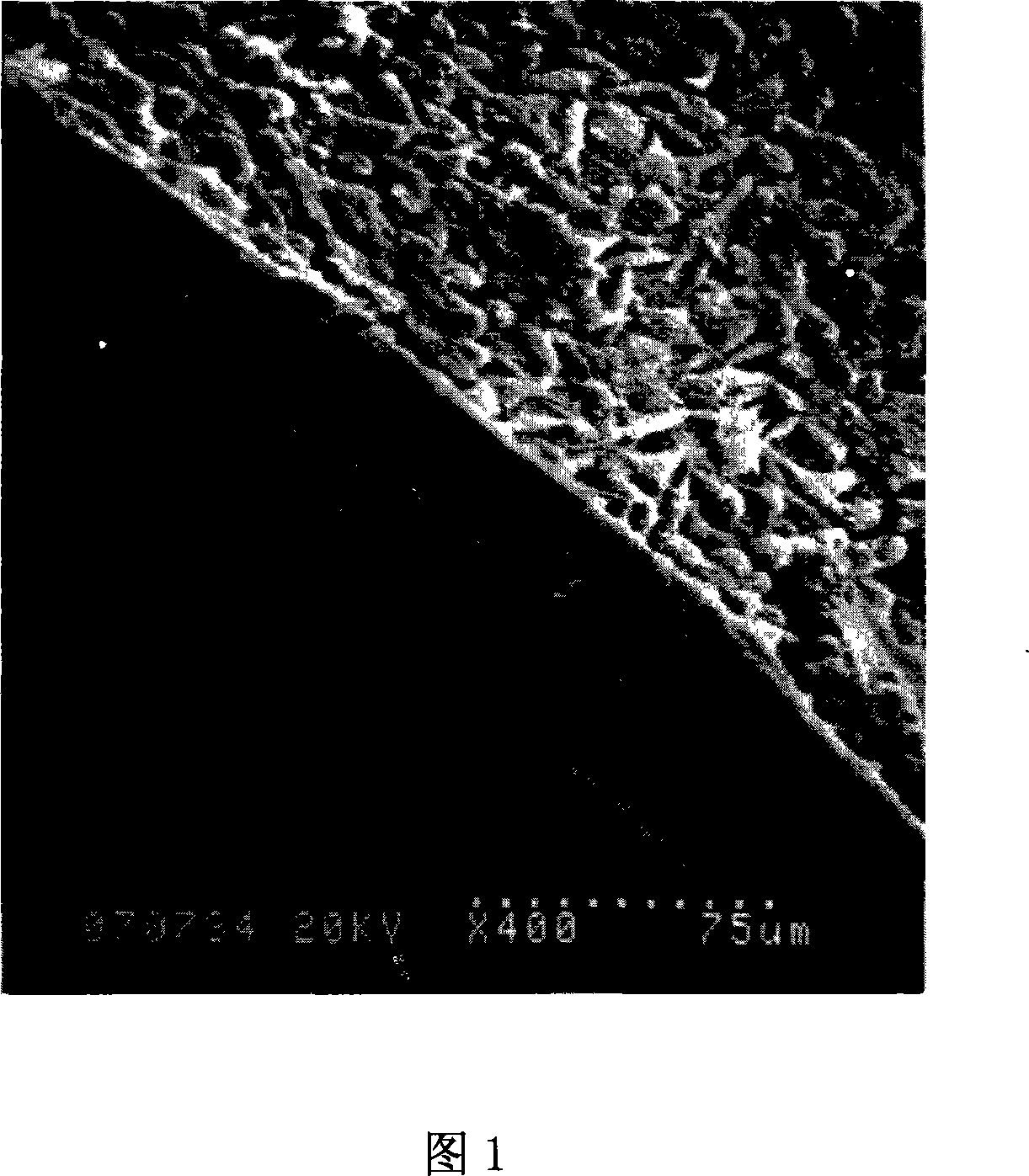Nano fibrous tissue engineering blood vessel and preparation thereof
A nanofiber, tissue engineering technology, applied in the field of biomedical applications of polymer materials, to prevent embolism, firm and uniform binding, and prevent blood penetration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] 1. Put 0.2kg of waste mulberry silk into 6L of 0.05% sodium carbonate aqueous solution, boil for 0.5h, repeat the boiling three times, remove all the sericin on the surface of the silk, and dry it at room temperature to obtain silk fibroin;
[0027] 2. Dissolve the dried silk fibroin with 1.2L calcium chloride, water and ethanol solution with a molar ratio of 1:8:2 at 75±2°C to form a silk fibroin solution;
[0028] 3. Pour the silk fibroin solution prepared in step 2 into a cellulose dialysis bag, first dialyze with tap water for 48 hours, then dialyze with deionized water for 8 hours, remove ethanol and small calcium chloride molecules in the solution, and filter to obtain Pure silk fibroin solution;
[0029] 4. Take 100ml of pure silk fibroin solution and pour it into an area of 20×20cm 2 In a polystyrene plastic tray, dry and form a film at constant temperature and humidity (25°C, RH65%);
[0030] 5. Weigh 6.58g of regenerated silk fibroin film and 3.49g of medi...
Embodiment 2
[0036] 1. Put 0.1kg of waste silk into 3L of 0.05% sodium carbonate aqueous solution, boil for 0.5h, repeat the treatment three times, remove all the sericin around the silk, and obtain silk fibroin;
[0037] 2. Dissolve the dried silk fibroin obtained in step 1 with 0.6 L of calcium chloride, water, and ethanol solution with a molar ratio of 1:8:2 at 78±2° C. to form a silk fibroin solution;
[0038] 3. Pour the above-mentioned silk fibroin solution into a cellulose dialysis bag, dialyze with tap water first, and then dialyze with deionized water to remove ethanol and small calcium chloride molecules in the solution, and then filter with multi-layer degreasing gauze to prepare Obtain pure silk fibroin solution;
[0039] 4. Take 100ml of pure silk fibroin solution and pour it into an area of 20×20cm 2 In a stainless steel plate, freeze at -20°C for 8 hours, and then vacuum-dry in a freeze dryer for 20 hours to obtain a spongy regenerated silk fibroin film;
[0040] 5. Weig...
Embodiment 3
[0046] 1. Put 0.15kg of waste silk into 4.5L of 0.05% sodium carbonate aqueous solution, boil for 0.5h, and repeat the treatment three times to obtain silk fibroin;
[0047] 2. Dissolve the dried silk fibroin obtained in step 1 with 0.9 L of calcium chloride, water, and ethanol solution with a molar ratio of 1:8:2 at 75±2° C. to form a silk fibroin solution;
[0048] 3. Pour the above-mentioned silk fibroin solution into a cellulose dialysis bag, dialyze with tap water first, and then dialyze with deionized water to remove ethanol and small calcium chloride molecules in the solution, and then filter with multi-layer degreasing gauze to prepare Obtain pure silk fibroin solution;
[0049] 4. Take 100ml of pure silk fibroin solution and pour it into an area of 20×20cm 2 In the ABS dish of , dry at room temperature to obtain regenerated silk fibroin film;
[0050] 5. Weigh 6.7g of regenerated silk fibroin film, 1.3g of gelatin and 0.7g of elastin, add to 70.5g of hexafluoroiso...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Caliber | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com