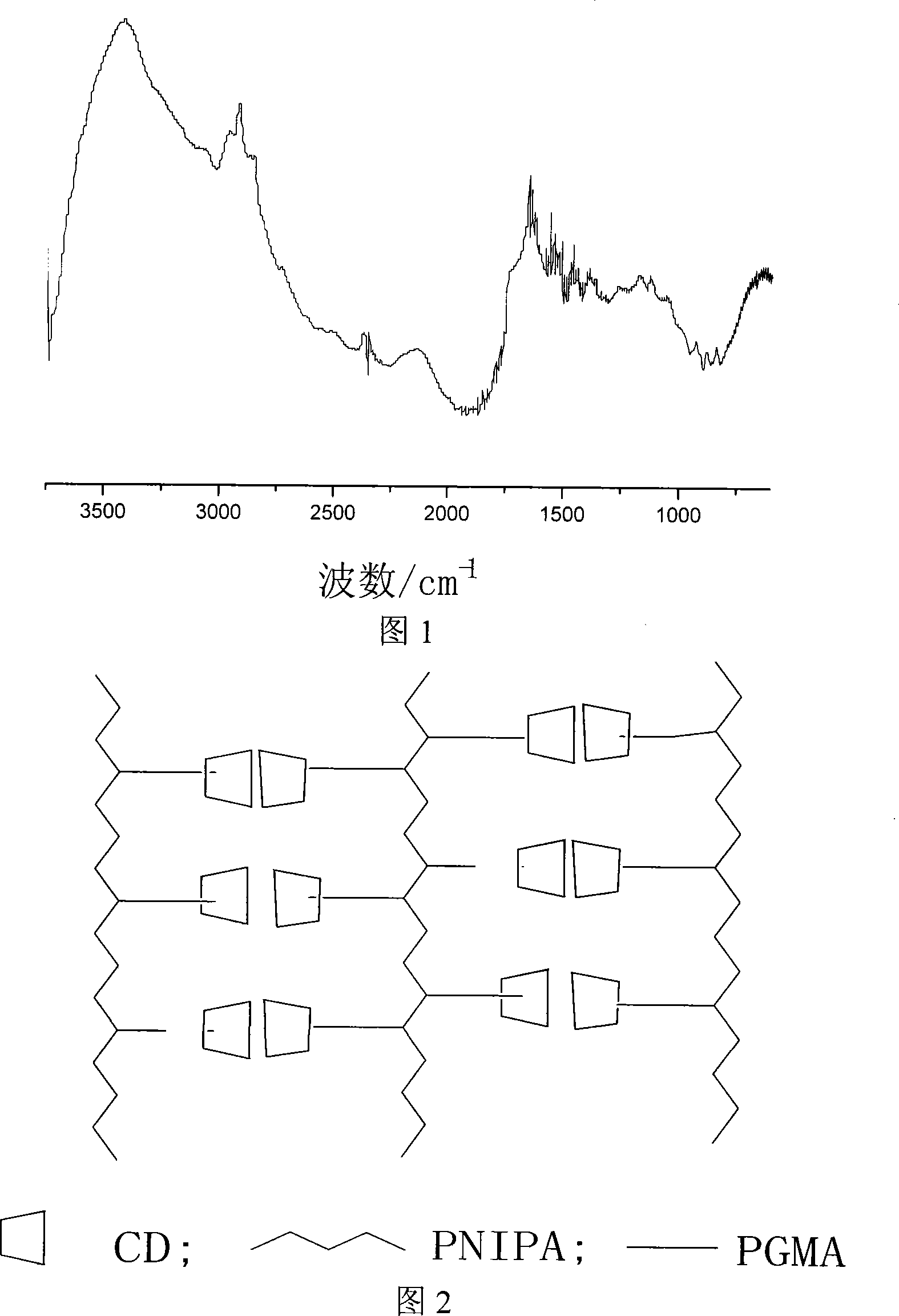
Method for preparing temperature sensitive hydrogel with supramolecular structure
A molecular structure and sensitivity technology, applied in the field of functional polymer materials, can solve the problems of cross-linking agent and pore forming agent residue, poor biocompatibility, difficult removal of pore forming agent, etc., to achieve temperature sensitivity improvement, The effect of increasing the ratio of hydrophilic/hydrophobic groups and increasing the number of hydrogen bonds
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
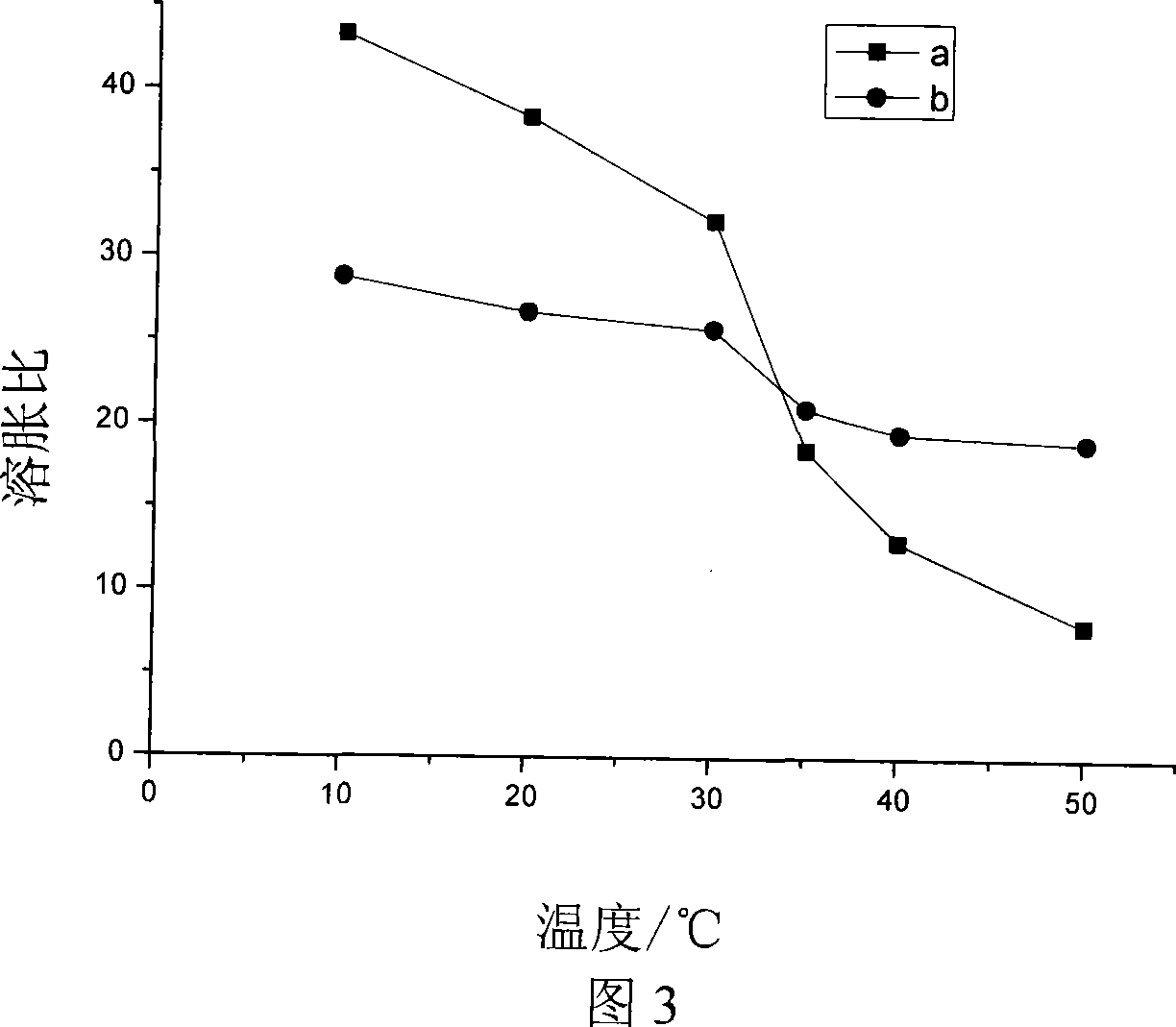
[0030] Example 1: Dissolve 1.05 g of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin in 10 ml of deionized water, add 0.17 g of glycidyl methacrylate, and stir at room temperature for 10 minutes. Add 4.29 g of N-isopropylacrylamide, and stir for 20 minutes under a nitrogen atmosphere. Add 0.01 g of potassium persulfate, maintain a nitrogen atmosphere, and continue stirring for 5 minutes. Seal the container, place it in a 40°C water bath, and react for 6 hours. The resulting product is washed and soaked with deionized water to remove small molecules that are not reacted, and the mass concentration of N-isopropylacrylamide is 30%, and the molar concentration of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and N-isopropylacrylamide is The ratio is 1:50, and the molar ratio of glycidyl methacrylate to N-isopropylacrylamide is 1:30, which is a supramolecular structure temperature-sensitive hydrogel. At 20°C, the swelling ratio is 30 times; at 50°C, 49% of water is lost in 10 minutes, and 61% of water is lost in 20...
example 2
[0031] Example 2: Dissolve 2.18g of β-cyclodextrin in 10ml of deionized water, add 0.44g of glycidyl methacrylate, and stir at room temperature for 25 minutes. Add 0.87 g of N-isopropylacrylamide, and stir for 10 minutes under nitrogen atmosphere. Add 0.1 g of potassium persulfate, maintain nitrogen atmosphere, and continue stirring for 10 minutes. Seal the container, place it in a 70°C water bath, and react for 24 hours. The obtained product was washed and soaked with deionized water to remove small molecules that were not reacted, so that the mass concentration of N-isopropylacrylamide was 8%, and the molar ratio of β-cyclodextrin to N-isopropylacrylamide was 1: 4. A temperature-sensitive hydrogel with a supramolecular structure at a molar ratio of glycidyl methacrylate to N-isopropylacrylamide of 1:2.5. At 20°C, the swelling ratio is 28.5 times; at 50°C, 43% of water is lost in 10 minutes, and 59% of water is lost in 20 minutes.
example 3
[0032] Example 3: Dissolve 1.44g of methyl-β-cyclodextrin in 10ml of deionized water, add 0.21g of glycidyl methacrylate, and stir at room temperature for 15 minutes. Add 2.5 g of N-isopropylacrylamide, and stir for 10 minutes under a nitrogen atmosphere. Add 0.1 g of ammonium persulfate, maintain nitrogen atmosphere, and continue stirring for 8 minutes. Seal the container, place it in a 55°C water bath, and react for 10 hours. The resulting product is washed and soaked with deionized water to remove small molecules that are not reacted, and the mass concentration of N-isopropylacrylamide is 20%, and the molar ratio of methyl-β-cyclodextrin to N-isopropylacrylamide 1:20, glycidyl methacrylate and N-isopropylacrylamide molar ratio of 1:15 supermolecular structure temperature sensitive hydrogel. At 20°C, the swelling ratio is 39.5 times; at 50°C, 60% of water is lost in 10 minutes, and 71% of water is lost in 20 minutes.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com