Preparation of liquid beta-diastase
An amylase and preparation technology, applied in the field of enzyme preparation preparation, can solve the problems of waste liquid treatment, high product impurity content and high production cost, and achieve the effects of reducing production energy consumption, low product impurity content and low production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
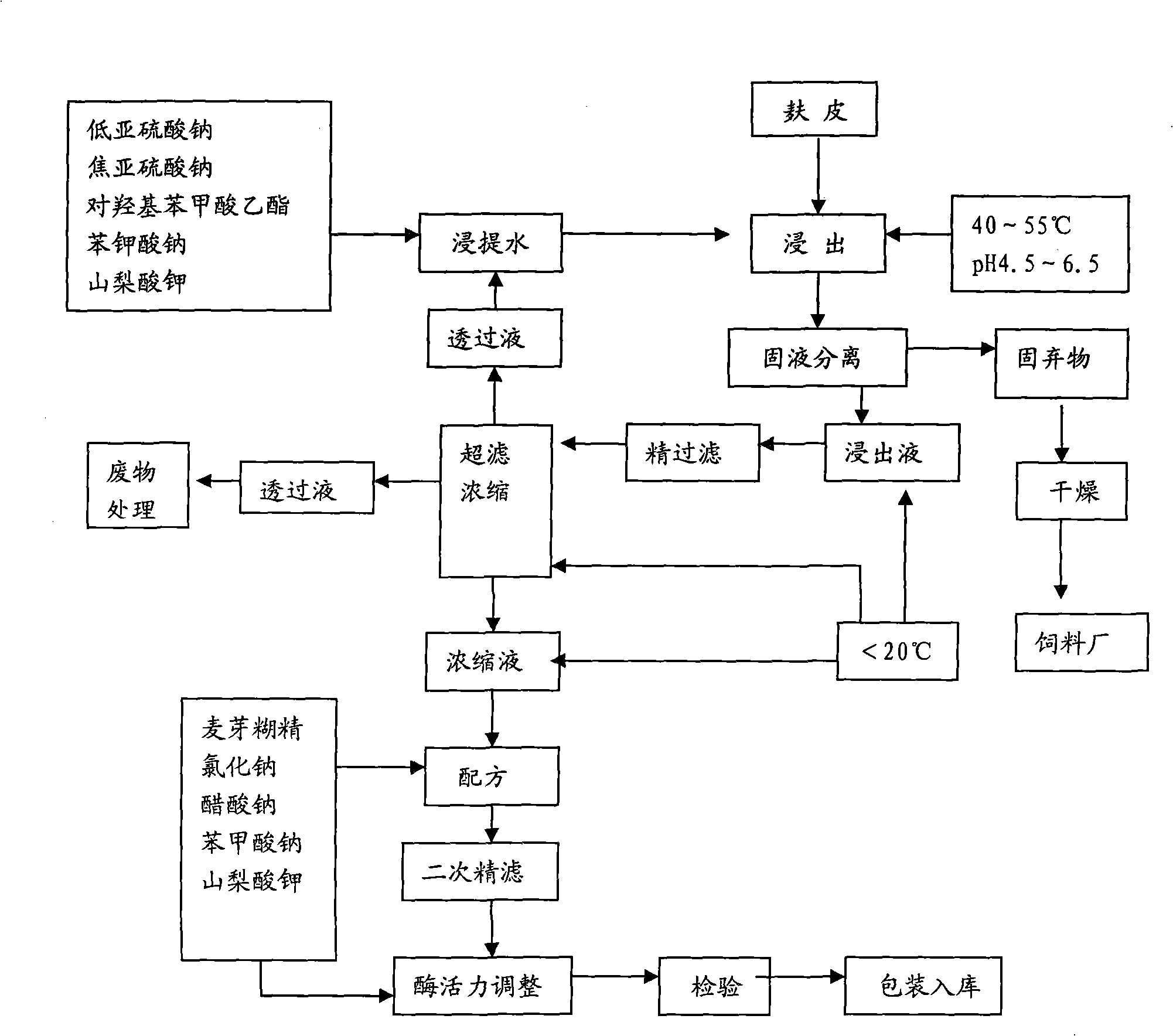
[0027] 1. Extraction:
[0028] (1) Preparation of extraction water: add preservatives ethyl p-hydroxybenzoate 0.025Kg, potassium sorbate 0.625Kg, sodium benzoate 0.875Kg, reducing agent sodium metabisulfite 1.25Kg, low sodium sulfite 3.75Kg in 250L water, stir to dissolve;
[0029] (2) Extraction: Take 50Kg bran and add it to the extraction water prepared in step (1); under normal pressure, the water bath is heated to 45°C to keep warm, adjust the pH to 4.5, stir once per hour, and extract for 6 hours;
[0030] 2. Solid-liquid separation: After leaching, solid-liquid separation is carried out with a plate frame or screw press;
[0031] 3. Fine filtration: The separated extract solution is quickly cooled to below 20°C, and 3.75Kg of diatomaceous earth is added to the extract solution, and fine filtration is carried out through a fine filter plate frame;
[0032] 4. Ultrafiltration concentration: the fine filtrate obtained in step 3 enters the ultrafiltration concentrator for u...
Embodiment 2
[0037] 1. Extraction:
[0038] (1) Preparation of extraction water: add preservative ethyl p-hydroxybenzoate 1.4Kg, potassium sorbate 14Kg, sodium benzoate 14Kg, reducing agent sodium metabisulfite 70Kg, low sodium sulfite 70Kg in 7000L water, stir and dissolve;
[0039] (2) Extraction: Weigh 1000Kg bran and add it to the extraction water prepared in step (1); under normal pressure, the water bath is heated to 55°C to keep warm, adjust the pH to 5.0, stir once per hour, and extract for 7 hours;
[0040] 2. Solid-liquid separation: After leaching, solid-liquid separation is carried out with a plate frame or screw press;
[0041] 3. Fine filtration: The separated extract solution is quickly cooled to below 20°C, and 84Kg of diatomaceous earth is added to the extract solution, and fine filtration is carried out through a fine filter plate frame;
[0042] 4. Ultrafiltration concentration: the fine filtrate obtained in step 3 is subjected to ultrafiltration concentration, and the ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] 1. Extraction:
[0048] (1) Preparation of extraction water: add preservative ethyl p-hydroxybenzoate 9Kg, potassium sorbate 30Kg, sodium benzoate 150Kg, reducing agent sodium metabisulfite 450Kg, low sodium sulfite 150Kg in 30000L water, stir and dissolve;
[0049] (2) Extraction: Take 5000Kg bran and add it to the extraction water prepared in step (1); under normal pressure, the water bath is heated to 50°C to keep warm, adjust the pH to 6.5, stir once per hour, and extract for 8 hours;
[0050] 2. Solid-liquid separation: After leaching, solid-liquid separation is carried out with a plate frame or screw press;
[0051] 3. Fine filtration: The separated extract solution is quickly cooled to below 20°C, and 84Kg of diatomaceous earth is added to the extract solution, and fine filtration is carried out through a fine filter plate frame;
[0052] 4. Ultrafiltration concentration: the fine filtrate obtained in step 3 is subjected to ultrafiltration concentration, and the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com