Labelling foodstuff pathogenic bacteria growth checking method
A detection method and a pathogenic technology, which are applied in the field of rapid detection of tracer bacterial growth conditions, can solve the problems of unsolved key technical problems, limited development and application, etc., and achieve the effect of low selectivity and enhanced accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
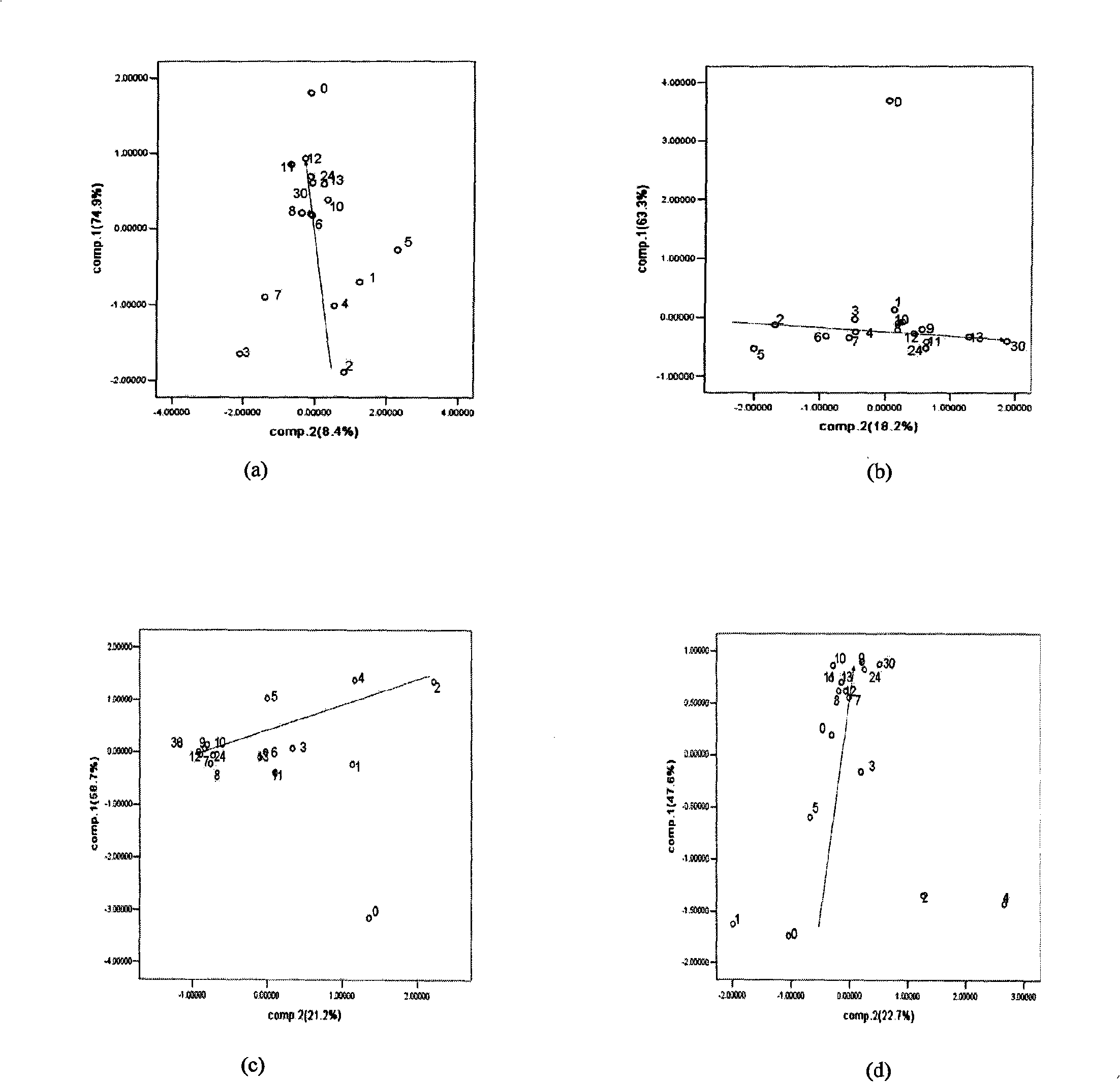
[0032] Embodiment 1: Analysis of the growth situation of Staphylococcus aureus
[0033] Inoculate Staphylococcus aureus strains in 1% glucose broth medium, culture statically for 18-24 hours, and prepare seed solution.
[0034] Transfer equal amounts of the seed solution to Erlenmeyer flasks containing 50ml of 1% glucose broth medium, and culture at 37°C for 0h, 1h, 2h, 3h, 4h, 5h, 6h, 7h, 8h, 9h, 10h , 11h, 12h, 13h, 24h, and 30h, inactivate the culture medium in a water bath at 100°C for 40min.
[0035] The inactivated culture medium was detected by a multi-frequency large-scale pulse intelligent chemical analysis system. The sensor array uses Wu electrodes, Pt electrodes, Ag electrodes, and Ti electrodes as working electrodes, platinum electrodes as auxiliary electrodes, and Ag / AgCl as reference electrodes.
[0036] The multi-frequency large-scale pulse excitation potential consists of three pulse frequency segments of 1Hz, 10Hz and 100Hz, which are equivalent to large-sc...
Embodiment 2
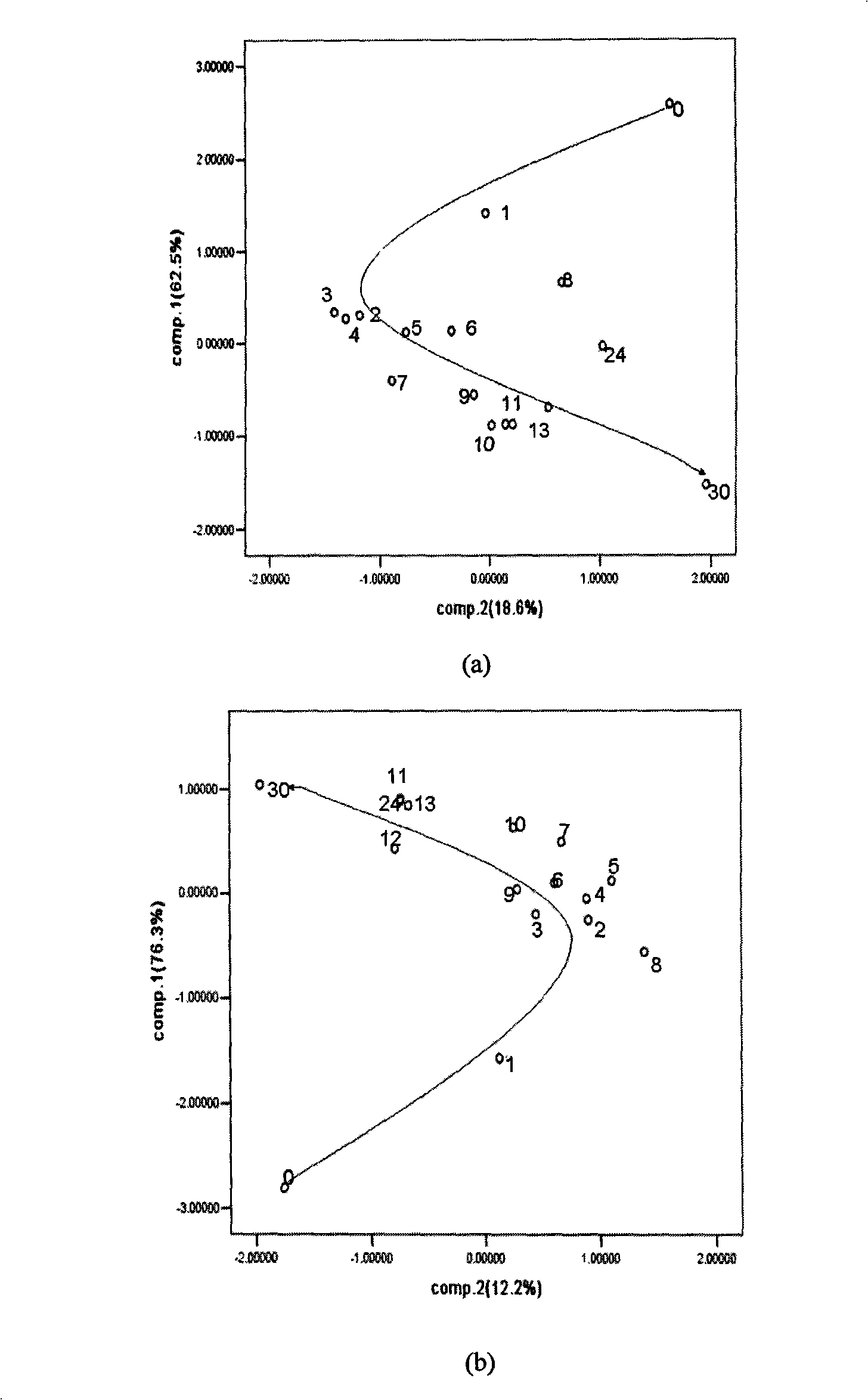
[0041] Embodiment 2: Escherichia coli O157: H7 growth analysis
[0042] Escherichia coli O157:H7 strains were inoculated in 1% glucose broth medium, and cultured statically for 18-24 hours to prepare seed liquid.
[0043] Transfer the same amount of the seed solution to the Erlenmeyer flasks equipped with 50ml of 1% glucose broth medium, and cultivate them for 0h, 1h, 2h, 3h, 4h, 5h, 6h, 7h, 8h, 9h, 10h, 11h, 12h , 13h, 24h, and 30h later, inactivate the culture medium.
[0044] The inactivated culture medium was detected by a multi-frequency large-scale pulse intelligent chemical analysis system. The sensor array uses Pt electrodes and Au electrodes as working electrodes, platinum electrodes as auxiliary electrodes, and Ag / AgCl as reference electrodes.
[0045] The pulse voltage, pulse frequency, pulse interval time, detection method and signal analysis method are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
[0046] Finally, the 1Hz frequency band of the Pt electrode and the 100Hz ...
Embodiment 3
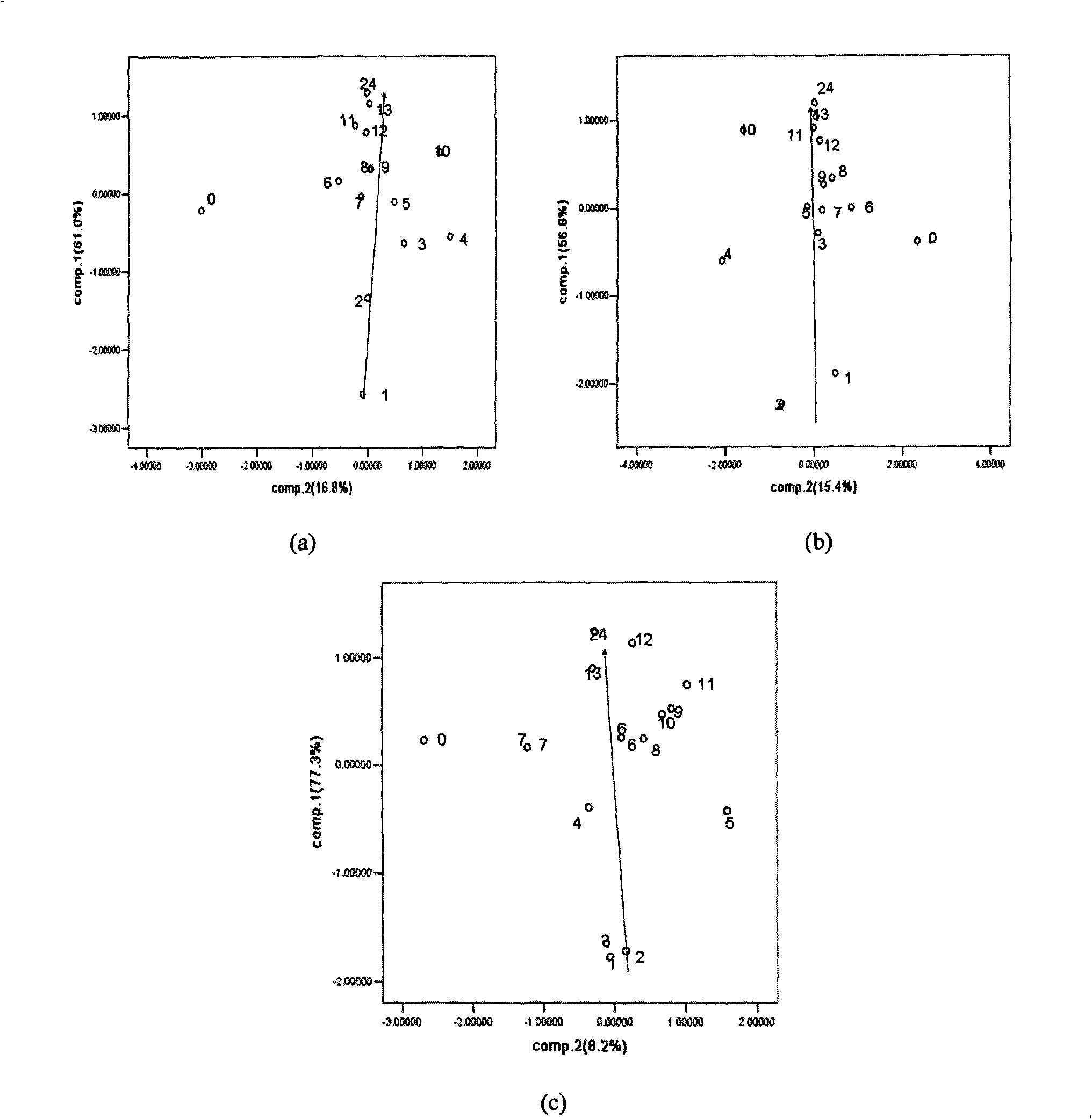
[0049] Embodiment 3: Analysis of the growth of Bacillus subtilis
[0050] The Bacillus subtilis strain is inoculated in 1% glucose broth medium, and cultured statically for 18-24 hours to prepare a seed liquid.
[0051] The seed solution was transferred in equal amounts to the Erlenmeyer flasks equipped with 50ml 1% glucose broth medium, and cultured for 0h, 1h, 2h, 3h, 4h, 5h, 6h, 7h, 8h, 9h, 10h, 11h, respectively. After 12h, 13h, 24h, and 30h, the culture medium was inactivated.
[0052] The inactivated culture medium was detected by a multi-frequency large-scale pulse intelligent chemical analysis system. The sensor array uses Ba electrode as the working electrode, platinum electrode as the auxiliary electrode, and Ag / AgCl as the reference electrode.
[0053] The pulse voltage, pulse frequency, pulse interval time, detection method and signal analysis method are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
[0054] The 1Hz frequency section, 10Hz frequency section, and 100Hz freq...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com