Method for producing hydrogen and methane by kitchen waste diphasic anaerobic fermentation
A technology of kitchen waste and anaerobic fermentation, applied in organic fertilizers, climate change adaptation, biosynthesis, etc., to achieve the effects of low operating costs, reduced energy consumption, and improved thermal efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
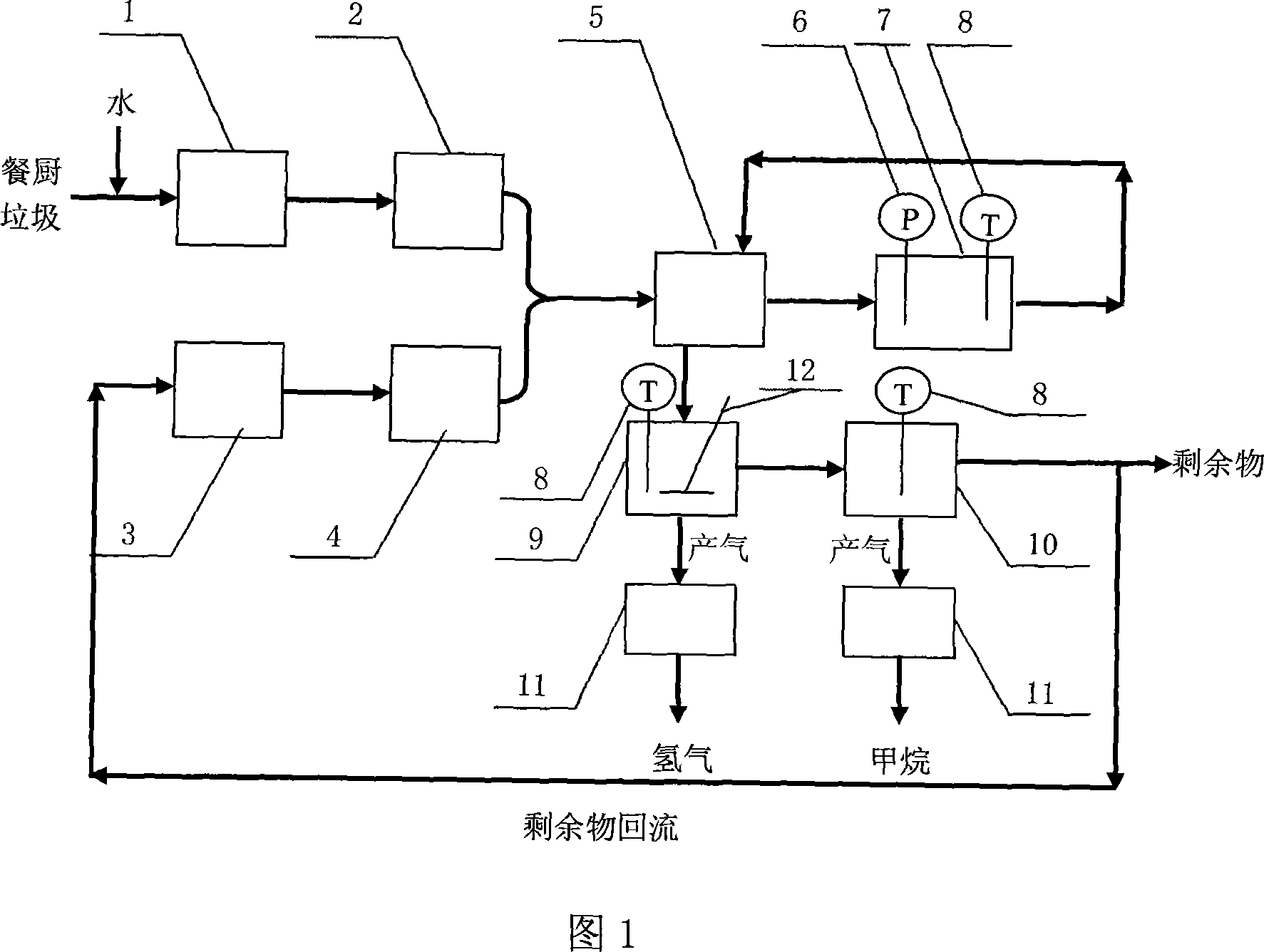
[0029] Composition of food waste: rice and flour products: vegetables: meat = 6:3:1; room temperature conditions: 24-28°C during the day and 15-20°C at night.
[0030] Mix the kitchen waste and water evenly at a weight ratio of 1:2, then crush them, and filter through an 80-mesh screen to remove larger substances; adjust the remaining sludge to a concentration of about 10g / L in the sludge conditioning tank, and use the same 80-mesh sieve to remove larger substances.
[0031] Mix the kitchen waste obtained above with the remaining sludge at a weight ratio of 2:1. After passing through a heat exchanger, enter the thermal pretreatment tank for heating. The heating condition is 80°C for 30 minutes.
[0032] The heat-treated mixture enters a heat exchanger where it exchanges heat with the non-heat-treated mixture.
[0033] After heat exchange, the temperature of the mixture of food waste and excess sludge entering the anaerobic reaction tank is about 35-40°C. Under the agitation o...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Food waste composition: by weight, rice and flour products: vegetables: meat = 6:3:1, room temperature conditions: 26-29°C during the day, 19-25°C at night.
[0037] After mixing the kitchen waste and water at a ratio of 1:3 by weight and crushing them evenly, filter them with an 80-mesh screen to remove larger substances.
[0038] Adjust the remaining sludge to a concentration of about 20g / L in the sludge conditioning tank, and filter through an 80-mesh screen to remove larger substances.
[0039] The kitchen waste obtained above is mixed with the remaining sludge at a weight ratio of 3:1. After passing through a heat exchanger, it enters a thermal pretreatment tank for heating. The heating condition is 121° C. for 10 minutes.
[0040] The heat-treated mixture enters a heat exchanger where it exchanges heat with the non-heat-treated mixture.
[0041] After heat exchange, the temperature of the mixture of food waste and excess sludge entering the first phase anaerobic ...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Food waste composition: by weight, rice and flour products: vegetables: meat = 6:3:1, room temperature conditions: 24-28°C during the day, 15-20°C at night.
[0045] After the kitchen waste and water are mixed at a weight ratio of 1:4 and evenly crushed, the larger substances are filtered through a 60-mesh screen.
[0046] The second-phase anaerobic fermentation methane-producing fermentation residue was adjusted to a concentration of about 15 g / L in the sludge conditioning tank, and larger substances were also filtered through a 60-mesh screen.
[0047] The kitchen waste obtained above is mixed with the fermentation residue of the second phase at a weight ratio of 3:1. After passing through the heat exchanger, it enters the thermal pretreatment pool for heating. The heating temperature is 150° C. for 10 minutes.
[0048] The heat-treated mixture enters a heat exchanger where it exchanges heat with the non-heat-treated mixture.
[0049] After heat exchange, the tempera...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com