Precipitation modifying method for cellulose type solid enteric coatings
An enteric coating material, cellulose technology, applied in the field of polymer chemistry, can solve the problems of unsuitability for industrial production, high free acid content, large pollution, etc., to shorten the preparation period, simplify the reaction process, and be easy to operate. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
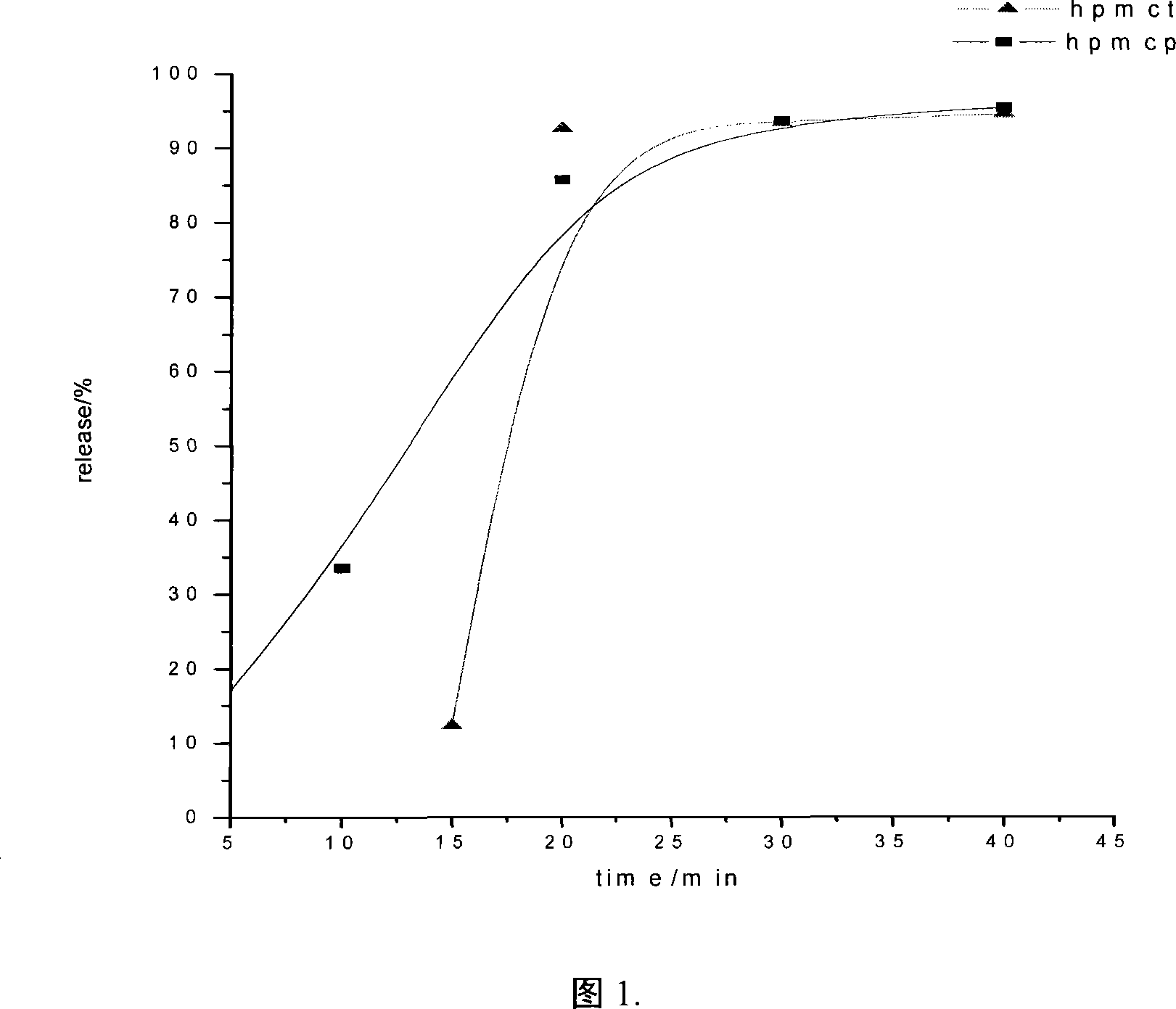
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Add 80 g of glacial acetic acid, 24 g of phthalic anhydride, and 16 g of sodium acetate into a 500 ml three-neck flask with a stirring rod. Stir and warm to 65°C. Then 20 g of hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (60HD10) were added slowly. The mixture was heated to 83.5°C and stirred for 3.5h to complete esterification. After the esterification reaction, slowly add 80 g of 15% diluent of acetic acid and a mixed solution of 0.5 g of hydrogen peroxide. Then cool down to 30°C within 40 minutes. Slowly add 75g of purified water into the system, stir evenly, precipitate product particles, and dry to obtain the product.
[0032] 1) Compare the self-made product with Japan Shin-Etsu HP-55 as follows:
[0033] Adopt sodium hydroxide standard solution titration method to measure its esterification rate and free acid content: homemade HPMCP esterification rate is 31.05%, free acid content is 0.17%; Shin-Etsu HP-55 esterification rate is 31.05%, free acid content 0.17%;
[0034] 2)...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Add 80 g of glacial acetic acid, 30 g of trimellitic anhydride, and 20 g of sodium acetate in a 500 ml three-necked flask with a stirring bar. Stir and warm to 65°C. Then 20 g of hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (60HD5) were added slowly. The mixture was heated to 88.5°C and stirred for 5h for complete esterification. After the esterification reaction, slowly add 80 g of 15% diluent of acetic acid and a mixed solution of 0.5 g of hydrogen peroxide. Then cool down to 30°C within 40 minutes. Slowly add 90g of purified water into the system, stir evenly, precipitate product particles, and dry to obtain the product.
[0043]1) The esterification rate and free acid content of the synthesized HPMCT product were measured by sodium hydroxide standard solution titration method, and the results were: the esterification rate was 34.52%, and the free acid content was 0.34%.
[0044] 2) The properties of the synthesized HPMCT products are shown in Table 3.
[0045] Table 3. Common ...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Add 80 g of glacial acetic acid, 2.5 g of butyric anhydride, 10 g of acetic anhydride, and 20 g of sodium acetate into a 500 ml three-necked flask with a stirring rod. Stir and warm to 65°C. Then 20 g of hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (60HD10) were added slowly. The mixture was heated to 83.5°C and stirred for 3.5h to complete esterification. After the esterification reaction, slowly add 80 g of 15% diluent of acetic acid and a mixed solution of 0.5 g of hydrogen peroxide. Then cool down to 30°C within 40 minutes. Slowly add 100g of purified water to the system, stir evenly, precipitate product particles, and dry to obtain the product. The esterification rate and free acid content of the synthesized HPMCAS product were measured by sodium hydroxide standard solution titration method, and the results showed that the succinyl group content was 16.22%, and the acetyl group content was 7.98%. Free acid content 0.34%.
[0054] 1) The properties of the synthesized HPMCAS pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com