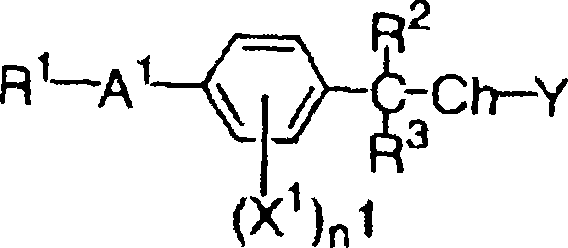
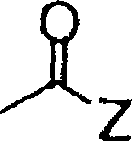
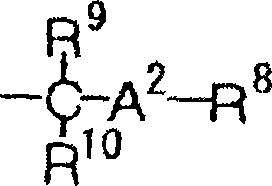Silver halide color photographic light-sensitive material
A photosensitive material, silver halide technology, applied in photosensitive materials, multi-color photography technology, photography, etc., can solve the problems of unsatisfactory, low stability, etc., and achieve good storability, increased sensitivity, and high sensitivity degree of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0332] (Preparation of blue photosensitive layer emulsion BH-1)
[0333] High silver chloride cubic grains were prepared using the simultaneous addition of aqueous silver nitrate and aqueous sodium chloride to stirred deionized and distilled water containing deionized gelatin. In this preparation, the period when 0%-5% silver nitrate addition is complete is called nucleation. During the period between when 5% of the silver nitrate addition was completed and when 85% of the silver nitrate addition was completed, the addition rates of the aqueous silver nitrate solution and the aqueous sodium chloride solution each increased linearly with time. Set the solute addition rate at which accelerated addition is complete at 85% of the critical growth rate. Potassium bromide (2.5 mole percent per mole of final silver halide) was added during the period between when 85% of the silver nitrate addition was complete and when 100% of the silver nitrate addition was complete. During the per...
Embodiment 2
[0596] (Preparation of blue photosensitive layer emulsion BH-2)
[0597] In addition to changing the temperature and the addition rate in the step of mixing the silver nitrate aqueous solution and the sodium chloride aqueous solution by simultaneous addition, and changing the amounts of various metal complexes added during the addition of the silver nitrate aqueous solution and the sodium chloride aqueous solution, according to the Emulsion BH-1 in Example 1 was prepared in the same manner as emulsion grains. The emulsion grains thus obtained were monodisperse cubic silver iodobromochloride grains with a side length of 0.45 μm and a coefficient of variation of 8.9%. After redispersing the emulsion, Emulsion BH-2 was prepared by undergoing spectral sensitization and chemical sensitization in the same manner as Emulsion BH-1 except changing the amounts of the various compounds added in Emulsion BH-1.
[0598] (Preparation of blue photosensitive layer emulsion BH-3)
[0599] In...
Embodiment 3
[0611] Evaluation was performed in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the following Treatment B was used instead of Treatment A in Example 1. Resistance to process variation is expressed as an increase in Dmin (ΔDmin) between the treatment with the developing time set at 30 seconds and the treatment with the developing time set at 12 seconds. The evaluation results performed on the yellow image are shown in Table 5.
[0612] The above-mentioned sample 101 was made into a roll with a width of 127 mm; the resulting sample was exposed to a standard photographic image using the following laser exposure; Continuously process (run the test) the exposed samples until the cumulative replenishment of the color developer reaches twice the volume of the color developer tank. The treatment under this running treatment solution is referred to as treatment B. The processing machine was modified by modifying the processing rack, thereby changing the conveying speed, thereby settin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| optical density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com