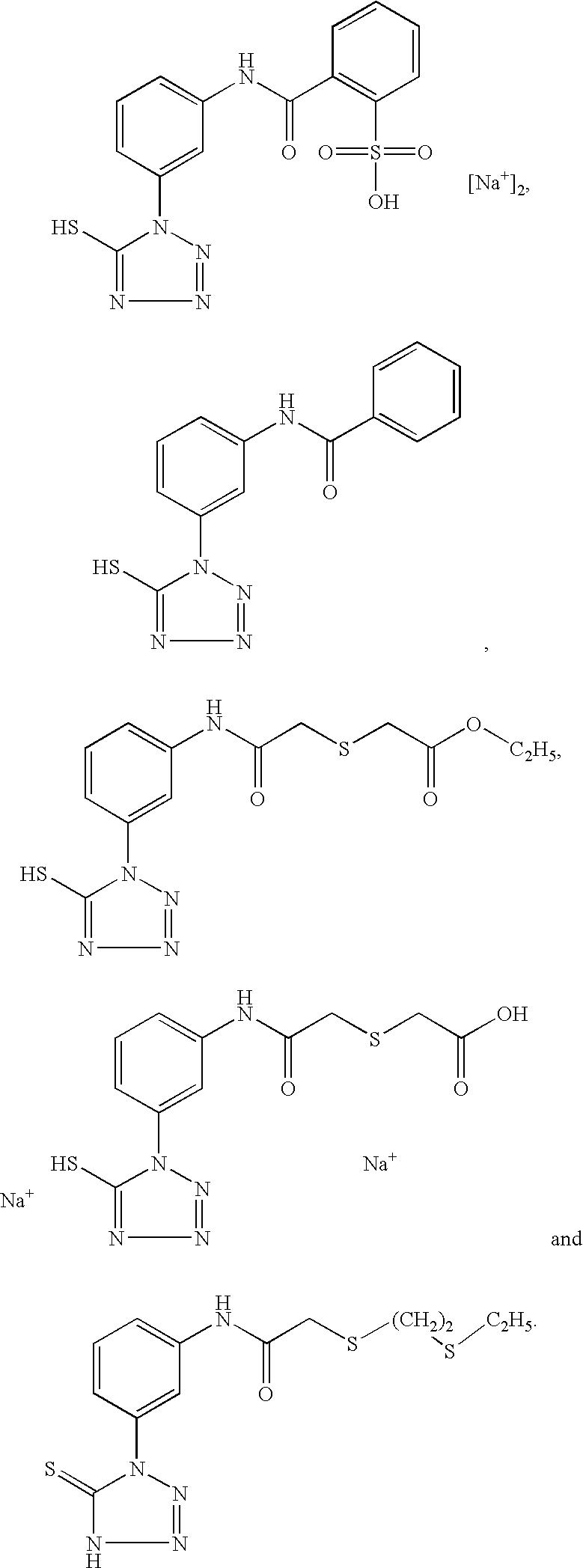
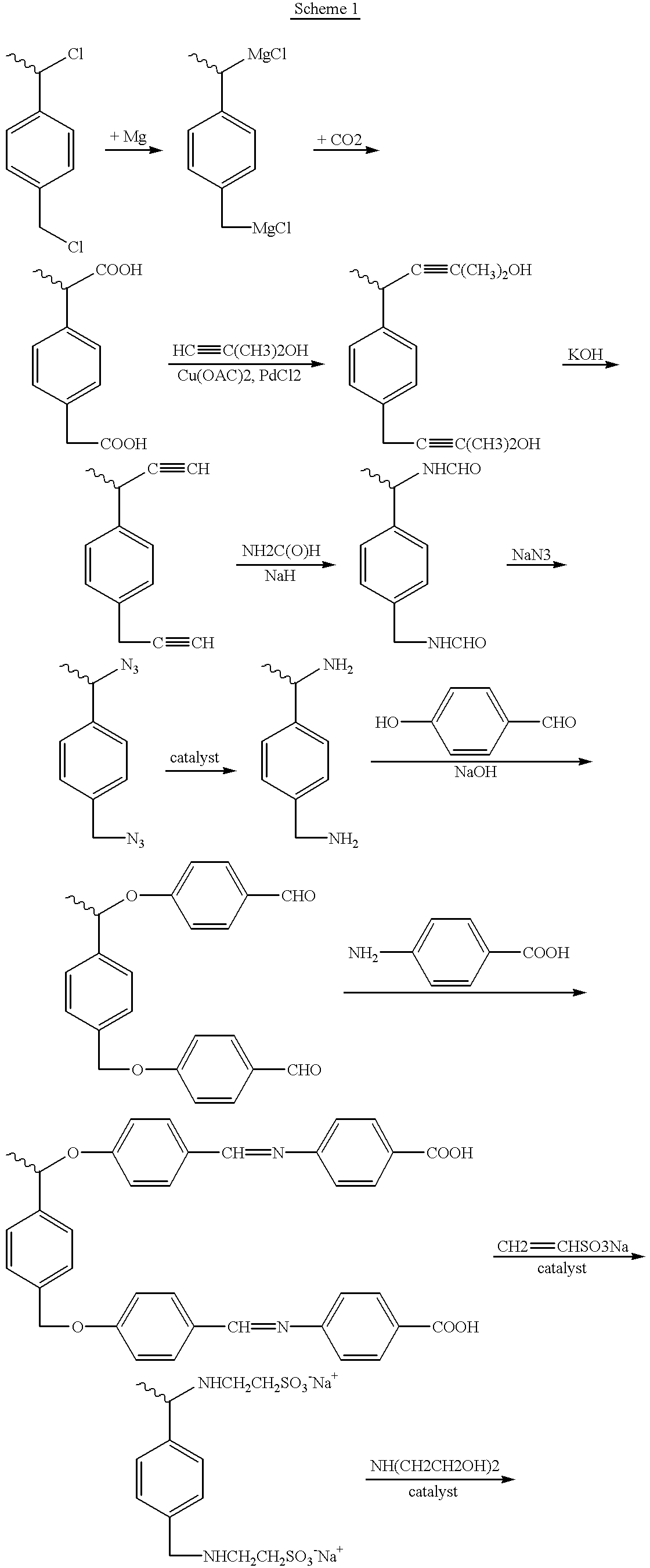
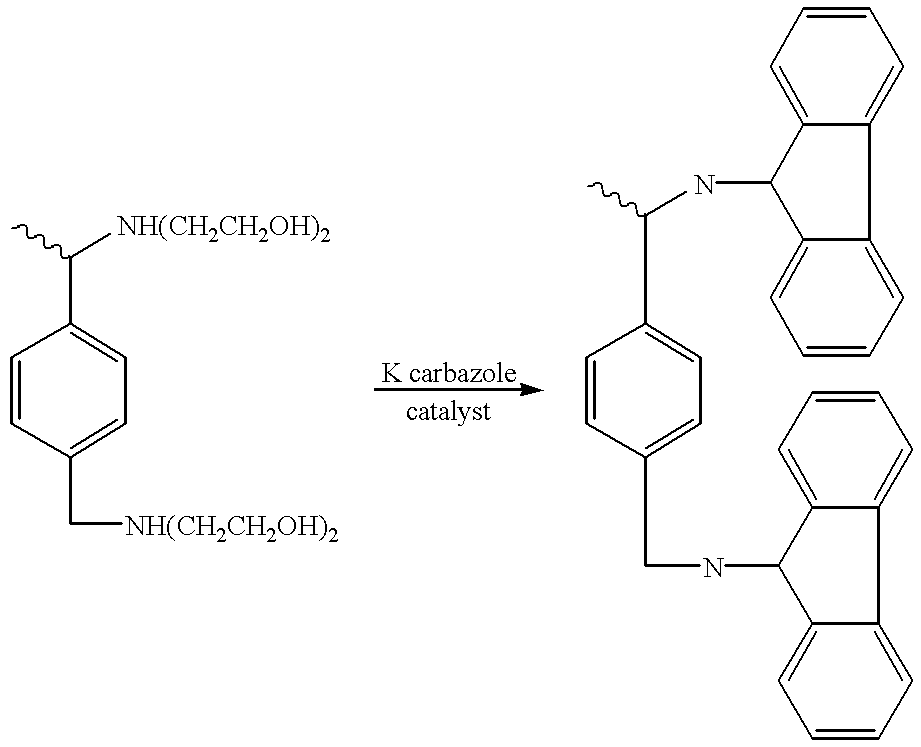
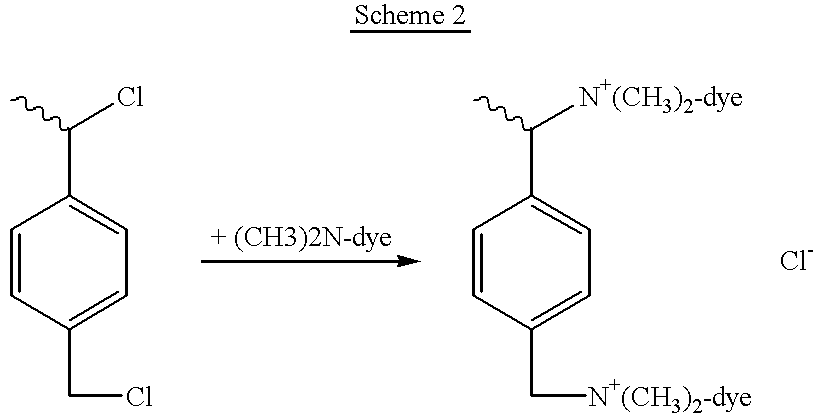
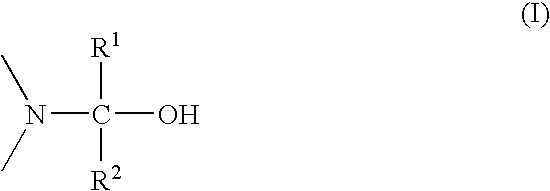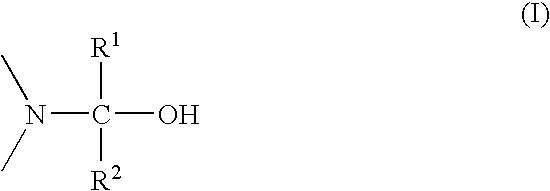Patents
Literature
502results about "Multicolor photographic processing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
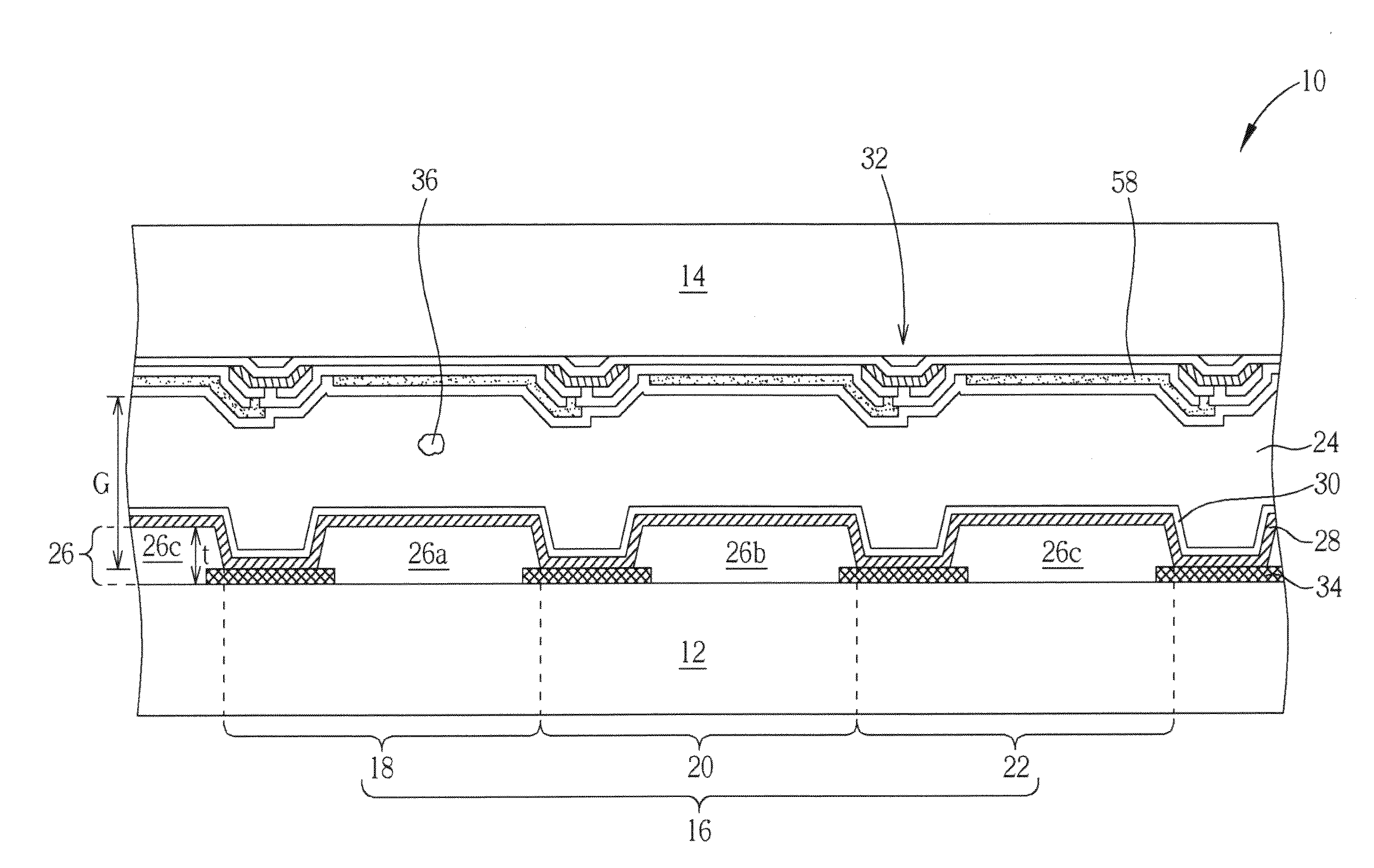
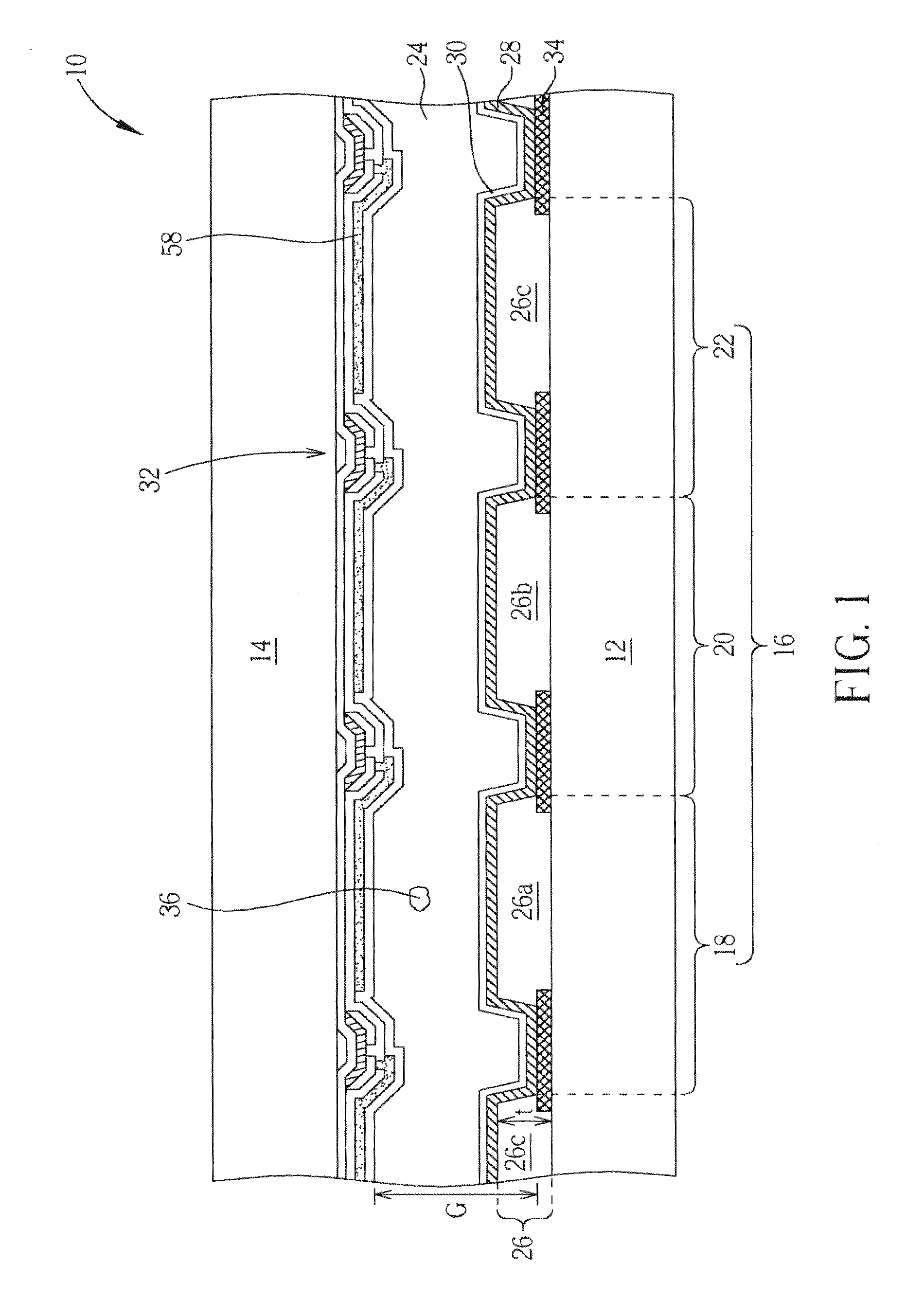
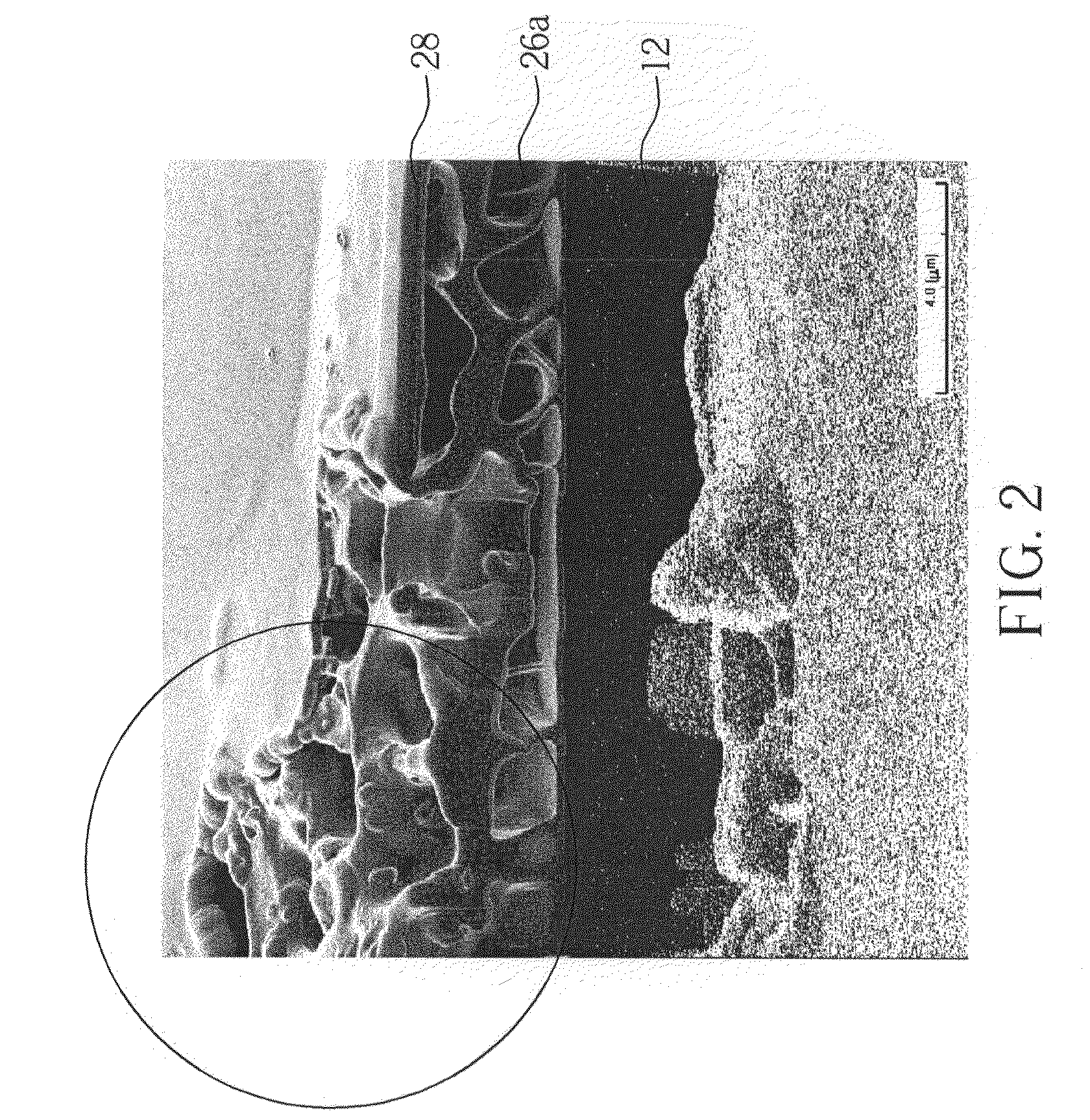
Laminate body, method, and apparatus for manufacturing ultrathin substrate using the laminate body
ActiveUS20050233547A1Easy to peelReduce pressureDiffusion transfer processesPhotosensitive materialsPolymer sciencePhotothermal conversion
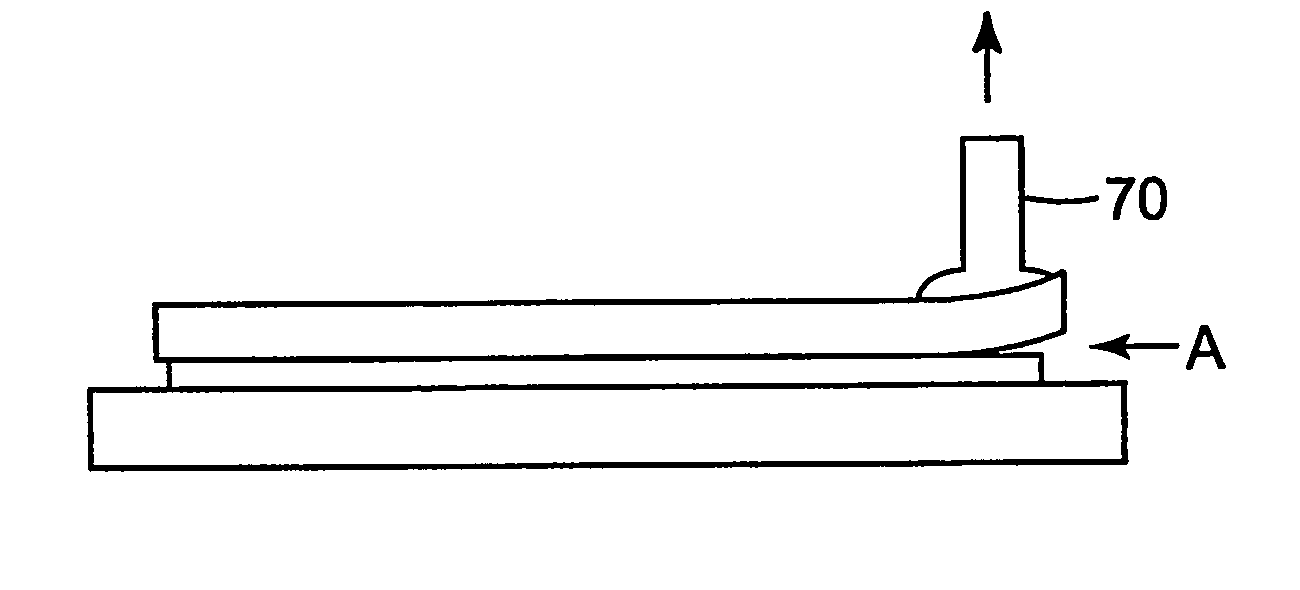
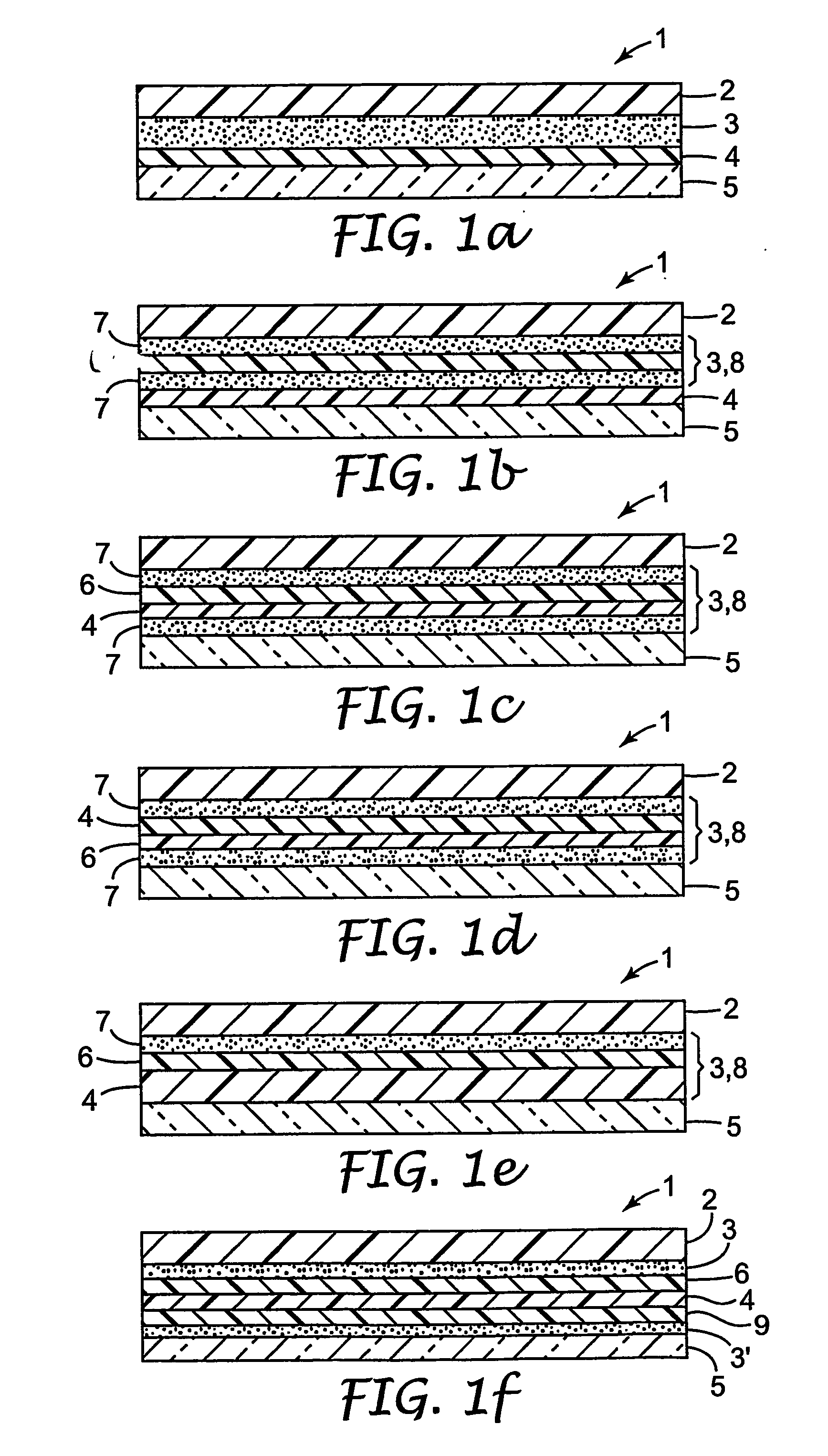
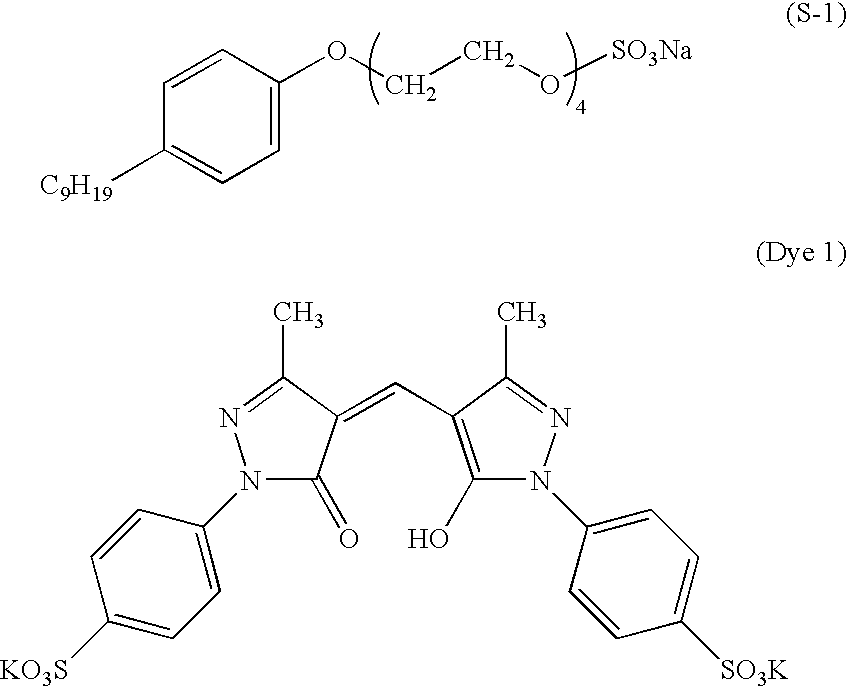
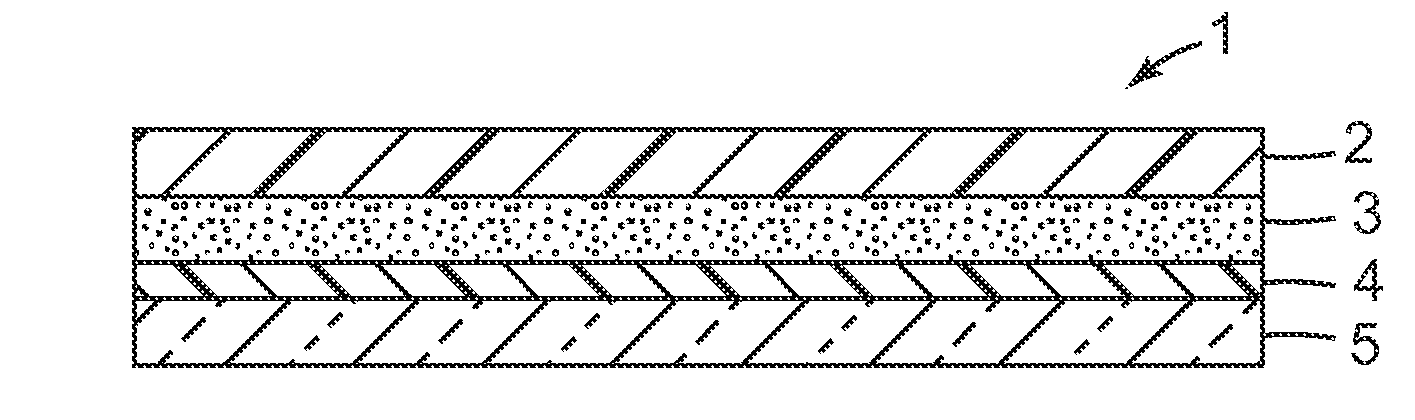
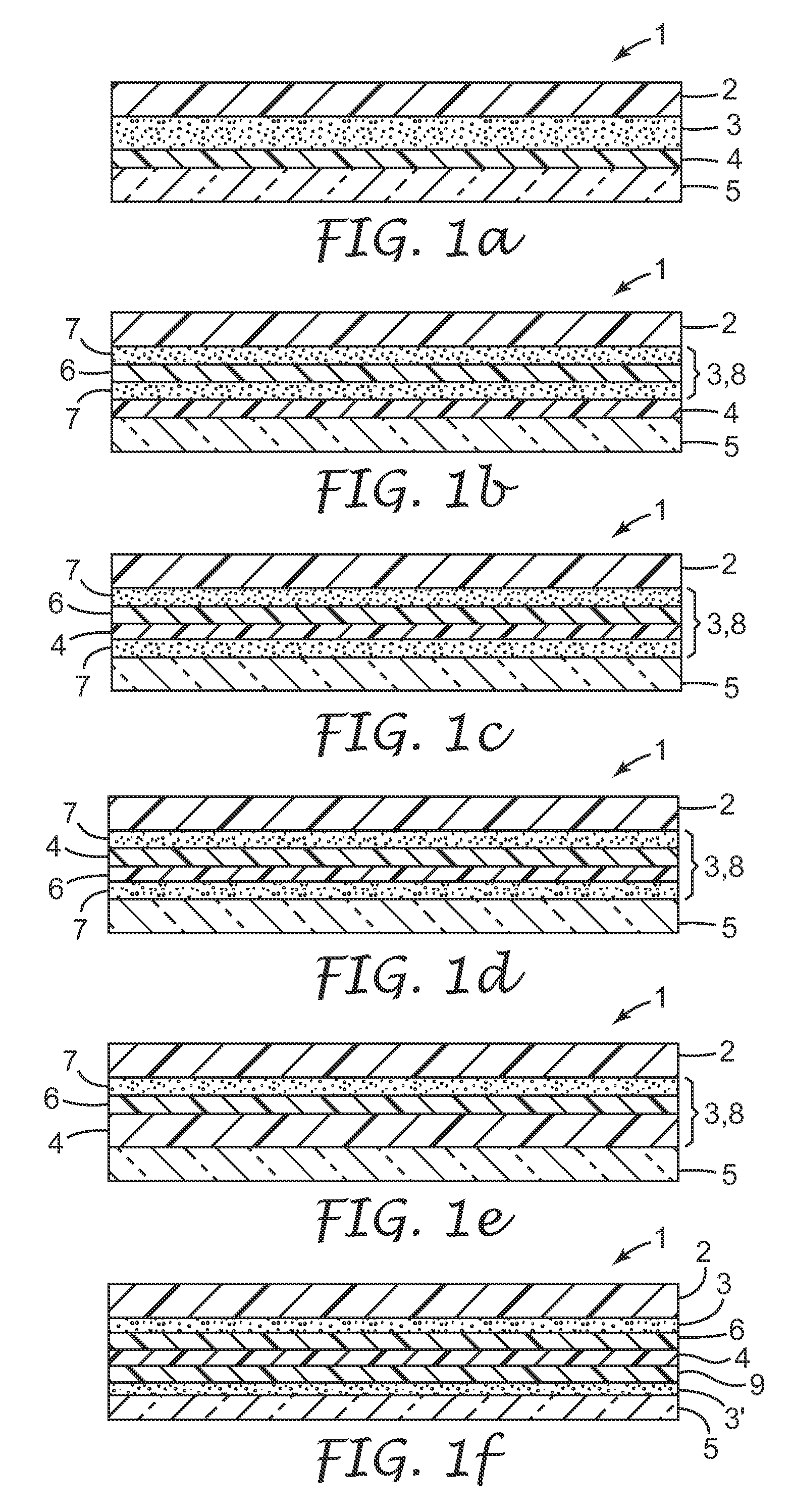
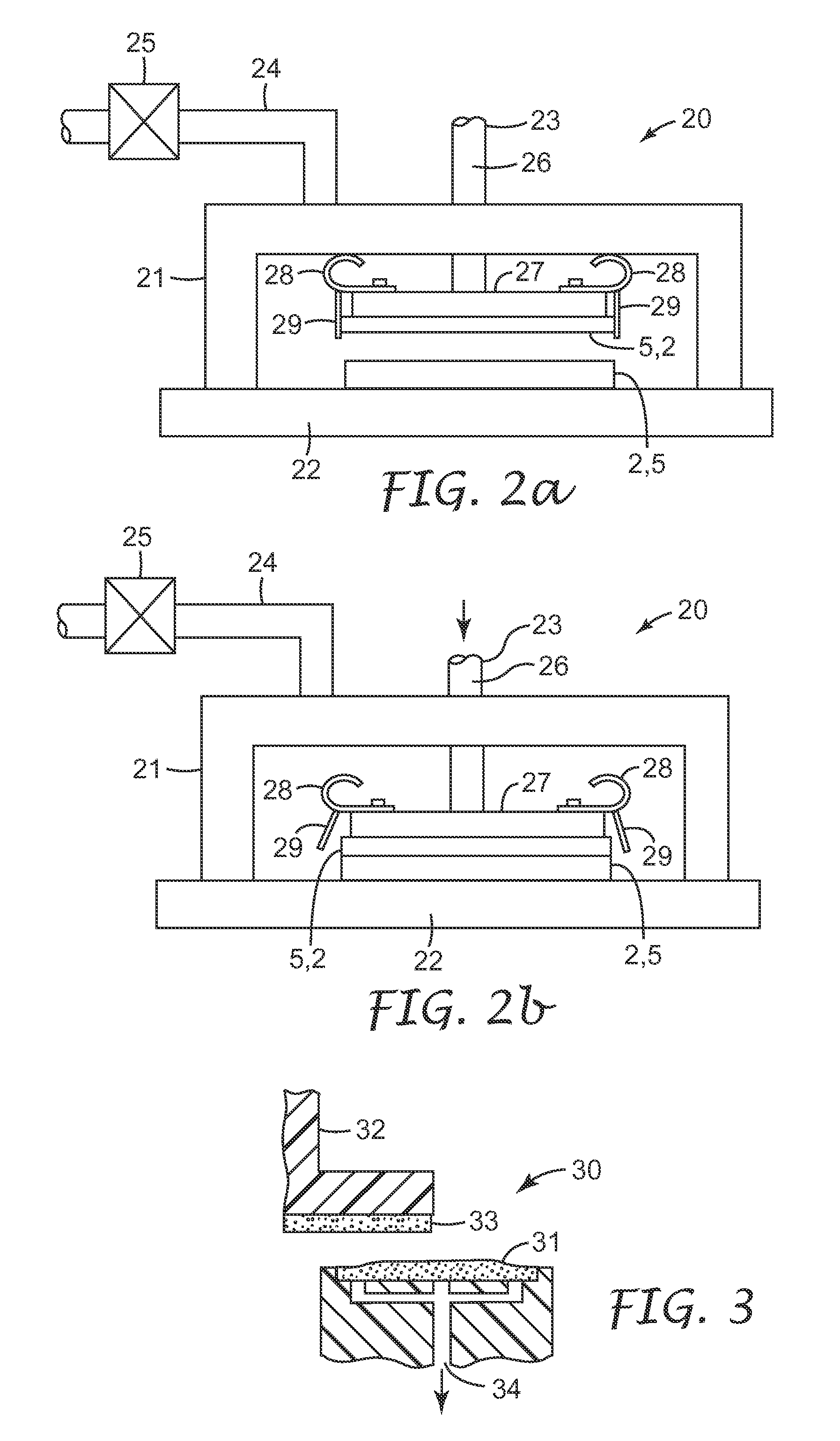
Provided is a laminated body (1) comprising a substrate (2) to be ground and a support (5), where the substrate (2) is ground to a very small thickness and can then be separated from the support (5) without damaging the substrate (2). One embodiment of the present invention is a laminated body (1) comprising a substrate (2) to be ground, a joining layer (3) in contact with the substrate (2) to be ground, a photothermal conversion layer (4) comprising a light absorbing agent and a heat decomposable resin, and a light transmitting support (5). After grinding the substrate surface which is opposite that in contact with the joining layer (3), the laminated body (1) is irradiated through the light transmitting support (5) and the photothermal conversion layer (4) decomposes to separate the substrate (2) and the light transmitting support (5).
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
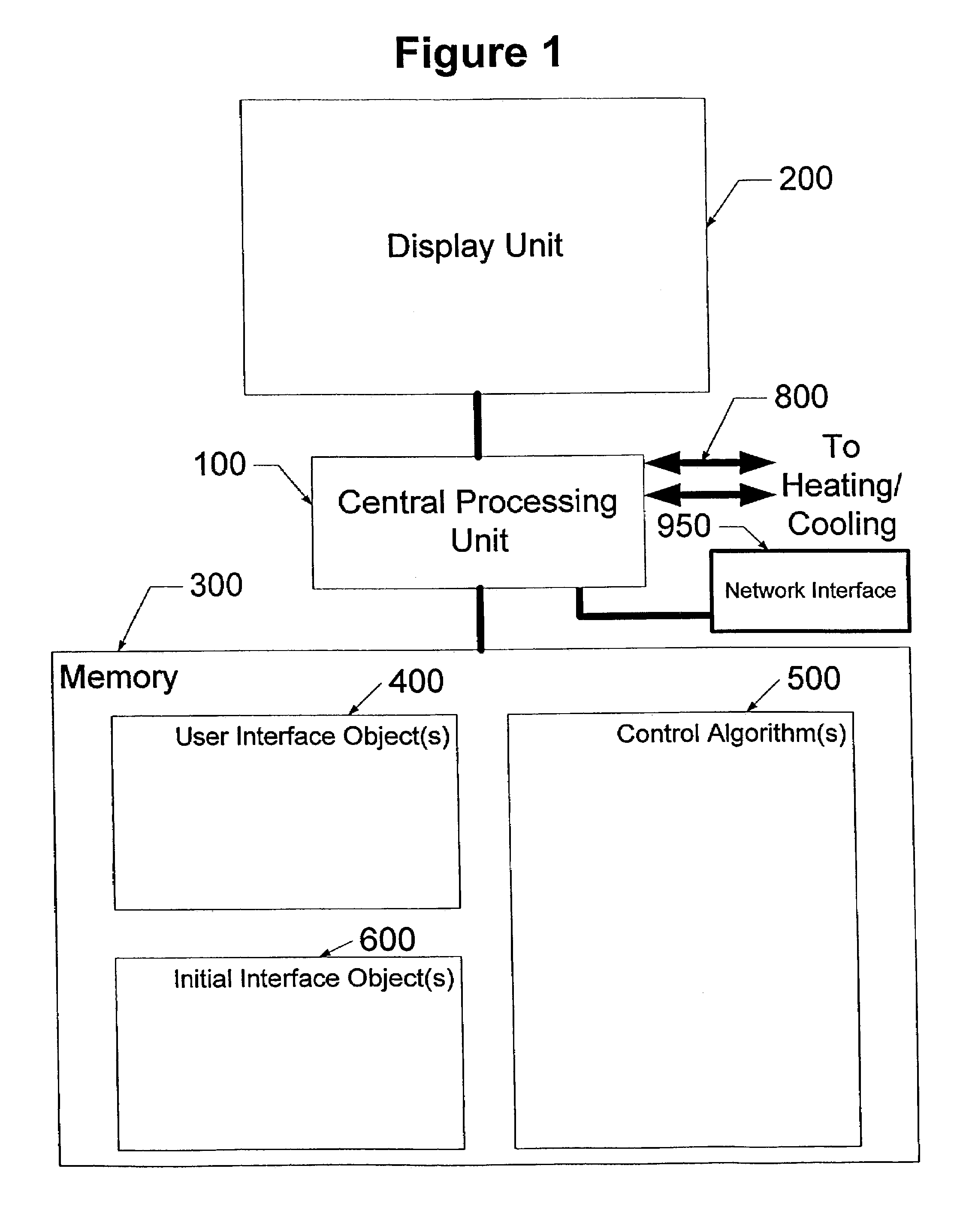
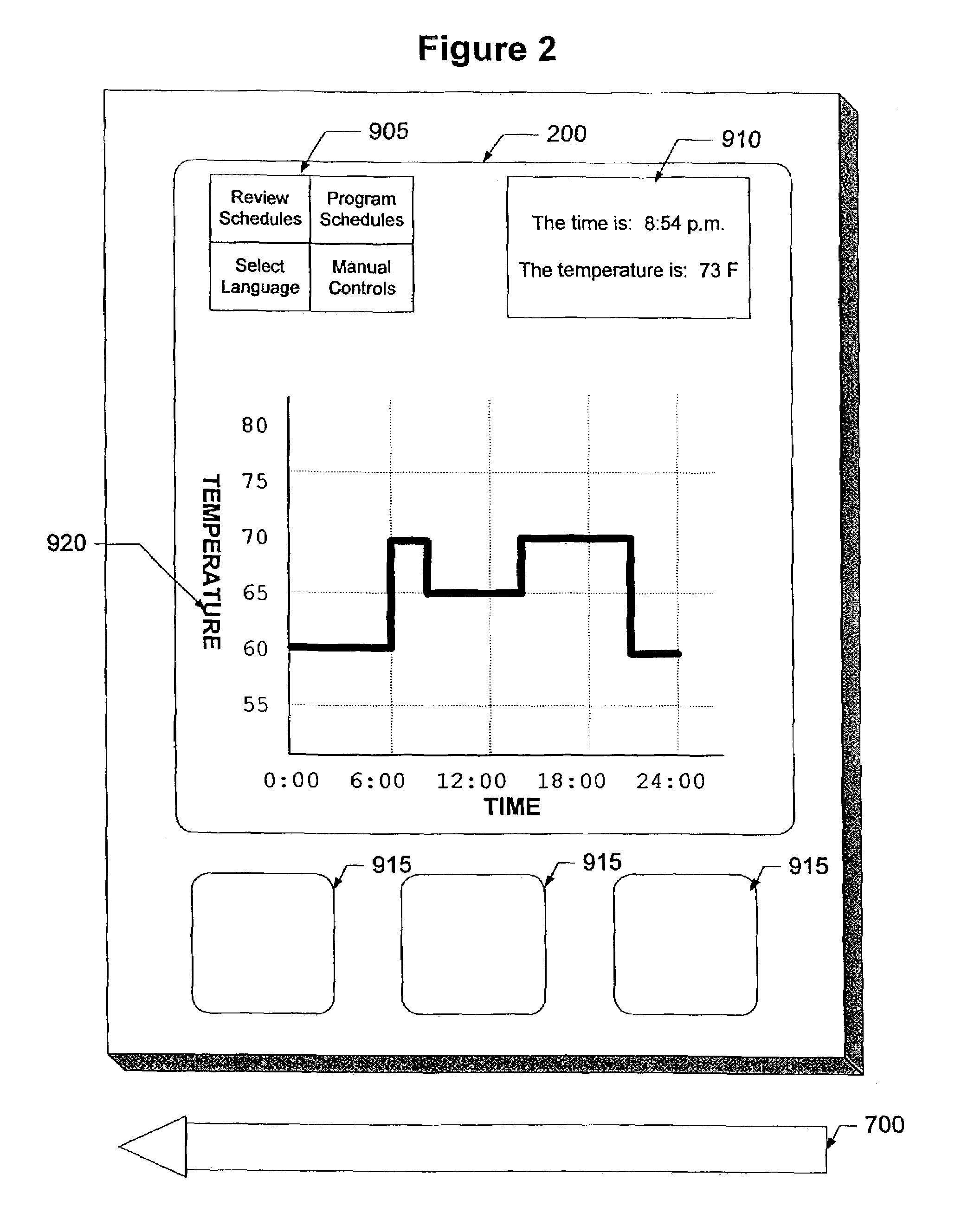
Multiple language user interface for thermal comfort controller
InactiveUS7320110B2X-ray/infra-red processesSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsMulti languageThe Internet
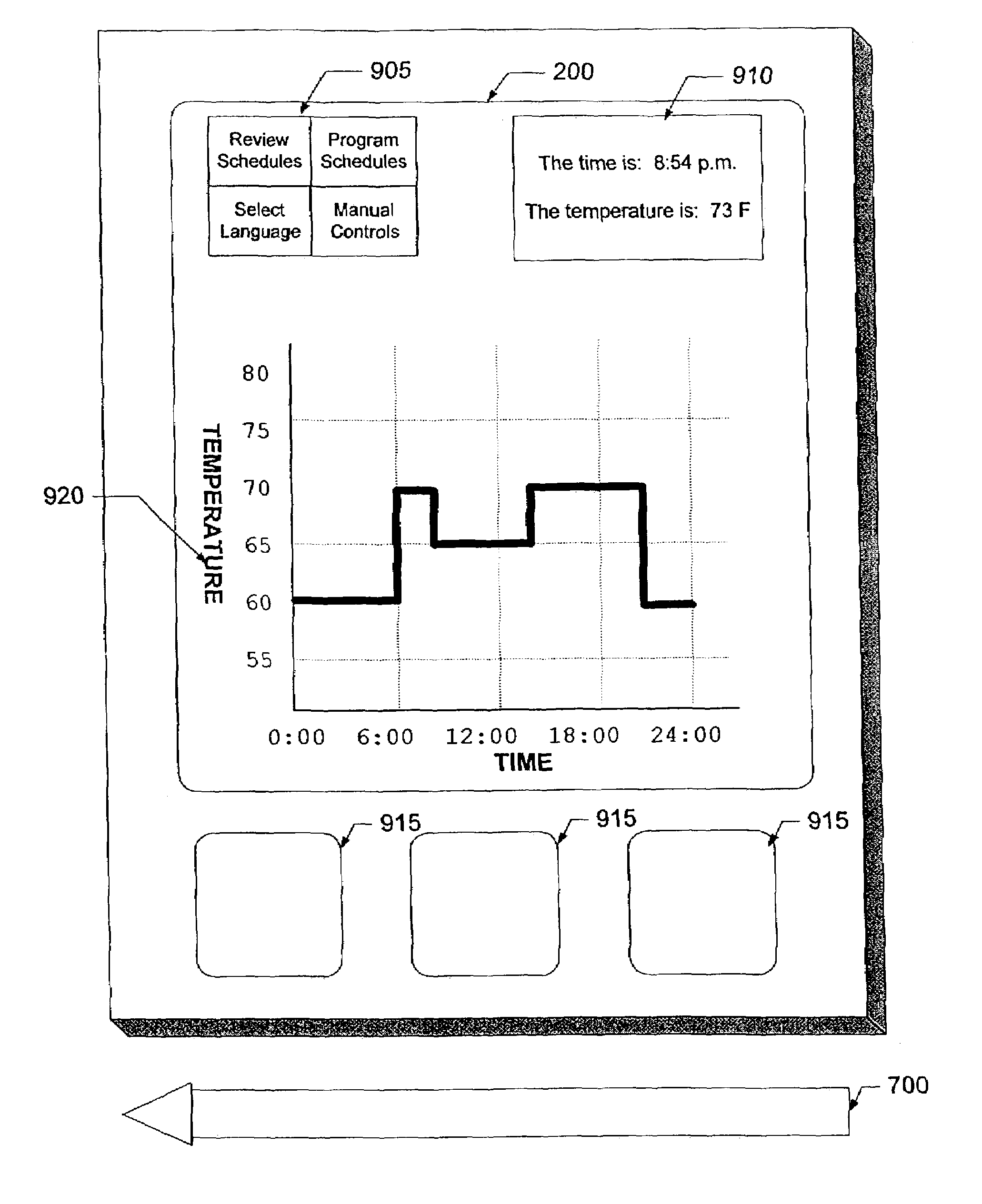
A multiple language user interface system for a thermal comfort controller. The user interface system has a central processing unit coupled to a memory, a language selector and a touch sensitive display unit. The memory can store at least one user interface object and at least one control algorithm. In some embodiments, the user interface system also has a network interface for connecting to the Internet or other network. In some embodiments, the first time the user interface system is powered-up after installation, a first set of user interface objects are displayed on the display unit and the user selects a preferred language. Once a preferred language is chosen, user interface objects can be loaded into the memory and the display unit will display the user interface objects in the preferred language. In some embodiments, control algorithms are loaded into memory.
Owner:ADEMCO INC
Optical element containing nano-composite particles
ActiveUS6888663B2High light transmittanceLiquid crystal compositionsOptical filtersParticulatesLayer thickness
The invention relates to an optical component comprising a dispersion of layered minute particulate materials in a binder, the layered materials having a layer thickness, a concentration of particulate in the binder, and a basal plane spacing sufficient to provide a component having a light transmissivity of at least 50%.
Owner:SK MICROWORKS SOLUTIONS CO LTD
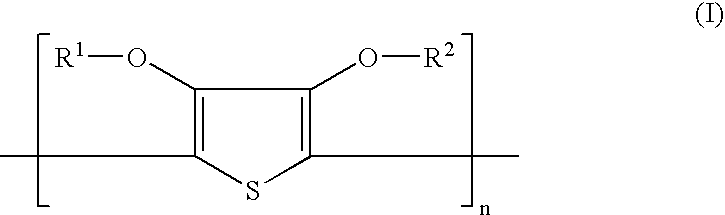
Process for preparing a substantially transparent conductive layer configuration
InactiveUS20040149962A1Improve flatnessPrevent ion migrationPhotosensitive materialsHybrid capacitor electrodesHydrogenConductive polymer
A substantially transparent conductive layer on a support, the layer comprising an intrinsically conductive polymer e.g. containing an intrinsically conductive polymer optionally containing structural units represented by formula (I): wherein n is larger than 1 and each of R<1 >and R<2 >independently represents hydrogen or an optionally substituted C1-4 alkyl group or together represent an optionally substituted C1-4 alkylene group or an optionally substituted cycloalkylene group, preferably an ethylene group, an optionally alkyl-substituted methylene group, an optionally C1-12 alkyl- or phenyl-substituted ethylene group, a 1,3-propylene group or a 1,2-cyclohexylene group; and a conductive metal non-uniformly distributed therein and forming of itself a conductive entity; a process for preparing the transparently conductive layer; and light emitting diodes, photovoltaic devices, transistors and electroluminescent devices comprising the above-described conductive layer.
Owner:AGFA GEVAERT AG
Vinyl hyperbranched polymer with photographically useful end groups
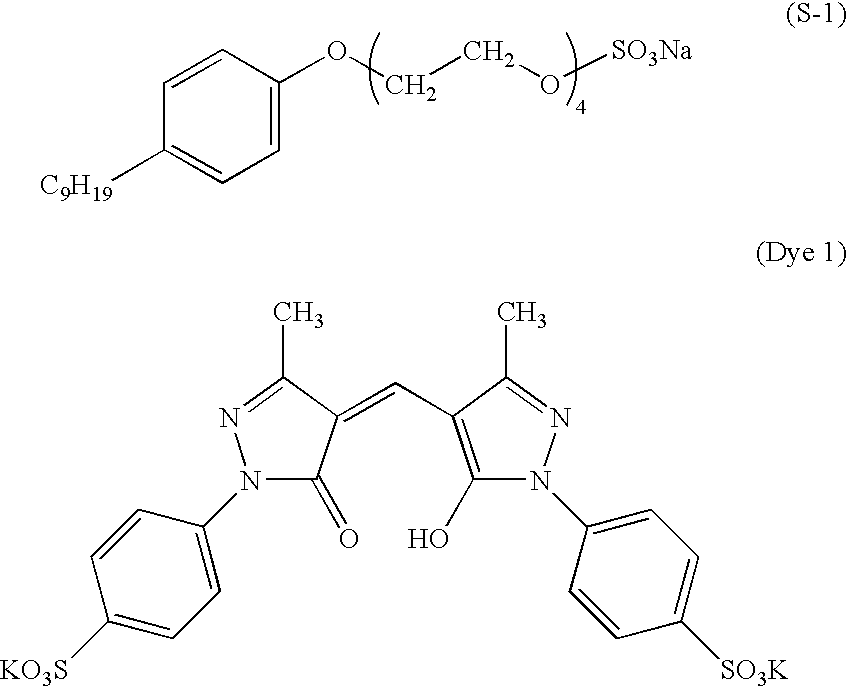
InactiveUS6252025B1Photoprinting processesMulticolor photographic processingDendrimerPolymer science
Photographically useful materials are disclosed comprising a hyperbranched polymer segment and multiple pendant photographically useful groups. Such materials may be prepared by forming an active hyperbranched polymer segment with multiple functionalized end group sites, and reacting the active hyperbranched polymer segment with an active compound comprising a photographically useful group to form a hyperbranched polymer ended with photographically useful groups. The hyperbranched segment may comprise any kind of polymer segment with hyperbranched architecture, and the active end groups may comprise any kind of reactive site. The active hyperbranched polymer may comprise any kind of other functional groups which are located in either backbone or the ends. The hyperbranched polymers containing photographically useful groups obtained in accordance with the invention are particularly advantageous in that they enable polymer structures comprising components exhibiting different photographically useful properties, while maintaining relatively low intrinsic viscosities compared to non-hyperbranched polymers containing photographically useful groups of similar chemical compositions. Additionally, the hyperbranched polymers are advantageous with respect to dendrimer type polymers in that a wide variety of hyperbranched polymer compositions may be synthesized in accordance with commercially acceptable processes.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Process For Preparing Conductive Material
ActiveUS20090233237A1High transparencyImprove conductivityConductive layers on insulating-supportsConductive materialHalogenPolymer science
It is to provide a process for preparing a conductive material in which transparency and conductivity are both high, and storage stability is high, and further, in a process for preparing a conductive material utilizing ultra fine silver particles, to provide a process for preparing a conductive material having high conductivity without requiring a calcination step which has conventionally been required.A process for preparing a conductive material having a conductive pattern containing silver on a support, which process for preparing a conductive material comprises acting at least one of the following mentioned (I) to (IV) on the pattern portion containing silver provided on the support:(I) a reducing substance,(II) a water-soluble phosphorus oxo acid compound,(III) a water-soluble halogen compound,(IV) warm water of 55° C. or higher.
Owner:MITSUBISHI PAPER MILLS LTD
Laminate body, method, and apparatus for manufacturing ultrathin substrate using the laminate body
ActiveUS7534498B2Easy to peelNot to damageDiffusion transfer processesPhotosensitive materialsPhotothermal conversionEngineering
Provided is a laminated body (1) comprising a substrate (2) to be ground and a support (5), where the substrate (2) is ground to a very small thickness and can then be separated from the support (5) without damaging the substrate (2). One embodiment of the present invention is a laminated body (1) comprising a substrate (2) to be ground, a joining layer (3) in contact with the substrate (2) to be ground, a photothermal conversion layer (4) comprising a light absorbing agent and a heat decomposable resin, and a light transmitting support (5). After grinding the substrate surface which is opposite that in contact with the joining layer (3), the laminated body (1) is irradiated through the light transmitting support (5) and the photothermal conversion layer (4) decomposes to separate the substrate (2) and the light transmitting support (5).
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
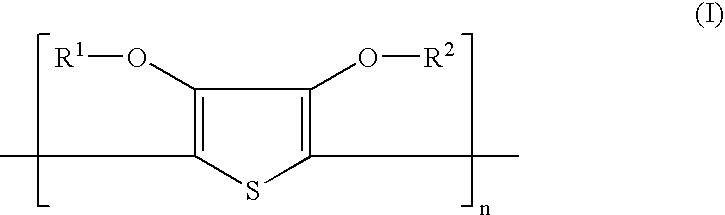
Resist stripping agent and process of producing semiconductor devices using the same
InactiveUS20030186175A1Easy to disassembleShort timeMulticolor photographic processingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistHydrogen atom
A resist stripping agent comprising a specific alkanolamine having at least one functional group represented by the following formula (I): wherein R<1 >and R<2 >are each hydrogen atom, C1-C8 alkyl or C1-C8 alkenyl. The resist stripping agent easily and efficiently removes resist films and resist residues remaining after etching or after ashing subsequent to etching in manufacturing semiconductor devices at low temperatures in short period of time. The resist stripping agent is resistant to corrosion against materials for substrate, circuits and insulating films.
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
Binderless storage phosphor screen with needle shaped crystals
InactiveUS20010007352A1Improve compromiseImprove clarityX-ray/infra-red processesElectrical apparatusNeedle ShapePhysics
A binderless storage phosphor screen with needle shaped crystals, wherein the phosphor is an alkalihalide phosphor and the needles show high [100] unit cell orientation in the plane of the screen.
Owner:AGFA GEVAERT AG
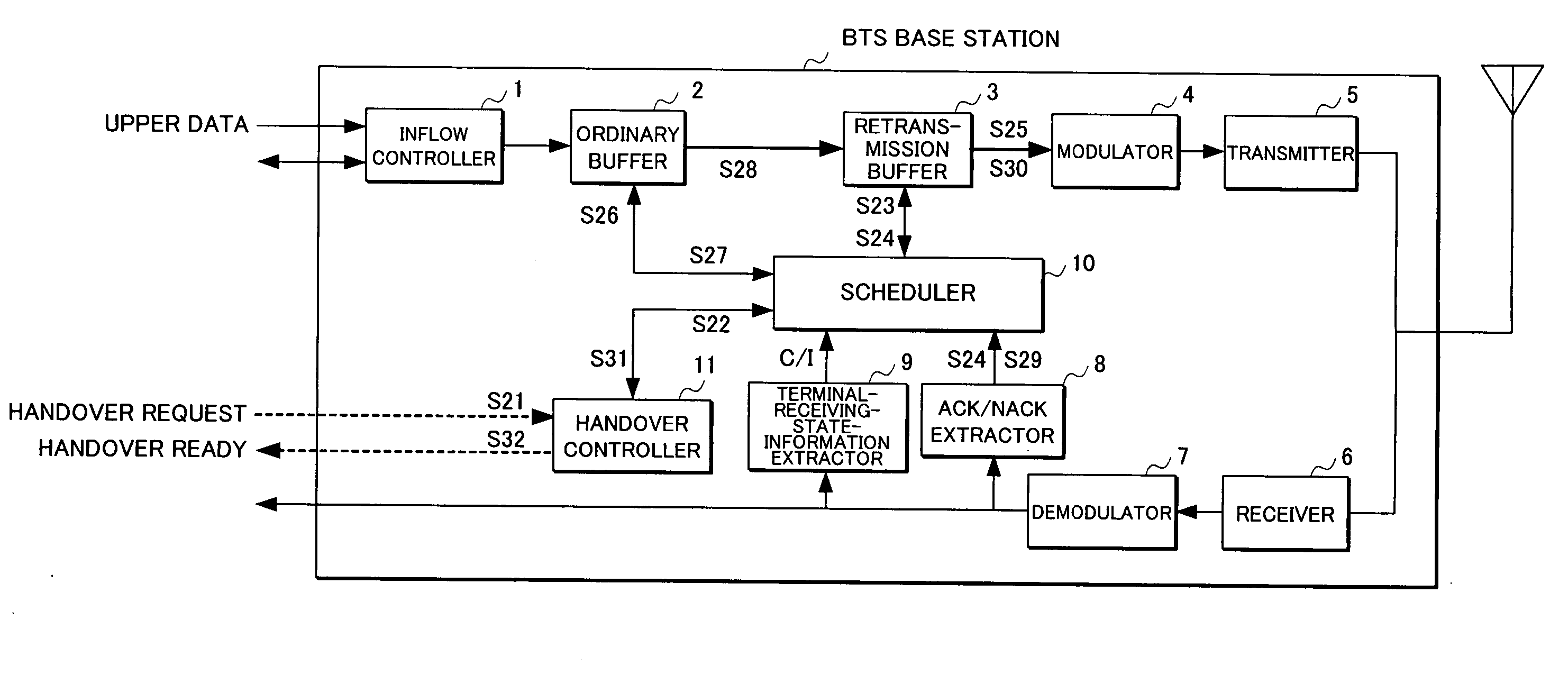
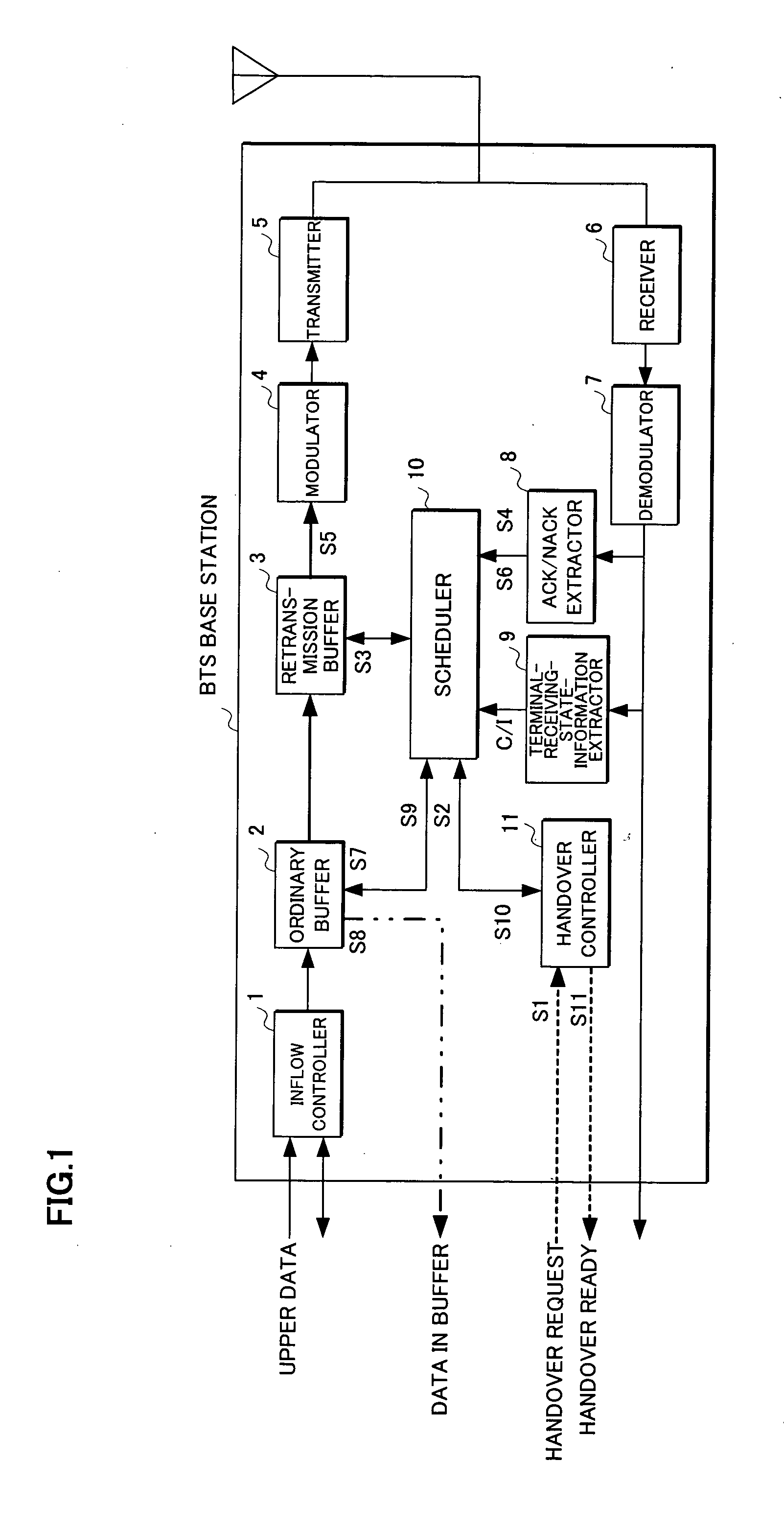
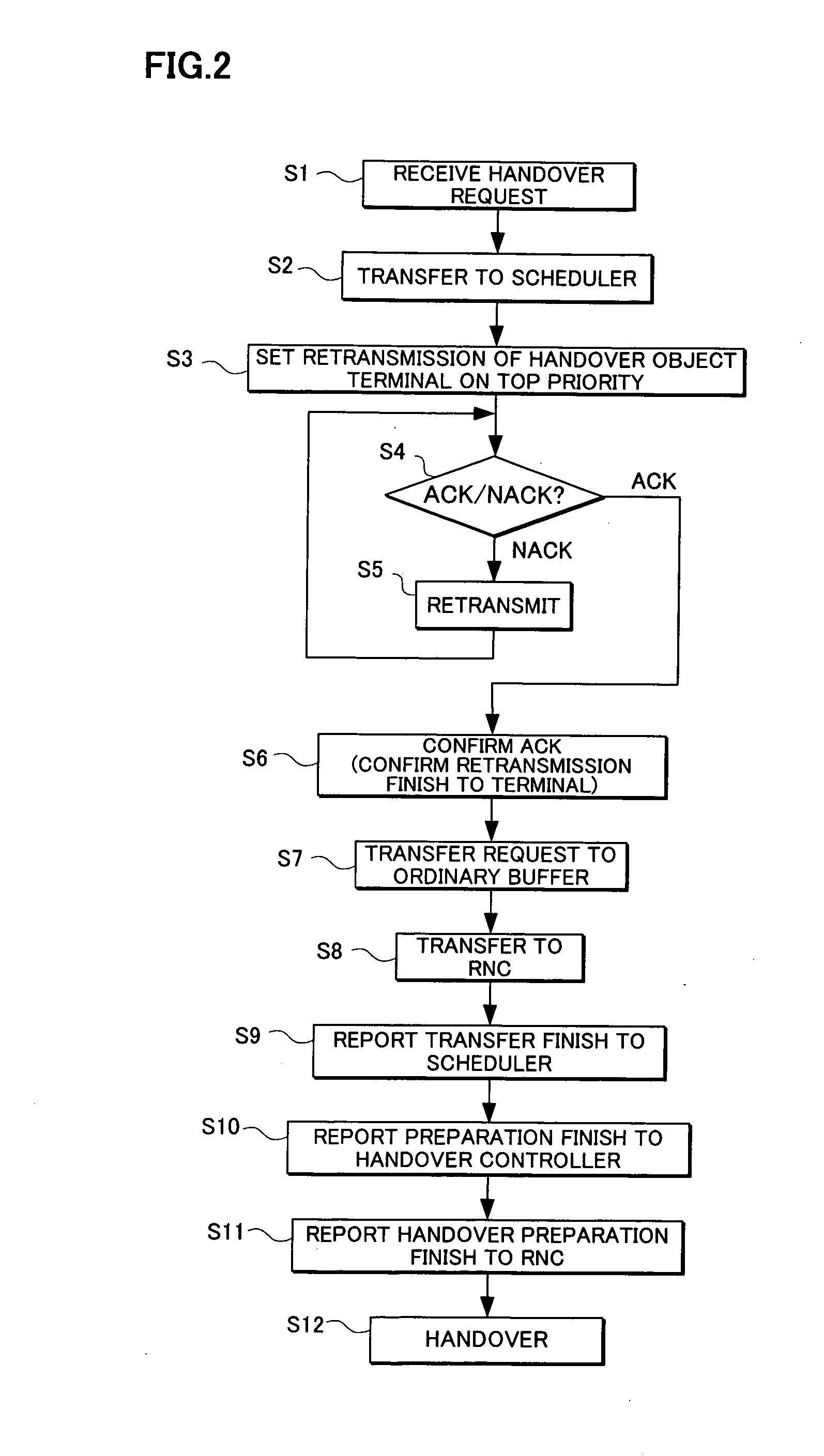
Radio base station and mobile communication system
InactiveUS20050259663A1Reduce transfer timeShorten the timeMulticolor photographic processingData switching by path configurationTelecommunicationsMobile communication systems
A radio base station and a mobile communication system where a hand-over request is detected and retransmission data is preferentially processed for a hand-over object terminal. A radio base station may include a buffer holding communication data for transmission to a terminal, an extractor extracting a communication request signal from a received signal, and a scheduler controlling transmission of the communication data based on an output signal of the extractor. Also a scheduler, upon detection of a hand-over request, controls transmission so as to preferentially perform the data transmission by raising an order of the data transmission for a hand-over terminal before hand-over.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Printed polymeric film and process for making same
InactiveUS6051305ADecorative surface effectsDuplicating/marking methodsPolymer sciencePolymer thin films
A printed film includes a substrate film with a surface polymeric layer that includes a thermoplastic polymer having a melting point of no more than about 130 DEG C. and, on a surface of the film, a printed image in the form of a polymeric film. The substrate film can be printed without chemically and / or oxidatively priming the surface to be printed and exhibits superior retention of the image after undergoing heat treatment.
Owner:CRYOVAC INC
Process for preparing conductive material
InactiveUS8012676B2High transparencyImprove conductivityConductive layers on insulating-supportsConductive materialPolymer scienceWarm water
It is to provide a process for preparing a conductive material in which transparency and conductivity are both high, and storage stability is high, and further, in a process for preparing a conductive material utilizing ultra fine silver particles, to provide a process for preparing a conductive material having high conductivity without requiring a calcination step which has conventionally been required.A process for preparing a conductive material having a conductive pattern containing silver on a support, which process for preparing a conductive material comprises acting at least one of the following mentioned (I) to (IV) on the pattern portion containing silver provided on the support:(I) a reducing substance,(II) a water-soluble phosphorus oxo acid compound,(III) a water-soluble halogen compound,(IV) warm water of 55° C. or higher.
Owner:MITSUBISHI PAPER MILLS LTD
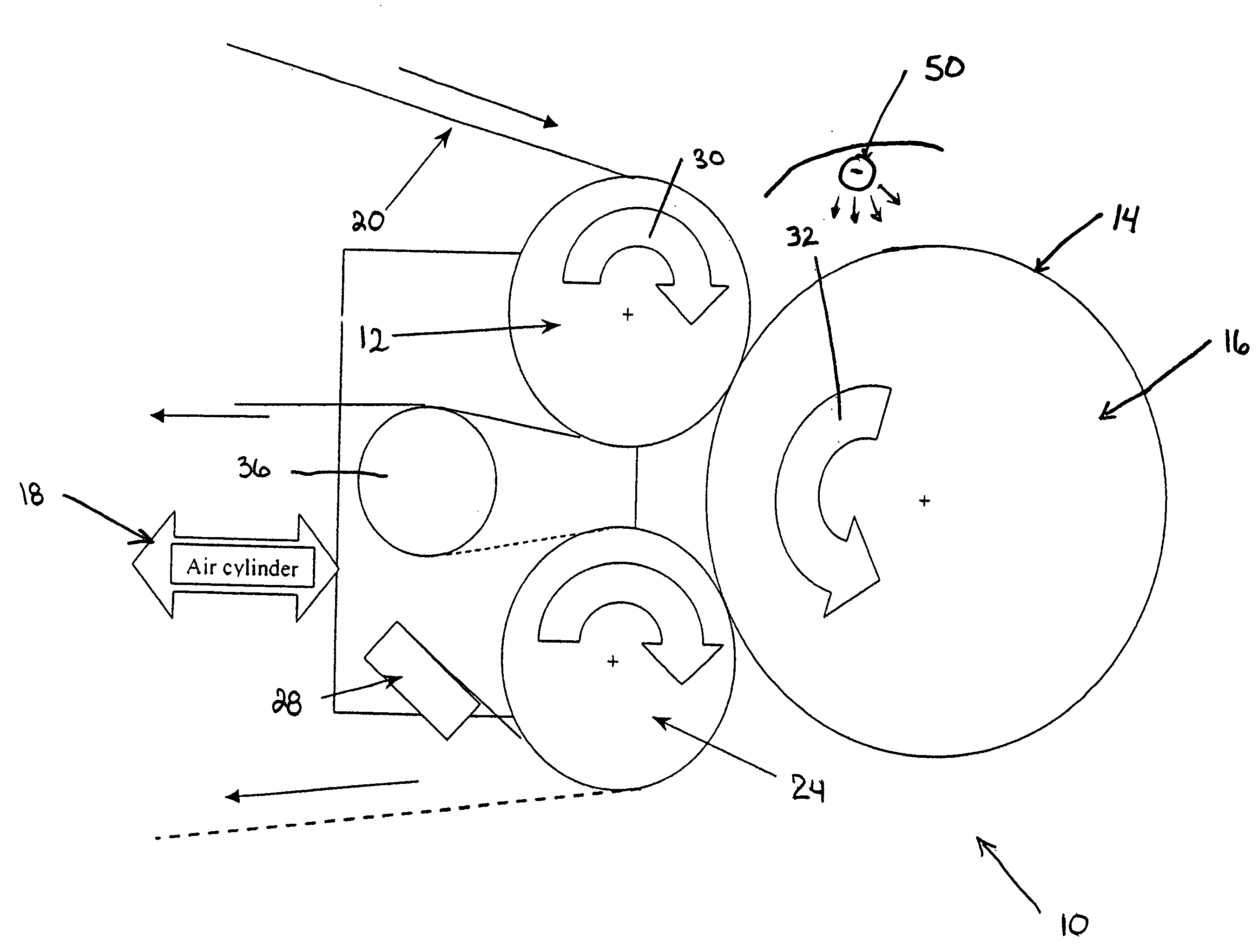
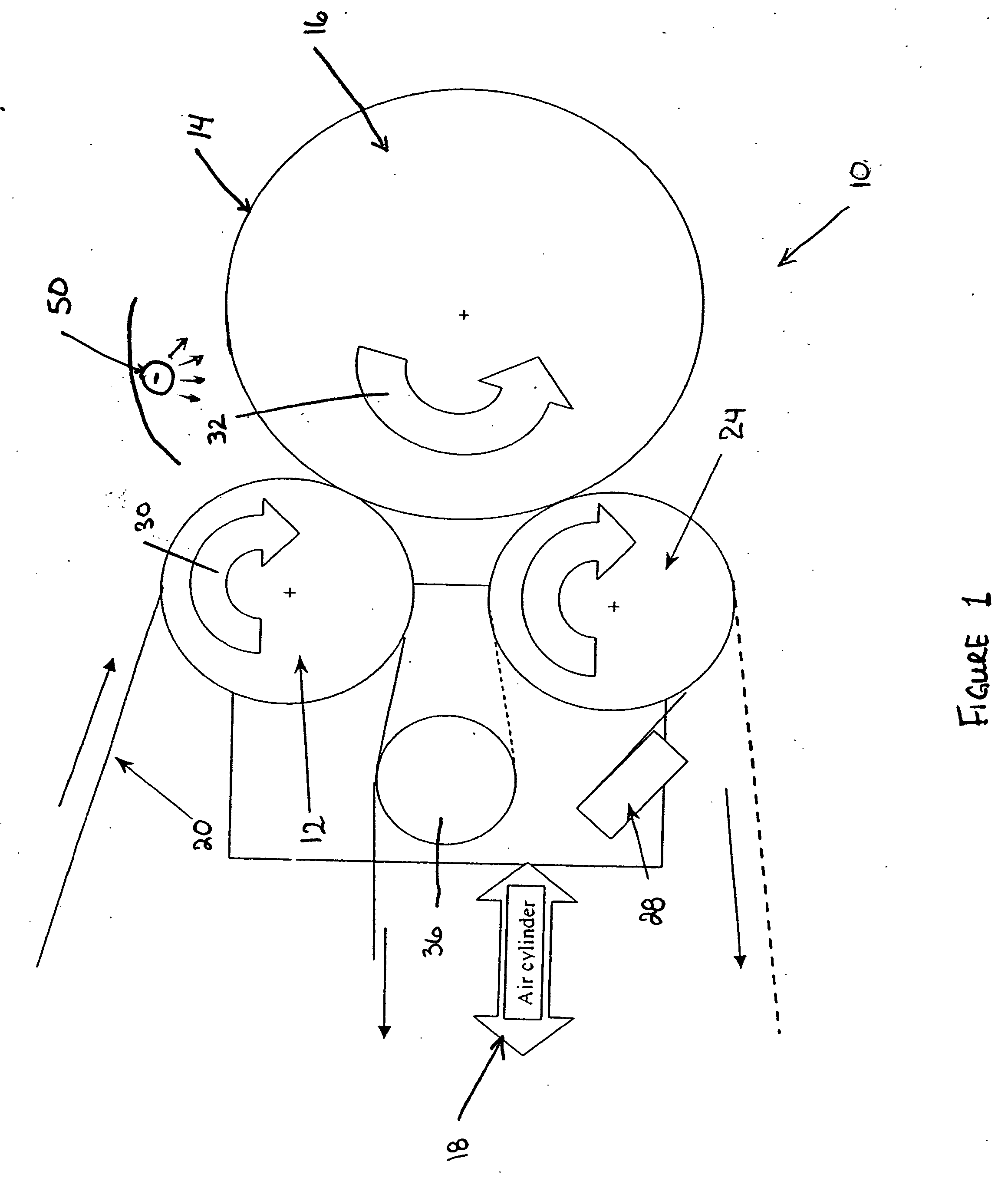
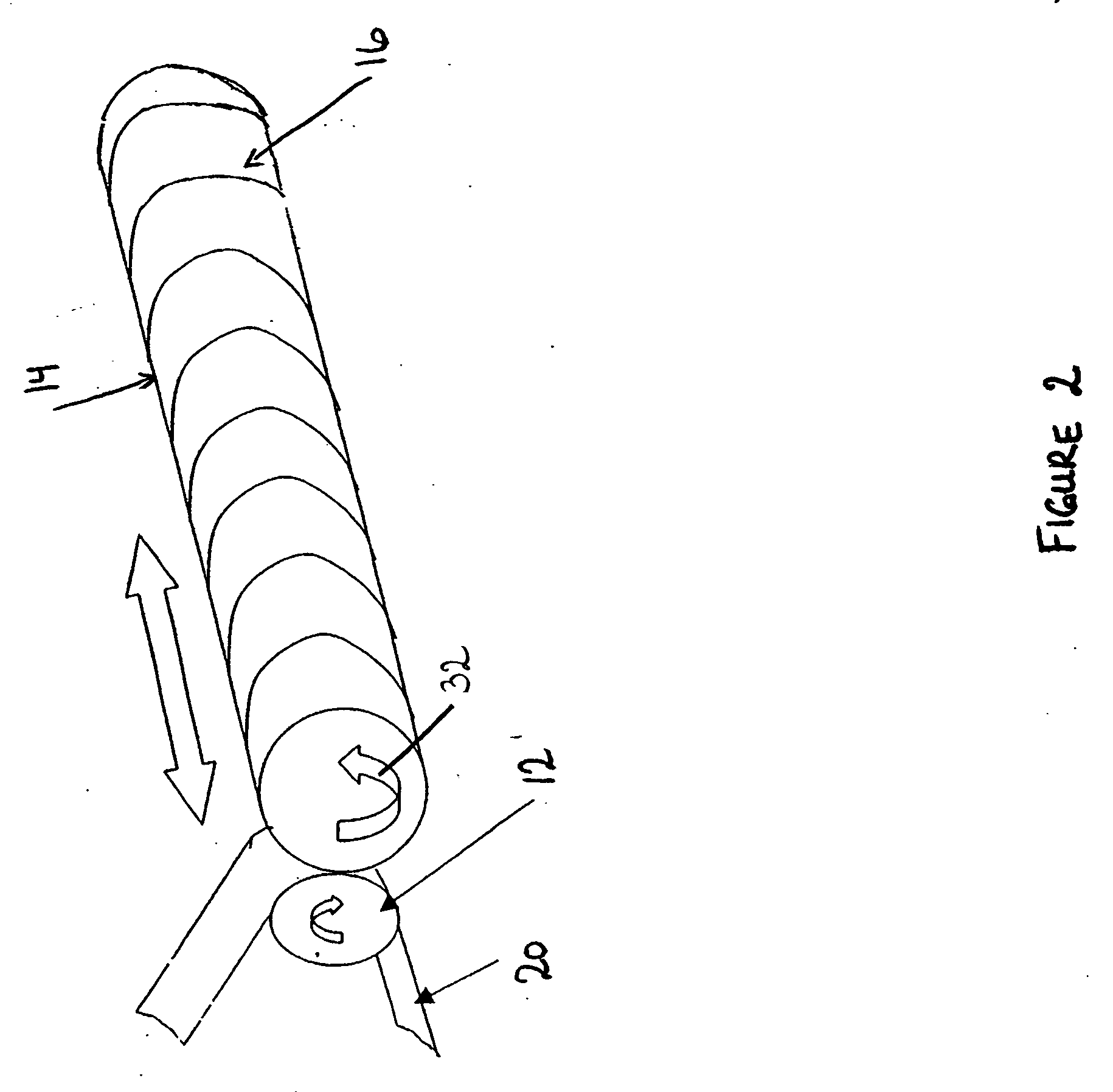
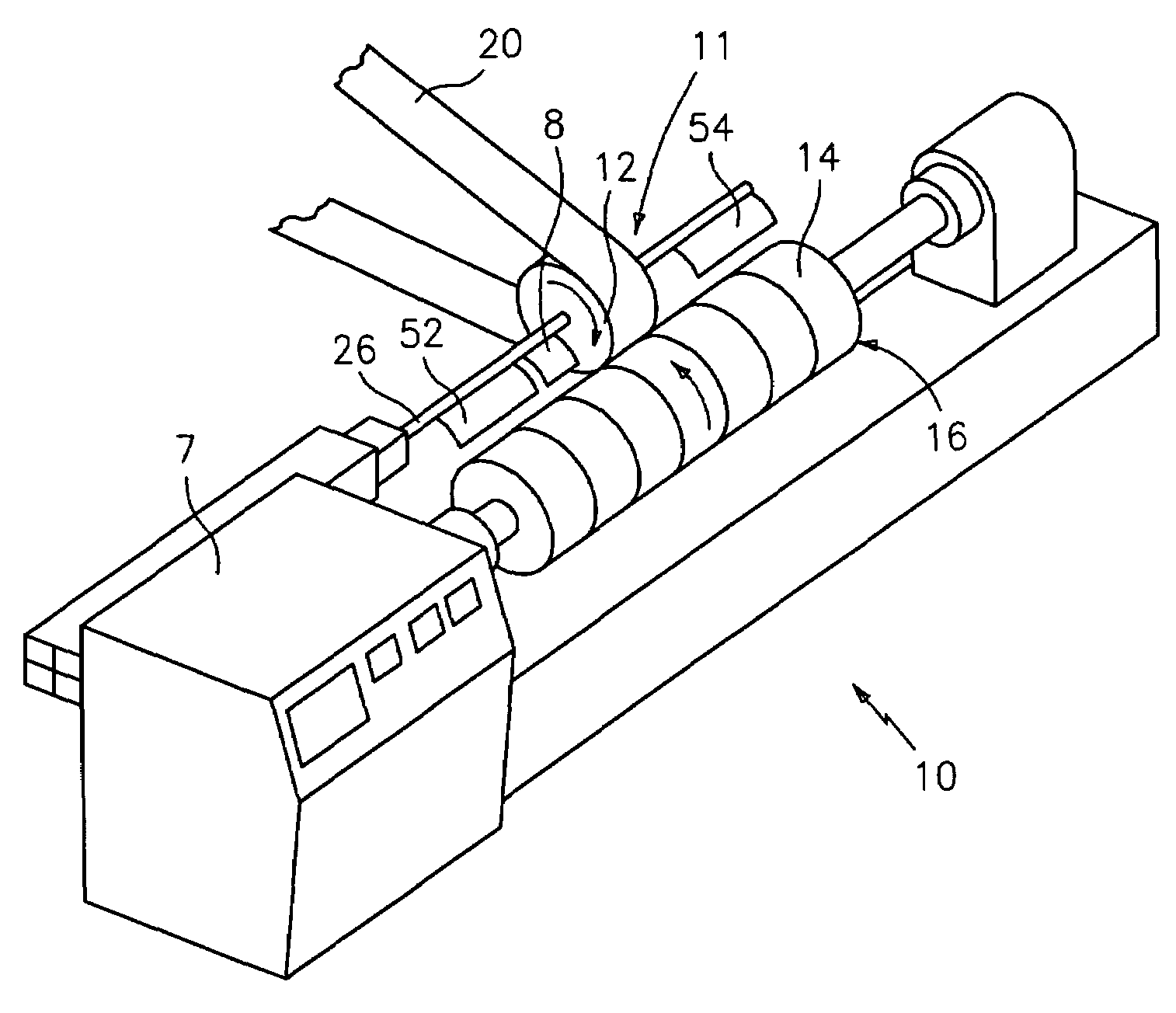
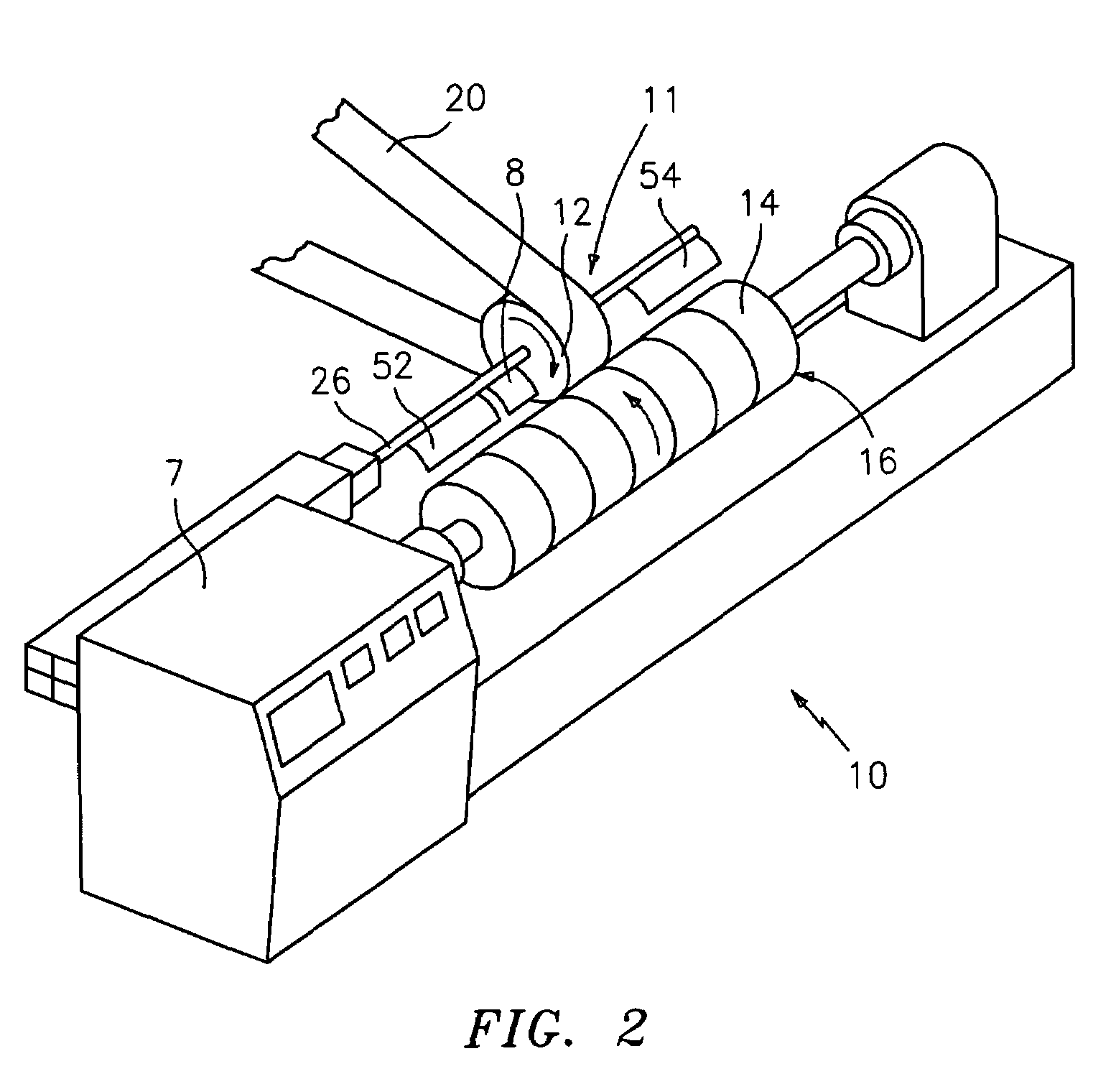
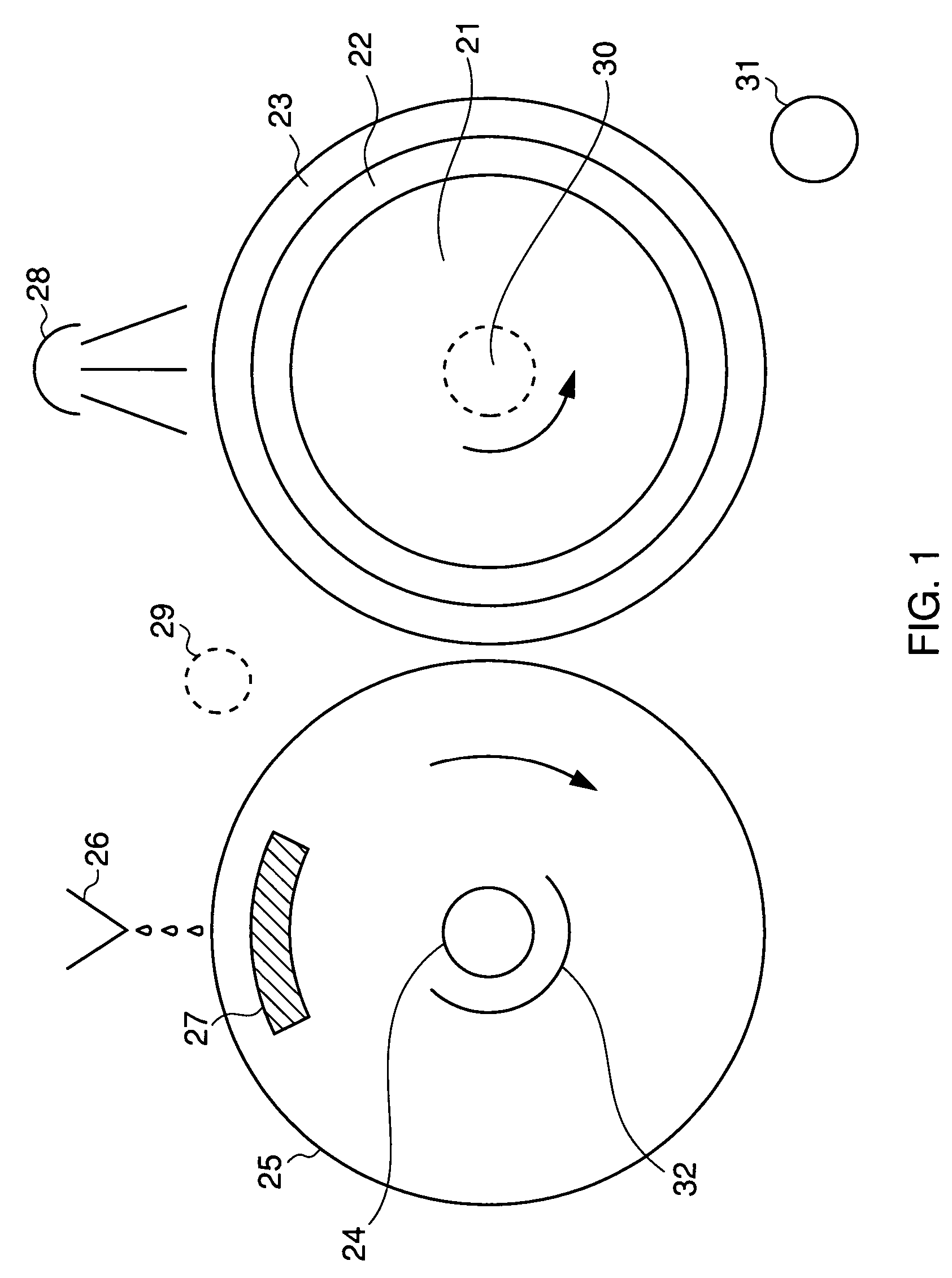
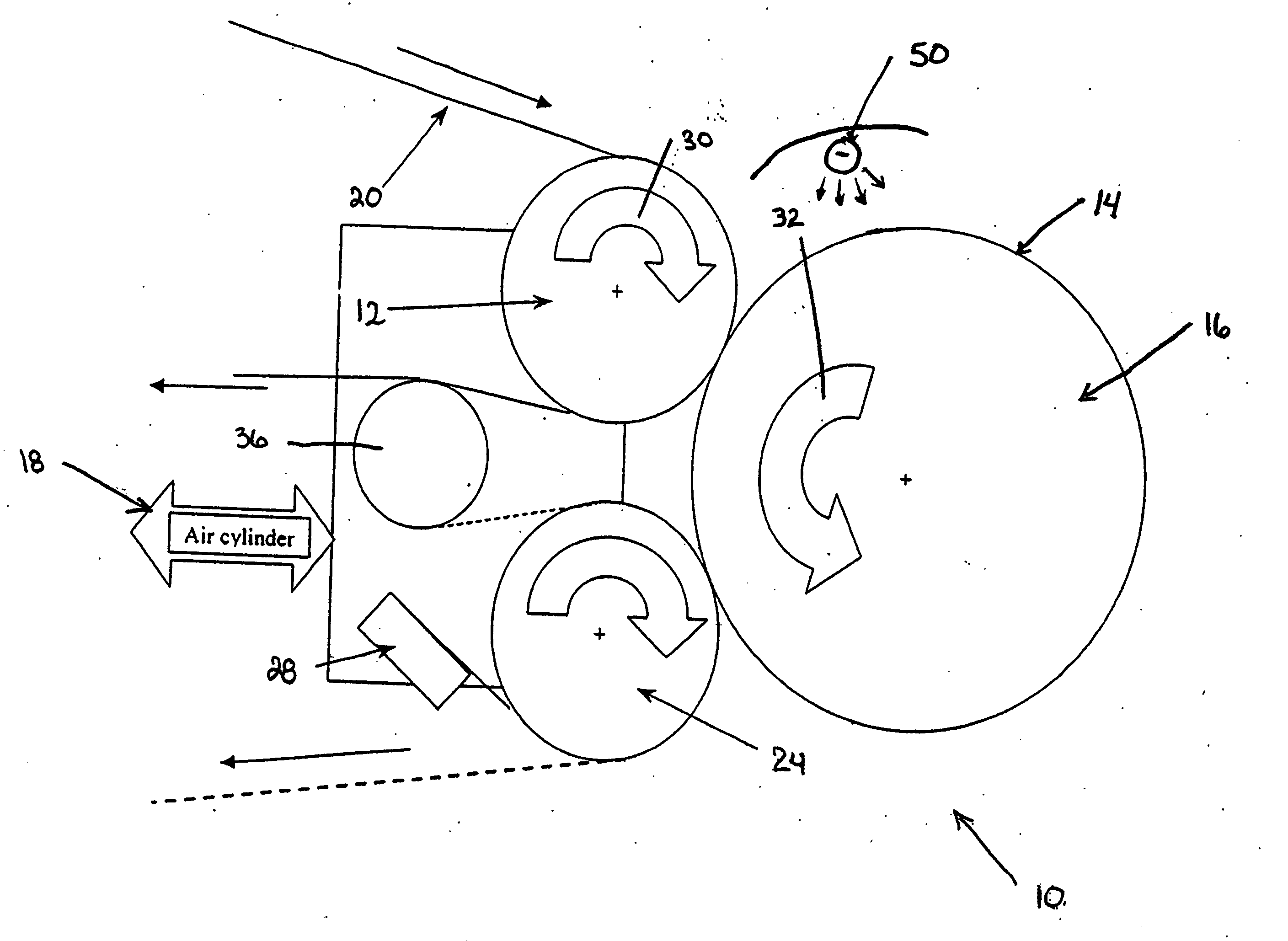
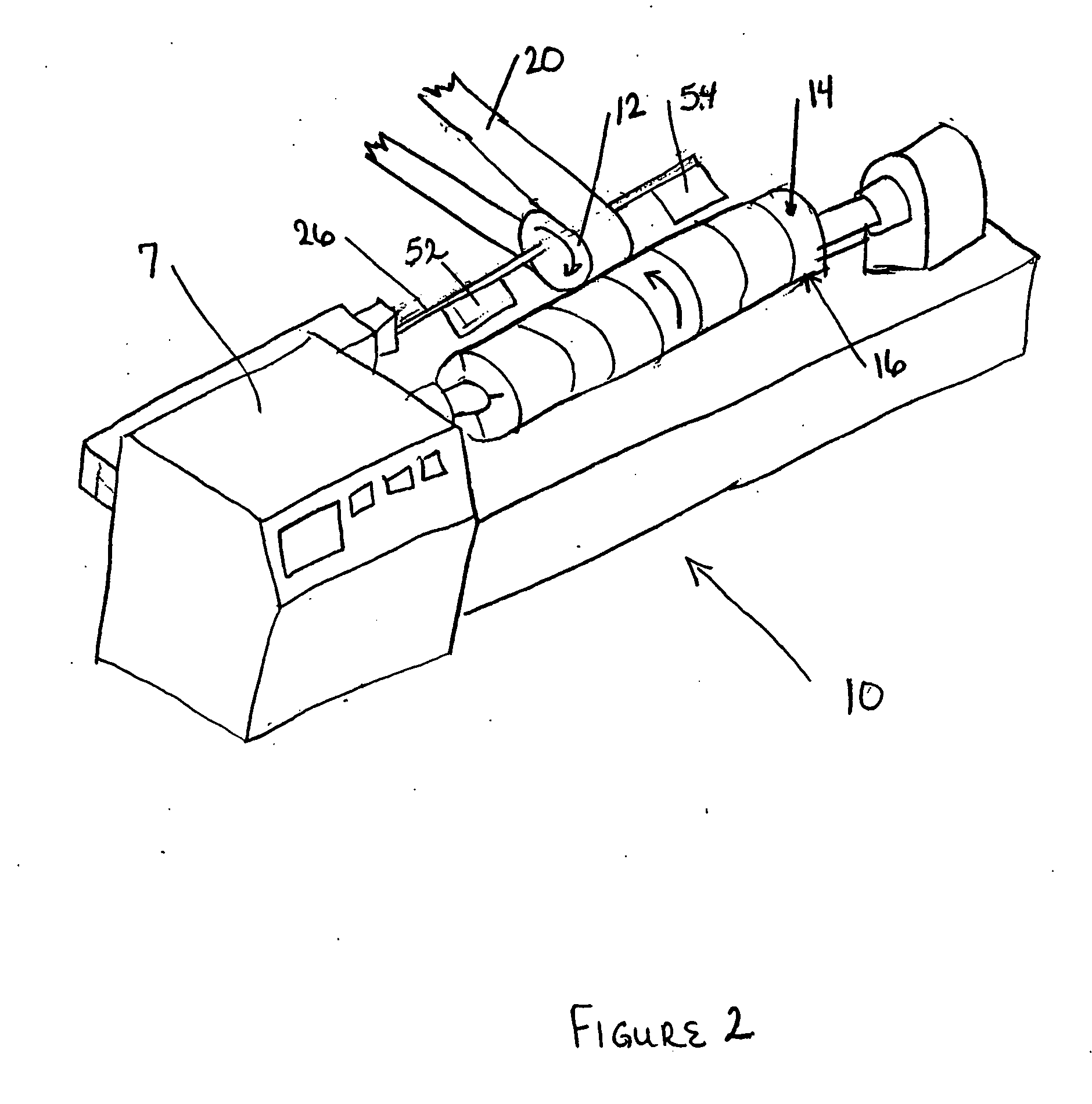
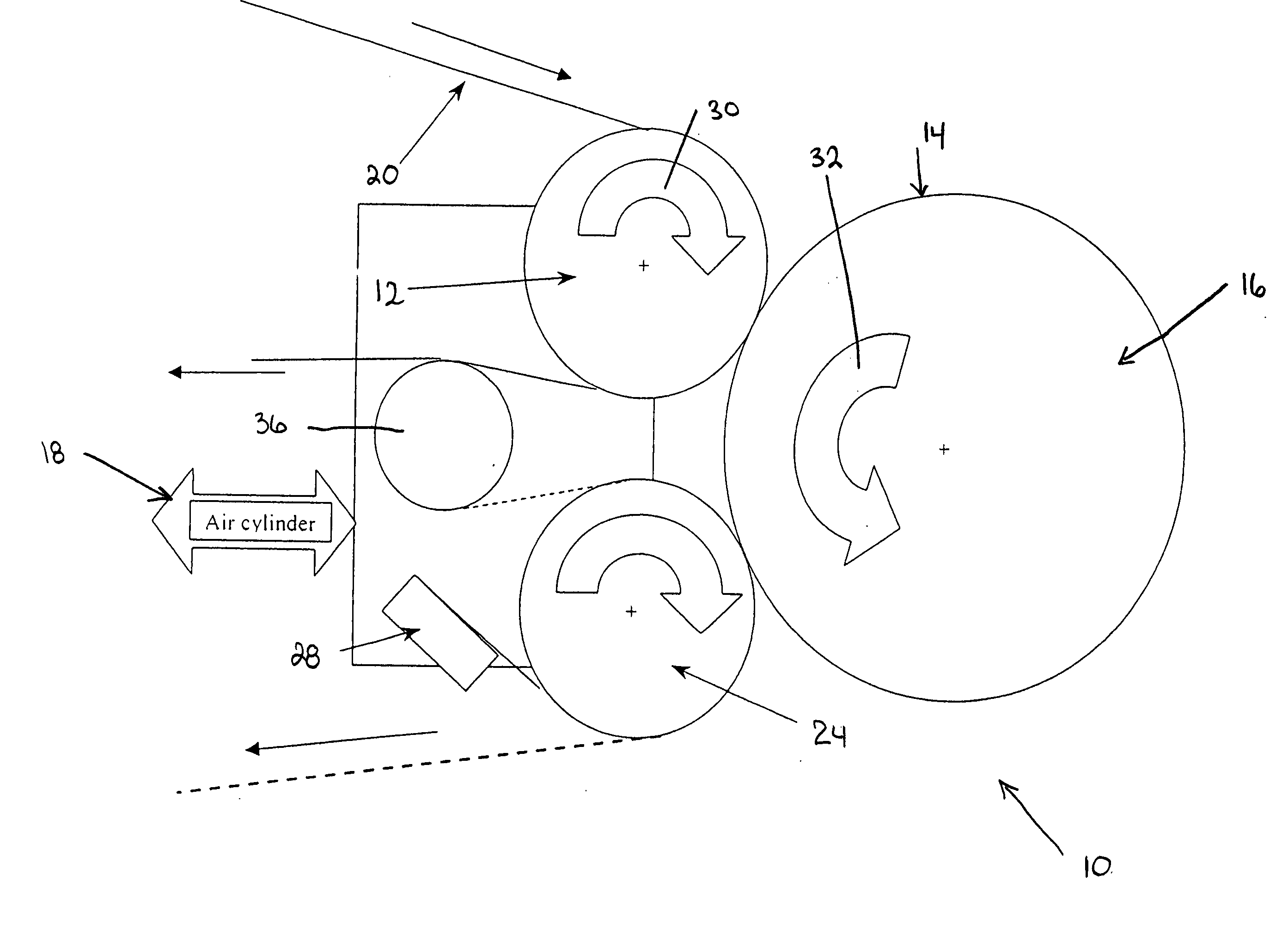
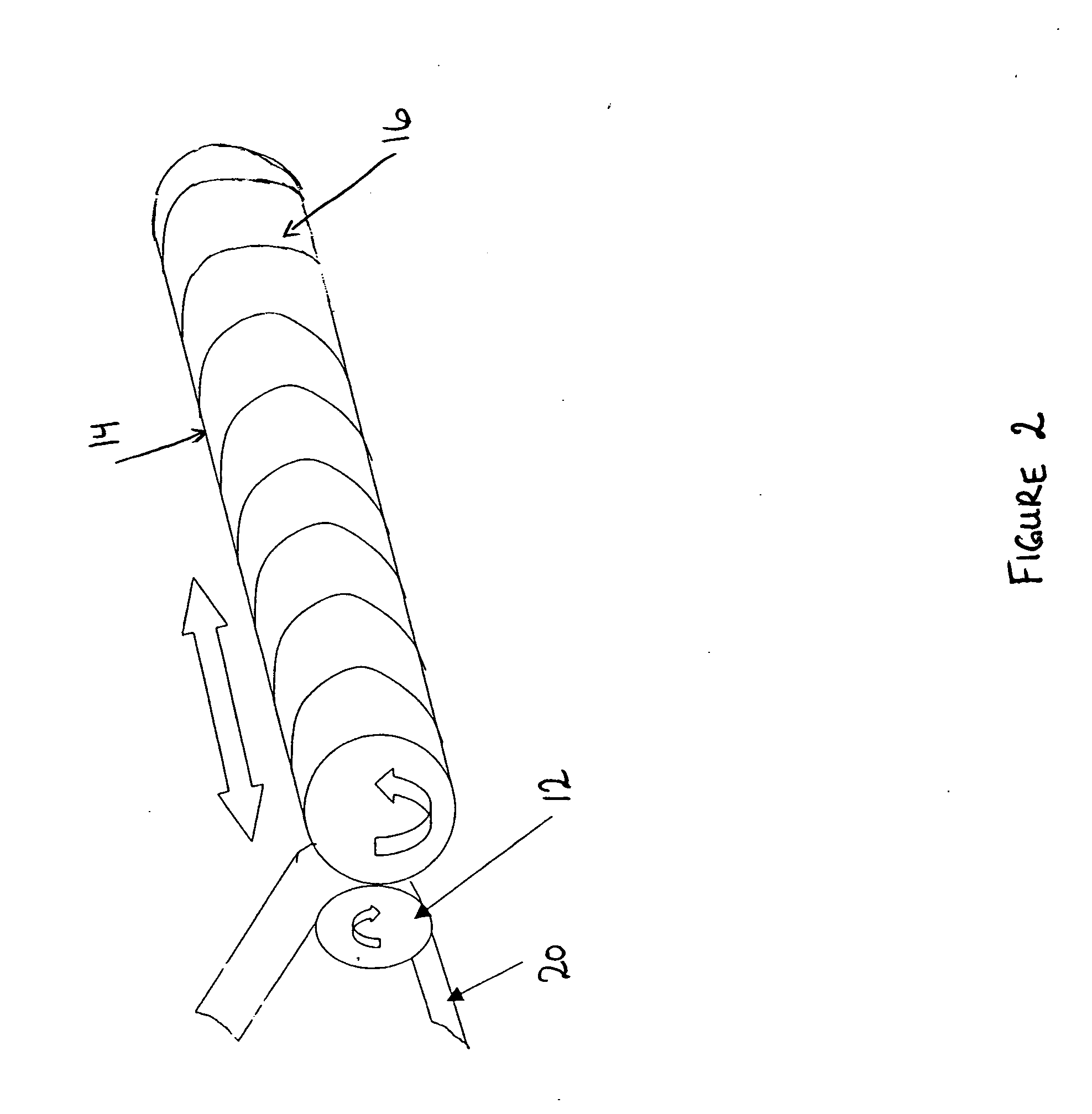
Apparatus and method for thermally developing flexographic printing elements
ActiveUS20050211120A1Improve developmentGood removal effectX-ray/infra-red processesDuplicating/marking methodsPhotopolymerElectrical and Electronics engineering
An improved apparatus for thermally developing a flexographic printing element to reveal a relief image on the surface and a method of using the apparatus to expose and develop a flexographic printing element. The apparatus typically comprises means for softening or melting non-crosslinked photopolymer on the imaged and exposed surface of the flexographic printing element; at least one roll that is contactable with the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element and capable of moving over at least a portion of the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element to remove the softened or melted non-crosslinked photopolymer on the imaged and exposed surface of the flexographic printing element; and means for maintaining contact between the at least one roll and the imaged and exposed surface of the flexographic printing element. The means for softening or melting non-crosslinked photopolymer on the imaged and exposed surface of the flexographic printing element comprise a heater positioned adjacent to the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element and / or heating the at least one roll that contactable with the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element. The apparatus may also contain an exposure device to crosslink and cure the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element prior to thermal development.
Owner:MACDERMID PRINTING SOLUTIONS
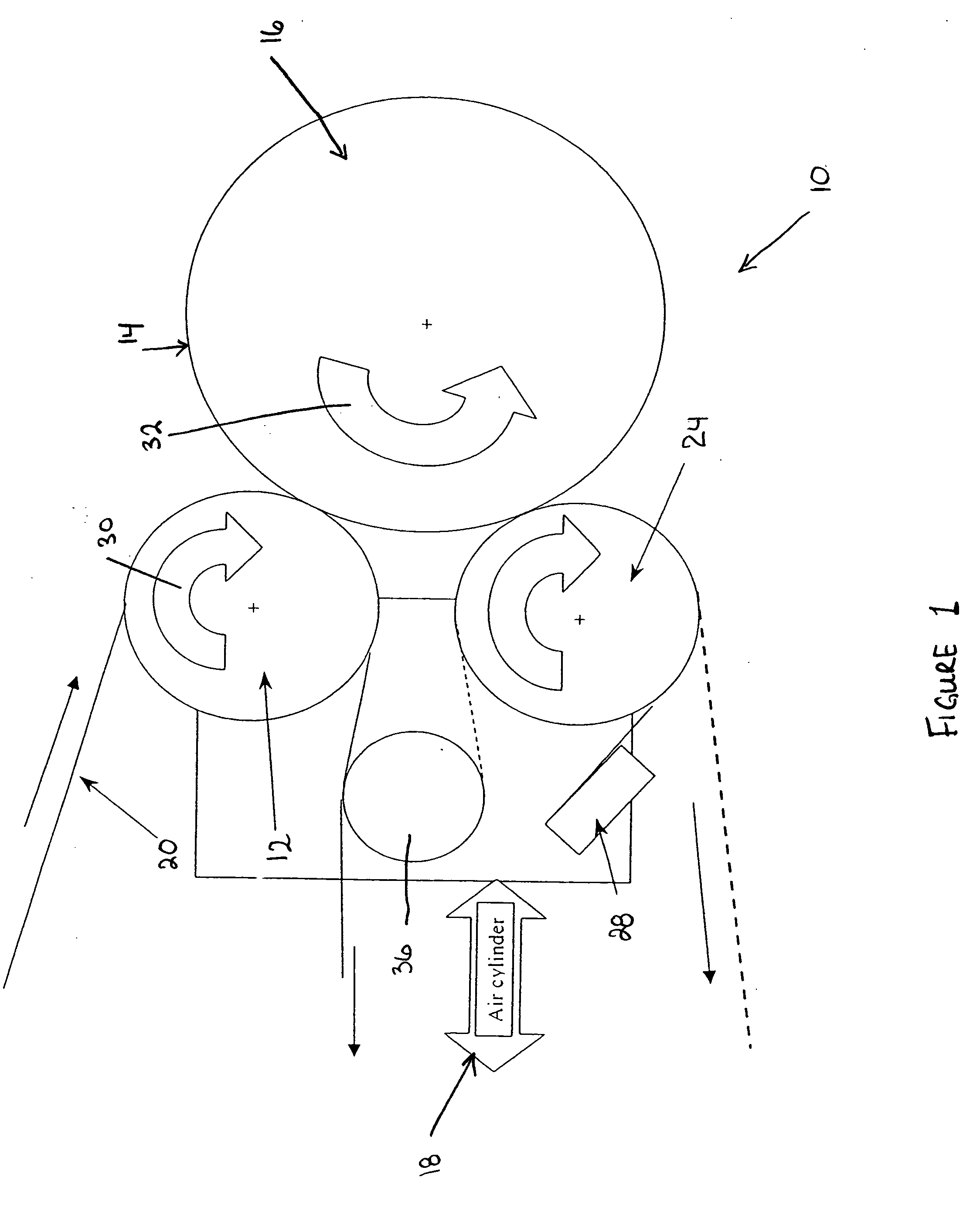
Apparatus and method for thermally developing flexographic printing sleeves
ActiveUS6998218B2Good removal effectIncrease speedMulticolor photographic processingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotopolymerCrosslinked polymers
An improved thermal development apparatus is used to remove uncured photopolymer from the imaged surface of a flexographic printing element. The apparatus typically comprises one or more heatable rolls that are contactable with an imaged surface of a flexographic printing element; and means for maintaining contact between the one or more heatable rolls and the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element. The one or more heatable rolls are heated and is moved over at least a portion of the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element, and non-crosslinked polymer on the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element is melted and removed by the one or more heatable rolls.
Owner:MACDERMID PRINTING SOLUTIONS
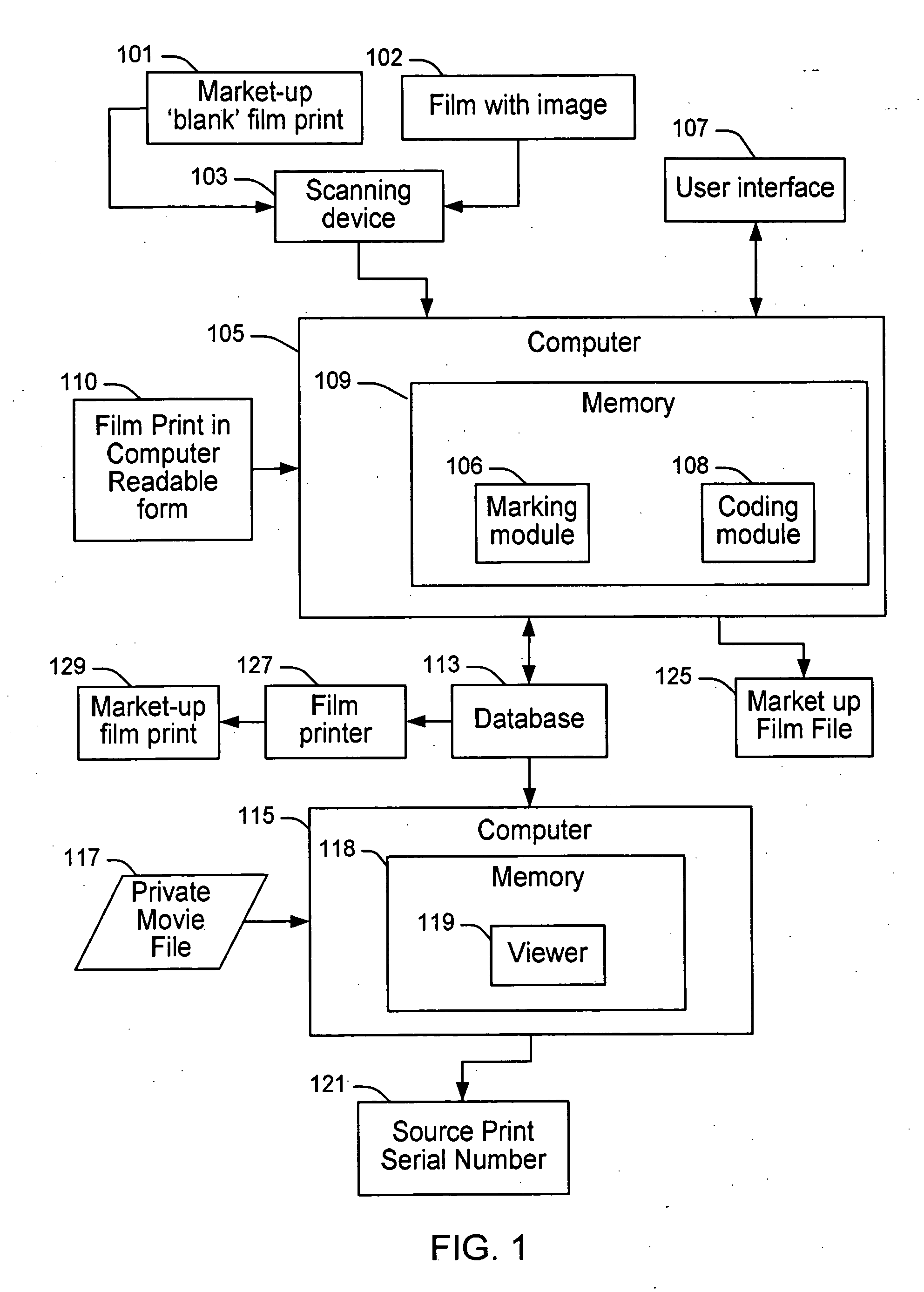
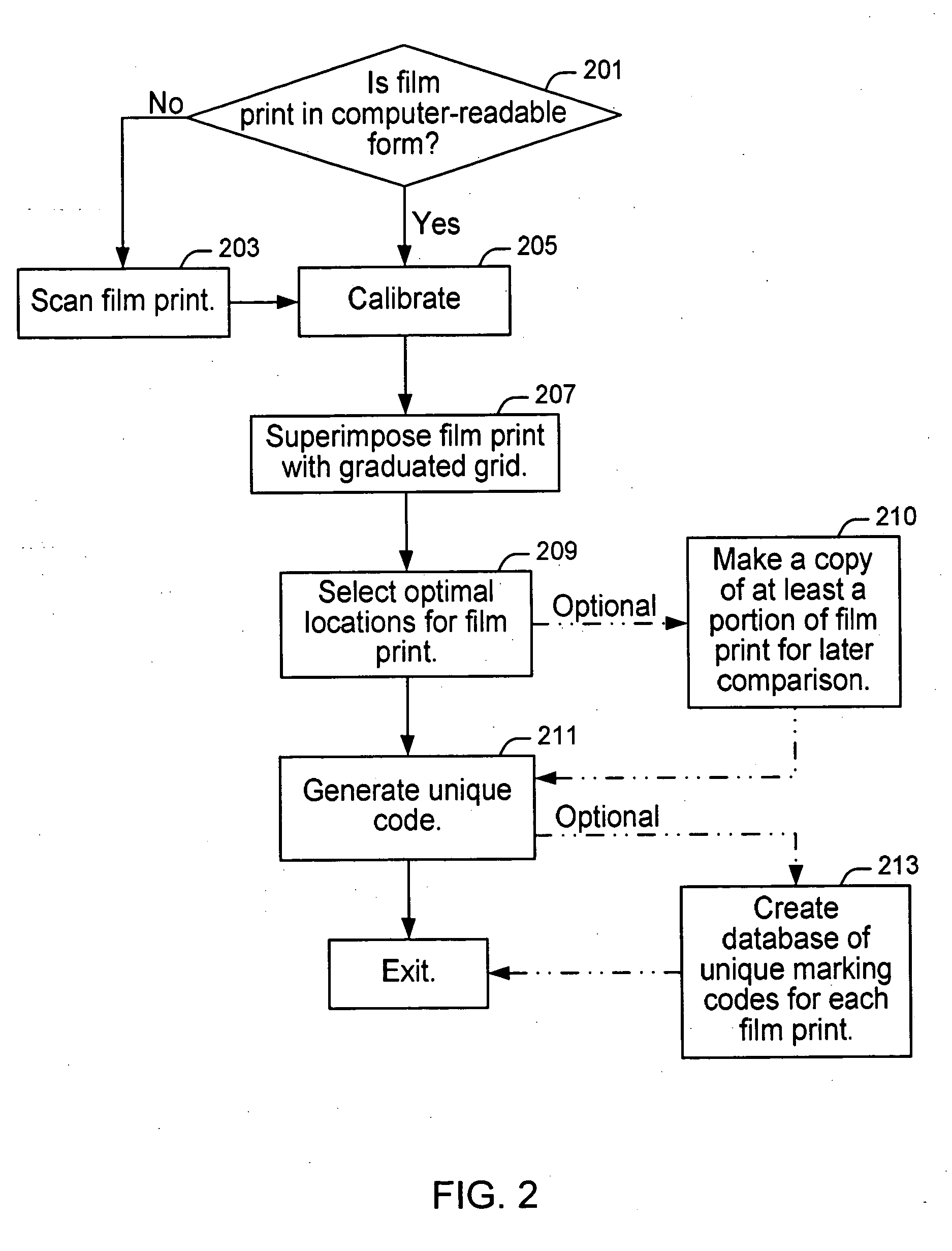
System and method for adaptive marking and coding of film prints
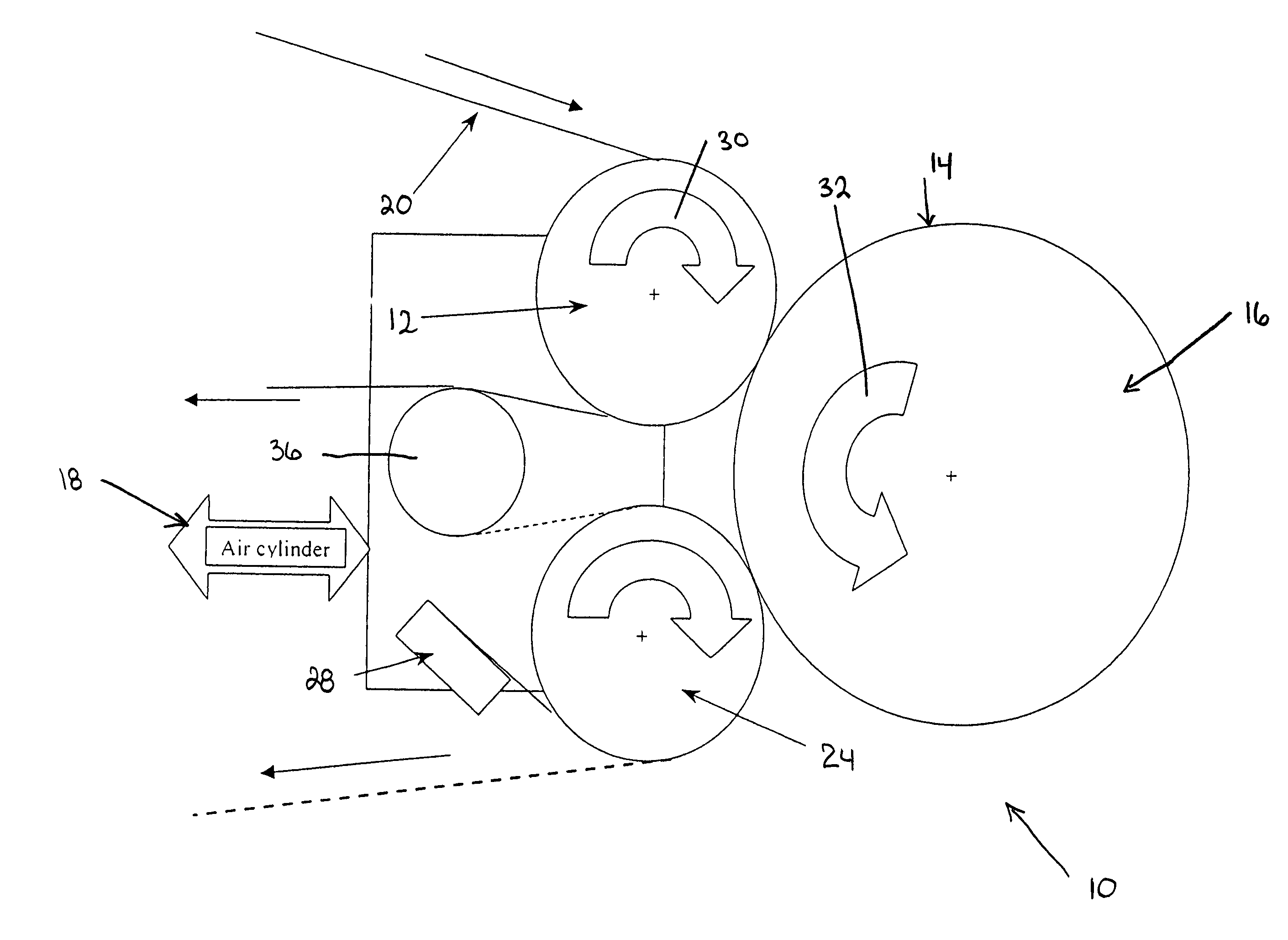
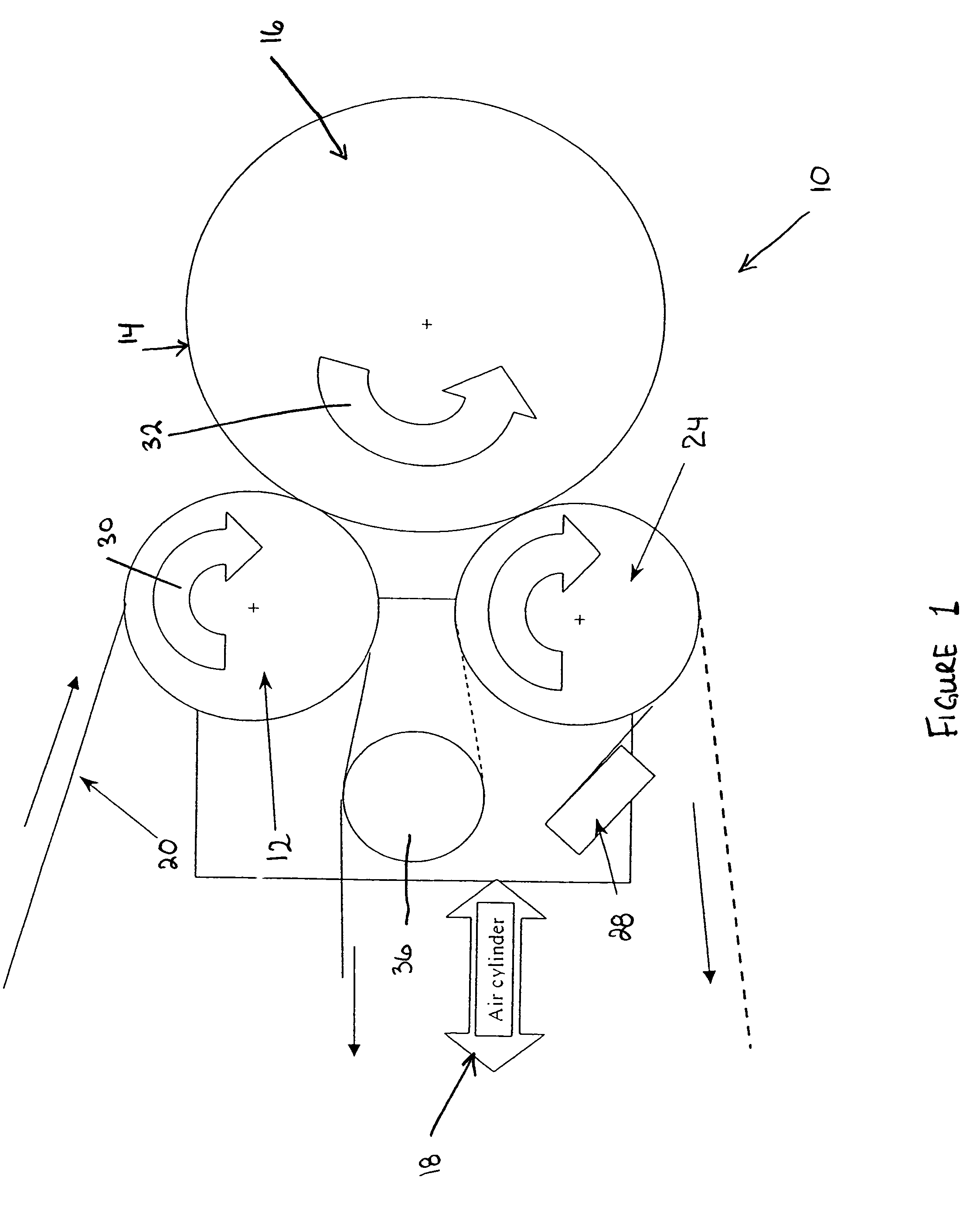
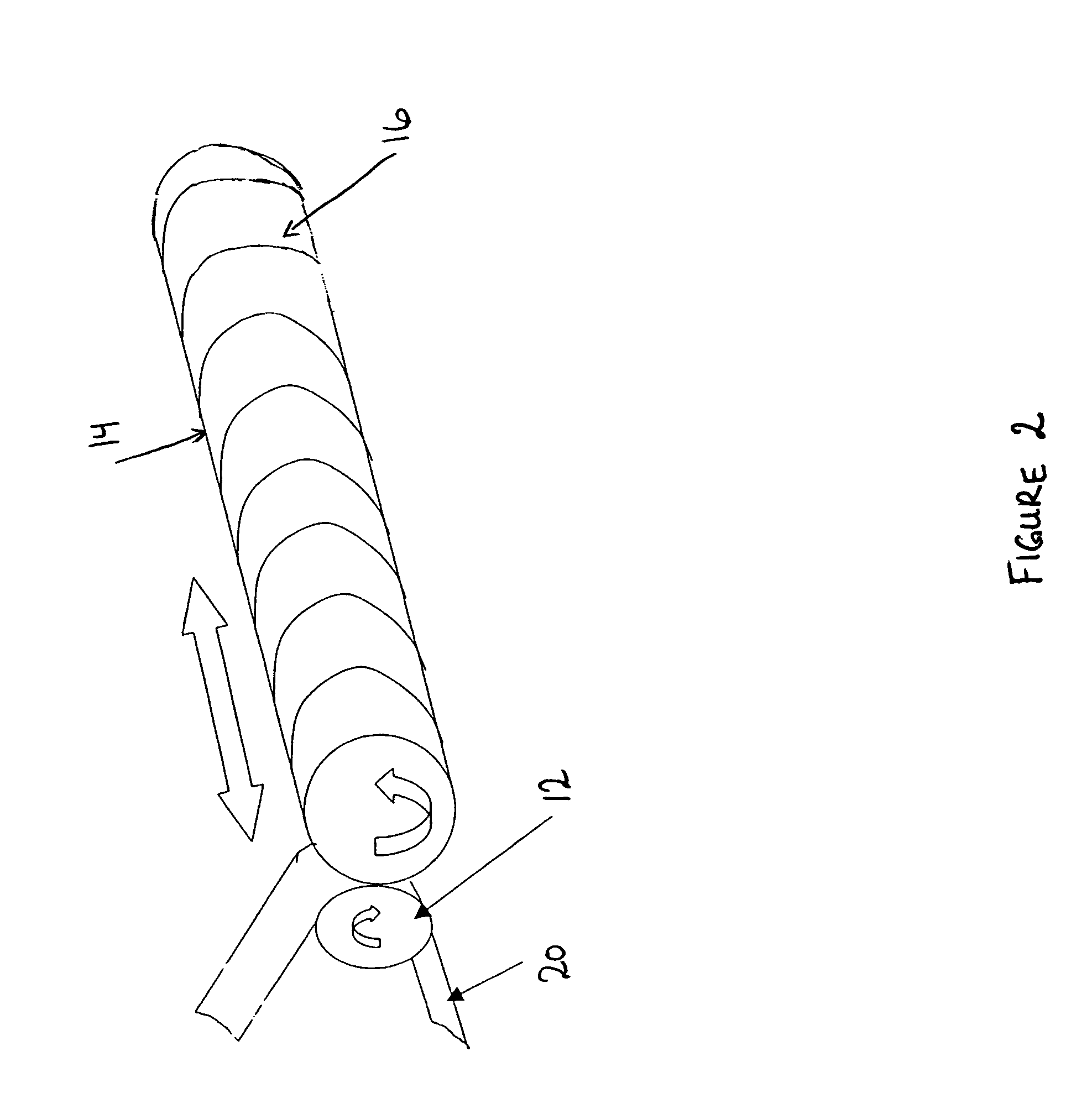
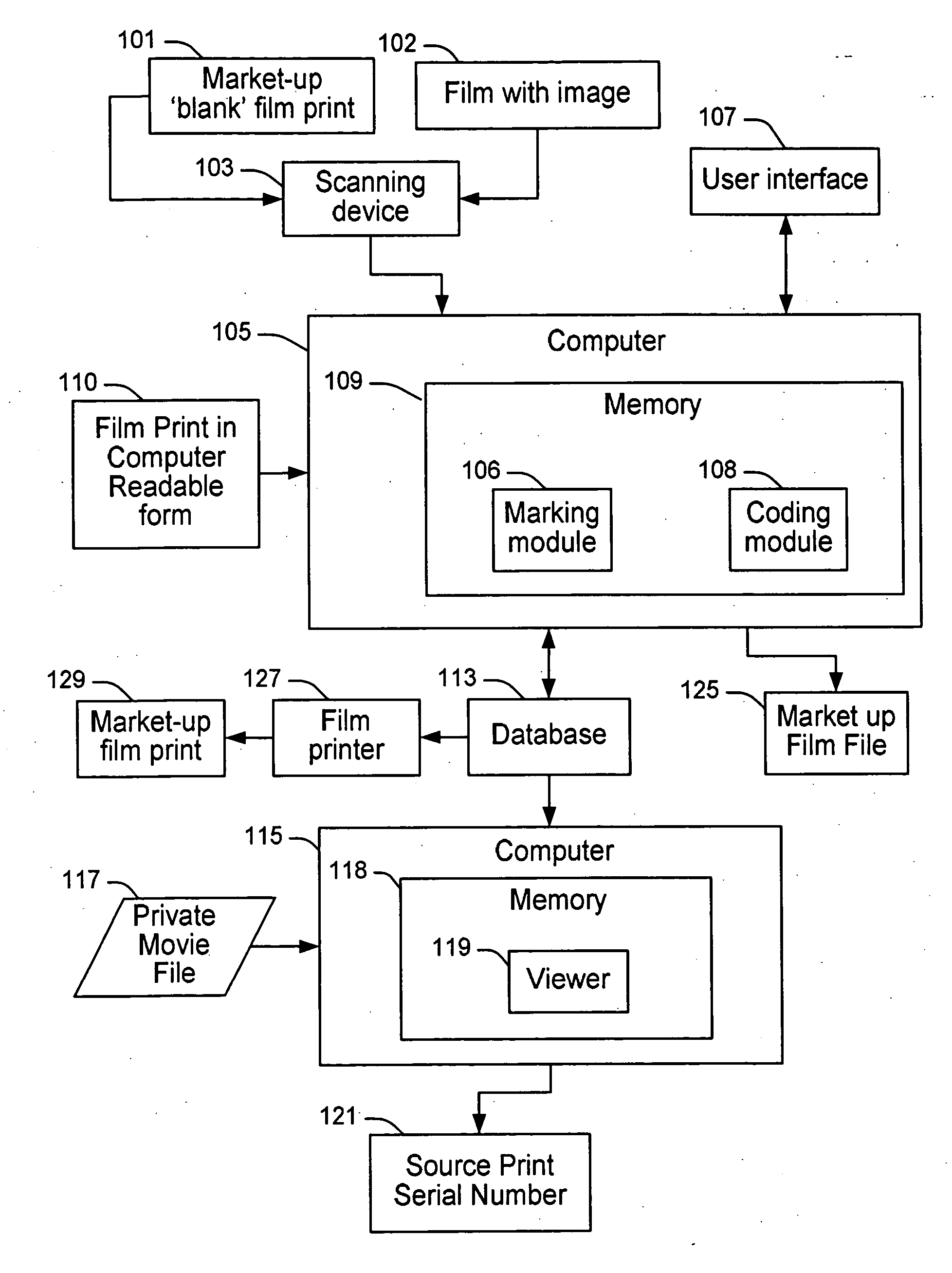
InactiveUS20060286489A1Easy to trackAccurately determining possible marking locationPhotography auxillary processesProcessed material treatmentComputer scienceSerial code
The present invention provides a system and method for marking, coding and tracking a film print in an efficient, adaptive and customized manner for providing unique and robust identification of each individual film print and facilitating accurate tracking of the origin of a pirated copy. A film print to be marked is calibrated and provided in computer-readable form for input to a prescreening device. The calibrated film print is reviewed and ideal locations on each frame of the film print are chosen for applying a mark. A unique coding scheme is generated for each desired print. If a pirate copy is found, all marks are located and a matching serial number (e.g., coding scheme) is determined for the pirated copy based on marks found in the pirate copy when compared to a database storing film print mark information generated during the marking and coding process.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Catalyzer for catalyzing wet oxidation in treating wastewater of sensitization glue, and its application
InactiveCN1498860AImprove biodegradabilityEmission complianceMulticolor photographic processingMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsActive componentReaction temperature
A catalyst for treating the photoresist sewage by catalytic wet oxidizing process is prepared from the active component chosen from Pt, Pd, Rh and Ru, the auxiliary component chosen from La, Ce, Pr and Nd, and TiO2-ZrO2 carrier through baking at 60-180 deg.c for 2-18 hrs and calcining at 300-800 deg.C for 2-18 hrs. It is applied under the conditions: 220-280 deg.c for reaction temp, 4-8 MPa for reaction pressure, 50-300 for air / sewage ratio and 0.5-6 / hr for space speed. Its advantages are high reaction efficiency, high removal rate of COD up to 99%, and high BOD5 / CODcr ratio increased from 0.02 to 0.6.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Use of transition metal compounds in imageable coatings
ActiveUS20060040217A1Effective markingSuitable imagePhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsChange colourPhotochemistry
A process for forming an image on a substrate, which comprises coati ng the substrate with an amine of molybdenum, tungsten or vanadium that changes colour on heating or irradiation as an aqueous dispersion or suspension or as a solution in an organic solvent. Also described is a coated substrate, wherein the coating is a substantially visible light-transparent layer comprising an amine compound of molybdenum, tungsten or vanadium, and a solution of said amine compound and a thermoplastic polymer or a photo-polymerisable monomer.
Owner:DATALASE
Microcapsules and processes for producing the same
InactiveUS20050129946A1Improve stabilityExcellent in durability along mechanical strengthDiffusion transfer processesLiquid surface applicatorsOrganic solventOil phase
A microcapsule is produced by dispersing a liquid organic dispersion in an aqueous medium to form a capsule particle in the aqueous medium, the liquid organic dispersion containing an acid group-containing resin, a colored particle and an organic solvent, and the capsule particle comprising a disperse system containing the liquid organic dispersion, and a wall encapsulating the disperse system, wherein the acid group of the resin has been at least partly neutralized with an alkanolamine. The wall comprises the resin, and the resin may be crosslinked or cured with a crosslinking agent. Moreover, the process may comprise crosslinking or curing the resin constituting the wall with the crosslinking agent, and further crosslinking or curing the residual crosslinking agent with a polyfunctional compound. Such a process can produce a microcapsule has a small and uniform particle size while encapsulating a disperse system dispersed a colored particle in an oil phase.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Apparatus and method for thermally developing flexographic printing elements
ActiveUS7041432B2Good removal effectIncrease speedX-ray/infra-red processesDuplicating/marking methodsPhotopolymerElectrical and Electronics engineering
An improved apparatus for thermally developing a flexographic printing element to reveal a relief image on the surface and a method of using the apparatus to expose and develop a flexographic printing element. The apparatus typically comprises means for softening or melting non-crosslinked photopolymer on the imaged and exposed surface of the flexographic printing element; at least one roll that is contactable with the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element and capable of moving over at least a portion of the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element to remove the softened or melted non-crosslinked photopolymer on the imaged and exposed surface of the flexographic printing element; and means for maintaining contact between the at least one roll and the imaged and exposed surface of the flexographic printing element. The means for softening or melting non-crosslinked photopolymer on the imaged and exposed surface of the flexographic printing element comprise a heater positioned adjacent to the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element and / or heating the at least one roll that contactable with the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element. The apparatus may also contain an exposure device to crosslink and cure the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element prior to thermal development.
Owner:MACDERMID PRINTING SOLUTIONS
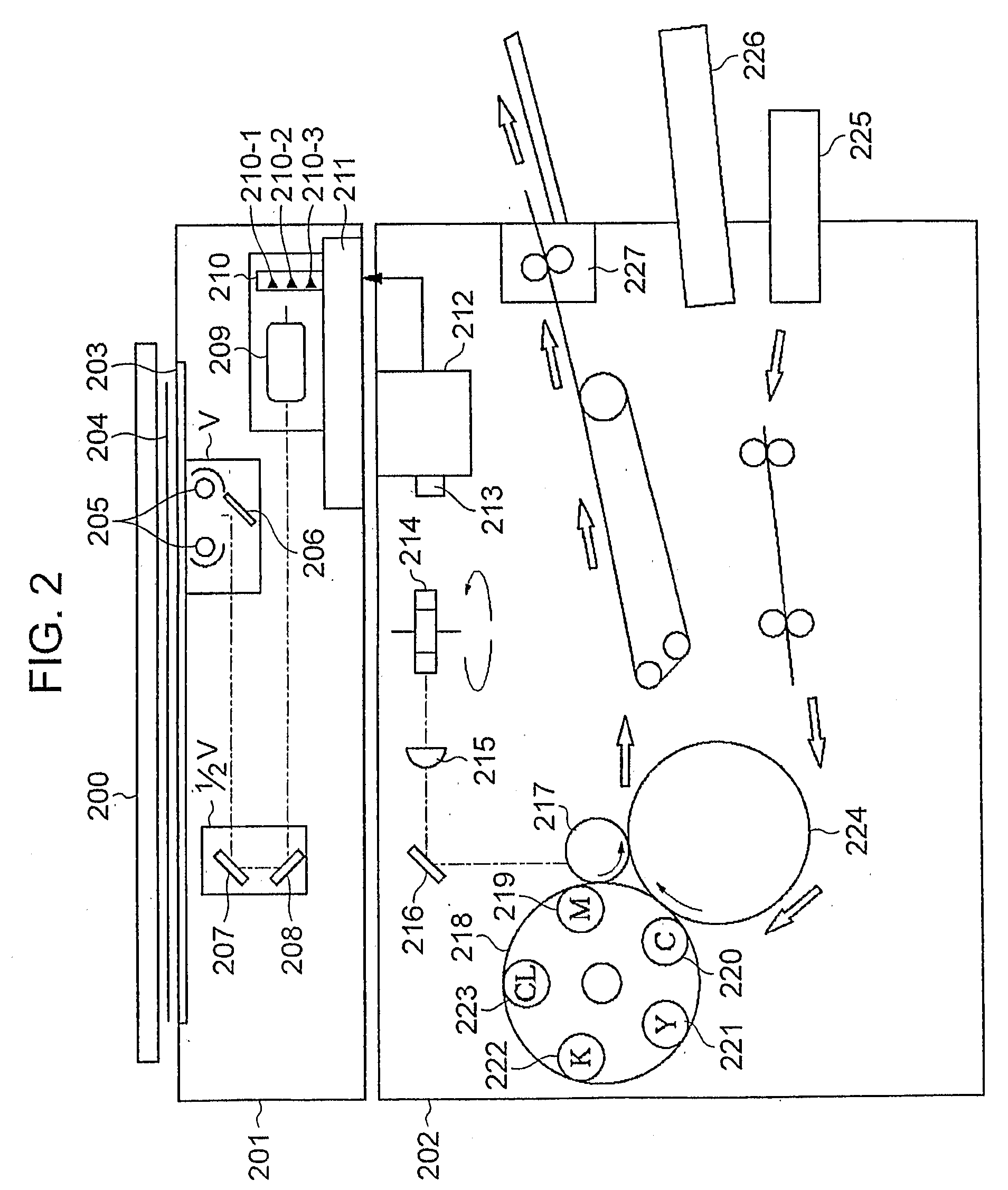
Flexo processor
ActiveUS7237482B2The process is convenient and fastGood flexibilityPlaten pressesMulticolor photographic processingHeat sensitivePost exposure
An improved flexo processor and a method of using the improved flexo processor to increase the flexibility of both the type and the size of the flexographic printing element that may be processed. The novel thermal plate processor system is capable of processing both flat and round photosensitive printing elements with only minimal changes to the system. The thermal plate processor system may also include means for exposure and post-exposure / detack in the same system.
Owner:MACDERMID PRINTING SOLUTIONS
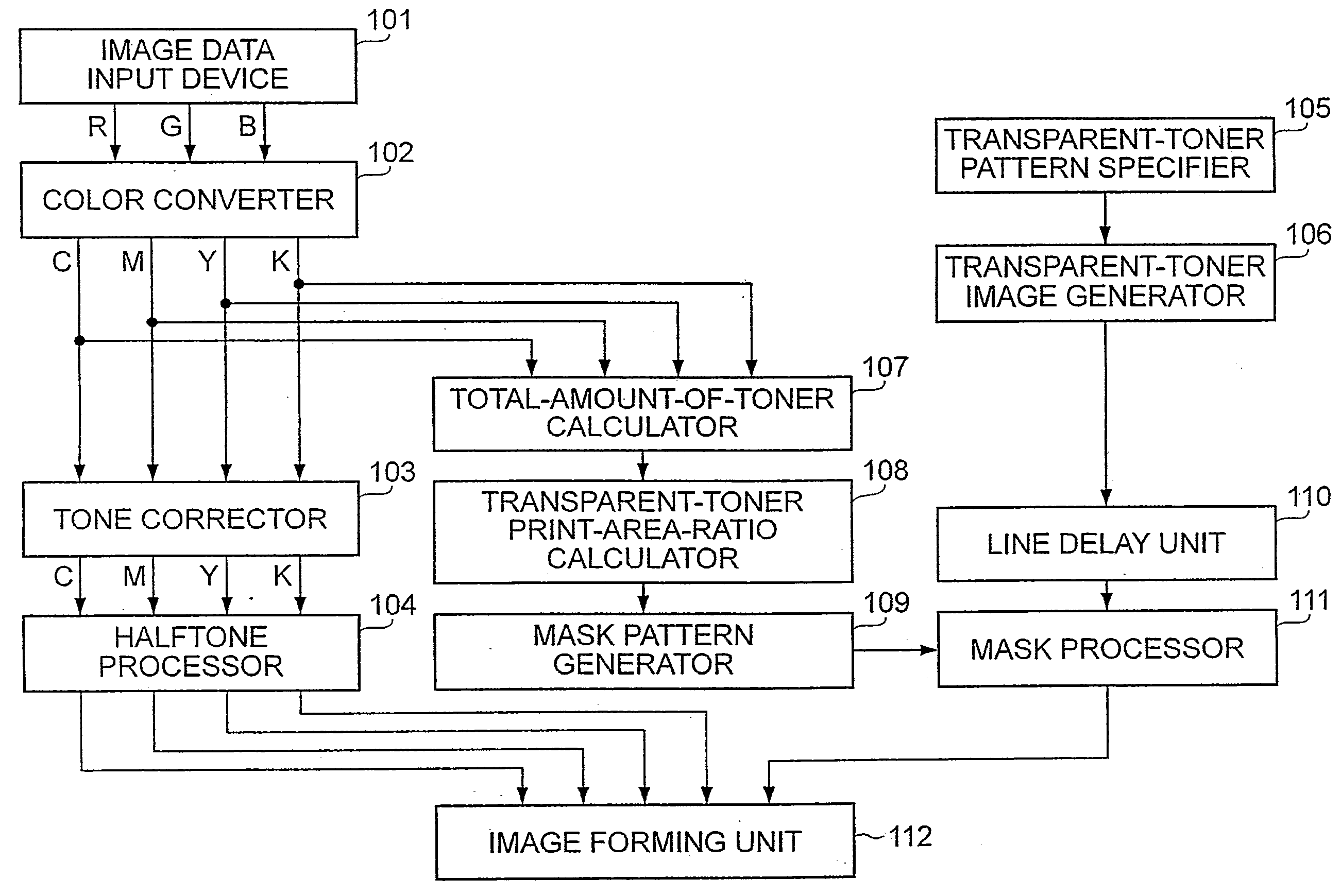
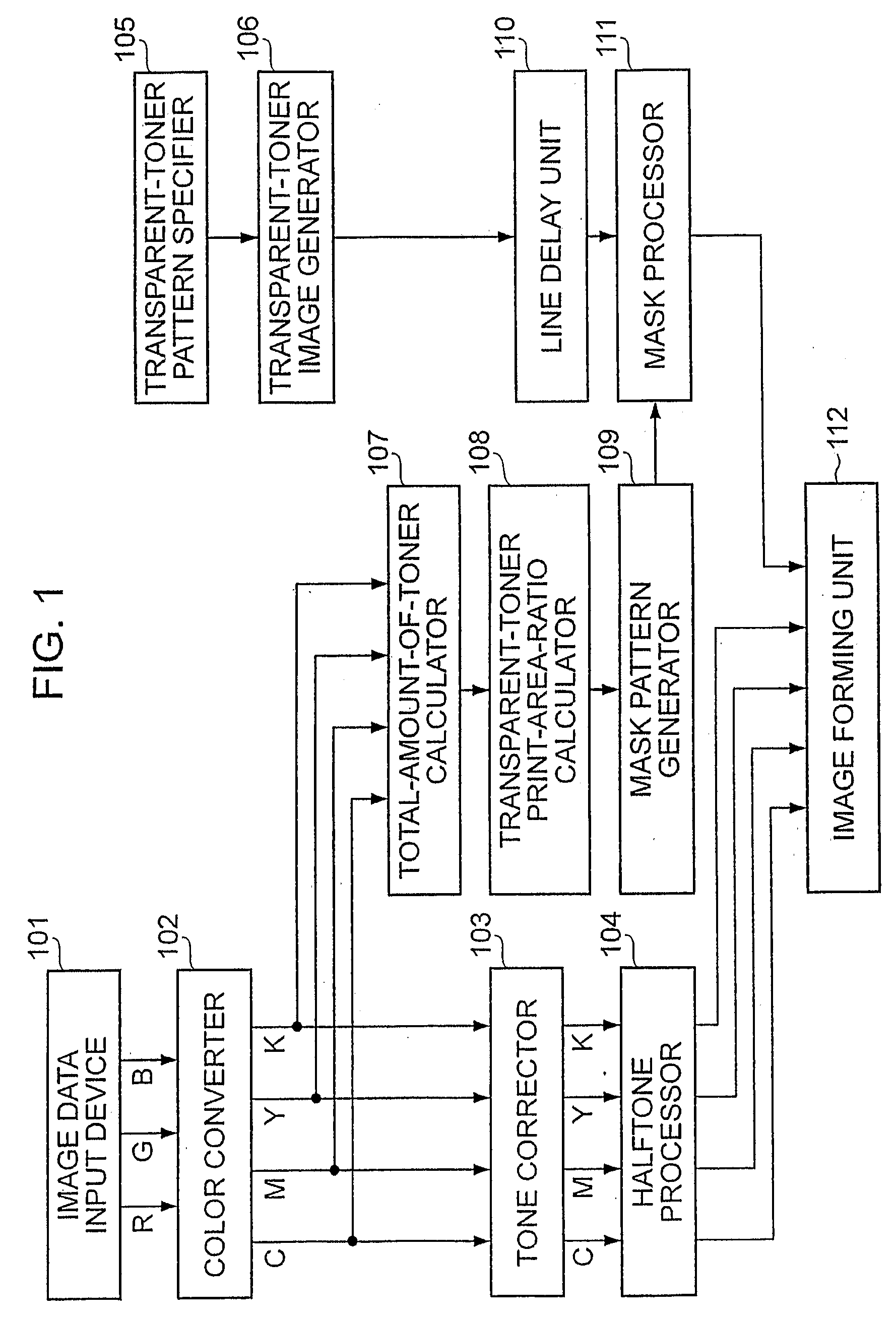
Image processing apparatus and method controlling the amount of transparent ink for recording
InactiveUS20090097046A1Without reducing productivityLimited amountDigitally marking record carriersMulticolor photographic processingImaging processingMagenta
An image processing apparatus includes a calculation unit configured to calculate an amount of a first coloring material (at least one of cyan, magenta, yellow and black) in an area including a plurality of pixels; a determination unit configured to determine an allowable amount of a second coloring material, being substantially colorless and transparent, in the area on the basis of the amount of the first coloring material, calculated by the calculation unit, and a limit of the amount of the coloring material; and a control unit configured to control an amount of the second coloring material in the area so as not to exceed the allowable amount of the second coloring material.
Owner:CANON KK
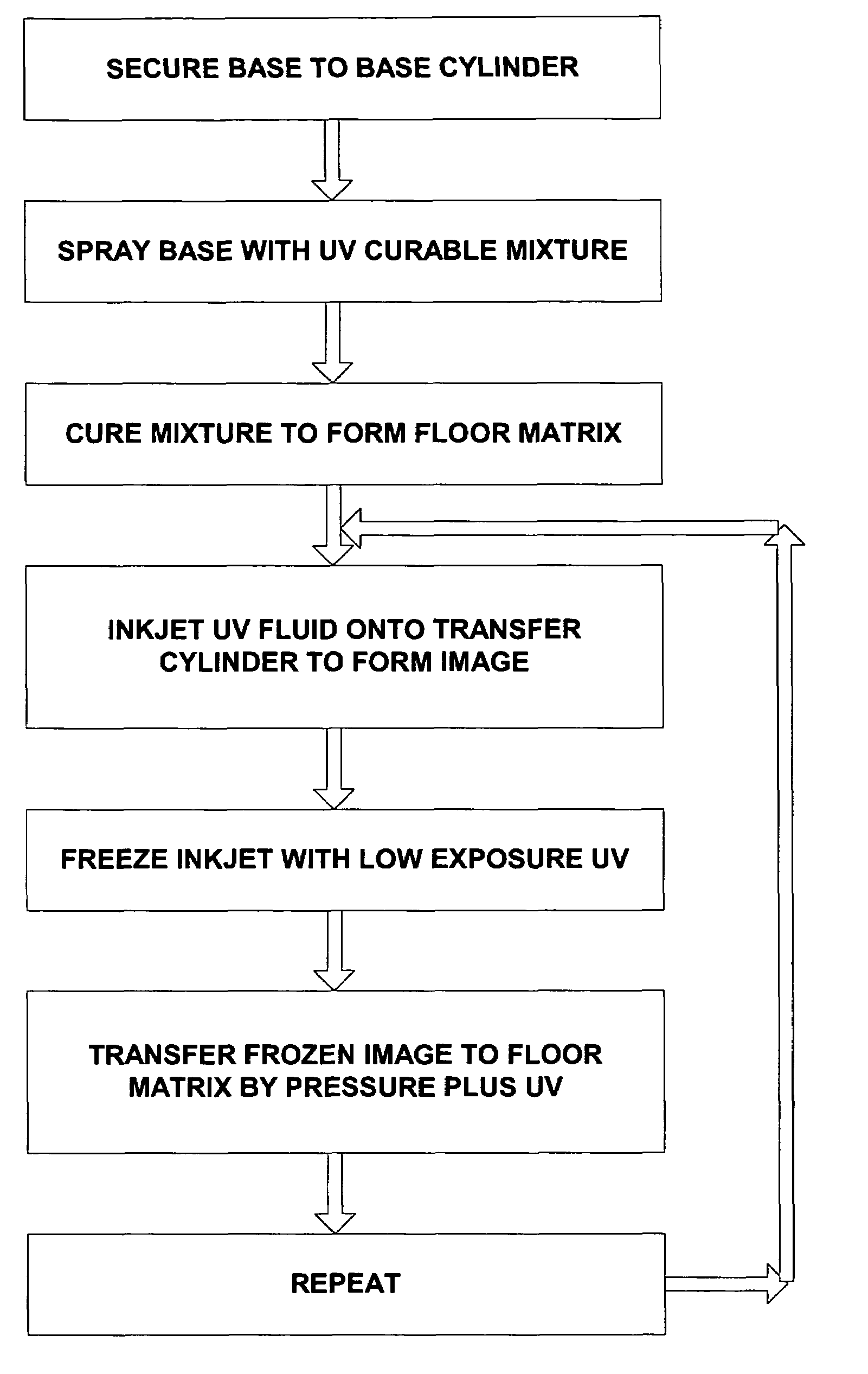
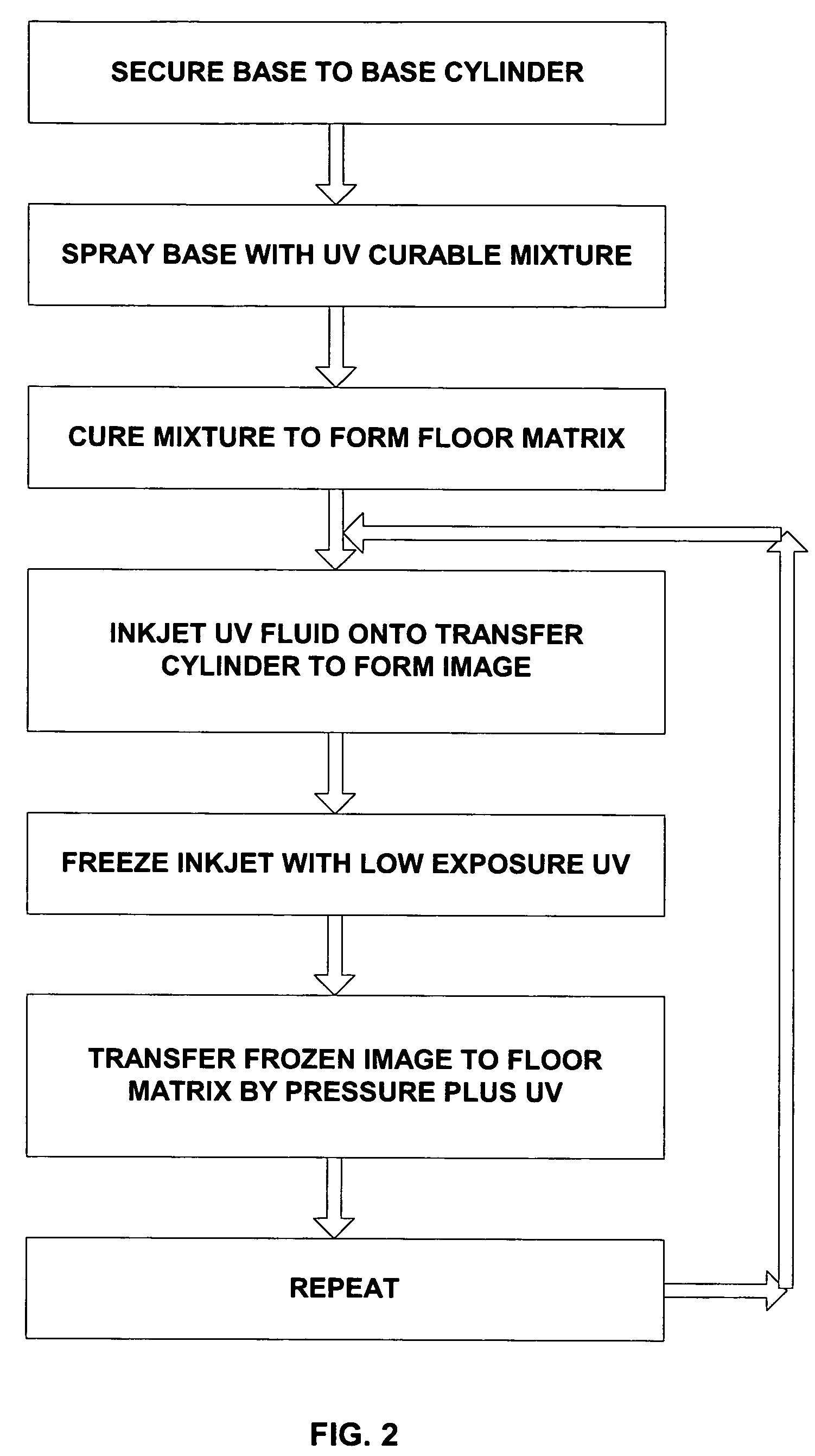
Method for producing a flexographic printing plate formed by inkjetted fluid
InactiveUS7036430B2Rapid and inexpensive mannerDuplicating/marking methodsMulticolor photographic processingEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:KODAK IL
Imaging compositions and methods
InactiveUS7144676B2Stable changeColor stablePhotography auxillary processesRadiation applicationsChange colorOrganic chemistry
Imaging compositions and methods of using the compositions are disclosed. The imaging compositions are sensitive to low levels of energy such that upon application of the low levels of energy the compositions change color or shade. The compositions may be applied to a work piece to mark it and removed from the work piece by peeling.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS LLC
Transmission duplitized display materials with biaxially oriented polyolefin sheets
InactiveUS6017685ABrighter imageEfficient diffusion of lightRadiation applicationsMulticolor photographic processingSpectral transmissionPolyolefin
The invention relates to a photographic element comprising a transparent polymer sheet, a biaxially oriented polyolefin sheet laminated to said transparent polymer sheet, one image layer coated on the top of said biaxially oriented polyolefin sheet and one image layer coated on the bottom of said transparent polymer sheet wherein said polymer sheet has a stiffness of between 20 and 100 millinewtons, and said biaxially oriented polyolefin sheet has a spectral transmission of at least 40% and a reflection density less than 60%.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Display panel and method of repairing bright point thereof
ActiveUS20100238386A1Reduce light transmittanceImprove efficiencyMulticolor photographic processingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight beamBright spot
A display panel has a portion of a color filter or patterned color layer with a thickness of at least half of the cell gap of the display panel, wherein the repair method includes providing a energy light beam to the portion of the color filter or the patterned color layer in the sub-pixel region with a bright point defect to make the portion of the color filter or patterned color layer have porous structure so that bright point is repaired to become a grey point or a dark point
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Apparatus for protecting cables or other elongated objects from traffic damage
ActiveUS7394025B1Low costEasy to manufactureRail switchesMulticolor photographic processingMechanical engineering
Owner:WONG THOMAS K
Method for producing image using a photothermographic material
Provided is a method for producing image using a photothermographic material in which the photothermographic material is exposed with a laser light using an image producing apparatus having a recording section and heat developing section, and then developed by heating, the photothermographic material containing elsewhere at least on one plane of the a support at least one kind of photosensitive silver halide, a non-photosensitive organic silver salt, a reducing agent for silver ion and a binder; characterized in that the photosensitive silver halide contains an iridium compound, and the image producing apparatus has an exposure corrective control means for correctively controlling exposure output according to a temperature profile of photothermographic material within the apparatus. This method can provide an image with a stable quality while not being affected by environmental conditions during the image production.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Photosensitive material for forming conductive film, and conductive material
ActiveUS20110070404A1High transparencyImprove conductivityFinal product manufactureLayered productsFiberEmulsion
A photosensitive material for forming a conductive film including a silver salt-containing emulsion layer, and a conductive layer containing conductive fibers, wherein the amount of the conductive fibers in the conductive layer is 0.005 g / m2 to 0.2 g / m2.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Flexo processor
ActiveUS20050211121A1Good flexibilityThe process is convenient and fastPlaten pressesMulticolor photographic processingPost exposureEmbedded system
An improved flexo processor and a method of using the improved flexo processor to increase the flexibility of both the type and the size of the flexographic printing element that may be processed. The novel thermal plate processor system is capable of processing both flat and round photosensitive printing elements with only minimal changes to the system. The thermal plate processor system may also include means for exposure and post-exposure / detack in the same system.
Owner:MACDERMID PRINTING SOLUTIONS
Apparatus and method for thermally developing flexographic printing sleeves
ActiveUS20050211119A1Good removal effectIncrease imaging speedMulticolor photographic processingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotopolymerEngineering
An improved thermal development apparatus is used to remove uncured photopolymer from the imaged surface of a flexographic printing element. The apparatus typically comprises one or more heatable rolls that are contactable with an imaged surface of a flexographic printing element; and means for maintaining contact between the one or more heatable rolls and the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element. The one or more heatable rolls are heated and is moved over at least a portion of the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element, and non-crosslinked polymer on the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element is melted and removed by the one or more heatable rolls.
Owner:MACDERMID PRINTING SOLUTIONS
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com