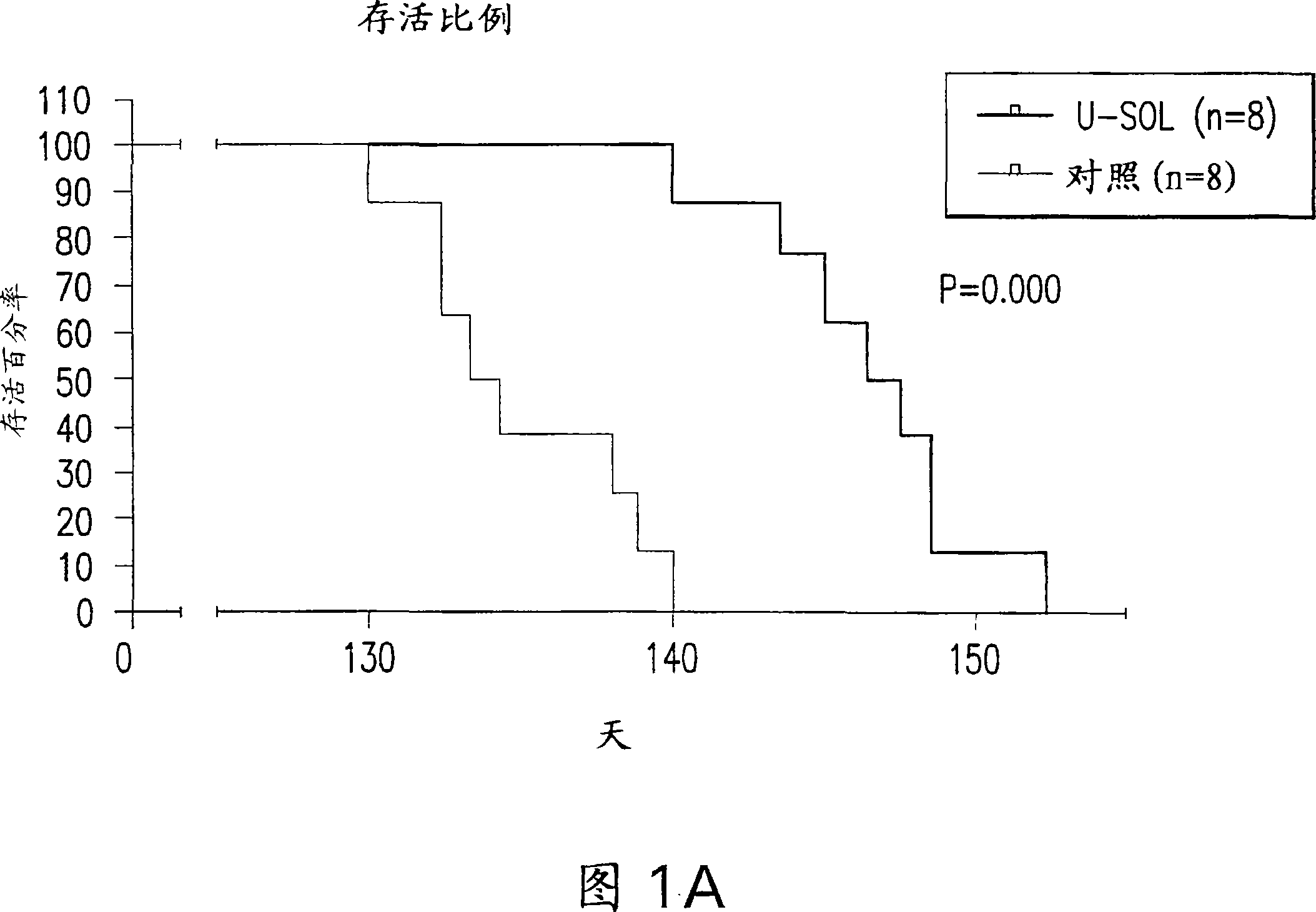
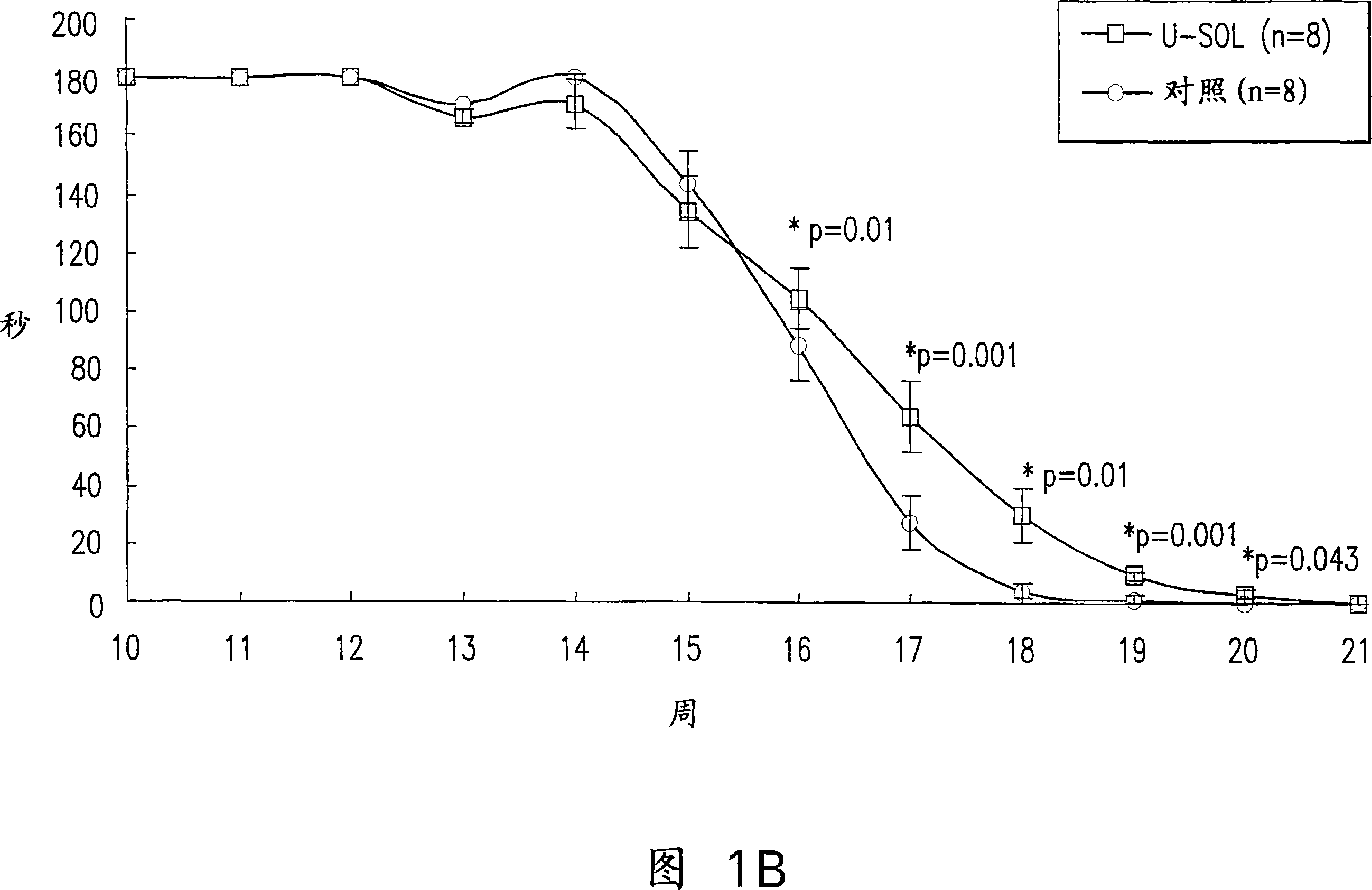
[0081] Transgenic rats; the transgenic animals used in this example are heterozygous hSOD1 carrying a glycine 93-alanine mutation (G93A). This line exhibited B6SJL-TgN(SOD1-G93A)1Gur (The Jackson Lab., Bar Harbor, ME, USA) containing a reduced copy number of hSOD1, purchased from Jackson Laboratories. Transgenic mice that overexpress the human SOD1 gene containing mutations identified in ALS patients develop adult-onset, progressive motor deterioration. These transgenic mice are considered a model of the disease and have been used to test a number of strategies to delay disease progression and mortality.
[0082] To evaluate the potential benefit of the present invention on ALS, G93A transgenic mice were orally administered twice weekly with 240 mg / kg of the present solution dissolved in UDCA, starting at 70 days of age and continuing until death.
[0083] Life expectancy and its outcomes; Figure 1 shows the mean life expectancy of control ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com