Material with porous structure and preparation method thereof
A porous structure and compound technology, applied in the direction of silica, silicon oxide, etc., can solve the problems of colloids that cannot be reached, low thermal conductivity, cracking, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing surface tension, low thermal conductivity, and low density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
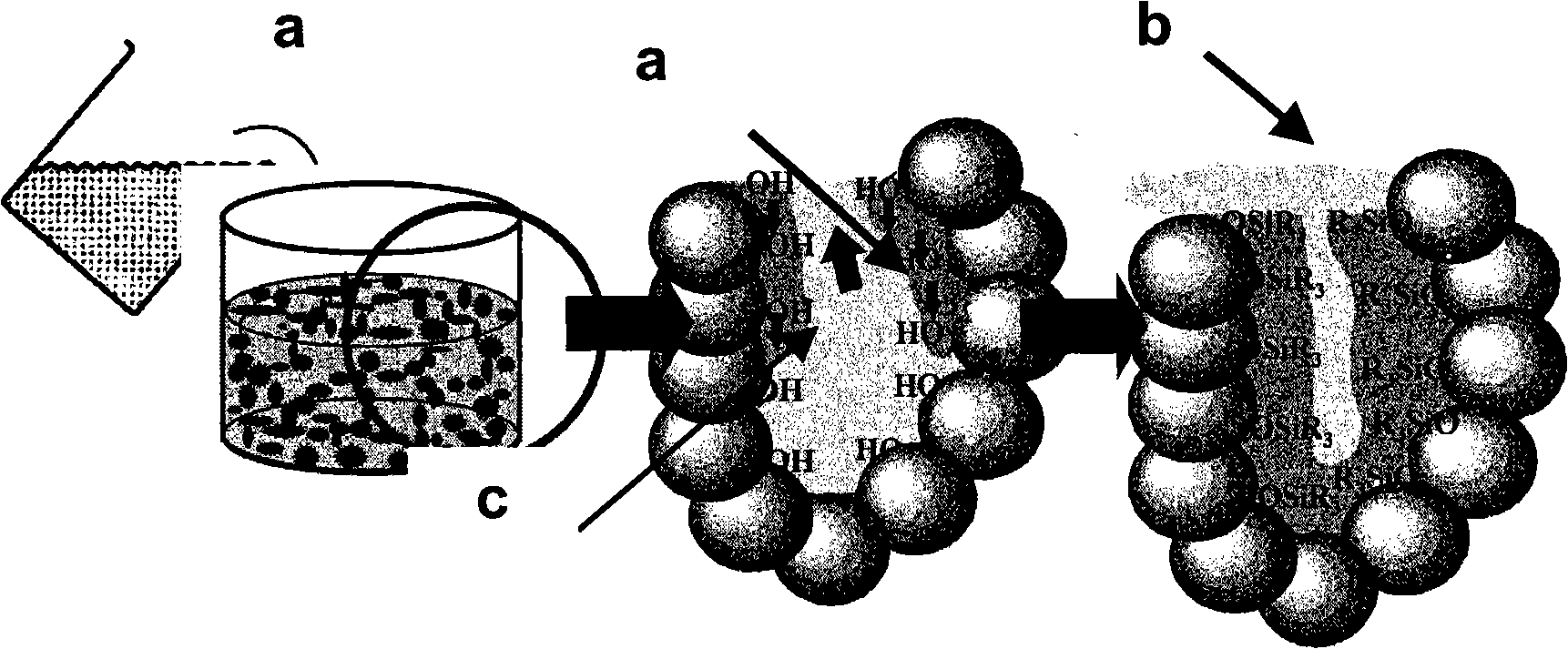
[0030] When the existing airgel is prepared, the surface of the colloid usually appears as a hydrophilic aerogel, as shown in the following formula (I). Therefore, once it contacts the atmosphere, it will absorb the water vapor in the atmosphere, resulting in a porous structure of the colloid. It is destroyed, and at the same time reduces the heat insulation performance of the material, making it unable to be used for a long time, without weather resistance and continuous use. And because the thermal conductivity of the airgel itself will decrease rapidly due to the high ambient temperature, it cannot be used at high temperatures.
[0031]
[0032] Generally, aerogels prepared by using silicon alkoxide or silicate, the surface functional group is mainly -OH, and this kind of hydrophilic functional group will break due to the huge surface tension contraction when it comes into contact with air. , in order to enable the drying procedure to be carried out under normal pressure...
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1. Preparation of Modified Porous Airgel
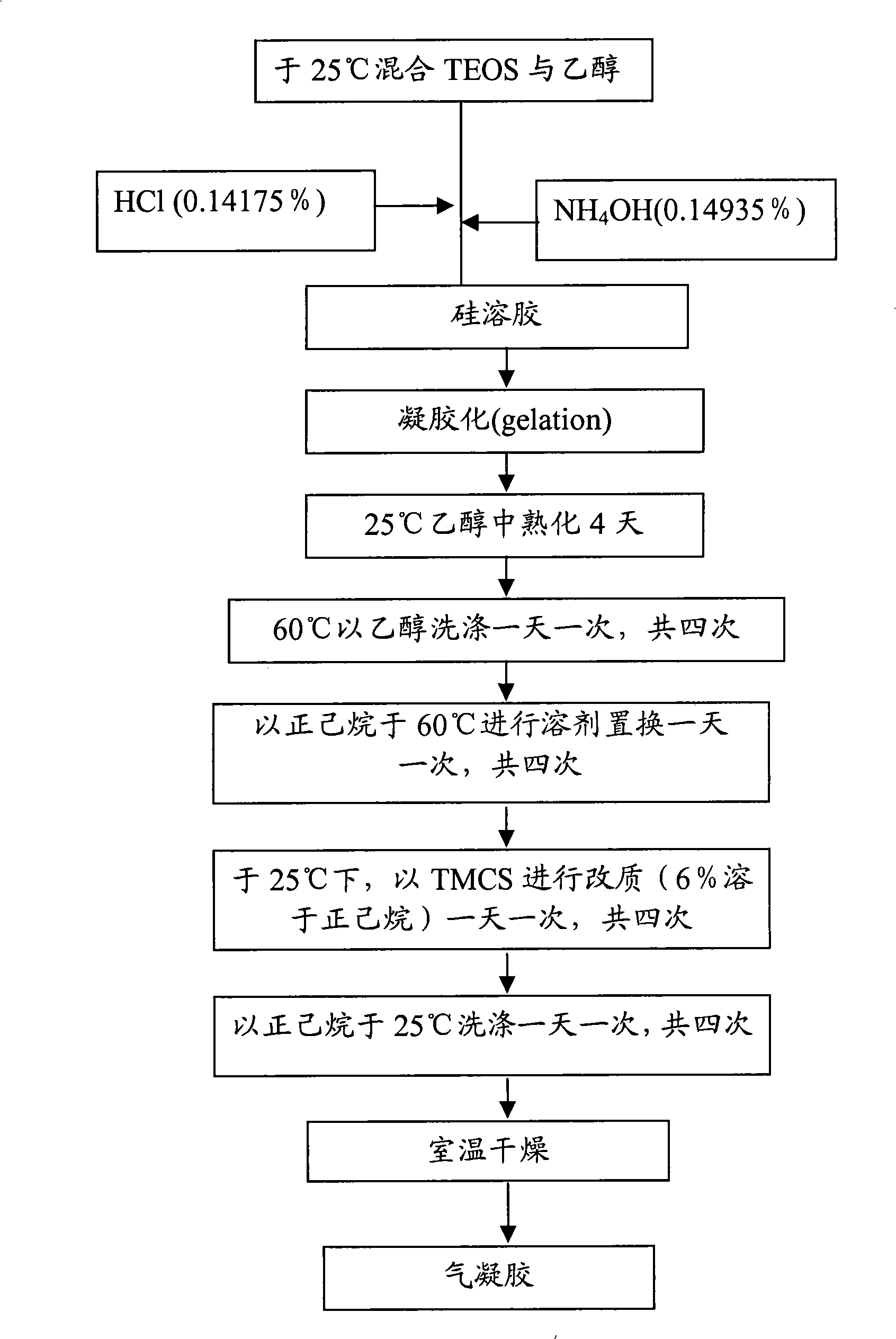
[0041] This example is to make an airgel heat insulating material with a nano-scale porous network structure, and the preparation process is as follows figure 2 shown. First, using the sol-gel method, after the precursor material (precursor material) is mixed with an organic solvent, an acid catalyst is added for hydrolysis reaction; then an alkali catalyst is added for condensation reaction (condensation), and a sol (sol) will be formed after the reaction. Sol refers to extremely small colloidal particles. In the sol stage, the colloidal particles will be evenly distributed in the solution. Then, the molecules in the sol will continue to undergo condensation reactions to form bonds, gradually forming a semi-solid polymer gel, and after a period of aging, the colloid will gradually form a three-dimensional network structure with stable structure.
[0042] The precursor material of this embodiment is tetraethoxysilane...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Embodiment 2, characteristic test of porous airgel
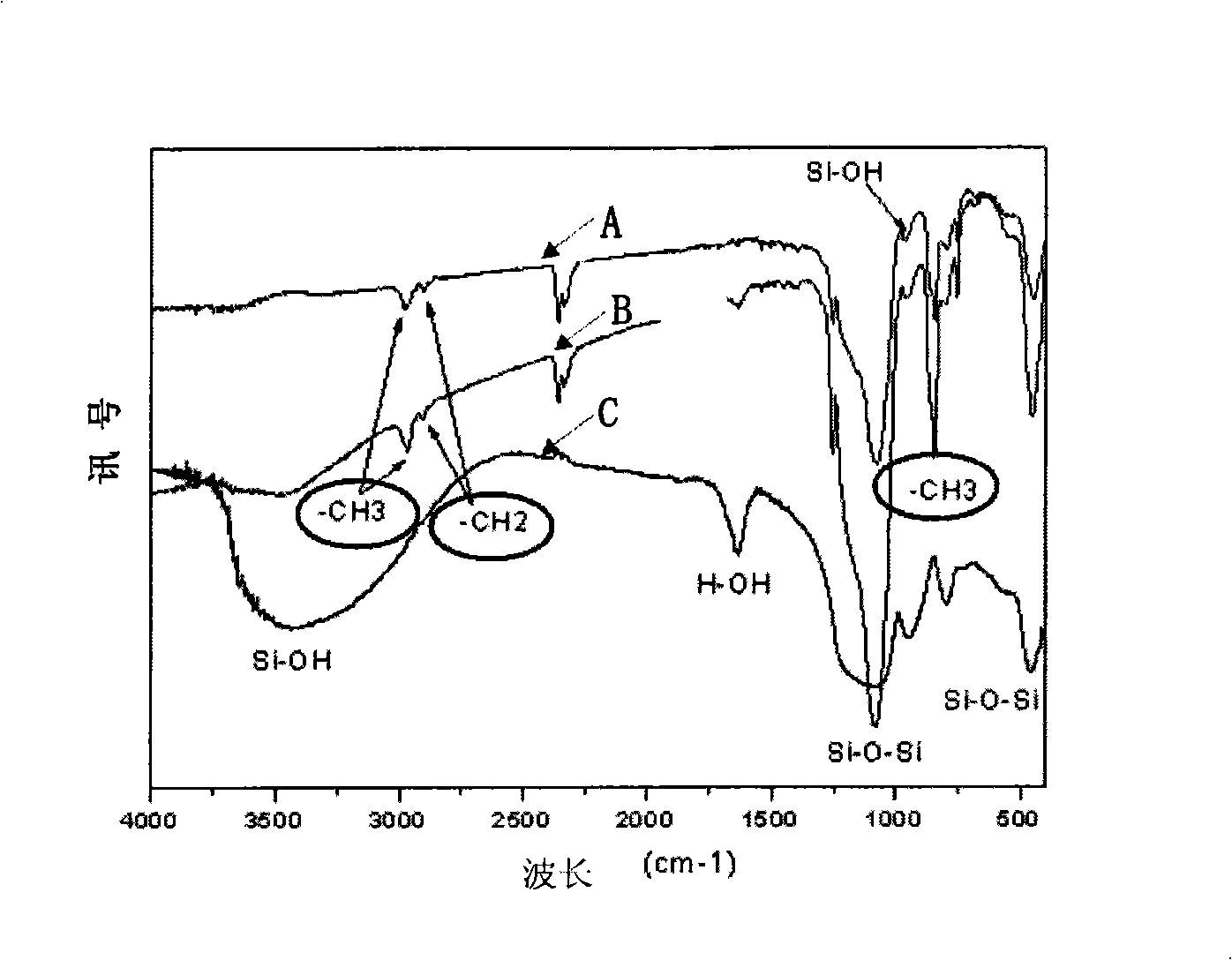
[0049] In this example, the porous aerogels before modification and after modification in Example 1 were tested for density, porosity, volume shrinkage, thermal conductivity, BET specific surface area, average pore diameter, and average pore volume, and were measured by IR The structure and composition of the porous airgel were observed with an electron microscope. Various characteristic tests of the present invention use dead volume developed in Japan as a method for analyzing and measuring the pore structure of porous materials.
[0050] The characteristics of the porous airgel before modification and after modification in Example 1 are shown in Table 1. The results show that after modification and with the increase in the number of modification times, the density of the airgel will decrease or even drop to about 0.069 (g / cm 3 ), the porosity can increase to about 97%, and the specific surface area increases, whil...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com