Method for preparing bismuth ferrite based multifunctioanl oxide ceramic material
A technology based on oxide ceramics and bismuth ferrite, applied in the field of material science, can solve the problems of poor repeatability of results, low density, and inability to prepare bulk ceramics.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
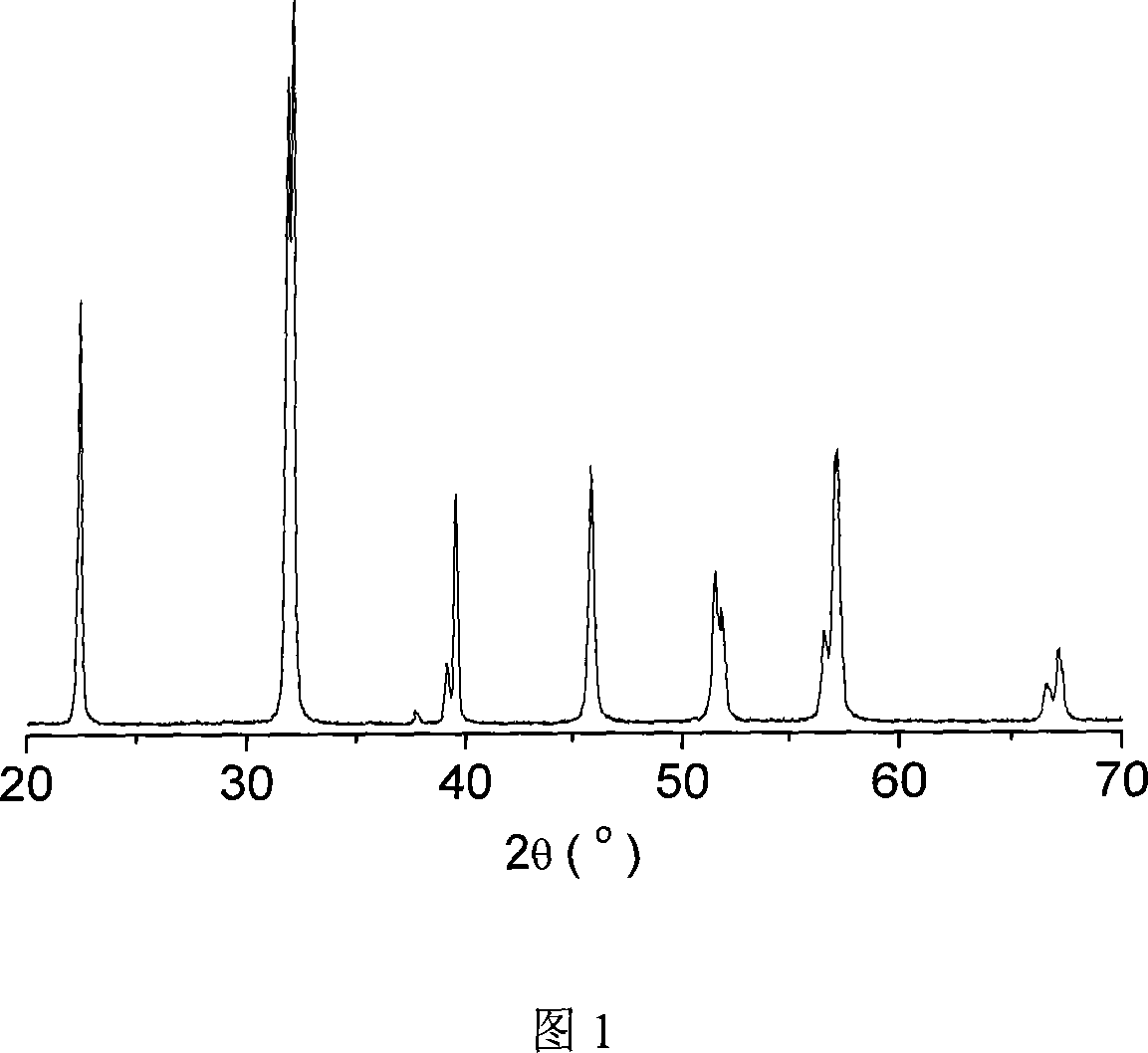
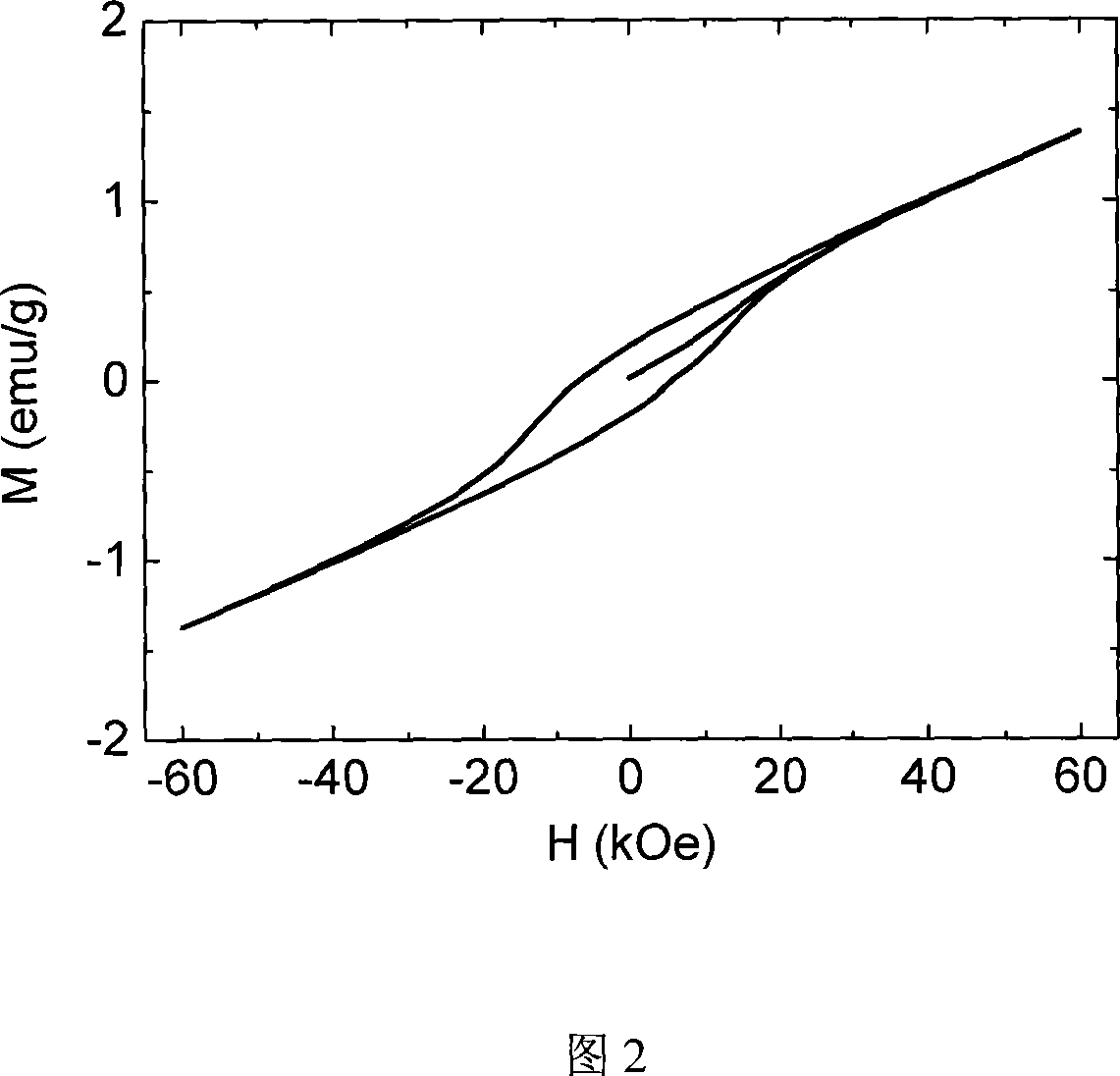
[0033] Mix ferric nitrate, lanthanum nitrate and citric acid according to a certain stoichiometric ratio (the molar ratio of citric acid and all metal ions is 1.5:1), prepare a transparent solution, heat and stir for several hours to form a viscous sol, then mix and add ammonia water to adjust pH to 1. The stoichiometric ratio of bismuth nitrate was then added slowly to avoid precipitation of bismuth subnitrate. Stir for 30 minutes to make it fully mixed, place in an oven, and keep warm at 120°C to form a xerogel. The temperature of the gel was slowly raised to 200°C, and a dark fire self-propagating decomposition reaction occurred to remove organic matter. Rapid heat treatment was performed at 860°C and kept for 5 minutes to obtain BLTFO8 powder. X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD) test results show that the phase is single-phase powder with R3c structure. At room temperature, under a test magnetic field of 60kOe, the saturation magnetization can reach 1.4emu / g, and the residu...
Embodiment 2
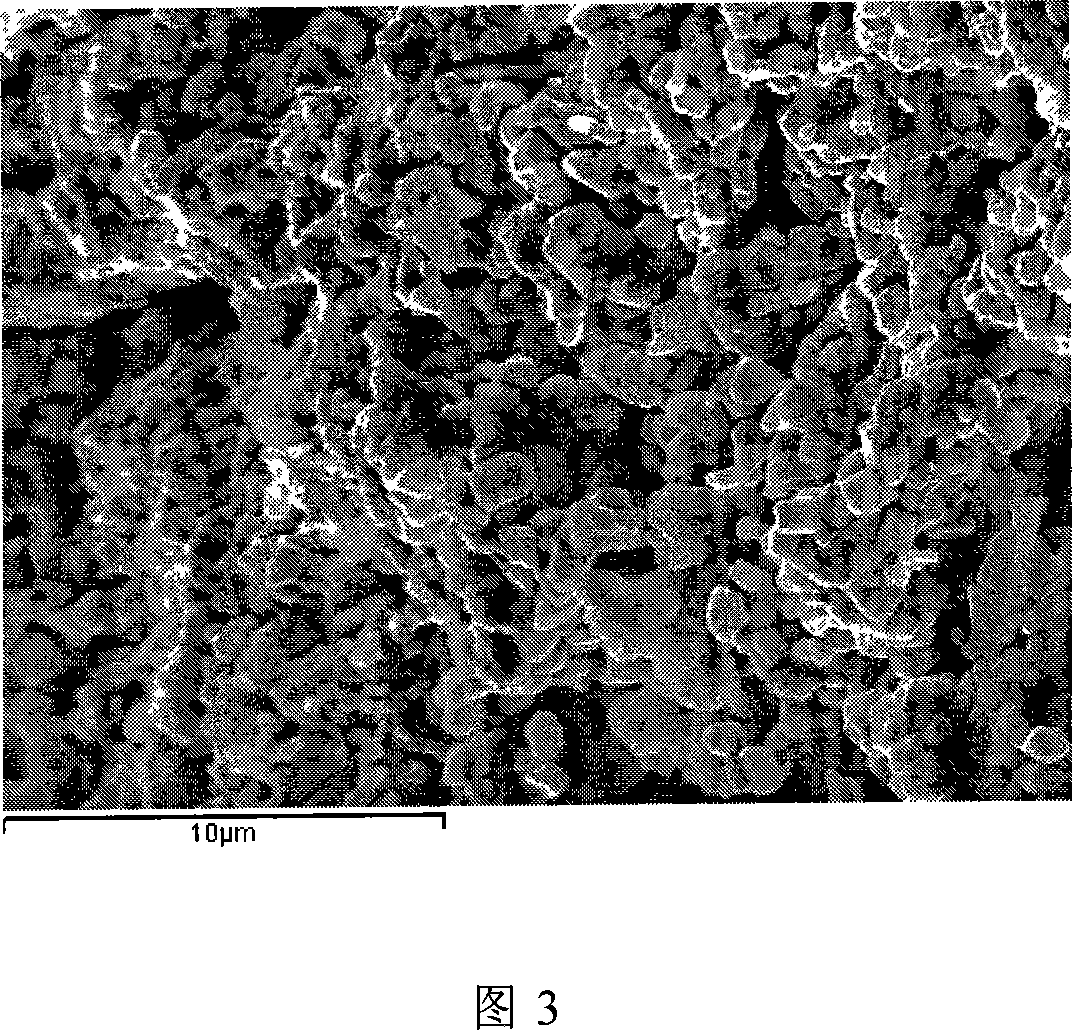
[0035] Weigh an appropriate amount of BLTFO8 powder, put it into a graphite mold (Ф15mm), and compact it at 20MPa; then move the mold into an SPS sintering furnace, and use the traditional SPS method for sintering. Rise to 600°C within 3 minutes, then rise to the sintering temperature at a speed of 50°C / min, keep the temperature for several minutes to sinter the sample. After the sintering is completed, the sample is taken out, and the carbon is removed by heat treatment at 650°C for 2 hours. The dielectric properties of ceramics are very sensitive to the sintering temperature: when sintered below 690°C, the ceramic loss is low (tanδ is below 10%), the dielectric constant is stable (about 120), the ceramic density is low, and the grain size is about 1 micron ; When the temperature exceeds 690°C, the loss of ceramics increases significantly and the dielectric properties deteriorate. As shown in Figure 3, Figure 4, and Figure 5.
Embodiment 3
[0037] Weigh an appropriate amount of BLTFO8 powder, pre-press 20MPa into a disc of Ф12×2mm; add a small amount of Al 2 o 3 Put the powder into the graphite mold (Ф15mm) and compact it at 20MPa; move the pressed tablet into the Al 2 o 3 layer, adjust to the center position; continue to add Al to the mold 2 o 3Embed the BLTFO8 disc with powder and compact it with 20MPa; then move the mold into the SPS sintering furnace, raise it to 600°C within 3 minutes, then raise it to the sintering temperature at a speed of 50°C / min, and keep the temperature for several minutes to sinter the sample. The sintering pressure is 50MPa. After the sintering is completed, the sample is taken out, and the outer Al 2 o 3 The powder is removed to obtain BLTFO8 ceramics. When sintered below 850°C, the dielectric properties of ceramics are not sensitive to temperature changes, the ceramics have high density (>99%), low loss (tanδ2 . As shown in Figure 6, Figure 7, and Figure 8.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Saturation magnetization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Residual magnetization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Grain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com