Fire resistant permanent magnet alloy and manufacturing method thereof
A permanent magnet, high temperature resistant technology, applied in the direction of magnetic objects, magnetic materials, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of uniform mixing of main phase alloy and grain boundary phase alloy, no clear improvement of magnet temperature resistance, no public sintering High temperature resistance of magnets and other problems, to improve the poor temperature resistance, make up for the low temperature of use, and reasonably control the effect of grain size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
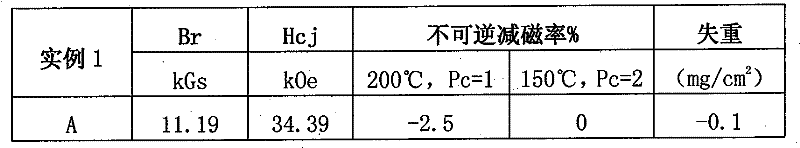
Embodiment 1
[0072] The composition and content of the high temperature resistant permanent magnet alloy prepared in this embodiment are:
[0073] B: 1.02; Co: 4.5;
[0074] Nd: 19.5; Dy: 12;
[0075] Nb: 0.3; Cu: 0.14;
[0076] Ga: 0.12; Zr: 0.029; the above are percentages by weight;
[0077] Fe: 62.391 and above are weight percentages.
[0078] Wherein, the Zr is added in the form of nano-zirconia during the mixing of fine powder in the following step (3).
[0079] The high temperature resistant permanent magnet alloy manufacturing method of the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0080] 1. Weigh the raw materials according to the above alloy composition and content;
[0081] 2. Melting in a vacuum induction furnace until it is completely melted, pouring the resulting solution into a water-cooled ingot mold for casting to obtain an alloy ingot, and performing a solid melting treatment on the alloy ingot in a vacuum sintering furnace at 1080°C for 5 hours; using the ...
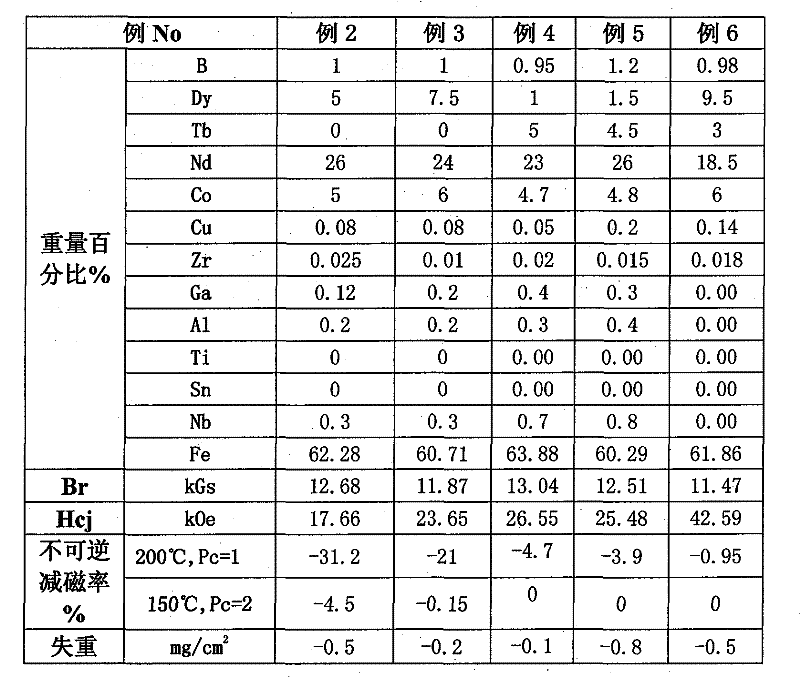
Embodiment 2-3
[0102] The composition and weight percentage of the high-temperature-resistant permanent magnet alloy to be prepared are listed in Table 2, and the rest of the preparation process is the same as in Example 1; the difference lies in step 4: the sintering temperature in a vacuum sintering furnace is 1100° C., and the sintering time is 5.5 hours. Further tempering at 470°C for 5 hours, followed by rapid cooling. The characteristics of the sintered magnet were measured in the same manner as in Example 1, and the results are recorded in Table 2.
[0103] Table 2 Example 2, 3 Irreversible demagnetization rate and weight loss results
[0104]
[0105] From the results of Table 2, when Example 2 is at 200°C (Pc=1), the irreversible demagnetization rate is -31.2%, and at 150°C (Pc=2), the irreversible demagnetization rate is -4.5%; Example 3 At 200°C (Pc=1), the irreversible demagnetization rate is -21%, and at 150°C (Pc=2), the irreversible demagnetization rate is -0.15%, so the m...
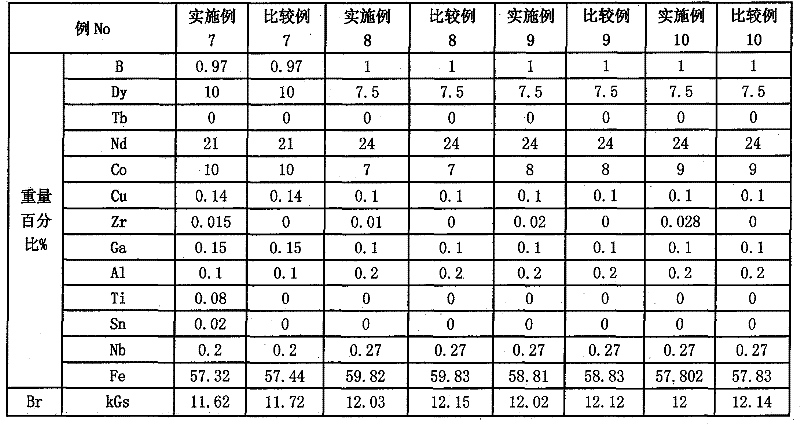
Embodiment 4
[0107] Embodiment 4, 5? The irreversible demagnetization rate of conventional sintered iron boron magnets with the same performance is about -17% at 200°C (Pc=1). It can be seen that the irreversible demagnetization rate at high temperature is lower than that of sintered NdFeB magnets of the same grade. It can be greatly improved, and the effect of maintaining high magnetic properties can be achieved even at high temperatures.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Curie point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com