Fluorescence quantitative PCR method for fast detecting Campylobacter jejuni macrolide drug resistant mutational site
A technology of Campylobacter jejuni and macrolides, which is applied in the fields of fluorescence/phosphorescence, biochemical equipment and methods, and microbial measurement/inspection, can solve the problems of cumbersome experiments, high technical requirements, and many influencing factors, and achieve Effects of inhibiting PCR amplification, improving amplification efficiency, and high amplification efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] Example 1. Selection of target gene sequences related to Campylobacter macrolide drug resistance, design and synthesis of primers and probes
[0058] Using the BLAST tool in NCBI, the differences between the 23S rDNA gene sequence of Campylobacter jejuni and other intestinal bacteria were compared. A pair of primers were designed by using Beacon Designer 2.1 (molecular beacon design software 2.1) to specifically amplify the target genes related to the resistance to macrolides in Campylobacter jejuni. The length of the amplified target gene is 147bp, and its gene sequence is not highly homologous with other intestinal bacteria, which can ensure the specific amplification of the macrolide resistance-related gene of Campylobacter jejuni by PCR reaction. The specificity of the primers was checked by ordinary PCR amplification. From figure 1 It can be seen from the results that the designed primers can only specifically amplify the Campylobacter jejuni bacterial strain, bu...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Embodiment 2, the construction of three kinds of control plasmids
[0066] 1. Construction of wild-type control plasmid (plasmid WT)
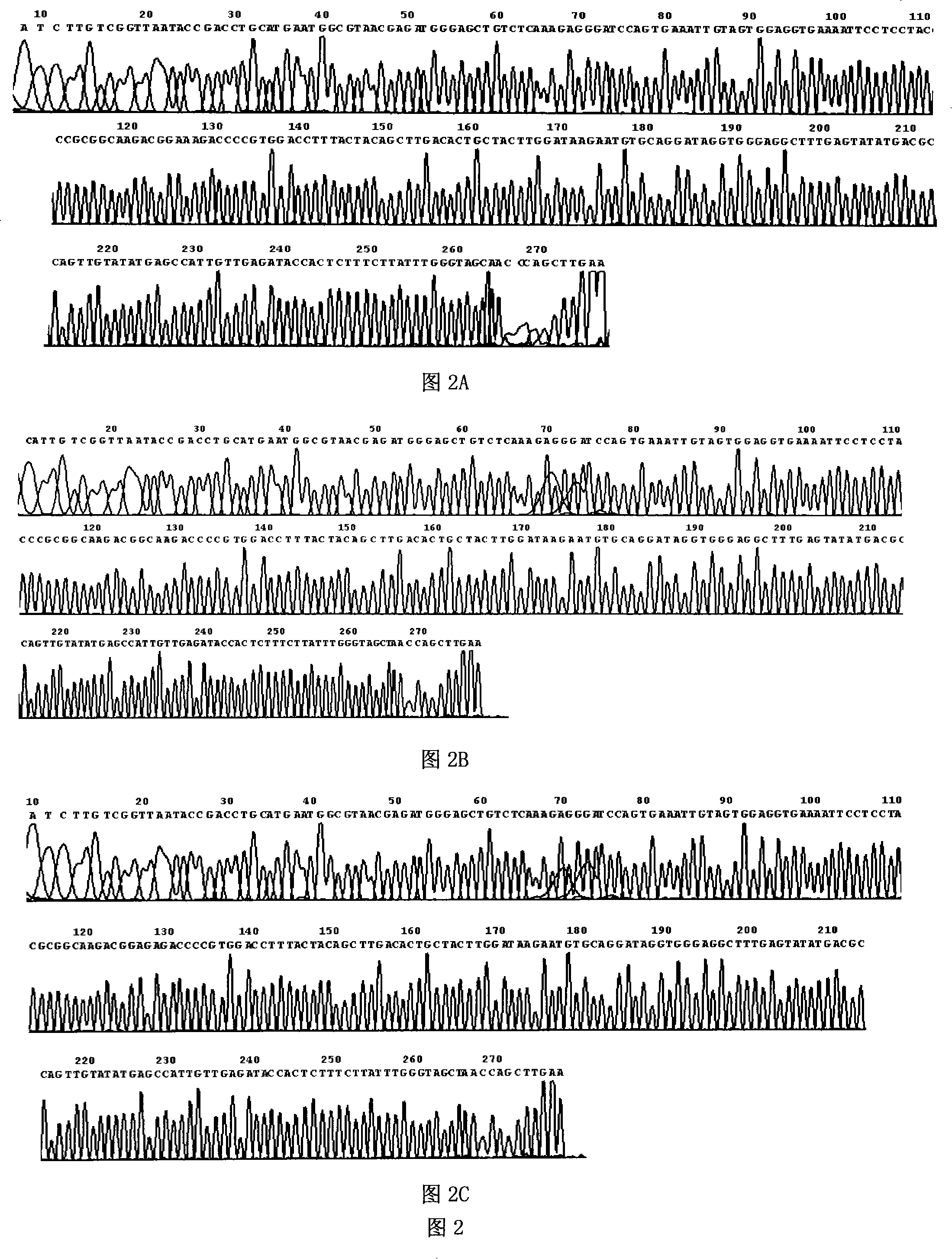
[0067] Referring to Amera Gibreel (Gibreel, A., and D.E.Taylor.2006.Macrolide resistance inCampylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli.J.Antimicrob.Chemother.58:243-255.), PCR amplification of Campylobacter jejuni standard strain ATCC 33291 (purchased A 308bp nucleic acid sequence from the 23S rDNAV region of the American Standards Depository. After the gel of the amplified PCR product was recovered, the PCR product was connected to the pMD18-T carrier (the carrier was provided by the kit itself) using the TA cloning kit produced by Dalian Bao Biological Co., Ltd., according to the method described in the kit instruction manual. band), and transformed into Escherichia coli DH5α to construct a wild-type recombinant plasmid. The PCR product of the recombinant plasmid was sequenced, and it was determined that the inserted sequence was a w...
Embodiment 3
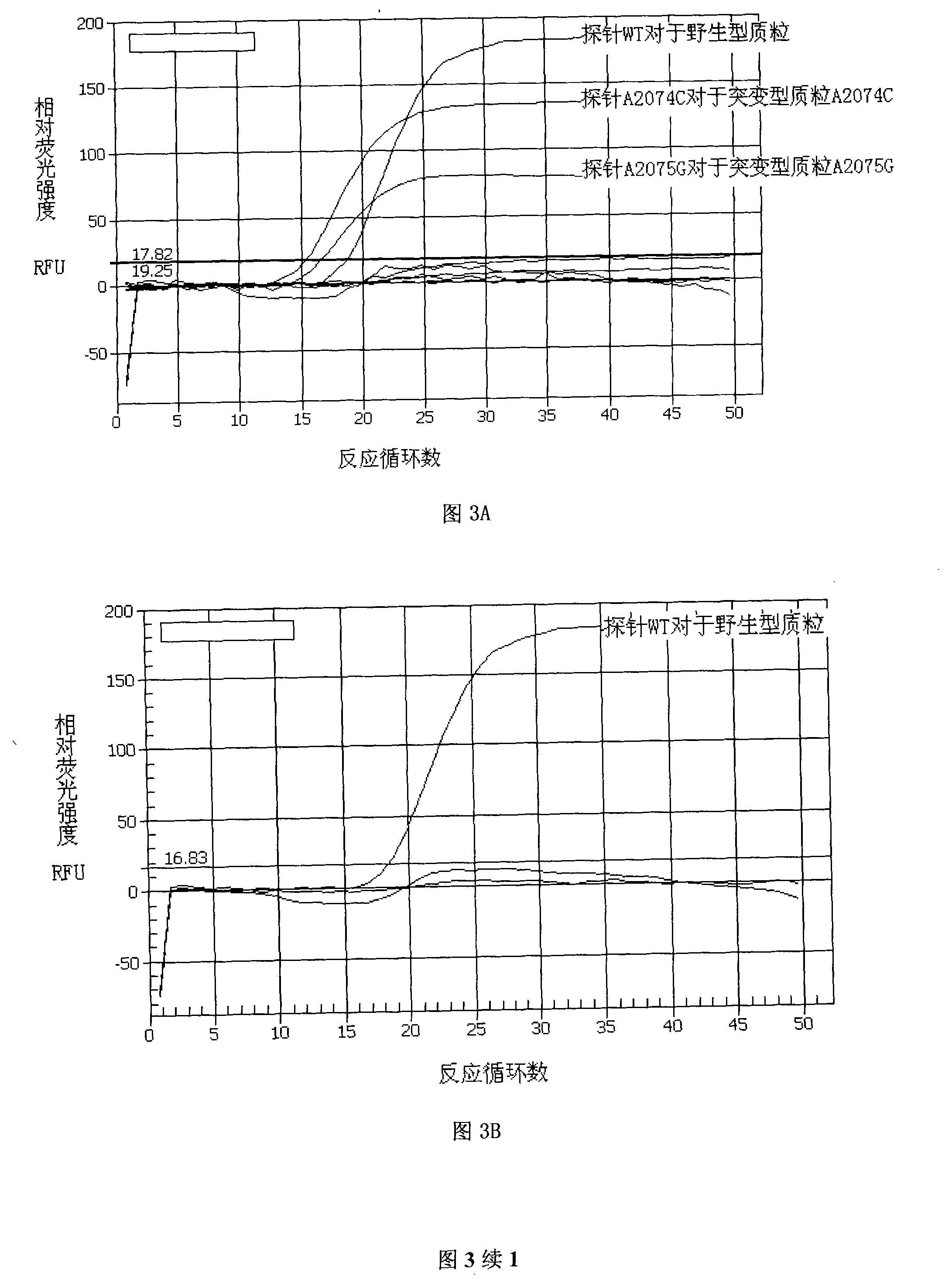
[0089] Embodiment 3, TaqMan fluorescent quantitative PCR reaction system and reaction condition optimization
[0090] Selection of annealing temperature for TaqMan fluorescent quantitative PCR reaction: In order to reduce non-specific amplification and ensure high amplification efficiency, we combined the Tm values of primers and probes, and set three annealing temperatures of 58°C, 62°C and 64°C temperature.
[0091] Optimization of the ratio of primers and probes in TaqMan fluorescent quantitative PCR reactions: In order to avoid non-specific binding of probes and templates, referring to the concentration settings of primers and probes in other related TaqMan fluorescent quantitative PCR reactions, using the principle of square array design, we selected Three ratios of 10:3, 5:3 and 5:1 were determined for comparison to determine the optimal ratio of primers and probes (see Table 1-4).
[0092] The TaqMan fluorescent quantitative PCR reaction system is 25 μl, which includ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com