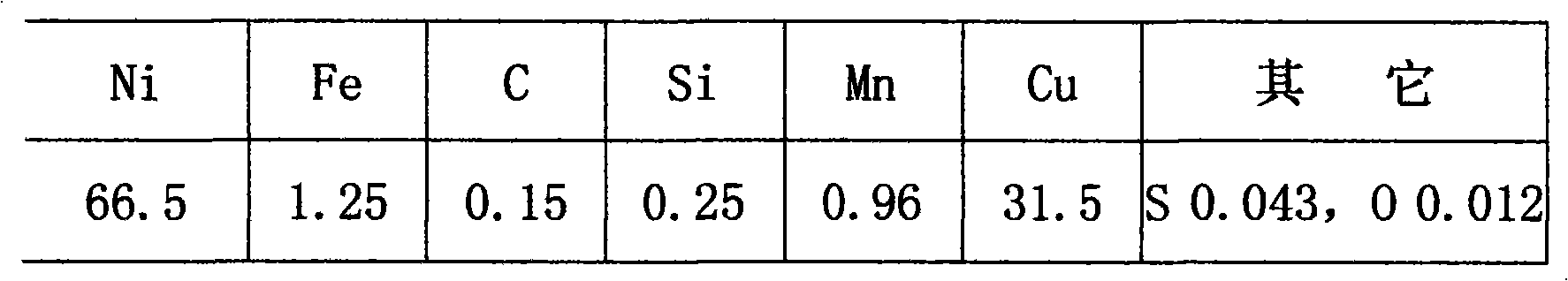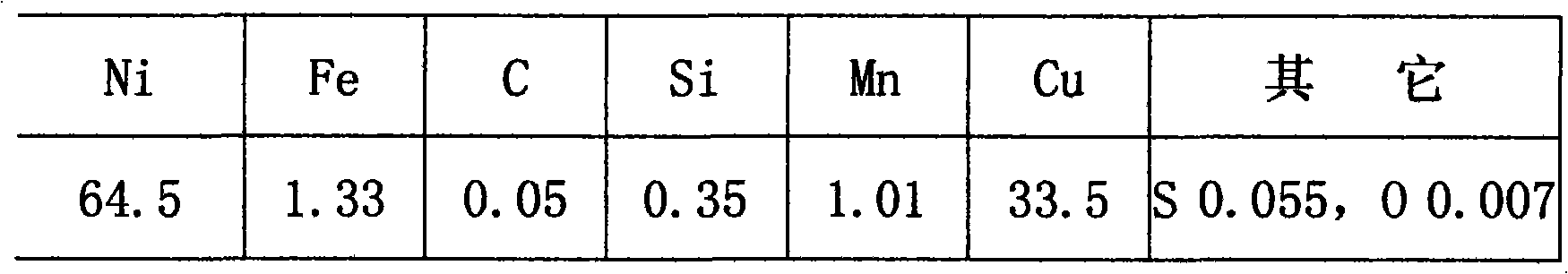Preparation for free-cutting adnic alloy
A nickel-copper alloy and easy-cutting technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of free-cutting nickel-copper alloys, can solve the problems of steel cutting performance, poor fluidity, and easy-cutting uniformity, so as to reduce cutting force and cutting temperature, and reduce surface Effect of roughness and improved chip control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] In the nickel-copper alloy, after refining at 1600° C. for 20 minutes, add carbon and nickel-magnesium alloy for deoxidation, and finally add 0.06% (sulfur weight) MnS to the nickel-copper alloy liquid.
[0021] Analysis results of cast alloy ingot composition:
[0022]
[0023] Results Forging process, sample turning performance is good;
Embodiment 2
[0025] In the nickel-copper alloy, after refining for 20 minutes, add calcium-silicon alloy for deoxidation, and finally add 0.07% (sulfur weight) FeS to the nickel-copper alloy liquid.
[0026] Analysis results of cast alloy ingot composition:
[0027]
[0028] Results Hot-rolled processing, the turning performance of the sample is good;
Embodiment 3
[0030] In the nickel-copper alloy, add carbon, after refining for 15 minutes, add copper-zirconium alloy for deoxidation, and finally add 0.07% (sulfur weight) high nickel matte to the nickel-copper alloy liquid.
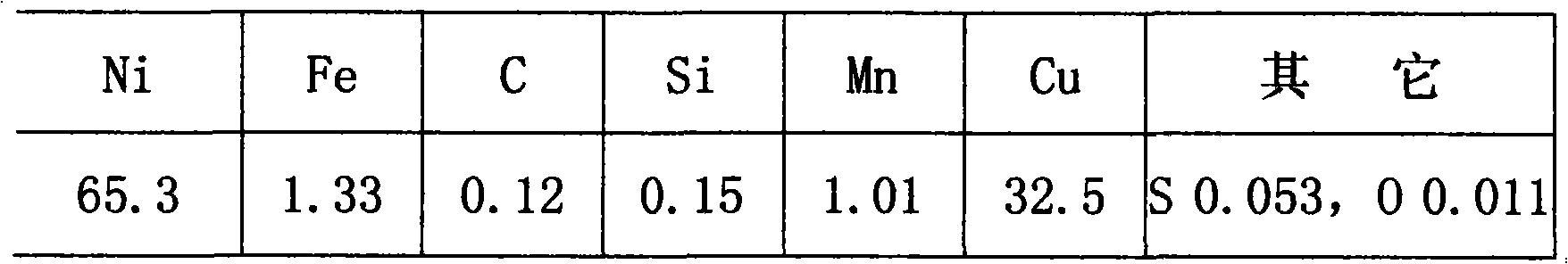
[0031] Analysis results of cast alloy ingot composition:
[0032]
[0033] Castings are processed directly, and the sample turning performance is good;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com