Method for zero discharge processing of waste saponification lye of cyclohexanone produced by cyclohexane oxidation technology
An oxidation process and cyclohexane technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, multi-stage water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc. Emissions and other issues, to achieve significant environmental benefits, less energy consumption, simple process effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] The basic material components and weight percentages of the saponification waste lye (hereinafter referred to as waste liquid) that the inventive method radically handles are:
[0022] Inorganic matter: sodium carbonate (Na 2 CO 3 ) about 7%
[0023] Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) about 8%
[0024] Organic matter: organic acids, alcohols, ketones, about 35%
[0025] The rest: about 50% water
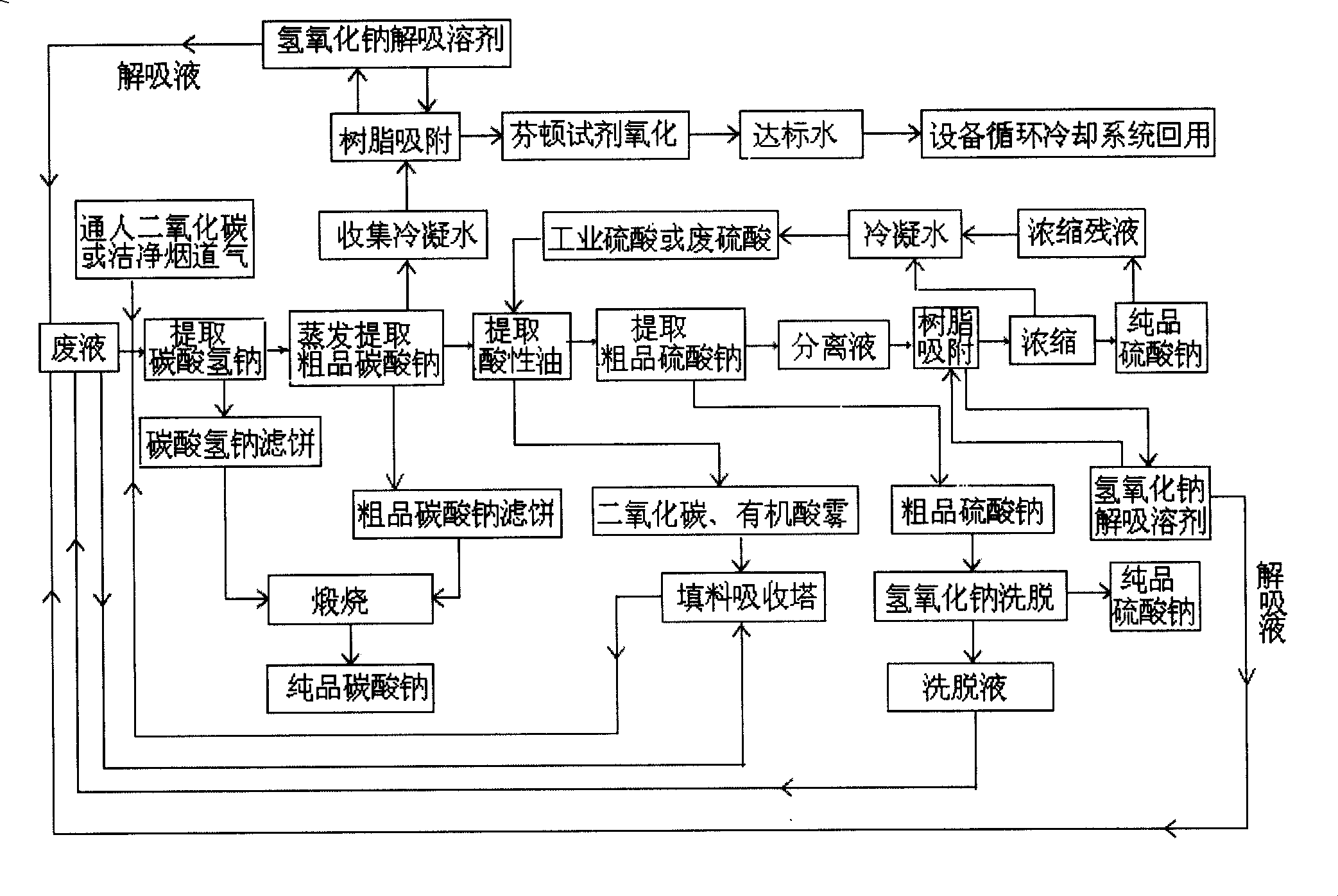
[0026] Below in conjunction with technological process block diagram, briefly describe the implementation process of the inventive method:
[0027] (1) Feed a sufficient amount of carbon dioxide gas or clean flue gas into the waste liquid at normal temperature to extract sodium bicarbonate; the feed amount of carbon dioxide needs to meet the balance requirements of the following chemical reaction equation:
[0028] CO 2 +NaOH=NaHCO 3
[0029] CO 2 +Na 2 CO 3 +H 2 O=2NaHCO 3
[0030] This process is based on: Since the waste liquid contains about 15% of alkali substa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com