Technique for extracting anti-oxidant from low value sea water fish and leftover protein
An antioxidant and seawater fish technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of carcinogenesis, achieve low production cost, significant anti-oxidative biological activity, realize high-value development and high utilization effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
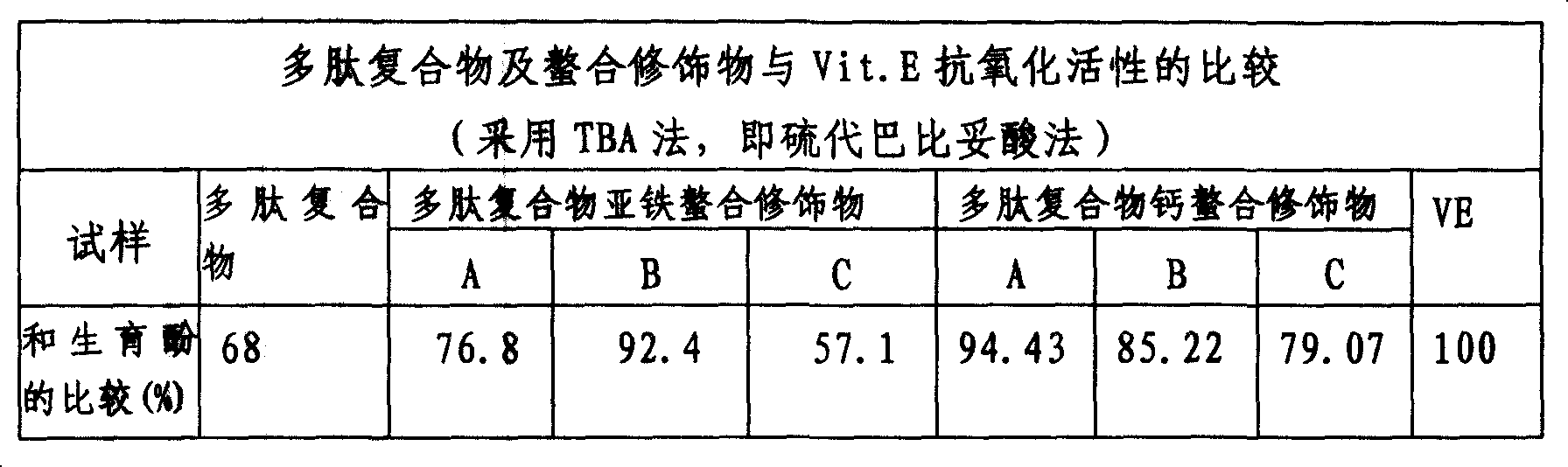
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] (1) The raw materials used are fresh low-value sea fish and their processed skin, bone, viscera and other leftovers as raw materials;
[0021] (2) Pre-treatment: After the raw materials are cleaned, they are pulverized with a pulverizer, and water is added in a ratio of 1 to 2, that is, 1 part by weight of raw materials is added to 2 parts by weight of water, and ground into a meat slurry;
[0022] (3) Compound enzyme hydrolysis: adjust the pH of the meat slurry to be 5, add papain (solid powder, 400,000 IU) and flavor enzyme (liquid, 2 million IU) in a ratio of 1:1 of activity, and control the enzyme amount to 600 IU. Limited hydrolysis for 2 hours at a temperature of 40-60°C. Heat the hydrolyzate to 90°C and keep it for 15 minutes to kill the enzyme activity;
[0023] (4) Centrifugal filtration and ultrafiltration: use a plate and frame filter or centrifuge to roughly filter the enzymatic hydrolyzate, and then filter it with an ultrafiltration membrane with a membran...
Embodiment 2
[0028] (1) The raw materials used are fresh low-value sea fish and their processed skin, bone, viscera and other leftovers as raw materials;
[0029] (2) Pre-treatment: After the raw materials are washed, they are pulverized with a pulverizer, and water is added in a ratio of 1 to 3, that is, 1 part by weight of raw materials is added to 3 parts by weight of water, and ground into a meat slurry;
[0030] (3) Compound enzyme hydrolysis: adjust the pH of the meat slurry to be 6, add papain (solid powder, 400,000 IU) and flavor enzyme (liquid, 2 million IU) in a ratio of 1:1 of activity, and control the enzyme amount to 1500 IU. Limited hydrolysis at 50°C for 3 hours. Heat the hydrolyzate to 95°C and keep it for 15 minutes to kill the enzyme activity;
[0031] (4) Centrifugal filtration and ultrafiltration: use a plate and frame filter or centrifuge to roughly filter the enzymatic hydrolyzate, and then filter it with an ultrafiltration membrane with a membrane pore size of 0.3 μ...
Embodiment 3
[0035] (1) The raw materials used are fresh low-value sea fish and their processed skin, bone, viscera and other leftovers as raw materials;
[0036] (2) Pre-treatment: After the raw materials are cleaned, they are pulverized with a pulverizer, and water is added in a ratio of 1 to 4, that is, 1 part by weight of raw materials is added to 4 parts by weight of raw materials, and ground into a meat slurry;
[0037] (3) Compound enzyme hydrolysis: adjust the pH of the meat pulp to be 7, add papain (solid powder, 400,000 IU) and flavor enzyme (liquid, 2 million IU) in a ratio of 1:1 of activity, and control the enzyme amount to 2400 IU. Limited hydrolysis at 60°C for 3 hours. Heat the hydrolyzate to 100°C and keep it for 15 minutes to kill the enzyme activity;
[0038] (4) Centrifugal filtration and ultrafiltration: use a plate and frame filter or centrifuge to roughly filter the enzymatic hydrolyzate, and then filter it with an ultrafiltration membrane with a membrane pore size ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com