Rice fat synthesis related gene and use thereof
A fat content, amino acid technology, applied in the field of gene technology and botany, can solve the problems of no gene cloning and functional research, no gene production application, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
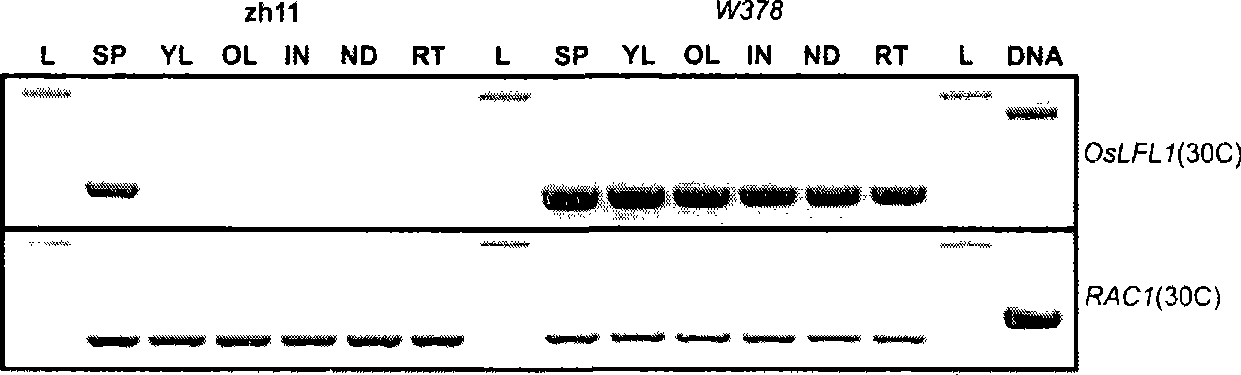
[0202] Example 1 Obtaining of OsLFL1 Mutant Plants
[0203] T-DNA tag isolation of genes is still one of the most important means for the study of plant functional genes. T-DNA (transfer DNA) is a piece of DNA located on the Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti (tumor inducing) plasmid or Agrobacterium rhizogenes Ri (root inducing) plasmid, which can be transferred from Agrobacterium And it is stably integrated into the plant chromosome, so it can be used as a kind of exogenous gene carrier to transfer exogenous DNA to plant cells and regenerate transgenic plants capable of expressing exogenous genes; As the T-DNA sequence is known, once the genetic analysis confirms that the mutant phenotype is linked to the inserted tag, the flanking sequences at both ends of the tag can be obtained by IPCR or TAIL-PCR, and then The flanking sequences are compared with the genomic sequence to obtain information about the mutant gene. Since Agrobacterium is very effective in transforming heterologo...
Embodiment 2
[0205] Example 2 Cloning of OsLFL1 gene
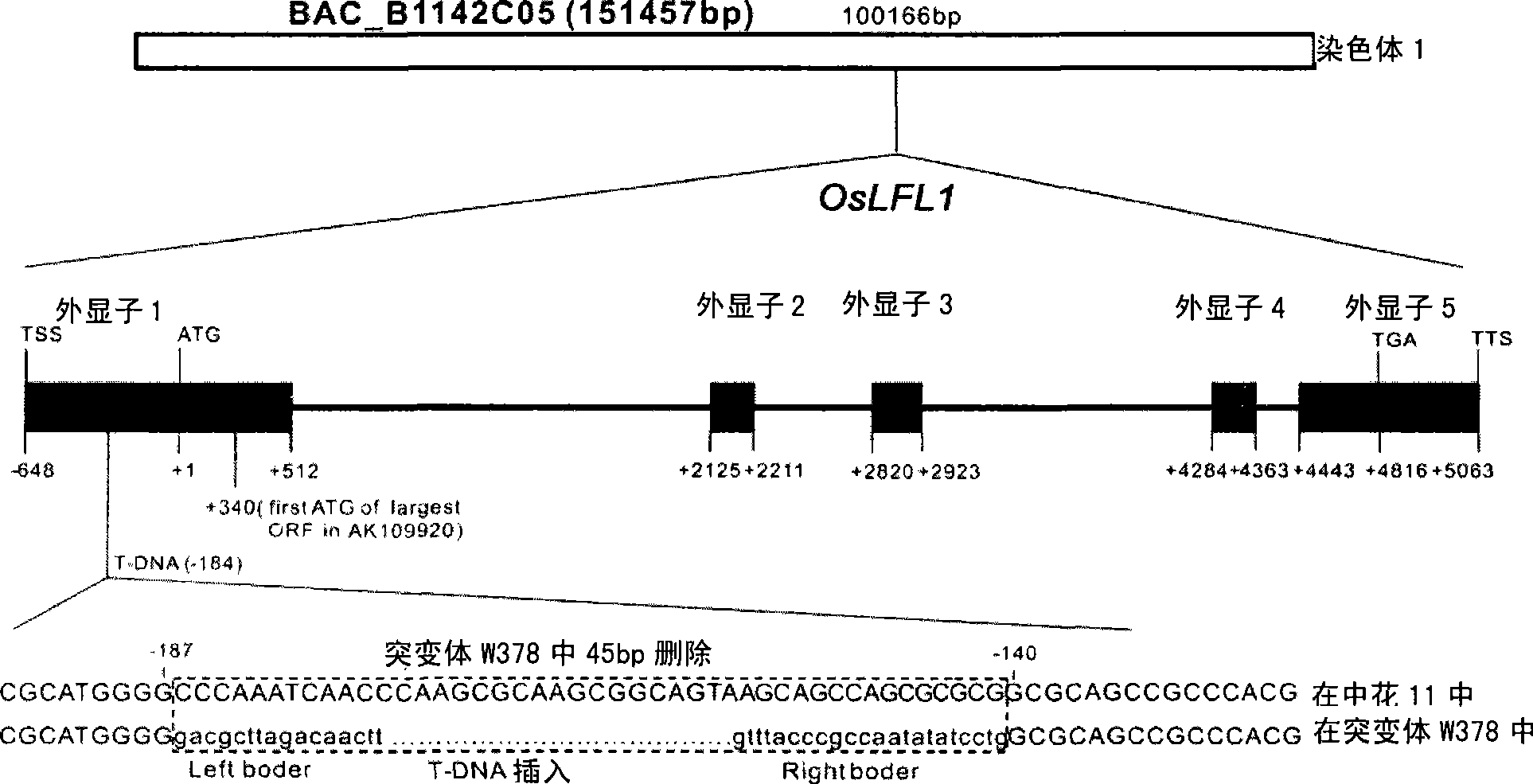
[0206] Separation of adjacent sequence of T-DNA insertion site by Tail-PCR showed that T-DNA was inserted on rice chromosome 1 and located in the promoter region of OsLFL1 gene locus, 186bp away from the start codon ATG. See figure 1 .
[0207] The rice chromosomal site where the T-DNA was inserted was analyzed by this adjacent sequence. The full-length sequence of the gene was obtained from the rice BAC clone B1142C05 (from the International Rice Genome Sequencing Project Research Organization) according to the comparison analysis, which is SEQ ID NO:1. Using the total RNA extracted from rice, the mRNA fragment of the OsLFL1 gene was isolated and sequenced by 5' and 3' RACE (rapid amplification of ends), and the coding sequence of the OsLFL1 gene, SEQ ID NO: 2, was integrated. The sequence of the OsLFL1 protein is deduced according to the rice universal codon coding rule and the coding sequence SEQ ID NO: 2 of the OsLFL1 gene.
Embodiment 3
[0208] Example 3 Sequence Analysis of OsLFL1 Gene
[0209]The sequence of the OsLFL1 gene was analyzed using the analysis tools "Align two sequences (bl2seq)" and "Protein-protein BLAST (blastp)" in http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / BLAST / . The analysis results are as follows:
[0210] SEQ ID NO: 1 shows that in the OsLFL1 genome sequence, the 1-3915 region is the promoter, the 3916-3918 position is the start codon ATG, the 8734-8736 position is the stop codon TAG, 3268-4428, 5885-5926, 6040 -6126, 6735-6838, 8200-8282, 8362-8978 are exons, 4429-5884, 5927-6039, 6127-6734, 6839-8199, 8283-8361 are introns.
[0211] SEQ ID NO: 2 shows that the 48th-50th position in the coding sequence of the OsLFL1 gene mRNA is the initiation codon ATG, and the 1254-1256th position is the termination codon TAG.
[0212] In SEQ ID NO: 3, positions 177-296 of the OsLFL1 protein coding sequence are B3 DNA binding domains, and positions 296-402 are transcriptional activation domains.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com