Method for producing D-ribose by fermenting bacillus subtilis
A technology for Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus subtilis is applied in the field of using Bacillus subtilis to ferment D-ribose, which can solve the problems of low yield and long fermentation period, and achieve the effects of easy industrialization, reduction of by-products, and simple and easy control.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] A method utilizing Bacillus subtilis to ferment and produce D-ribose, the specific steps of which are:
[0030] (1) select transketolase-deficient Bacillus subtilis as bacterial strain;
[0031] (2) strain culture,
[0032] A. The glycerol suspension of the transketolase-deficient Bacillus subtilis EC2 that was cryopreserved was connected to the slant medium, and cultivated in a constant temperature incubator at 37° C. for 40 hours;
[0033] The components of the slant medium are: sorbitol 5g / l, peptone 10g / l, NaCl 2g / l, yeast extract 2g / l, KH 2 PO 4 1g / l, K 2 HPO 4 2g / l, agar 20-22g / l, prepared with deionized water, pH 7.0~7.2.
[0034] B. Under sterile conditions, insert the strains on the slant of the two inoculation loops into a 250mL shake flask equipped with sterilized 20ml seed medium, and cultivate them on a shaker at 220rpm at 37°C for 47 hours, as the primary seed;
[0035] The components of the seed medium are: glucose monohydrate 20g / l, KH 2 PO 4 1g / ...
Embodiment 2
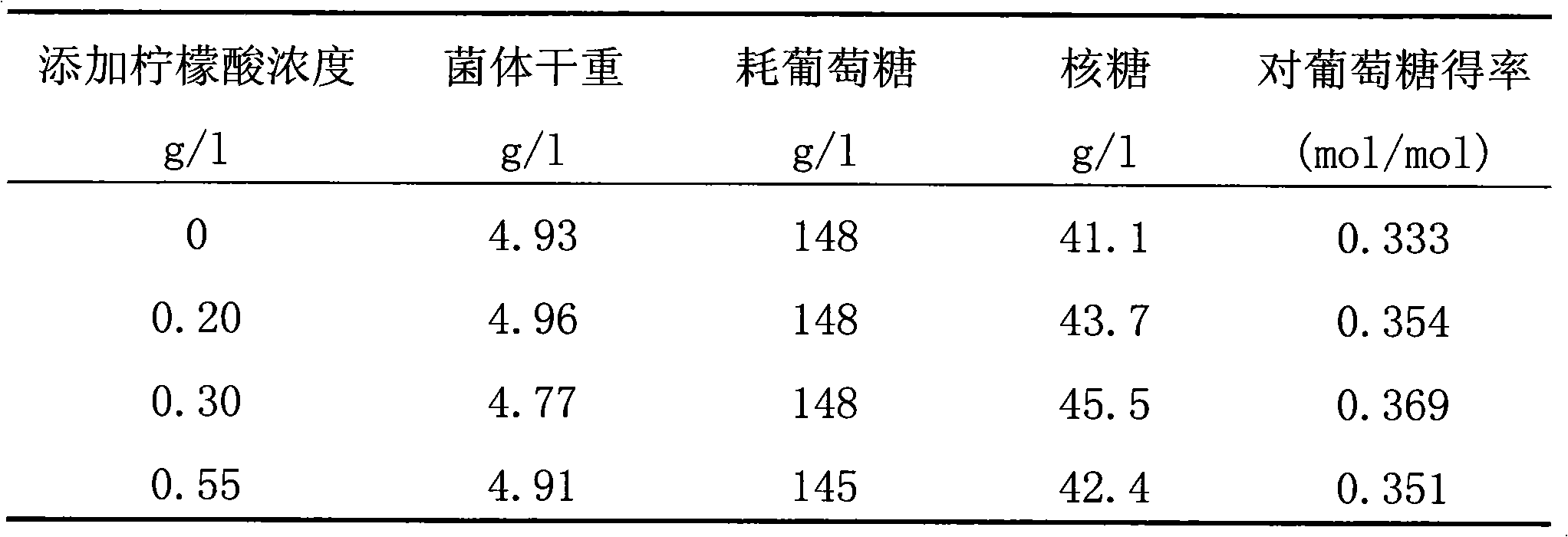
[0041] Shake flask fermentation was carried out according to the method described in Example 1, but in the fermentation medium described in Example 1, 0.2g / l, 0.3g / l, 0.55g / l of citric acid were added respectively to form three groups of experiments Group, after 70 hours of fermentation, compare with the fermentation result of embodiment 1, the results are shown in Table 1:
[0042] Table 1
[0043]
[0044] Experimental results:
[0045] Adding the citric acid shown in the amount can improve the output and yield of D-ribose in the fermentation process of the transketolase-deficient Bacillus subtilis, especially when adding 0.3g / l citric acid, the D-ribose output increases the most, compared with The output of the control group increased by 10.7%, and the yield increased by 10.8%.
Embodiment 3
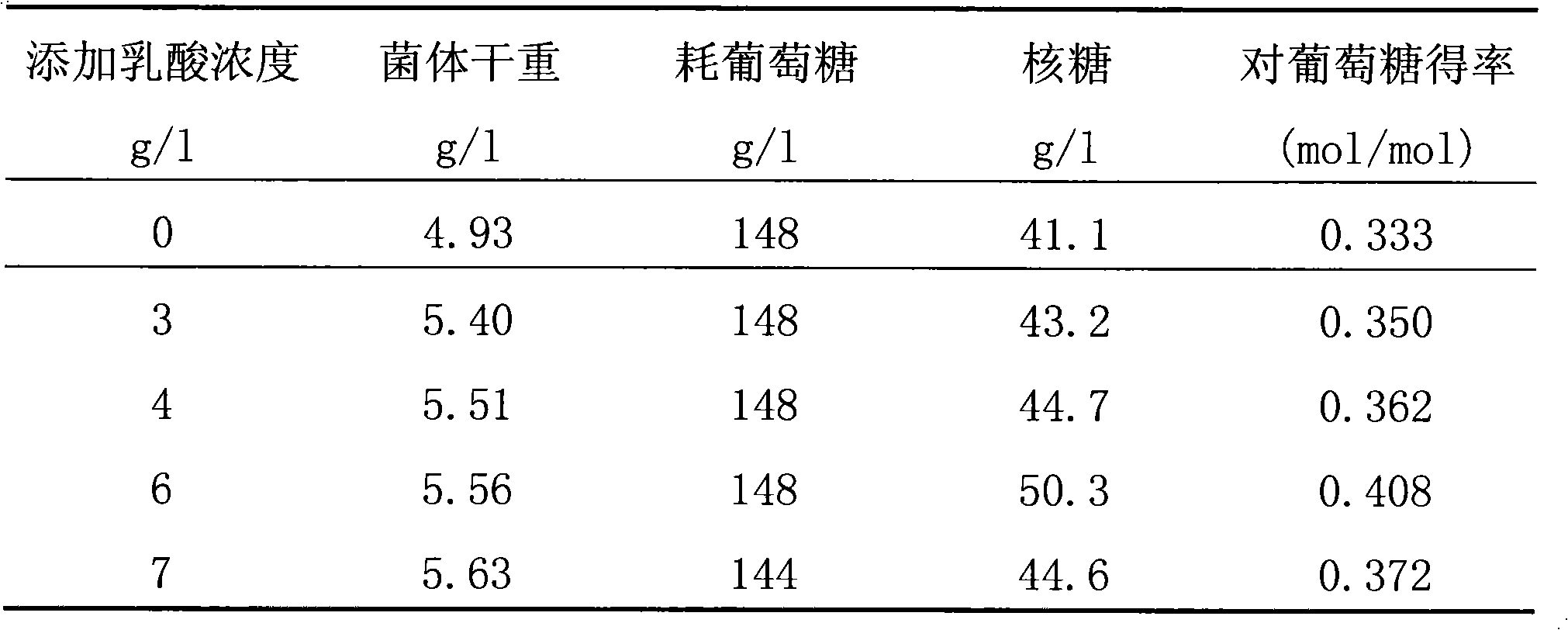
[0047] Shake flask fermentation was carried out according to the method described in Example 1, but 3 g / l, 4 g / l, 6 g / l, and 7 g / l of lactic acid were added respectively to the fermentation medium described in Example 1 to form four groups of experiments Group, after 70 hours of fermentation, compare with the fermentation result of embodiment 1, the results are shown in Table 2:
[0048] Table 2
[0049]
[0050] Experimental results:
[0051]Adding the indicated amount of lactic acid can improve the output and yield of D-ribose in the fermentation process of transketolase-deficient Bacillus subtilis, especially when adding 6g / l lactic acid, the D-ribose output increases the most, which is higher than that of the control group. Increased by 22.4%, yield increased by 22.5%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com