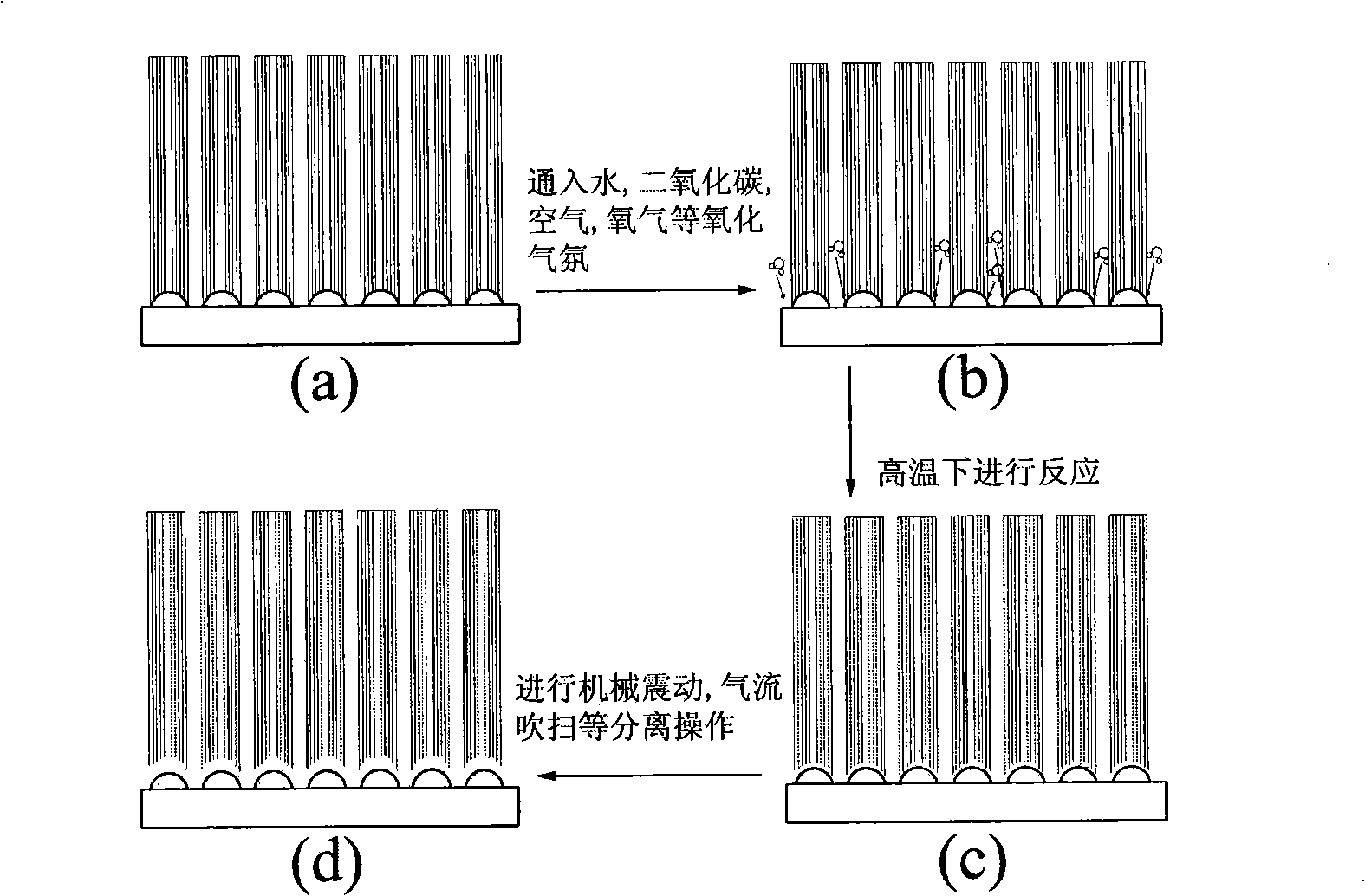
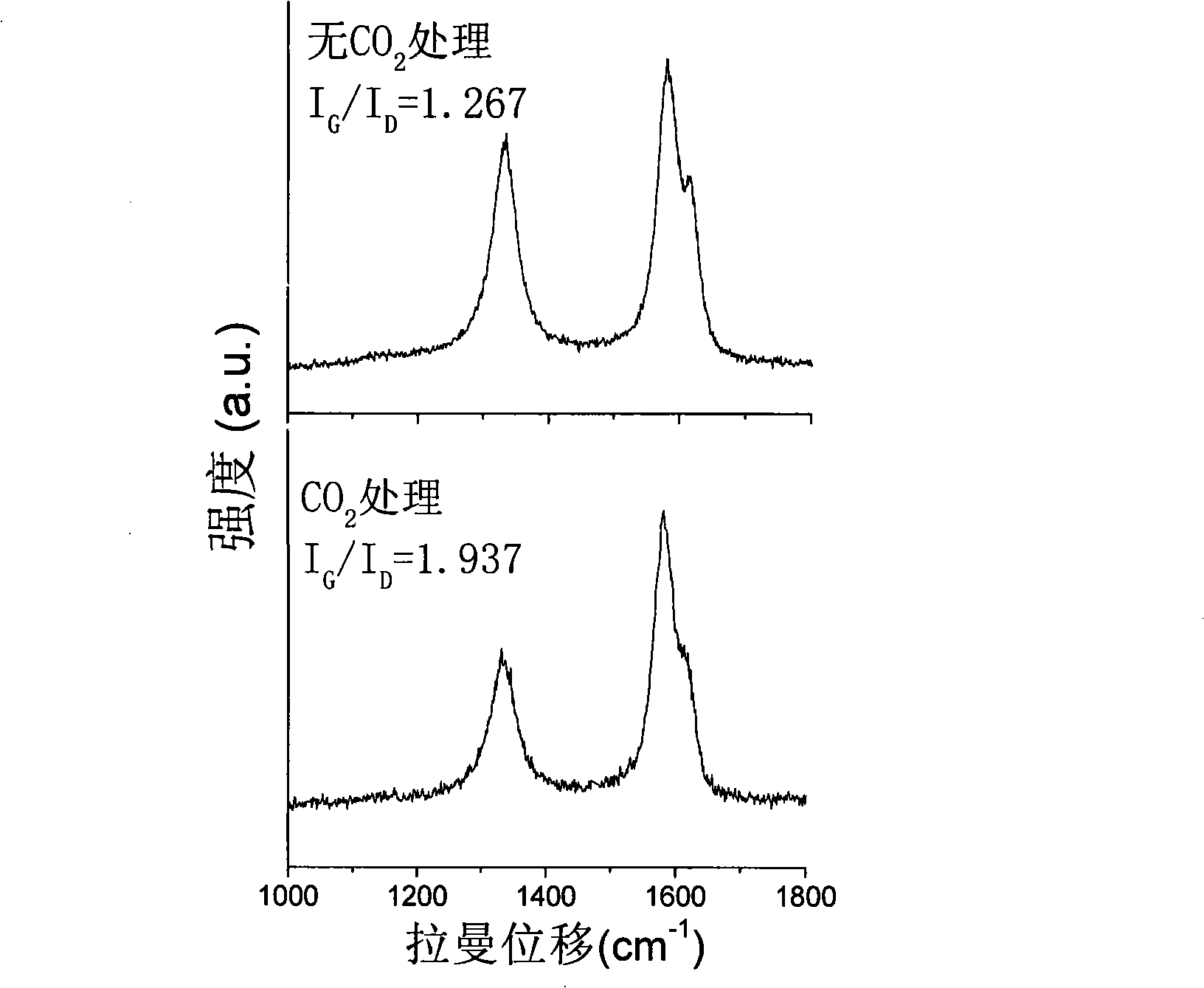
Oxidation treatment based method for separating carbon nano-tube array and substrate
A carbon nanotube array and oxidation treatment technology, which is applied in the field of post-processing technology for the preparation of carbon nanotube arrays, to achieve the effect of reducing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1: Carbon nanotube array prepared by planktonic chemical vapor deposition by carbon dioxide oxidation
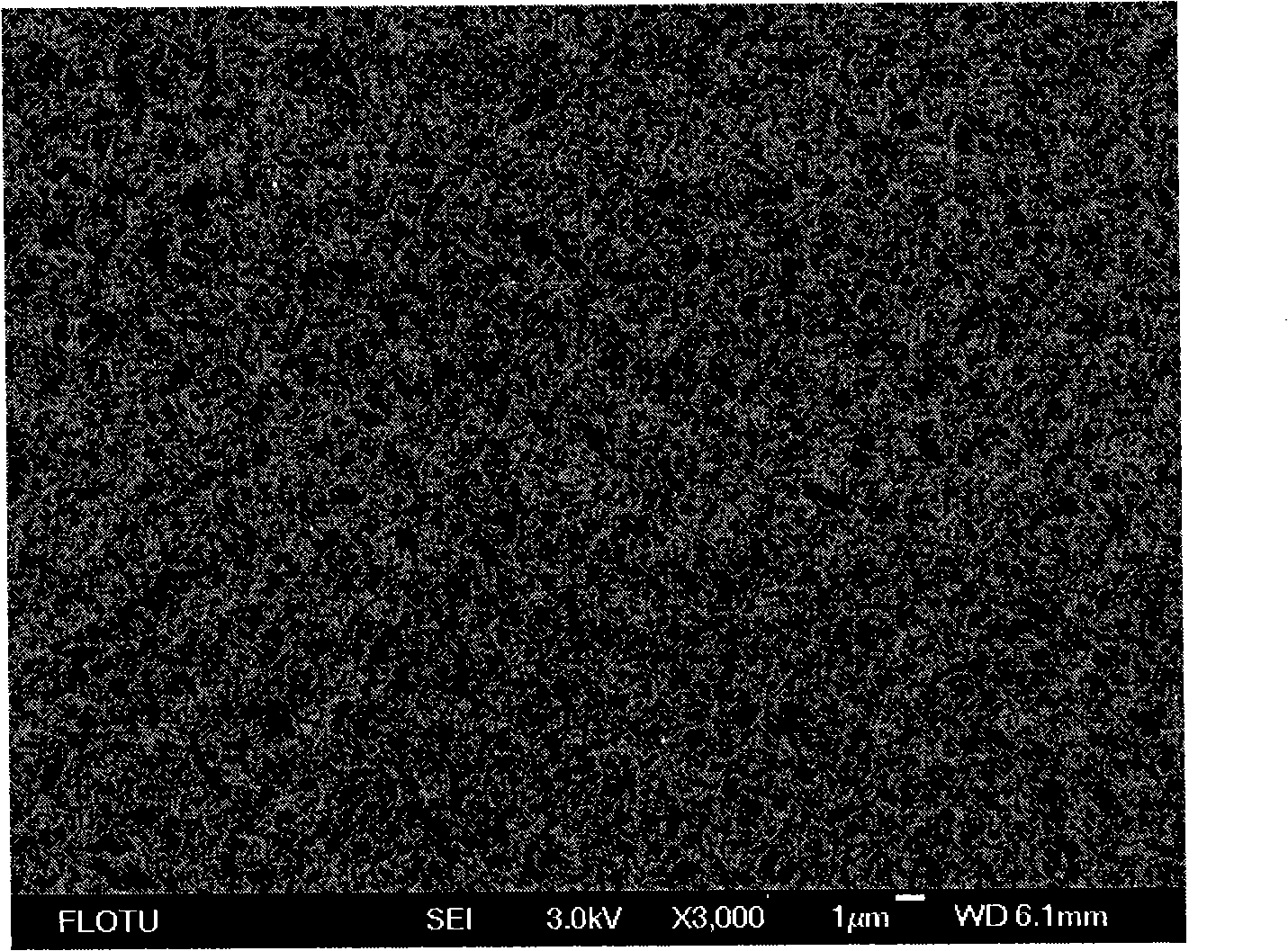
[0026] A quartz substrate is used as the substrate, which is then placed in a fixed-bed reactor. The temperature was raised to a reaction temperature of 800° C. under an atmosphere of hydrogen and argon. Then pass through the xylene solution of ferrocene, and the xylene is catalyzed and cracked to form the carbon nanotube array. After 1 hr, the feed of the xylene solution was turned off, carbon dioxide was introduced at 800° C. for oxidation treatment, and the volume concentration of carbon dioxide was 0.030%. After the oxidation treatment process continued for 30 minutes, the feed of carbon dioxide was cut off and the reactor was lowered to room temperature under a protective gas. A carbon nanotube array with a length of 1 mm can be obtained on the quartz surface. The carbon nanotubes at the bottom of the carbon nanotube array and the substrate and the carbo...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Example 2: Carbon Nanotube Arrays Prepared by Air Oxidation Treatment by Planktonic Chemical Vapor Deposition
[0028] Ceramic balls whose main component is Al2O3 are used as the substrate, and then put into a two-stage fixed-bed reactor. The first section is the catalyst evaporation section, using ferric chloride as the catalyst precursor, and the evaporation temperature is controlled at 260°C; the second section is the carbon nanotube array growth area. The temperature was raised to a reaction temperature of 1000° C. under a helium atmosphere. Then liquefied petroleum gas is introduced, and the carbon nanotube catalyst precursor ferric chloride enters the second-stage reactor through evaporation, where in-situ decomposition occurs to form an iron catalyst, and the liquefied petroleum gas is catalytically cracked to form a carbon nanotube array on the spherical surface. After the reaction was carried out for 10 minutes, the feeding of liquefied petroleum gas was stopp...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Example 3: Carbon nanotube array prepared by chemical vapor deposition using water vapor assisted substrate method
[0030] Using aluminum foil as the substrate, the surface is plated with 10nm iron catalyst by electroplating, then dried, put it into a fixed-bed reactor with a diameter of 25mm, and raise the temperature to the reaction temperature of 600°C under the atmosphere of hydrogen and argon. annealing. The catalyst film ruptures, forming catalyst particles. Nitrogen is used as the carrier gas and it enters the reactor after passing through a scrubber bottle filled with distilled water. The volume concentration of water vapor in the reactor inlet is controlled to be 0.05%, and the inlet temperature of the benzene solution is controlled at 300°C to form an iron catalyst for catalytic cracking. Benzene forms carbon nanotube arrays. After 1 hr, a multi-walled carbon nanotube array with a length of about 20 μm can be obtained on the surface of the aluminum foil. U...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com